0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views19 pagesEng'g Data Analysis Module 1
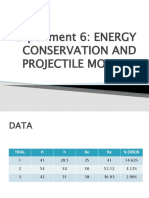
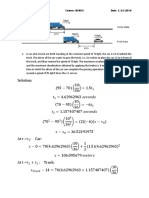
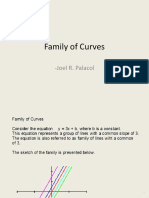
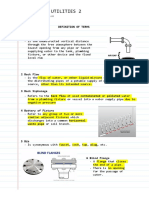
This document outlines a course on engineering data analysis. It covers 10 modules on topics related to statistics, including introduction to statistics, probability, discrete and continuous probability distributions, joint probability distributions, sampling distributions, statistics intervals, hypothesis testing, and simple linear regression. The course aims to teach students to compute probability distributions, apply statistical methods to analyze data, and solve problems in engineering. It provides learning outcomes, activities and assessments for students to demonstrate their mastery of the statistical concepts covered in each module.
Uploaded by
Joab Gabriel Elegado CalumpianoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views19 pagesEng'g Data Analysis Module 1
This document outlines a course on engineering data analysis. It covers 10 modules on topics related to statistics, including introduction to statistics, probability, discrete and continuous probability distributions, joint probability distributions, sampling distributions, statistics intervals, hypothesis testing, and simple linear regression. The course aims to teach students to compute probability distributions, apply statistical methods to analyze data, and solve problems in engineering. It provides learning outcomes, activities and assessments for students to demonstrate their mastery of the statistical concepts covered in each module.
Uploaded by
Joab Gabriel Elegado CalumpianoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 19