Class 12 Chapter 4 Planning
Uploaded by
deepanshu kumarClass 12 Chapter 4 Planning
Uploaded by
deepanshu kumarCommon questions
Powered by AIPlanning reduces the risk of uncertainty by allowing managers to make future predictions based on past experiences and assumptions. These assumptions, which form the premises of planning, help in foreseeing potential changes and uncertainties in the business environment. By having a structured plan, organizations can minimize the impacts of unexpected events and adapt quickly to maintain stability and pursue their goals. Assumptions in planning include both internal factors like cost and resource availability and external factors like technological advances, competition, and government policies .
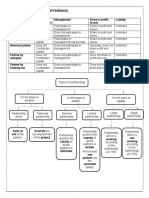
Single-use plans are designed for one-time events or projects that typically have a unique objective, such as a specific marketing campaign or an organizational restructuring. For example, a budget for a special-offer promotion is a single-use plan because it addresses a specific situation that does not recur. In contrast, standing plans, like policies and procedures, are used repeatedly in organizational scenarios that occur regularly. For instance, a company policy on employee conduct or a procedural guide for handling customer complaints are standing plans, as they offer continuous guidance over extended periods .
Decision-making in planning involves selecting the best possible alternative from various options to achieve organizational objectives. This selective process is crucial as planning inherently involves making choices about what is to be done, when, how, and by whom. The impact of decision-making in planning is significant because it determines the course of action that can best achieve the desired goals efficiently and effectively. By evaluating the positive and negative aspects of each potential course of action, managers can decide on the most feasible and successful path .
Setting objectives is a critical initial step in the planning process as it defines the desired outcomes for the organization. Clearly set objectives provide a direction for the entire organization's efforts, ensuring all activities align towards achieving common goals. Objectives also serve as a benchmark for evaluating performance and guide decision-making processes. They must be SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) to effectively influence organizational direction and help in coordinating efforts across various departments .
In a dynamic business environment, planning faces limitations due to its inherent rigidity and the difficulty in predicting future changes accurately. This can result in plans failing if they cannot adapt to rapid changes in customer preferences, competitor strategies, or external situations like natural disasters. To mitigate these limitations, organizations can adopt flexible planning processes, encouraging adaptive strategies that allow continuous modifications. This can include contingency planning and fostering a culture that values innovation and responsiveness, thus maintaining relevance in a fast-evolving market .
Planning as a primary function of management acts as the foundation upon which other managerial activities such as organizing, leading, and controlling are built. Without planning, there would be no framework or direction, making the execution of organizing and leading less effective. It ensures that there are clear objectives, thus organizing resources becomes more structured and purposeful. Furthermore, planning establishes the standards for controlling, as it provides the benchmarks against which actual performance is measured. This structured sequence significantly enhances the overall efficiency and effectiveness of management practices .
Planning provides direction by establishing clear goals and objectives in advance, which ensures that all managerial efforts are focused consistently toward achieving the organizational goals. This fosters a unified approach, preventing aimless work, and enhances coordination among different departments. As a result, it improves organizational performance by ensuring resources are used efficiently and effectively, leading to higher productivity and achievement of goals. Planning also allows anticipation of potential challenges, enabling proactive strategies to address them, thus maintaining consistent performance levels .
Planning facilitates innovation by providing a structured environment where managers are encouraged to think creatively about the future. With clear goals set, managers can focus their creative energies on developing new methods, products, or processes to achieve these objectives. For example, in planning for market expansion, a manager might innovate by proposing a new digital marketing strategy or developing a novel product to meet untapped consumer needs. This creative problem-solving and exploratory thinking during the planning phase can lead to innovative solutions that drive business growth and competitiveness .
Planning can lead to increased organizational rigidity as it often involves establishing fixed procedures and guidelines, which can discourage spontaneous and adaptive decision-making. This rigidity may result in resistance to change and inability to quickly respond to new market conditions or innovative disruptions. Consequently, organizations may struggle to remain competitive, leading to missed opportunities and potential declines in market share. To combat this, businesses should integrate flexibility in their planning processes, allowing for adjustments that reflect real-time changes in the environment .
Establishing standards for controlling in planning is crucial because it provides benchmarks against which actual performance can be measured. This comparison is essential for identifying variances and taking corrective actions. By establishing these standards through planning, managers have clear criteria to evaluate the success of executed plans and to make informed decisions to enhance effectiveness. It ensures that organizational activities align with the planned objectives, thereby improving accountability and resource utilization, and ultimately leading to improved performance and goal achievement .