Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Taste Brochure
Uploaded by
Courtney GomezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Taste Brochure
Uploaded by
Courtney GomezCopyright:
Available Formats
The three nerve associated with taste are:
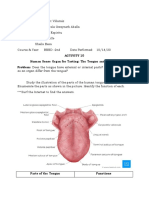
The tongue
TASTE
Facial nerve( cranial nerve VII)-provides
fibers to the anterior two third of the The Tongue:
Is a muscular organ in the mouth covered with a moist, pink tissue called mucosa.
tongue. Occupies floor of the mouth
Glossopharyngeal nerve( cranial nerve It is 3 inches long
IX)-provides fibers to the posterior third of Superior surface consists of
the tongue. stratified squamous epithelium
Vagus nerve ( cranial nerve X)-provides Has numerous papillae containing
fibers to the epiglottis region. sensory receptors for the sense of
Taste sense is served by cranial nerves VII, IX, taste in taste bud.
and X, that send impulses to the solitary
nucleus of the medulla. From there, impulses
are sent to the thalamus and the gustatory
cortex.
Two major types of Epithelial cells in the
taste bud: .
Gustatory Epithelial cells: Parts of the Tongue:
Gustatory hair projects from the tip of the Root: Taste refers to the
gustatory epithelial cells located between the hyoid bone and throughout of flavour
Sensory dendrites, surround the gustatory the mandible felt in the mouth and
epithelial cells, this represents the initial Attaches the tongue to the roof of the
gustatory pathway to the brain
the throat in touch
mouth
with any substance.
Body:
Makes up the anterior ⅔ of the tongue
Basal Epithelial cells: Rough surface due to the lingual Is a muscular organ in
Taste buds are frequently exposed to friction papillae the mouth covered
and burns, by hot food thus, the buds are Apex(tip): with a moist,pink
replaced every 7-10 days Rest against the incisor teeth
The basal epithelial cells divide and tissue called mucosa.
Is highly mobile
differentiate into new gustatory cells
Fibers carrying taster from the
tongue are found in two cranial Gustatory Pathway
nerves pairs.
fibers synapse in the solidarity
nucleus the medulla,and from
there impulse stream to the
thalamus and to the gustatory
cortex in the insula.
fibers also project to the
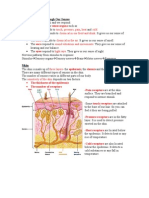
hypothalamus and limbic system Taste Receptors
structure region determine the
The seven most common flavors in
appreciation of what we are
food that are directly detected by the
tasting.
tongue are: sweet, bitter, sour, salty,
meaty (umami), cool, and hot.
Each taste bud has between 50 to
150 taste receptor cells. These cells
contain receptors that extend
upward inside the taste pore. These
Three nerves that carries taste signals to extensions are taste hairs called
the brain stem: microvilli. The microvilli come into
1. The chorda tympani nerve-provides fiber contact with the chemicals in the
to anterior two-thirds of the tongue food and drink you consume.
2. The glossopharyngeal nerve- provides
The three types of papillae Each type of receptor has a different
fiber to posterior third of the tongue
are: 3. The vagus nerve (from the throat area manner of sensory transduction: that
fungiform (mushroom like) and palate) is, of detecting the presence of a
filiform (filum - thread like) certain compound and starting an
circumvallate. action potential which alerts the
brain.
You might also like
- Anatomy of the tongue and related mouth structuresDocument13 pagesAnatomy of the tongue and related mouth structureslala landNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Tutorial Task 6 & 7Document19 pages2.1 Tutorial Task 6 & 7ENOCH NAPARI ABRAMANNo ratings yet
- Hearing Anatomy OverviewDocument8 pagesHearing Anatomy OverviewMarie HwangNo ratings yet
- Special Senses NotesDocument17 pagesSpecial Senses NotesizabelaNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Physiology Chapter 12 Sensory Organ NotesDocument9 pagesHuman Anatomy Physiology Chapter 12 Sensory Organ NotesadarshNo ratings yet
- Ansci Lec ReviewerDocument15 pagesAnsci Lec ReviewerKarla CarbonelNo ratings yet
- How the Human Brain Can Discriminate a Trillion SmellsDocument2 pagesHow the Human Brain Can Discriminate a Trillion SmellsNsubuga ArthurNo ratings yet
- L5 - Special SensesDocument39 pagesL5 - Special SensesNana Boakye Anthony AmpongNo ratings yet
- Five Sense: DR - Rr. Sri Ratna Rahayu M.Kes, PHDDocument37 pagesFive Sense: DR - Rr. Sri Ratna Rahayu M.Kes, PHDDewi Rahma PutriNo ratings yet
- The SensesDocument46 pagesThe SensesRizqi Putra ZaraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Special Senses NotesDocument58 pagesAnatomy of Special Senses Notesglenian560No ratings yet
- Vap3 Ch15 Lecture PresentationDocument190 pagesVap3 Ch15 Lecture PresentationlisbethNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Sensory SystemDocument3 pagesLesson 6 Sensory SystemElijah Melo FloresNo ratings yet
- UNIT 5 (Special Sense Organs)Document7 pagesUNIT 5 (Special Sense Organs)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloNo ratings yet
- Bio Psy Finals ReviewerDocument9 pagesBio Psy Finals ReviewerZian Lei MienNo ratings yet
- Sensory Organs: ANS 215 Anatomy & Physiology of Domesticated AnimalsDocument62 pagesSensory Organs: ANS 215 Anatomy & Physiology of Domesticated AnimalsRizqi Putra ZaraNo ratings yet
- Specialized Areas of The CerebrumDocument7 pagesSpecialized Areas of The Cerebrumapi-303067223No ratings yet
- Anatomi Copy 241 31Document10 pagesAnatomi Copy 241 31HAKAMNo ratings yet
- Organ SensorikDocument62 pagesOrgan SensorikPutri Dwi lestariNo ratings yet
- Pretest Faal 19Document4 pagesPretest Faal 19Tasya SunandarNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of ToungeDocument1 pageStructure and Function of ToungeDevendra RawatNo ratings yet
- Special Assignment Lab PortfolioDocument13 pagesSpecial Assignment Lab Portfolioveer the robo boyNo ratings yet
- Your 5 Senses and How They WorkDocument6 pagesYour 5 Senses and How They WorkKarl Angelo Velasco PorrasNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Reviewer: Special Senses and the Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesHuman Anatomy Reviewer: Special Senses and the Endocrine SystemAzodNo ratings yet
- Activity 11 The Tongue and The SkinDocument7 pagesActivity 11 The Tongue and The SkinRoi Vincent VillaraizNo ratings yet
- TS - EN - 5 - GS - Our Body Parts - Sense Organs - Karnati VenkatReddyDocument12 pagesTS - EN - 5 - GS - Our Body Parts - Sense Organs - Karnati VenkatReddyKaira SaxenaNo ratings yet
- CSF Flow and Somatic SensesDocument6 pagesCSF Flow and Somatic SensesJERIKO EGBALIC CABREZOSNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Midterms Shebby-CabalhinDocument15 pagesAnaphy Midterms Shebby-CabalhinVILMA SABLA-ONNo ratings yet
- The MouthDocument13 pagesThe MouthAjigotto ubiq.No ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology Class 2Document83 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology Class 2breanna coyneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 World Through Our SensesDocument6 pagesChapter 1 World Through Our Sensesdeviltim88% (8)
- Chapter 12 The Sense Organs Anatomy and Physiology of Eye Ear Skin Tongue NoseDocument7 pagesChapter 12 The Sense Organs Anatomy and Physiology of Eye Ear Skin Tongue NoseSanketraje JadhavNo ratings yet
- The Senses: Sensory Receptors and PathwaysDocument28 pagesThe Senses: Sensory Receptors and PathwaysChona FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument2 pagesUntitled Documentapi-614390592No ratings yet
- Assistant Clinical Denture Prosthetics, Francisco,: UniversityDocument8 pagesAssistant Clinical Denture Prosthetics, Francisco,: UniversityMaqbul AlamNo ratings yet
- Science Form 2Document6 pagesScience Form 2EriqNo ratings yet
- Specialized Mucosa, Oral Mucous MembraneDocument19 pagesSpecialized Mucosa, Oral Mucous MembraneAMIT GUPTANo ratings yet
- Theme: Management and Continuity of LifeDocument10 pagesTheme: Management and Continuity of LifeAnonymous 7pn3HEbYLNo ratings yet
- The Tongue: Anatomy, Taste, and Common ConditionsDocument5 pagesThe Tongue: Anatomy, Taste, and Common ConditionsMark TiongsonNo ratings yet
- Science Form 2Document9 pagesScience Form 2yvonne vonne vonneNo ratings yet
- Five Senses and Their ReceptorsDocument63 pagesFive Senses and Their ReceptorsGresia FalentinaNo ratings yet
- Is Your Skin, Nose, Tongue, Ears, and Eyes Right? I. ObjectivesDocument11 pagesIs Your Skin, Nose, Tongue, Ears, and Eyes Right? I. ObjectivesHafizah Ghany HayudinnaNo ratings yet
- Science Folio Form 2: The World Through Our SensesDocument19 pagesScience Folio Form 2: The World Through Our Sensesfikery100% (1)
- Lecture 26Document9 pagesLecture 26Shakeel ButtNo ratings yet
- SENSES & SENSATION REVIEWDocument11 pagesSENSES & SENSATION REVIEWNicole Ken AgdanaNo ratings yet
- AV Smell TasteDocument9 pagesAV Smell TasteKiyo RaNo ratings yet
- Sensory Mechanism: Almozara Francisco Villaflores LorenzoDocument29 pagesSensory Mechanism: Almozara Francisco Villaflores LorenzoMerrylFranciscoNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Senses-TasteDocument16 pagesThe Chemical Senses-TastejolilarmatarNo ratings yet
- TICMAN - GZP 3101 6 - Activity 14Document12 pagesTICMAN - GZP 3101 6 - Activity 14Abram TicmanNo ratings yet
- 33-3 The SensesDocument19 pages33-3 The Sensesnancie8No ratings yet
- Pragyan College of Nursing-Bhopal BSC Nursing 1 Year Subject-Anatomy and Physiology Topic-Sense of Taste/TongueDocument3 pagesPragyan College of Nursing-Bhopal BSC Nursing 1 Year Subject-Anatomy and Physiology Topic-Sense of Taste/TongueNeelofur Ibran AliNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE F3 (Chapter 1)Document49 pagesSCIENCE F3 (Chapter 1)Nurul NasaruddinNo ratings yet
- The World through our senses: An overview of sensory organs and their functionsDocument8 pagesThe World through our senses: An overview of sensory organs and their functionsMathew Hon Jun YoonNo ratings yet
- Sense Organs: Taste, Smell, Hearing, Vision, and EquilibriumDocument50 pagesSense Organs: Taste, Smell, Hearing, Vision, and EquilibriumjosephNo ratings yet
- Physiology Aspect of The Special SensesDocument31 pagesPhysiology Aspect of The Special SensesDaniel MendozaNo ratings yet
- Five Human Senses, What & Why? : 3rd Grade Science Books Series: Third Grade BooksFrom EverandFive Human Senses, What & Why? : 3rd Grade Science Books Series: Third Grade BooksNo ratings yet
- Ent AnaDocument79 pagesEnt AnaGyanendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Ent MCQ (All Team) PDFDocument40 pagesEnt MCQ (All Team) PDFHaitham Haytham90% (30)
- Important clinical notes for medical examsDocument89 pagesImportant clinical notes for medical examsShariq ShaNo ratings yet
- Textbook of Trigeminal NeuralgiaDocument255 pagesTextbook of Trigeminal NeuralgiaOmar VillamizarNo ratings yet
- Infratemporalna FossaDocument64 pagesInfratemporalna FossaJelena TasikNo ratings yet
- Facial Nerve ParalysisDocument36 pagesFacial Nerve ParalysisSylvia DiamondNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Cranial NervesDocument3 pagesAnatomy - Cranial NervesKaradex DexondNo ratings yet
- Dentistry Questions Final 2016 PDFDocument393 pagesDentistry Questions Final 2016 PDFWasiAliMemon0% (1)
- Facial Nerve and Its Applied AnatomyDocument37 pagesFacial Nerve and Its Applied Anatomyherojittlc100% (1)
- High Yield Gross Anatomy: Course SupplementDocument15 pagesHigh Yield Gross Anatomy: Course Supplementmaria martinez100% (1)
- ScalpDocument17 pagesScalpKaruna PrabhuNo ratings yet
- MCQ - 1 Head and NeckDocument5 pagesMCQ - 1 Head and NeckNinie Sharkhan95% (22)
- Physiotherapy in Neuro Conditions Glady Samuel Raj PDFDocument331 pagesPhysiotherapy in Neuro Conditions Glady Samuel Raj PDFAnkita Tiwari82% (50)
- A Very Rare Type of NeuralgiaDocument2 pagesA Very Rare Type of NeuralgiarosaNo ratings yet
- Surgical Anatomy Facial NerveDocument4 pagesSurgical Anatomy Facial NervedominicdefNo ratings yet
- Clinical OSCE Notes PDFDocument49 pagesClinical OSCE Notes PDFArwa QishtaNo ratings yet
- Block 6 SEQsDocument49 pagesBlock 6 SEQsBosco785No ratings yet
- 1st Prof MBBS Supplementary 10 Years CompilationDocument67 pages1st Prof MBBS Supplementary 10 Years CompilationDebasis PramanikNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy Quizbank QuestionsDocument18 pagesNeuroanatomy Quizbank Questionskishorechandra86% (29)
- (K33) Cranial and Spinal NerveDocument68 pages(K33) Cranial and Spinal NerveCut Putri Astritd Adelina100% (1)
- 10.7556 Jaoa.2015.022Document5 pages10.7556 Jaoa.2015.022CarolinaNo ratings yet
- Kulkarni Anatomy A Problem Solving Approach 2nd EditionDocument979 pagesKulkarni Anatomy A Problem Solving Approach 2nd EditionDevanshi Pandey100% (1)
- Bell''s PalsyDocument54 pagesBell''s Palsywahyu_sitaNo ratings yet
- Dentistry: Orofacial Pain: A ReviewDocument6 pagesDentistry: Orofacial Pain: A ReviewAstriAl-hutamiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Imporatant Points by Dr. Asif AliDocument31 pagesAnatomy Imporatant Points by Dr. Asif AliSyed imran AbbasNo ratings yet
- Topographic and Neural Anatomy of The Depressor Anguli Oris Muscle and Implications For Treatment of Synkinectic Facial ParalysisDocument11 pagesTopographic and Neural Anatomy of The Depressor Anguli Oris Muscle and Implications For Treatment of Synkinectic Facial ParalysisJohn NinNo ratings yet
- The Innervation of The Soft Palate MusclesDocument7 pagesThe Innervation of The Soft Palate MusclesjmccoyNo ratings yet
- TongueDocument10 pagesTongueBhuwanesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy McqsDocument20 pagesNeuroanatomy McqsNuman Khan0% (1)
- Anatomy of The Facial NerveDocument75 pagesAnatomy of The Facial NerveSerene Batra100% (2)