Professional Documents
Culture Documents
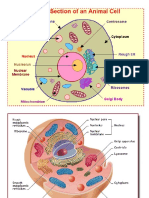
Ribosomes
Ribosomes
Uploaded by
atanu mitraOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ribosomes
Ribosomes
Uploaded by
atanu mitraCopyright:
Available Formats
• Ribosomes: The ribosome is a large complex of RNA and protein molecules.
They each
consist of two subunits, and act as an assembly line where RNA from the nucleus is used
to synthesise proteins from amino acids. Ribosomes can be found either floating freely
or bound to a membrane (the rough endoplasmatic reticulum in eukaryotes, or the cell
membrane in prokaryotes).
• Lysosomes and Peroxisomes – eukaryotes only: Lysosomes contain digestive enzymes
(acid hydrolases). They digest excess or worn-out organelles, food particles, and
engulfed viruses or bacteria.
• Centrosome – the cytoskeleton organiser: The centrosome produces the microtubules
of a cell – a key component of the cytoskeleton. It directs the transport through the ER
and the Golgi apparatus.
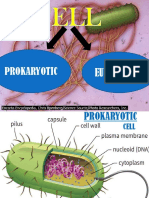
Many types of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell have a cell wall. The cell wall acts to protect the
cell mechanically and chemically from its environment, and is an additional layer of protection
to the cell membrane. Different types of cell have cell walls made up of different materials; plant
cell walls are primarily made up of pectin, fungi cell walls are made up of chitin and bacteria cell
walls are made up of peptidoglycan.
Prokaryotic
Capsule
A gelatinous capsule is present in some bacteria outside the cell membrane and cell wall. The
capsule may be polysaccharide as in pneumococci, meningococci or polypeptide as Bacillus
You might also like
- Biology Prelim NotesDocument47 pagesBiology Prelim NotesAmanie SidawiNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument24 pagesCellsapi-95529788100% (1)
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Microbiology For The Health Sciences: Section II. Introduction To MicroorganismsDocument48 pagesMicrobiology For The Health Sciences: Section II. Introduction To MicroorganismsHashim Ghazo100% (1)
- OrganellesDocument13 pagesOrganellesjanaNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument70 pagesFunctional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsTrixie De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure Function and PropertiesDocument10 pagesCell Structure Function and PropertiesWanda JohnNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biochemical Aspects) : Dr. Abid AliDocument49 pagesCell (Biochemical Aspects) : Dr. Abid AliShahzad MazharNo ratings yet
- RibosomesDocument1 pageRibosomesatanu mitraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document29 pagesChapter 4skywalkerNo ratings yet
- Pro and EuDocument15 pagesPro and EuCy BathanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.Document11 pagesLecture 3.rahaf.khalid226No ratings yet
- BIO ReviewerDocument14 pagesBIO ReviewerRenjyl Gay DeguinionNo ratings yet
- General Biology ReviewerDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerBaby AleiraNo ratings yet
- Science PROKARYOTICEUKARYOTICDocument8 pagesScience PROKARYOTICEUKARYOTICsecurity securedNo ratings yet
- Structures Outside The Cell MembraneDocument1 pageStructures Outside The Cell Membranepiping stressNo ratings yet
- CellDocument8 pagesCellWhyL NificentNo ratings yet
- Biology Sem1 - Chap1Document78 pagesBiology Sem1 - Chap1kotaknotaku100% (1)
- Cell - The Unit of LifeDocument8 pagesCell - The Unit of Lifelpc4944No ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Biology NotesDocument22 pagesUnit 1 - Biology Noteshuman tie lineNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument2 pagesCell OrganellesSurminie Muksin100% (1)
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument22 pagesCell Structure and FunctionRavi DesaiNo ratings yet
- Lipids: Functions, Including Storage of Metabolic Energy, Protection Against Dehydration and Pathogens, TheDocument3 pagesLipids: Functions, Including Storage of Metabolic Energy, Protection Against Dehydration and Pathogens, Theulanrain311No ratings yet
- Module IDocument18 pagesModule IAdvith A JNo ratings yet
- 8 Cell The Unit of LifeDocument5 pages8 Cell The Unit of Lifebikram keshari pradhanNo ratings yet
- Biology Study Material - Xi - 22-23-Compressed - 0Document14 pagesBiology Study Material - Xi - 22-23-Compressed - 0gana63693No ratings yet
- Lec-8,9 CellsDocument30 pagesLec-8,9 CellsAbdullah-Al-mehedi HiraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Biochemical Characteristics of Living MatterDocument69 pagesChapter 1 Biochemical Characteristics of Living MatterJoyce Jimenez0% (1)
- CellDocument16 pagesCellanantchouhdary1709No ratings yet
- Parts of A Bacterial CellDocument41 pagesParts of A Bacterial CellAbegail AguirreNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Chem 322Document86 pagesCarbohydrates Chem 322www.fatimahussain22No ratings yet
- 1 Lecture Intro SeminarDocument26 pages1 Lecture Intro SeminarAnonymous guyNo ratings yet
- Cellular Structure and Function Lectrue 4Document24 pagesCellular Structure and Function Lectrue 4madhav biyaniNo ratings yet
- NucleusDocument10 pagesNucleusjhariesargente05No ratings yet
- بايو م 2Document7 pagesبايو م 2alidoctor678No ratings yet
- Microbiology For The Health Sciences: Section II. Introduction To MicroorganismsDocument48 pagesMicrobiology For The Health Sciences: Section II. Introduction To MicroorganismsHiba Abu-jumahNo ratings yet
- 2 - The Cell and The Epithelium LectureDocument82 pages2 - The Cell and The Epithelium Lecturegodara28pNo ratings yet
- Cells, Organelles, Microscopy TechniquesDocument34 pagesCells, Organelles, Microscopy TechniquesJeffrey100% (1)
- Topic 2 NotesDocument53 pagesTopic 2 Notessuperhigh06No ratings yet
- MCB 203 EUKARYOTIC CELLDocument9 pagesMCB 203 EUKARYOTIC CELLGabi taofeekatNo ratings yet
- Cell StructuresDocument25 pagesCell StructuresAminul Islam Arafat 2132536642No ratings yet
- L.3 - The CellDocument3 pagesL.3 - The CellJari JariNo ratings yet
- Plant Cells: by Fortunate Refil Bsed Sci 2Document20 pagesPlant Cells: by Fortunate Refil Bsed Sci 2Marifer DapatNo ratings yet
- CellDocument22 pagesCellrapidalerthubNo ratings yet
- Cells PDFDocument107 pagesCells PDFida hadiNo ratings yet
- CellDocument21 pagesCellsouravNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 CytoplasmmDocument46 pagesLecture 2 Cytoplasmmdiyarberwari15No ratings yet
- 1.cell PhysiologyDocument5 pages1.cell PhysiologyNektarios TsakalosNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Crop PhysiologyDocument19 pagesFundamentals of Crop PhysiologyRsNo ratings yet
- DNA, The Genetic MaterialDocument6 pagesDNA, The Genetic MaterialMarinelle TumanguilNo ratings yet
- Cell - The Unit of LifeDocument12 pagesCell - The Unit of LifeannindikuzhiyilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Micropara (Outline)Document5 pagesChapter 3 Micropara (Outline)Jezrylle BalaongNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument17 pagesThe CelluissojohnyzNo ratings yet
- EukaryotesDocument4 pagesEukaryotesWareesha BatoolNo ratings yet
- (H2 Bio) Chapter 1 Cell BiologyDocument29 pages(H2 Bio) Chapter 1 Cell BiologywengiemotshegweNo ratings yet
- Chapter6 AnswersDocument2 pagesChapter6 AnswersSammy AhmedNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument6 pagesProkaryotes and Eukaryoteshussainm1234No ratings yet
- Cell Basics by MuneebDocument45 pagesCell Basics by MuneebMuneeb Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Cell Structure & FunctionDocument27 pagesLecture 3 - Cell Structure & Functionlazysadoon09No ratings yet
- Cell NucleusDocument1 pageCell Nucleusatanu mitraNo ratings yet
- TipsDocument2 pagesTipsatanu mitraNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria and ChloroplastsDocument2 pagesMitochondria and Chloroplastsatanu mitraNo ratings yet
- Resume Headline For FresherDocument2 pagesResume Headline For Fresheratanu mitraNo ratings yet
- Transitioning From College To WorkplaceDocument4 pagesTransitioning From College To Workplaceatanu mitraNo ratings yet