Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Nucleus
Uploaded by
atanu mitraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell Nucleus
Uploaded by
atanu mitraCopyright:
Available Formats
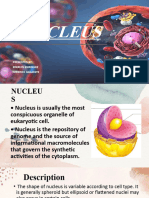
• Cell nucleus – eukaryotes only - A cell's information center, the cell nucleus is the most
conspicuous organelle found in a eukaryotic cell. It houses the cell's chromosomes, and
is the place where almost all DNA replication and RNA synthesis (transcription) occur.
The nucleus is spherical and separated from the cytoplasm by a double membrane
called the nuclear envelope. The nuclear envelope isolates and protects a cell's DNA
from various molecules that could accidentally damage its structure or interfere with its
processing. During processing, DNA is transcribed, or copied into a special RNA, called
messenger RNA (mRNA). This mRNA is then transported out of the nucleus, where it is
translated into a specific protein molecule. The nucleolus is a specialized region within
the nucleus where ribosome subunits are assembled. In prokaryotes, DNA processing
takes place in the cytoplasm.
Liver
The liver is located primarily in the right side of the body, just beneath the
diaphragm. It is the largest gland in the body. On the surface, the liver is divided
into two major lobes and two smaller lobes. The cells of liver are called
hepatocytes.
The liver receives blood from two sources. Freshly oxygenated blood is brought to
the liver by the common hepatic artery, a branch of the celiac trunk from the
abdominal aorta. Blood that is rich in nutrients from the digestive tract is carried to
the liver by the hepatic portal vein.
You might also like
- Distinguishing Characteristics: Cytoplasm Cell Membrane PhospholipidsDocument2 pagesDistinguishing Characteristics: Cytoplasm Cell Membrane PhospholipidsNamra ZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- NucleusDocument5 pagesNucleussiddharthr954No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The CELLDocument14 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The CELLlorelie asisNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell StructureDocument13 pagesPlant Cell Structureshamosa85.saNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 1 Study GuideDocument3 pagesBiology Unit 1 Study GuideJohans MascardoNo ratings yet
- Cell TheoryDocument146 pagesCell TheoryGynewNo ratings yet
- Nucleus: The Head Quarter of CellDocument11 pagesNucleus: The Head Quarter of CellJigarS.MehtaNo ratings yet
- Biomedi Sem3 149306NOLDocument102 pagesBiomedi Sem3 149306NOLDennis Ebenezer DhanarajNo ratings yet
- Weel 4 SurveyDocument29 pagesWeel 4 SurveyAaron MostNo ratings yet
- Membrane Main Article: Cell MembraneDocument3 pagesMembrane Main Article: Cell MembraneAriella ZoeyNo ratings yet
- NucleusDocument10 pagesNucleusPinak ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Structure of A CellDocument17 pagesStructure of A CellBlake KamminNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument17 pagesThe CelluissojohnyzNo ratings yet
- Plant CellDocument21 pagesPlant CellAnedha AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Cell NucleusDocument4 pagesCell NucleusrajikrajanNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument36 pagesThe CellSam MumoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure: Rebecca MaynardDocument11 pagesCell Structure: Rebecca Maynardbecki93No ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Structures Notes SVDocument10 pagesEukaryotic Cell Structures Notes SValkbbushra25No ratings yet
- How Does Nucleus Protect DNADocument2 pagesHow Does Nucleus Protect DNADharmendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument5 pagesProkaryotes and EukaryotesFarhana AktharNo ratings yet
- NUCLEUSDocument2 pagesNUCLEUSSalma AslamNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology NotesDocument6 pagesCell Biology Notessaadc786100% (1)
- CELL Are The Small Living Units of An OrganismDocument6 pagesCELL Are The Small Living Units of An Organismsweet michaela paduaNo ratings yet
- Sample 67Document8 pagesSample 67Rica NorcioNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles - Lec. 1Document27 pagesCell Organelles - Lec. 1Hamza KaisNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell: Plasma MembraneDocument3 pagesAnimal Cell: Plasma MembraneArnolNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument40 pagesCellsemo mHAYNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument40 pagesEarth and Life ScienceGraceEstoleCaloNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiochemistryDocument8 pagesIntroduction To BiochemistrySudeshna KunduNo ratings yet
- Description of Cell Structure and FunctionDocument7 pagesDescription of Cell Structure and FunctionAin SoberanoNo ratings yet
- The Eukaryotic Cell's Genetic Instruction Are Haused in The Nucleus and Carried Out by The RibosomesDocument3 pagesThe Eukaryotic Cell's Genetic Instruction Are Haused in The Nucleus and Carried Out by The Ribosomesvin caNo ratings yet
- Major: Pre-PharmacyDocument4 pagesMajor: Pre-PharmacyFatima Al SayyedNo ratings yet
- Parts and FunctionDocument22 pagesParts and FunctionGalang AlphaNo ratings yet
- ىلوا هلحرم ناونعب ثحب cell nucleus فارشا دبع هبه م.م هذاتسلاا نيسحلاDocument9 pagesىلوا هلحرم ناونعب ثحب cell nucleus فارشا دبع هبه م.م هذاتسلاا نيسحلاعبد اللهNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Û CellsDocument18 pagesChapter 3 Û CellsRochelle Dorado BNo ratings yet
- Sec-6 BLG 311Document9 pagesSec-6 BLG 311stutiNo ratings yet
- Nuclei Nucleus Nuculeus Kernel SeedDocument1 pageNuclei Nucleus Nuculeus Kernel SeedValerie Ann FranciscoNo ratings yet
- EVANGELISTA - Task #1Document4 pagesEVANGELISTA - Task #1Gabrielle EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- NUCLEUSDocument24 pagesNUCLEUSJesa MoradaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells: ProkaryotesDocument8 pages1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells: Prokaryotesdavid tsaiNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology: Topic: The CellsDocument121 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology: Topic: The CellsJoan Ano CaneteNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures: The BasicsDocument4 pagesCell Structures: The BasicsParama CinthyaNo ratings yet
- CellDocument25 pagesCellHamada BakheetNo ratings yet
- 6 Cytology Nucleus 1Document35 pages6 Cytology Nucleus 1SamNo ratings yet
- Module IDocument18 pagesModule IAdvith A JNo ratings yet
- 2-Cell NucleusDocument35 pages2-Cell NucleusAthar Habib ShahaniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Cellular Level Part 2Document12 pagesLecture 3 Cellular Level Part 2Pia GalagalaNo ratings yet
- The Cell NucleusDocument7 pagesThe Cell NucleusvqarademirkovaNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument42 pagesCell OrganellesTrisha OxalesNo ratings yet
- LESSON - 2 and 3Document26 pagesLESSON - 2 and 3Kerberos DelabosNo ratings yet
- Cellular BiologyDocument8 pagesCellular BiologyStellaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Cell BiologyDocument43 pagesChapter 1-Cell Biologyapi-374357No ratings yet
- Cell Basics by MuneebDocument45 pagesCell Basics by MuneebMuneeb Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Interaction Between Two Different Organisms Living in Close Physical Association, Typically To The Advantage of BothDocument3 pagesInteraction Between Two Different Organisms Living in Close Physical Association, Typically To The Advantage of BothYana RbNo ratings yet
- Zoology IDocument8 pagesZoology ISalman AhmedNo ratings yet
- Interphasic NucleusDocument21 pagesInterphasic Nucleushamahamahama3No ratings yet
- NucleusDocument74 pagesNucleusbunniecaronan113003No ratings yet
- Cells and Tissues: J.C.CatolicoDocument85 pagesCells and Tissues: J.C.CatolicoGynew0% (1)
- Everything I Know About Cell Structure (I Learned From The Internet)Document4 pagesEverything I Know About Cell Structure (I Learned From The Internet)megleslieNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria and ChloroplastsDocument2 pagesMitochondria and Chloroplastsatanu mitraNo ratings yet
- TipsDocument2 pagesTipsatanu mitraNo ratings yet
- Resume Headline For FresherDocument2 pagesResume Headline For Fresheratanu mitraNo ratings yet
- Transitioning From College To WorkplaceDocument4 pagesTransitioning From College To Workplaceatanu mitraNo ratings yet