Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module - 1 - Question Bank
Uploaded by
ManjunathVGudurOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Module - 1 - Question Bank
Uploaded by
ManjunathVGudurCopyright:
Available Formats
Module_1 Question Bank
Diode Applications
1. Explain the working of PN junction diode under forward biased and reverse
biased.
2. What is rectifier circuit? Explain the classification of the rectifier. Derive the
following expressions for half wave rectifier: IDC, IRMS, ripple factor, efficiency.
3. Explain with the neat circuit diagram and waveforms full wave bridge rectifier.
Also derive VDC, Vrms values. Show that the efficiency of full wave bridge rectifier
is 81%.
4. Explain with neat circuit diagram and waveforms the working of center-tapped
full wave rectifier. Derive the following expressions for Full wave rectifier: IDC,
IRMS, ripple factor, efficiency.
5. A full wave rectifier uses 2 diodes having internal resistance of 20 Ω each. The
transformer rms secondary voltage from center to each end is 50 V. Find Im, Idc,
Irms and Vdc. if the load is 980 Ω.
6. A half wave rectifier is fed from a supply of 230 V, 50 Hz with step down
transformer of ratio 3:1. Resistive load connected is 10 KΩ. The diode forward
resistance is 75Ω and transformer secondary is 10 Ω. Calculate the DC load
current, DC load voltage, efficiency and ripple factor.
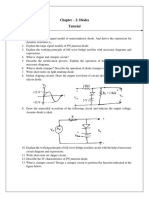
7. For the circuit shown in fig below find (i) current and voltages in the circuit for RL
= 450Ω. VZ = 10 V.
8. Explain the operation of half wave rectifier with capacitor filter with neat circuit
diagrams and waveforms.
9. Explain how the Zener diode helps in voltage regulation with neat circuit diagram.
Give detailed mathematical analysis.
10. Explain the working of photo diode.
11. What is semiconductor diode? Explain the different equivalent circuits of diode.
12. Explain the functional block diagram of 78XX series voltage regulator.
You might also like
- Ece 1001: Basic Electronics: Assignment Sheet - 1Document2 pagesEce 1001: Basic Electronics: Assignment Sheet - 1Deepanshu SehgalNo ratings yet
- ECE 301 Electronics 1: A. Half-Wave RectificationDocument24 pagesECE 301 Electronics 1: A. Half-Wave RectificationVince Hugo GutibNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For Module-I: DC, DC, RMS, RMSDocument1 pageQuestion Bank For Module-I: DC, DC, RMS, RMSShubhang CharantimathNo ratings yet
- 22223.BEE Tutorial Sheet 1 (Semiconductor Diodes and Applications)Document2 pages22223.BEE Tutorial Sheet 1 (Semiconductor Diodes and Applications)Rajiv SatijaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics (BBEE103/BBEE203) - Question Bank - VTUDocument11 pagesBasic Electronics (BBEE103/BBEE203) - Question Bank - VTUShrishail Bhat100% (1)
- Edc - Assignment Questions - NbaDocument5 pagesEdc - Assignment Questions - Nbagunda manasaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Question BankDocument1 pageModule 1 Question BankAbcNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (BEEE) (I Year I Sem) Unit - I Short QuestionsDocument4 pagesBasic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (BEEE) (I Year I Sem) Unit - I Short Questionsmonika0404No ratings yet
- EdcqbDocument10 pagesEdcqbPranveer Singh PariharNo ratings yet
- Rectifiers&filters NOTESDocument50 pagesRectifiers&filters NOTESMake the Best with SunithaGuganNo ratings yet
- Module-Wise Eln QBDocument5 pagesModule-Wise Eln QBRashmi SamantNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics question bankDocument6 pagesPower Electronics question bankDarshan B RNo ratings yet
- EMI Laboratory 2Document2 pagesEMI Laboratory 2DEO SALVACIONNo ratings yet
- Question of EE ProjectDocument5 pagesQuestion of EE ProjectANJALI KUMARINo ratings yet
- Edc Question BankDocument6 pagesEdc Question BankManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Edec Question Paper-IDocument8 pagesEdec Question Paper-IarunfriendsNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuits and Devices Laboratory - ELCE-221 Experiment No. 2 Diode Applications (Part A) Rectifiers, ClippersDocument6 pagesElectronic Circuits and Devices Laboratory - ELCE-221 Experiment No. 2 Diode Applications (Part A) Rectifiers, ClippersLittle VoiceNo ratings yet
- EDC - Question BankDocument7 pagesEDC - Question BankSwaum KisNo ratings yet
- EE1152- Circuits & ElectronicsDocument5 pagesEE1152- Circuits & ElectronicsSaranya PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Ece Vii Power Electronics (10ec73) AssignmentDocument6 pagesEce Vii Power Electronics (10ec73) AssignmentThomas PriceNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Concept in Power SystemsDocument9 pagesPower Electronics Concept in Power SystemsT.l. SelvamNo ratings yet
- Assignment QuestionsDocument9 pagesAssignment QuestionsSravan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ece-Vii-Power Electronics (10ec73) - Assignment PDFDocument6 pagesEce-Vii-Power Electronics (10ec73) - Assignment PDFAdarsh S Shettigar100% (1)
- Basic Electrical Engineering Laboratory Exp 3Document5 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Laboratory Exp 3Afiq BahaNo ratings yet
- EPD Lab#9Document8 pagesEPD Lab#9Muhammad ShaheerNo ratings yet
- Phys 222 Revision QuestionsDocument2 pagesPhys 222 Revision Questionswashingtone otieno oiroNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics - 102409025108 - 1Document7 pagesPower Electronics - 102409025108 - 1Herbert DeepakNo ratings yet
- ELN QBDocument3 pagesELN QBbalakrishnak eceNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronic Circuits Assignment QuestionsDocument6 pagesAnalog Electronic Circuits Assignment QuestionschaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Ehsan (3050) Lab 05Document7 pagesEhsan (3050) Lab 05Antenna /// Power ElectronicsNo ratings yet
- EC-BASIC ELECTRONICs and InsDocument6 pagesEC-BASIC ELECTRONICs and InsAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- Half Wave Rectifier and Full Wave RectifierDocument5 pagesHalf Wave Rectifier and Full Wave RectifierAdvyth Vaman AkalankamNo ratings yet
- Subject Name: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering / Ge 2151Document3 pagesSubject Name: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering / Ge 2151Gokul ChandrasekaranNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsLab - Manual March2010Document64 pagesElectronicsLab - Manual March2010pnarendrareddy.mscNo ratings yet
- E-Note 12425 Content Document 20231105014816AMDocument6 pagesE-Note 12425 Content Document 20231105014816AMkartik.doye2005No ratings yet
- Modified EXPERIMENT 10 (E) - 8.01.2020Document13 pagesModified EXPERIMENT 10 (E) - 8.01.2020VishalNo ratings yet
- BEEE Question BankDocument5 pagesBEEE Question Bankram rajaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-QB-Semicond Diodes& ApplicsDocument3 pagesChapter 1-QB-Semicond Diodes& ApplicsRamyaNo ratings yet
- SDC- Important Questions for Semiconductor Diodes and CircuitsDocument5 pagesSDC- Important Questions for Semiconductor Diodes and CircuitsInstagramNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document4 pagesAssignment 3Manasi JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document4 pagesChapter 2shoojeet adhikariNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 2 EE32200 - Ronny VintimillaDocument23 pagesLab Report 2 EE32200 - Ronny VintimillaRonny VintimillaNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Devices and Controlled RectifiersDocument7 pagesPower Electronics Devices and Controlled Rectifierssushil4056No ratings yet
- Full Wave RectifierDocument6 pagesFull Wave RectifierXavier0% (1)
- Pe Course File 9 198Document190 pagesPe Course File 9 198Dr ADITYA VORANo ratings yet
- Basic Electronic Devices and Circuits Lab ExperimentsDocument45 pagesBasic Electronic Devices and Circuits Lab ExperimentsChirag Sachdeva100% (2)
- QuestionsDocument2 pagesQuestionsmalladhinagarjunaNo ratings yet
- REEEFFFSESDocument6 pagesREEEFFFSESezradural99No ratings yet
- What Do You Mean by Transistor BiasingDocument4 pagesWhat Do You Mean by Transistor BiasinganupvasuNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5-Soliman - ECELABDocument10 pagesExperiment 5-Soliman - ECELABKim SolimanNo ratings yet
- Ee-304 Analog Electronics 75 QuestionsDocument5 pagesEe-304 Analog Electronics 75 QuestionsnaactitexcellenceNo ratings yet
- Study Guide EE225 Ver1Document6 pagesStudy Guide EE225 Ver1aonNo ratings yet
- Exp 5 Diodes 05Document5 pagesExp 5 Diodes 05api-3717843No ratings yet
- Beee Mid 2 Subjective 14.02.2023Document1 pageBeee Mid 2 Subjective 14.02.2023HarshithNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Lab (Experiment 2 Report) : Submitted By: Group: G7 Ashutosh Garg (2018MEB1213) Ashwin Goyal (2018MEB1214)Document8 pagesBasic Electronics Lab (Experiment 2 Report) : Submitted By: Group: G7 Ashutosh Garg (2018MEB1213) Ashwin Goyal (2018MEB1214)Ashutosh GargNo ratings yet
- Electronics Devices Lab - Exp 2 - Mid Term - Fall 22-23 - ACSDocument19 pagesElectronics Devices Lab - Exp 2 - Mid Term - Fall 22-23 - ACSdark lionNo ratings yet
- Mech-I-Basic Electronics Engg AssignmentDocument6 pagesMech-I-Basic Electronics Engg AssignmentArunNo ratings yet
- Diode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesFrom EverandDiode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)