Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP Ashra
Uploaded by
Sherry Rodriguez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views4 pagesThe nurse provided 8 hours of independent and dependent nursing interventions to a patient with acute confusion related to neurologic trauma from a vehicular accident. After the interventions, the patient was able to: maintain a baseline level of consciousness and not experience decreased memory; respond appropriately to questions. The nursing objectives and interventions helped reorient the patient and ensure safety, while keeping explanations short and simple to address cognitive impairment from traumatic brain injury.
Original Description:
Original Title
ncp ashra
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe nurse provided 8 hours of independent and dependent nursing interventions to a patient with acute confusion related to neurologic trauma from a vehicular accident. After the interventions, the patient was able to: maintain a baseline level of consciousness and not experience decreased memory; respond appropriately to questions. The nursing objectives and interventions helped reorient the patient and ensure safety, while keeping explanations short and simple to address cognitive impairment from traumatic brain injury.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views4 pagesNCP Ashra
Uploaded by
Sherry RodriguezThe nurse provided 8 hours of independent and dependent nursing interventions to a patient with acute confusion related to neurologic trauma from a vehicular accident. After the interventions, the patient was able to: maintain a baseline level of consciousness and not experience decreased memory; respond appropriately to questions. The nursing objectives and interventions helped reorient the patient and ensure safety, while keeping explanations short and simple to address cognitive impairment from traumatic brain injury.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
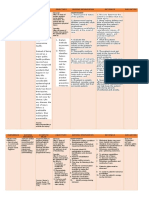
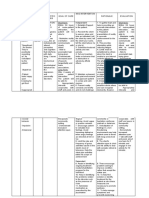
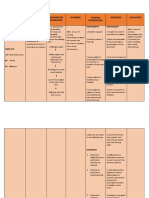
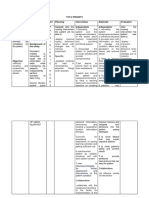
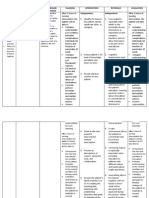
NCP NI ASHRA
CUES NURSING NURSING NURSING RATIONALE EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS OBJECTIVES INTERVENTIONS
Subjective cues: Acute After rendering 8 INDEPENDENT: After rendering 8
The patient confusion hours of independent hours of independent
is confused related to and dependent 1. Introduce 1. These and dependent
as neurologic nursing interventions, yourself measures are nursing interventions,
evidenced trauma as the patient will be before any part of the goals were
by the evidenced by: able to: interaction reorientation. completely met as
patient and Too much evidenced by the
stated “Hindi - Maintain a procedures. information at patient was able to:
ko maalala baseline level Explain care once might
kung kailan of in short and increase Maintained a
at saan ako consciousness simple confusion and baseline level
naaksidente and will not sentences make the of
eh.” experience before and patient more consciousness
decreased throughout irritable. and will not
Objective cues: memory. the process. experience
The decreased
patient’s Respond memory.
diagnosis is appropriately 2. Assess
Traumatic to questions. sensory 2. Assessment of Responded
Brain Injury awareness. sensory appropriately
secondary awareness is to questions.
to Vehicular crucial to patient
Accident safety. Injury to
Head the parietal lobe
Trauma. can cause loss
of sensory
The patient perception and
is prevent
disoriented appropriate
to time and responses to
place. environmental
stimuli.
3. Assess
changes in 3. The upper
orientation cerebral
and functions are
personality. the first to be
affected when
there is altered
circulation or
oxygenation.
The damage
can occur
initially at the
onset of the
injury or develop
later due to
swelling or
bleeding. Motor,
cognitive,
perceptual, and
personality
changes can
develop and
may persist.
4. Assess the
patient’s 4. Cognitive
level of impairment can
cognitive interfere with
impairment. how the patient
with TBI
functions.
Assessing the
patient’s level of
cognitive
impairment can
help determine
appropriate
rehabilitation.
5. Ensure
patient 5. Patients with
safety. acute confusion
are not able to
follow
directions. It is
important to
promote patient
safety by
providing a
hazard-free
6. Reorient the environment.
patient as
needed. 6. Patients with
mild TBI may be
disoriented and
may exhibit
short-term
memory loss.
Frequent
reorientation is
essential before
any interaction
to promote a
trusting
relationship and
cooperation
7. Keep from the patient.
explanations
and activities 7. This allows the
short and patient to better
simple. understand the
instructions and
procedures
performed. It is
vital to give
these
explanations
before and
throughout the
patient’s care.
They are
unlikely to
remember long
instructions so
keep teaching
8. Eliminate sessions short.
extraneous
noise as 8. This can help
necessary. reduce the
patient’s anxiety
, confusion, and
exaggerated
emotional
responses
associated with
sensory
overload.
You might also like
- Case Study (Mrs. Greene)Document9 pagesCase Study (Mrs. Greene)Trina Joy DomantayNo ratings yet
- Post-Placement Learning Plan 2018Document2 pagesPost-Placement Learning Plan 2018api-393048315No ratings yet
- Alzheimers Disease Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesAlzheimers Disease Nursing Care PlanMary Josette NavarraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Phinma University of IloiloDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Phinma University of IloiloBeatrice ManingasNo ratings yet
- Case Study 6Document4 pagesCase Study 6Mary Hope Bacuta0% (2)
- CHAPTER - 1 - Definitions and Foundations of ODDocument31 pagesCHAPTER - 1 - Definitions and Foundations of ODEshan Garg50% (2)
- Pedagogy of Biological Science PDFDocument135 pagesPedagogy of Biological Science PDFRahul Singh100% (1)
- Work-Life Balance in The New MillenniumDocument8 pagesWork-Life Balance in The New MillenniumAdrian BorleaNo ratings yet
- Piprams Lesson Plan On Topic: Subject:: Mental Status Examination Mental Health NursingDocument20 pagesPiprams Lesson Plan On Topic: Subject:: Mental Status Examination Mental Health NursingVaishali SinghNo ratings yet
- NCP Active SeizureDocument4 pagesNCP Active SeizureAngelica CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Catatonic Schizophrenia NCP (Revised)Document13 pagesCatatonic Schizophrenia NCP (Revised)Wen Silver100% (1)
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledKristil ChavezNo ratings yet
- NCP ALZHEIMERS DISEASE DX IMDocument3 pagesNCP ALZHEIMERS DISEASE DX IMPatty RomeroNo ratings yet
- NSG Care Plan - BipolarDocument17 pagesNSG Care Plan - BipolaraijelethdaldeavilaNo ratings yet
- Alzheimer'S Disease Definition: Signs and SymptomsDocument4 pagesAlzheimer'S Disease Definition: Signs and SymptomsMauren DazaNo ratings yet
- San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocument1 pageSan Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesTrisha Joy T. JumonongNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationALIANA KIMBERLY MALQUESTONo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationALIANA KIMBERLY MALQUESTONo ratings yet
- Bipolar 1 Disorder NCPDocument3 pagesBipolar 1 Disorder NCPJoy-Rena Sabinay OchondraNo ratings yet
- Hallucinations NCP PDFDocument3 pagesHallucinations NCP PDFANGELA ERES BALINGBING100% (2)
- NCP GrievingDocument5 pagesNCP GrievingEllenare Racion33% (3)
- Date Cues Nsg. DX Scientific Basis Goal of Care NSG Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesDate Cues Nsg. DX Scientific Basis Goal of Care NSG Intervention Rationale EvaluationWenalyn Grace Abella LlavanNo ratings yet
- NCP Chronic ConfusionDocument4 pagesNCP Chronic ConfusionLyka DianaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationMaye ArugayNo ratings yet
- Dementia NCPDocument3 pagesDementia NCPDonnalyn MillaresNo ratings yet
- NCP Inffective Individual CopingDocument1 pageNCP Inffective Individual CopingNatalie DulawanNo ratings yet
- NCP - Indi CSDocument6 pagesNCP - Indi CSFretzgine Lou ManuelNo ratings yet
- NCP PsychosisDocument3 pagesNCP PsychosisKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-is100% (1)
- Top 2 PriorityDocument6 pagesTop 2 PriorityRonel ResurricionNo ratings yet
- NCP - Major Depressive DisorderDocument7 pagesNCP - Major Depressive DisorderJaylord Verazon100% (1)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Inference Nursing Goal Nursing Interventions EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Inference Nursing Goal Nursing Interventions EvaluationtrishxianieNo ratings yet
- Lucie Fink NCPsss - BUAYA PIA N32Document7 pagesLucie Fink NCPsss - BUAYA PIA N32Pia Mae BuayaNo ratings yet
- Risk For Peripheral Neurodysfunction NCPDocument3 pagesRisk For Peripheral Neurodysfunction NCPLeonardo Martin FrivaldoNo ratings yet
- NCP Form 1Document2 pagesNCP Form 1Kate Aenyle AgsoyNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationjay5ar5jamorabon5torNo ratings yet
- NCM117 NCPDocument2 pagesNCM117 NCPHANNAH MICOLE GAERLANNo ratings yet
- NCP StrokeDocument6 pagesNCP StrokeIrish TatelNo ratings yet
- Edit - ch8 - and ch9Document4 pagesEdit - ch8 - and ch9BellRodriguezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Ellen Adarna, Borikat Na Siya. Ga Igat Igat Lang Na Siya"Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Ellen Adarna, Borikat Na Siya. Ga Igat Igat Lang Na Siya"dubouzettheresaNo ratings yet
- NCP-and-Drug-study For MENDocument8 pagesNCP-and-Drug-study For MENVillie SumandeNo ratings yet
- Schizo NCPDocument18 pagesSchizo NCPRoscheen Berg TutorNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Thought ProcessDocument3 pagesDisturbed Thought ProcesschessaNo ratings yet
- NCM 117 - Graded SeatworkDocument7 pagesNCM 117 - Graded SeatworkShamsa AfdalNo ratings yet
- Anxiety NCPDocument2 pagesAnxiety NCPAnaleah MalayaoNo ratings yet
- Dayda NursingcareplanDocument23 pagesDayda NursingcareplanMachelle lang sapat naNo ratings yet
- NCP PsychDocument7 pagesNCP PsychScarletNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Body ImageDocument2 pagesDisturbed Body ImageJohanna Elaine Tandoc50% (2)
- Dienizs Labini BSN-3E Brain Cancer Activities: B. Glioblastoma MultiformeDocument11 pagesDienizs Labini BSN-3E Brain Cancer Activities: B. Glioblastoma MultiformeDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Roldan NCP-G2CDocument4 pagesRoldan NCP-G2CCeegi Arville RoldanNo ratings yet
- NCM 116Document9 pagesNCM 116karen dapalNo ratings yet
- NCP - Psychiatric SettingDocument20 pagesNCP - Psychiatric SettingKyle Ü D. CunanersNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan On FatigueDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan On FatigueMelvin D. RamosNo ratings yet
- Fdar - Schizophrenia Jan 11-13Document2 pagesFdar - Schizophrenia Jan 11-13Grape Juice100% (1)
- Palo Ayen Trisha MCN Lab Module 5 NCPDocument5 pagesPalo Ayen Trisha MCN Lab Module 5 NCPAyen PaloNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Thought Processes DescribeDocument2 pagesDisturbed Thought Processes DescribePRINCESS LARA CASILAONo ratings yet
- Care Plan UndifferentiatedDocument11 pagesCare Plan Undifferentiatedilakkiya ilakkiyaNo ratings yet
- Graduate School Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Expected OutcomeDocument3 pagesGraduate School Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Expected OutcomeMary Rose F. MalaluanNo ratings yet
- Case 8 NCP (Multiple Sclerosis)Document2 pagesCase 8 NCP (Multiple Sclerosis)je-ann catedralNo ratings yet
- NCP Group 1Document3 pagesNCP Group 1Basema HashhashNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective Cues: Goal/objectiveDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective Cues: Goal/objectiveNikka PelayoNo ratings yet
- NCP CamsDocument3 pagesNCP CamsNica Cielo B. LibunaoNo ratings yet
- Independent: IndependentDocument6 pagesIndependent: IndependentGina PrancelisoNo ratings yet
- NCP - Final Na TalagaDocument2 pagesNCP - Final Na TalagaAmy GarciaNo ratings yet
- Summary of Janina Fisher's Healing the Fragmented Selves of Trauma SurvivorsFrom EverandSummary of Janina Fisher's Healing the Fragmented Selves of Trauma SurvivorsNo ratings yet
- Child Development 9th Edition Berk Solutions ManualDocument27 pagesChild Development 9th Edition Berk Solutions Manualbeyradicantdays100% (31)
- 01 1 Types of TestDocument17 pages01 1 Types of Testhello ya75% (4)
- DLP For Cot (Imperatives) To PrintDocument3 pagesDLP For Cot (Imperatives) To PrintJonard JocoNo ratings yet
- FarrisT. ICL 7106 MonsterDocument5 pagesFarrisT. ICL 7106 MonsterToushiba Wirt FarrisNo ratings yet
- ADMS 1010 - Week 6Document2 pagesADMS 1010 - Week 6Mohammad AmrajiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 The Science of PsychologyDocument20 pagesUnit 1 The Science of PsychologyDeneika MorganNo ratings yet
- Teaching Values: An Experiential ApproachDocument11 pagesTeaching Values: An Experiential ApproachJay-Ar Bangloy TuliaoNo ratings yet
- Charlotte Sharrad: Personal StatementDocument3 pagesCharlotte Sharrad: Personal Statementapi-428492384No ratings yet
- Leadership Excellence August 2022Document50 pagesLeadership Excellence August 2022Ashwini KumarNo ratings yet
- Digit SpanDocument10 pagesDigit SpanshanNo ratings yet
- Drama PortfolioDocument21 pagesDrama PortfolioCindy LakhramNo ratings yet
- Classroom Management PlanDocument2 pagesClassroom Management Planapi-541765085No ratings yet
- Lesson-Plan C Block Life Skills 2017Document2 pagesLesson-Plan C Block Life Skills 2017Braden SchraderNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Stress and Emotion On The VoiceDocument2 pagesThe Effects of Stress and Emotion On The VoiceNell KeeneNo ratings yet
- Do Your Genes Make You A CriminalDocument39 pagesDo Your Genes Make You A CriminalParisha SinghNo ratings yet
- Factors That Influence Media SelectionDocument11 pagesFactors That Influence Media SelectionAlona B. LincunaNo ratings yet
- Research Paper. FinalDocument49 pagesResearch Paper. FinalJeronica VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Oriana T Johnson Leach CV Weebly PDFDocument18 pagesOriana T Johnson Leach CV Weebly PDFapi-718408484No ratings yet
- Tomar Et Al 2021Document18 pagesTomar Et Al 2021De Eventia GuruNo ratings yet
- DLL Aug 27-30, 2019Document3 pagesDLL Aug 27-30, 2019Aq Nga To100% (1)
- Quality of Work Life (QWL) : Human Resource ManagementDocument17 pagesQuality of Work Life (QWL) : Human Resource ManagementVarsha PandeyNo ratings yet
- Creative Problem SolvingDocument24 pagesCreative Problem SolvingAlexandru ConstantinNo ratings yet
- Oral Test Teachers GuideDocument2 pagesOral Test Teachers GuideIrinedianSribudaya100% (1)
- Pictogram LessonDocument2 pagesPictogram Lessonapi-339056821No ratings yet
- Decision Analysis:: Nur Aini MasrurohDocument28 pagesDecision Analysis:: Nur Aini MasrurohluqitraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3. Market Research & Consumer Behavior. IDocument29 pagesLecture 3. Market Research & Consumer Behavior. ILip Keong Low100% (2)