Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Picric Acid Test and Iodine Test
Uploaded by
Francis CaloOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Picric Acid Test and Iodine Test
Uploaded by
Francis CaloCopyright:
Available Formats
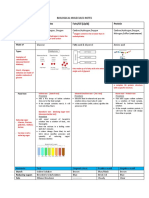
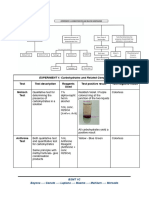
Picric acid Test Iodine test
To detect the presence of polysaccharides, primarily
Principle: starch.
is a very sensitive chemical test for the presence of
reducing sugars. Principle:
Reducing sugars contains a free aldehyde or ketone is based on the fact that polyiodide ions form colored
group possess reducing property. adsorption complex with helical chains of glucose
residue of amylase (blue-black), dextrin (black), or
glycogen (reddish-brown).
This test is used for the detection of starch in the
solution. The blue-black color is due to the formation
of starch-iodine complex.
Starch contain polymer of α-amylose and amylopectin
which forms a complex with iodine to give the blue-
black color.
Reaction:
The reducing sugars react with Picric Acid (toxic
yellow crystalline solid) also chemically known as
2,4,6-trinitrophenol (TNP) to form a red coloured
Picramic Acid
They reduce some organic acids when in alkaline
solution. The Sodium Carbonate (Na2CO3) is added
to make the solution alkaline or basic. Thus, reducing
sugars reduce picric acid (yellow solution) to picramic
acid (mahogany red solution).
Reaction:
Positive result: blue-black or purple color solution
Example: Starch
Reagent: Saturated picric acid solution and 5 drops 10%
Na2CO3
Positive result: mahogany red solution
Examples:
Positive: glucose, galactose, maltose, fructose,
lactose, xylose
Negative: sucrose, glycogen, starch
You might also like
- Bill Nye Energy Video WorksheetDocument2 pagesBill Nye Energy Video WorksheetJACOB SANCHEZ83% (6)
- Unit V: Principles of Histology and HistochemistryDocument14 pagesUnit V: Principles of Histology and Histochemistryمروة صلاح0% (1)
- Identification of Biomolecules LAB TEST RESULTSDocument2 pagesIdentification of Biomolecules LAB TEST RESULTSkathryn_bruyère100% (1)
- 시험 및 인증 정보 (Test & Certificate) : Nissan 자동차 규격 시험Document6 pages시험 및 인증 정보 (Test & Certificate) : Nissan 자동차 규격 시험daaaadNo ratings yet
- Technol: Winter Diesel Conditioner PlusDocument11 pagesTechnol: Winter Diesel Conditioner PlusAnonymous Ov6SPCmNo ratings yet
- Test Result Discussion/Explanation: CarbohydratesDocument11 pagesTest Result Discussion/Explanation: CarbohydratesAnnapril TasicNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Test For MacromoleculesDocument4 pagesLaboratory Test For MacromoleculesOdessa KwonNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules NotesDocument2 pagesBiological Molecules NotesJayasutha RamanNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-03-28 at 11.36.42 AMDocument48 pagesScreenshot 2023-03-28 at 11.36.42 AMSourayaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8 - CarbohydratesDocument1 pageExperiment 8 - CarbohydratesZhen SniperNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates ResultsDocument4 pagesCarbohydrates ResultsVincent ManganaanNo ratings yet
- Color Reactions Intact Protein (Gluten) Basic HydrolysisDocument6 pagesColor Reactions Intact Protein (Gluten) Basic HydrolysisJennifer CamaNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Shanny G. Estera RPH: 5-HydrixymethylfurfuralDocument4 pagesPrepared By: Shanny G. Estera RPH: 5-HydrixymethylfurfuralJennifer CamaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates TestsDocument3 pagesCarbohydrates TestsKings PrideNo ratings yet
- Bio 1 RasheedDocument26 pagesBio 1 RasheedRaghad AlNo ratings yet
- Picric Acid TestDocument2 pagesPicric Acid TestHOly makaroniNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lab ReviewerDocument6 pagesBiochem Lab ReviewerDarlin Maree JamonNo ratings yet
- Benedict'S Test: Qualitative Tests For CarbohydratesDocument5 pagesBenedict'S Test: Qualitative Tests For Carbohydrateskatherine m. superioridadNo ratings yet
- Test For CarbohydratesDocument4 pagesTest For Carbohydratesmishya.1904No ratings yet
- Characterization of CarbohydratesDocument3 pagesCharacterization of CarbohydratesHyvieNo ratings yet
- Proteins LASDocument6 pagesProteins LASelly scatusNo ratings yet
- Proteins: Prepared By: Cristopher P. Yting, RPHDocument30 pagesProteins: Prepared By: Cristopher P. Yting, RPHJane DuhhNo ratings yet
- Tests For The Presence of Various Organic MoleculesDocument7 pagesTests For The Presence of Various Organic MoleculesICAMisterPNo ratings yet
- Chem Lab Semi Final ReviewDocument10 pagesChem Lab Semi Final ReviewianlesteryugueNo ratings yet
- Lipids Week2Document6 pagesLipids Week2Princess Joy YabutNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Module Summary 1Document4 pagesLaboratory Module Summary 1Karina Kaye LlapitanNo ratings yet
- Benedict's Test For Reducing Sugars: CarbohydratesDocument9 pagesBenedict's Test For Reducing Sugars: CarbohydratesRica NorcioNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry MIDTERMS LABDocument1 pageBiochemistry MIDTERMS LABcha cuteNo ratings yet
- 1 - Biology LabDocument6 pages1 - Biology LabFranz NelmidaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 12: Digestion in The MouthDocument16 pagesExperiment 12: Digestion in The Mouthkirstie guill100% (2)
- Test For CarbohydratesDocument15 pagesTest For CarbohydratesRandy AminolaNo ratings yet
- BiochemDocument3 pagesBiochemPaulene Marie SicatNo ratings yet
- Biochem Moving Exam Reviewer 2Document19 pagesBiochem Moving Exam Reviewer 2gyleveloso21No ratings yet
- 3 Test For CarbohydratesDocument8 pages3 Test For CarbohydratesAllyssa Lorraine PrudencioNo ratings yet
- Qualitative TestsDocument36 pagesQualitative Testsanirbanmanna88320No ratings yet
- Iodine Test: Polysaccharides Color Reaction With IodineDocument2 pagesIodine Test: Polysaccharides Color Reaction With IodineAlexandra TarucNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Lab SlidesDocument42 pagesCarbohydrates Lab SlidesZeian Jacob BaylaNo ratings yet
- Biology Lab - PDF Summarization PDFDocument5 pagesBiology Lab - PDF Summarization PDFahmadshalhout21No ratings yet
- Lab 2 Discussion 2024Document21 pagesLab 2 Discussion 2024piyada.poNo ratings yet
- General and Specific Test of CarbohydratesDocument7 pagesGeneral and Specific Test of CarbohydratesAudrey DiolataNo ratings yet
- Results and Discussion CarbohydratesDocument4 pagesResults and Discussion CarbohydratesVincent A. Sunggayan-NiezNo ratings yet
- Postlab Discussion Expt 2 Detection of Carbohydrates, Proteins and LipidsDocument19 pagesPostlab Discussion Expt 2 Detection of Carbohydrates, Proteins and LipidsDale Miko SanchezNo ratings yet
- An ThroneDocument2 pagesAn ThroneJames EullaranNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Tests On Amino Acids and ProteinsDocument9 pagesQualitative Tests On Amino Acids and ProteinsCorine RepatoNo ratings yet
- Notes-Food Proximate AnalysisDocument23 pagesNotes-Food Proximate AnalysisMuhammad Raza UllahNo ratings yet
- Section3 Polysaccharides PDFDocument17 pagesSection3 Polysaccharides PDFSHNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1B NotesDocument5 pagesExperiment 1B NotesCharlie AbagonNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATES LabDocument42 pagesCARBOHYDRATES LabZiaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Experiment1 CarbohydratesDocument10 pagesBiochemistry Experiment1 CarbohydratesChery-an PletNo ratings yet
- Bio Lab Report (G2) PDFDocument10 pagesBio Lab Report (G2) PDFAina NabihaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Module 2Document4 pagesWorksheet Module 2YuraNo ratings yet
- Practical 1 Chemistry Salt AnalysisDocument30 pagesPractical 1 Chemistry Salt AnalysisFarhan ChNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7Document2 pagesExperiment 7Mian RoshaanNo ratings yet
- Characterization of LipidsDocument4 pagesCharacterization of LipidsJustin VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Test For Glucose and Albumin Laboratory in BiochemistryDocument10 pagesTest For Glucose and Albumin Laboratory in BiochemistryJe KirsteneNo ratings yet
- Molisch Test: Name of Test Reagent Used Positive Result Use of The Test Additional InformationDocument3 pagesMolisch Test: Name of Test Reagent Used Positive Result Use of The Test Additional InformationShine GatilloNo ratings yet
- BC Lab (Carbohydrates)Document4 pagesBC Lab (Carbohydrates)Cassandra HerreraNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 3Document4 pagesLaboratory 3lili ry100% (1)
- CARBOHYDRATES WPS OfficeDocument11 pagesCARBOHYDRATES WPS OfficeSyainaaa DalpasanNo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATES Qualitative TestsDocument3 pagesCARBOHYDRATES Qualitative TestsEdith BelenNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Tests For CarbohydratesDocument22 pagesQualitative Tests For CarbohydratesHelal HamadNo ratings yet
- Tds Dep 455sDocument3 pagesTds Dep 455sA MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Compressed Gas Association CGA V-1 Cylinder Valve ConnectionsDocument4 pagesCompressed Gas Association CGA V-1 Cylinder Valve ConnectionsmauroNo ratings yet
- Answers To Workbook Exercises: Unit 7 Material Changes Exercise 7.1 Acids and AlkalisDocument2 pagesAnswers To Workbook Exercises: Unit 7 Material Changes Exercise 7.1 Acids and AlkalisBhawana SinghNo ratings yet
- Coconut Milk Drop Velvet BB CreamDocument1 pageCoconut Milk Drop Velvet BB CreamSandieNo ratings yet
- Administration of Medication Through Subcutaneous and Intradermal InjectionDocument6 pagesAdministration of Medication Through Subcutaneous and Intradermal InjectionjeromeNo ratings yet
- Propileno: Robles Luna JoelDocument50 pagesPropileno: Robles Luna JoeldarkwolfxdNo ratings yet
- Investigation On Tensile Properties of Epoxy/graphene Nano-Platelets/ Carboxylated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber Ternary Nanocomposites Using Response Surface MethodologyDocument12 pagesInvestigation On Tensile Properties of Epoxy/graphene Nano-Platelets/ Carboxylated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber Ternary Nanocomposites Using Response Surface MethodologyAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNo ratings yet
- WCO - EFC White Paper2022 - Materials and CorrosionDocument22 pagesWCO - EFC White Paper2022 - Materials and CorrosionBANNOUR OthmaneNo ratings yet
- (Patent) US4915930Document9 pages(Patent) US4915930Pavita SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Astronomy A Beginner S Guide To The Universe 7th Edition Chaisson Test Bank PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Astronomy A Beginner S Guide To The Universe 7th Edition Chaisson Test Bank PDFwiggleberefts3t0100% (11)
- Sri Sathya Sai Institute of Higher Learning: Second Semester Examinations, April 2019Document125 pagesSri Sathya Sai Institute of Higher Learning: Second Semester Examinations, April 2019Pranav NNo ratings yet
- Flange Comparison Chart: Pipeline Solutions For The Water, Gas, Oil, and Petrochemical IndustriesDocument2 pagesFlange Comparison Chart: Pipeline Solutions For The Water, Gas, Oil, and Petrochemical IndustriesmarcalpiNo ratings yet
- 10 Chemical Bonding PDFDocument2 pages10 Chemical Bonding PDFShahid Basha SkNo ratings yet
- Activated Carbon Filters Seitz AKS BRO enDocument12 pagesActivated Carbon Filters Seitz AKS BRO enVarNo ratings yet
- List Besaran Diskon Maksimal Per Produk: NO Kode Produk Komposisi Kemasan HNADocument10 pagesList Besaran Diskon Maksimal Per Produk: NO Kode Produk Komposisi Kemasan HNAapotekerNo ratings yet
- AU Instructions For Use Creatine Kinase (CK NAC)Document8 pagesAU Instructions For Use Creatine Kinase (CK NAC)Anas TjNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2022Document28 pagesChemistry 2022Study remix100% (1)
- 1 s2.0 S0958946517310958 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S0958946517310958 MainDaniel Rosas ElguetaNo ratings yet
- Direct Hydrothermal Treatment of Sugarcane Juice For 3D Oxygen Rich Carbon Aerogel NiCo2O4 Based SupercapacitorDocument12 pagesDirect Hydrothermal Treatment of Sugarcane Juice For 3D Oxygen Rich Carbon Aerogel NiCo2O4 Based SupercapacitorAnh DuyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Pmc-1-36 (Paid) PaperDocument202 pagesChemistry Pmc-1-36 (Paid) PaperHaresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument20 pagesSecond Law of Thermodynamicsshzamel Tungala100% (1)
- Brief Course Synopsis: Recommended LiteratureDocument3 pagesBrief Course Synopsis: Recommended LiteratureBlessings MushayiNo ratings yet
- Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Micropropagated: Centella Asiatica L.UrbDocument5 pagesQualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Micropropagated: Centella Asiatica L.UrbNanda Trisna OliviaNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument27 pagesBio MoleculesMr XNo ratings yet
- Environmental Cleanliness in Enclosed Spaces - Guide To in Situ High Efficiency Filter Leak TestingDocument20 pagesEnvironmental Cleanliness in Enclosed Spaces - Guide To in Situ High Efficiency Filter Leak TestingОлег СоловьевNo ratings yet
- 3 PotentiometryDocument11 pages3 Potentiometry175-44-Faraz HussainNo ratings yet
- Hand Out-Biochemistry-2022Document3 pagesHand Out-Biochemistry-2022Rounak RajNo ratings yet