Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EC 405 MCQs
Uploaded by
Jayesh Joshi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views8 pagesOriginal Title
EC 405 MCQs (2)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views8 pagesEC 405 MCQs
Uploaded by
Jayesh JoshiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
Viva Questions
Subject Code: EC 405 Subject Name: Analog Circuits
1 When the input signal and the part of the output signal are in phase, the feedback is called
A Negative B Divisional feedback C Positive feedback D multiplicational
feedback feedback
2 When the input signal and the part of the output signal are in phase, the feedback is called
A Positive B Negative feedback C Divisional feedback D Multiplicational
feedback feedback
3 Use of positive feedback results in
A Oscillation B Amplification C Integration D Differentiation
4 Use of negative feedback results in
A Oscillation B Amplification C Integration D Differentiation
5 For voltage amplifier, with gain A and amplification factor β, the overall gain Af with negative
feedback is given as
A Af = A / 1-βA B Af = A / 1+βA C Af = A / 1-β D Af = A / 1+β
6 For voltage amplifier, with gain A and amplification factor β, the overall gain Af with positive
feedback is given as
A Af = A / 1+βA B Af = A / 1-βA C Af = A / 1-β D Af = A / 1+β
7 Stability of amplifier with positive feedback
A Increases B Decreases C Has no change D None of these
8 Stability of amplifier with negative feedback
A Decreases B Increases C Has no change D None of these
9 Voltage series feedback amplifier is also known as
A Current B Voltage amplifier C Transconductance D Transresistance
amplifier amplifier amplifier
10 Current shunt feedback amplifier is also known as
A Voltage B Current amplifier C Transconductance D Transresistance
amplifier amplifier amplifier
11 Current series feedback amplifier is also known as
A Voltage B Transconductance C Current amplifier D Transresistance
amplifier amplifier amplifier
12 Voltage shunt feedback amplifier is also known as
A Current B Transresistance C Transconductance D Voltage
amplifier amplifier amplifier amplifier
13 Barkhausen criterion states that, for oscillations the product of open loop gain (A) of the
amplifier and the feedback factor β is
A Greater than B Equal to one C Less than one D Equal to two
one
14 Frequency of oscillation of RC phase shift oscillator is given by
A F = 1/2RC B F = 1/2πRC C F = 1/2πR D F = 1/πRC
15 Frequency of oscillation of LC Hartley oscillator is given by
A F= 1/π√LC B F= 1/2π√LC C F= 1/2π√L D F= 1/2π√C
16 Technology used to construct integrated circuits by interconnecting a number of individual chips
is
A Monolithic B Hybrid technology C Thick film D Thin film
technology technology technology
17 In IC-packages, DIP stands for
A Double-in-line B Dual-in-line package C Dell-in-long package D Down-in-line
package package
18 In opamp IC μA741TC, T- represents the
A Device type B Package type C Commercial D None of these
temperature range
19 In opamp IC μA741TC, C- represents the
A Device type B Commercial C Package type D None of these
temperature range
20 In opamp IC μA741TC, μA741 - represents the
A Commercial B Device type C Package type D None of these
temperature
range
21 The basic building block of operational amplifier is
A Logrithmic B Differential amplifier C Instrumentation D Power
amplifier amplifier amplifier
22 In differential amplifier, if the output is measured between two collectors, it is reffered as
A Unbalanced B Balanced output C Balanced input D Unbalanced
output input
23 In differential amplifier, if the output is measured at one of the collector with respect to ground,
is referred as it
A Balanced B Unbalanced output C Balanced input D Unbalanced
output input
24 Differential amplifier is capable of amplifying
A AC signals only B Both AC and DC C DC signals only D None of these
input signals
25 When the same input is applied to both the input terminals of the differential amplifier,
amplifier is said to operate in
A Differential B Common mode C Double mode D None of these
mode configuration configuration
configuration
26 The input offset current equals the
A Average of the B Difference between C Collector electric D difference
two base the two base current divided by between the
currents. currents. electric current gain. two base-
emitter
voltages.
27 A common - mode signal is applied to
A The inverting B Both inputs C The non - inverting D None of these
input. input.
28 The input stage of an op amp is usually a
A Class B push-pull B Differential C CE amplifier. D Swamped
amplifier. amplifier. amplifier.
29 The common - mode rejection ratio is
A Very low. B As high as possible. C Equal to the voltage D Equal to the
gain. common-mode
voltage gain.
30 A 741 C has
A A voltage gain of B All of these C An input impedance D An output
200,000. of 2 MΩ. impedance of
75 Ω.
31 The voltage follower has a
A Small open - B Closed - loop voltage C Closed - loop D Large closed -
loop voltage gain of unity. bandwidth of zero. loop output
gain. impedance.
32 An opamp has a voltage gain of 200,000. If the output voltage is 1 V, the input voltage is
A 2.5 micro V. B 5 micro V. C 10 V. D 5 milli V.
33 The 741 C has a unity - gain frequency of
A 10 kHz. B 1 MHz. C 20 Hz. D 20 MHz.
34 The large signal bandwidth of an opamp is limited by its
A Loop gain B Slew rate C Output impedance D Input
frequency
35 Virtual ground of an op-amp means
A Terminal is B The terminal voltage C Either terminal is D None of these
grounded is zero due to the physicaly connected
directly other terminal is to ground or Voltage
connected to the is zero.
ground due to op-
amp properties.
36 Slew rate is defined as the
A Minimum rate B Maximum rate of C Moderate rate of D Maximum rate
of change of change of output change of output of change of
output voltage voltage with time voltage with time input voltage
with time with time
37 Output impedance of an ideal op-amp is
A Infinite B Zero C Low D Very high
38 Bandwidth of an ideal op-amp is:
A Very high B Infinite C Low D Very Low
39 CMRR of an ideal op-amp is
A Very high B Infinite C Low D Very Low
40 Slew rate of an ideal op-amp is
A Very high B Infinite C Low D Very Low
41 If op-amp has its closed loop gain 20 and UGB is 1MHz, then bandwidth of an amplifier is
A 20 KHz B 50 KHz C 100 KHz D 1 MHz
42 When a cosine-input is given to an op-amp integrator, the output will be
A A ramp. B A sinusoidal wave. C A rectangular wave. D A triangular
wave with dc
bias
43 When a rectangular-input is given to an op-amp differentiator, the output will be
A A step signal. B A triangular wave C A sinusoidal wave. D A rectangular
wave.
44 Voltage series feedback is used in
A Inverting B Non-Inverting C Differentiator D None of these
amplifier amplifier configuration
configuration configuration
45 Voltage shunt feedback is used in
A Non-Inverting B Inverting amplifier C Voltage Follower D None of these
amplifier configuration configuration
configuration
46 In the op-amp differentiator circuit the feedback component used is
A Semiconductor B Resistor C Capacitor D Inductor
component
47 In the op-amp Integrator circuit the feedback component used is
A Semiconductor B Capacitor C Inductor D Resistor
component
48 If the inputs to the inverting adder circuit is V1=0.1V, V2=0.2 and V3= - 0.1V, with gain 5, then
the output will be
A 10 V B -1 V C 1V D 0.2 V
49 If the inputs to the inverting adder circuits is V1=1V(DC) and V2=3Vp-p (Sinusoidal Signal), with
gain 1, then the output will be
A 3Vp-p B 3Vp-p (Sinusoidal C 4Vp-p (Sinusoidal D None of these
(Sinusoidal Signal) shift by -1V Signal)
Signal) shift by DC
1V DC
50 The gain of inverting amplifier is 5, the values of Rf and R1 will be
A 5k Ohm and 25k B 50k Ohm and 10k C 20k Ohm and 10k D None of these
Ohm Ohm respectively Ohm respectively
respectively
51 Basic Logrithmic amplifier is obtained by using a ____ in the negative feedback path.
A capacitor B Diode C Inductor D Resistor
52 Antilogrithmic amplifier is also known as
A Combinational B Exponential amplifier C Inverting Amplifier D Non Inverting
amplifier Amplifier
53 Output voltage is proportional to the exponential of input , is a
A Logrithmic B Antilogrithmic C Averaging amplifier D Summing
amplifier amplifier Amplifier
54 In triangular/rectangular wave generator, when ramp voltage attains a value equal to lower
threshold point of Schmitt trigger, the output of schmitt trigger changes its state from
A Negative B Positive saturation to C Remains in positive D Remains in
saturation negative saturation saturation negative
positive saturation
saturation
55 78XX series is a ________ voltage regulator.
A Negative fixed B Positive fixed C Positive adjustable D Negative
Adjustable
56 79XX series is a ________ voltage regulator.
A Positive fixed B Negative fixed C Positive adjustable D Negative
Adjustable
57 LM317 is a ___________ voltage regulator.
A Negative fixed B Positive adjustable C Positive fixed D Negative
Adjustable
58 LM337 is a ___________ voltage regulator.
A Negative fixed B Negative Adjustable C Positive fixed D Positive
adjustable
59 Conversion efficiency of a switching regulator can approach upto _____.
A 50% B 95% C 20% D 40%
60 Voltage controlled oscillator is also called as
A Frequency to B Voltage to frequency C Current to D Frequency to
voltage converter frequency converter current
converter converter
61 An active circuit in which the output voltage is proportional to the product of the two input
signals is called as
A Adder B A basic multiplier C Subtractor D Differentiator
62 IC AD534 is a
A Timer IC B Multiplier IC C OPAMP IC D Frequency
divider IC
63 IC 556 is a
A Timer IC B VCO IC C OPAMP IC D Frequency
divider IC
64 For a comparator, opamp is used in a
A Closed loop B Open loop mode C Neither open or D None of these
mode closed
65 In basic non inverting comparator, if input voltage is greater than reference voltage, the output
is
A Negative B Positive saturation C Zero voltage D None of these
saturation voltage
voltage
66 In basic non inverting comparator, if input voltage is less than reference voltage, the output is
A Positive B Negative saturation C Zero voltage D None of these
saturation voltage
voltage
67 In basic inverting comparator, if input voltage is less than reference voltage, the output is
A Negative B Positive saturation C Zero voltage D None of these
saturation voltage
voltage
68 In basic inverting comparator, if input voltage is greater than reference voltage, the output is
A Positive B Negative saturation C Zero voltage D None of these
saturation voltage
voltage
69 Inverting zero crossing detector is also called as
A Subtracter B Inverter C Differentiater D Adder
70 In zero crossing detector, the reference voltage is
A Positive B Zero C Negative D None of these
71 Schmitt trigger is also called as
A Non B Regenerative C Inverting D Non inverting
regenerative comparator comparator comparator
comparator
72 Filter that rejects the frequencies which are higher than the cut-off frequency is called as
A High pass filter B Low pass filter C Band pass filter D Band stop filter
73 Filter that rejects the frequencies which are less than the cut-off frequency is called as
A Low pass filter B High pass filter C Band pass filter D Band stop filter
74 In case of first order filter, roll off is at a rate of
A 40 dB/decade B 20 dB/decade C 80 dB/decade D 160 dB/decade
75 In case of second order filter, roll off is at a rate of
A 20 dB/decade B 40 dB/decade C 80 dB/decade D 160 dB/decade
You might also like
- AmplifiersDocument11 pagesAmplifiersJenalyn MacarilayNo ratings yet
- Special Topics - Opamps and Ics Feedback Amps and OscDocument8 pagesSpecial Topics - Opamps and Ics Feedback Amps and OscOrion LambdaNo ratings yet
- ECE - Op Amp QuestDocument11 pagesECE - Op Amp QuestSathyanatha PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Analog ElectronicsDocument4 pagesAnalog ElectronicsMD.RAKIBUL HASASNNo ratings yet
- False: True True True TrueDocument2 pagesFalse: True True True TrueSuubi brianNo ratings yet
- Ec 18Document11 pagesEc 18Darshan NakawalaNo ratings yet
- PPTDocument18 pagesPPTSaipreethiNo ratings yet
- Op AmpDocument3 pagesOp AmpAhnNo ratings yet
- AMPLIFIER CIRCUITS: TEEE/TETE 2103Document3 pagesAMPLIFIER CIRCUITS: TEEE/TETE 2103Suubi brianNo ratings yet
- Special Topics - Transistors and AmplifiersDocument4 pagesSpecial Topics - Transistors and AmplifiersOrion LambdaNo ratings yet
- Mapua Electronics 3 Final ExamDocument4 pagesMapua Electronics 3 Final ExamShir0 NobiNo ratings yet
- Analog ElectronicsDocument10 pagesAnalog ElectronicsRaj PatelNo ratings yet
- CompreDocument5 pagesCompreAunhel John Malinay AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics PDFDocument9 pagesAnalog Electronics PDFDoan BaoNo ratings yet
- The Current Gain For The Darlington Connection Is - 5 MaDocument13 pagesThe Current Gain For The Darlington Connection Is - 5 MaDenver G. MagtibayNo ratings yet
- Differential Amplifier & Op-Amp QuizDocument2 pagesDifferential Amplifier & Op-Amp QuizNarasimha KumarNo ratings yet
- Power Elex Finals PDFDocument5 pagesPower Elex Finals PDFDanilo PerezNo ratings yet
- MID1 ECA OnlineBitsDocument20 pagesMID1 ECA OnlineBitslucky j100% (1)
- Basic Elecs BillDocument202 pagesBasic Elecs BillAnneNo ratings yet
- Name: - Yr. & Sec: - DateDocument4 pagesName: - Yr. & Sec: - DateLara Kamelle Calinog Villasoto IINo ratings yet
- Elex Practice2334467Document3 pagesElex Practice2334467AnneNo ratings yet
- Op Amp Fundamentals AssessmentDocument2 pagesOp Amp Fundamentals AssessmentJastine GlobiogoNo ratings yet
- Put Your Answers (A, B, C or D) To The Question Numbers in The Score Sheet in The Last Page of This Question Paper. Time: 30 MinutesDocument8 pagesPut Your Answers (A, B, C or D) To The Question Numbers in The Score Sheet in The Last Page of This Question Paper. Time: 30 MinutesMani ThundiyilNo ratings yet
- Class A-D amplifier definitions and typesDocument24 pagesClass A-D amplifier definitions and typestikiraNo ratings yet
- Applied Multiple Choice - Typical QuestionsDocument10 pagesApplied Multiple Choice - Typical Questionsexe.dave.qNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Transistor Bias Circuits: Ac Ac e B CDocument3 pagesChapter 5: Transistor Bias Circuits: Ac Ac e B CDiana Ross CustodioNo ratings yet
- Analog ElectronicsDocument482 pagesAnalog ElectronicsCristina TungpalanNo ratings yet
- Electronics 2 Question Bank UnsDocument8 pagesElectronics 2 Question Bank UnsMohammad AntarNo ratings yet
- MCQ Chap 6Document16 pagesMCQ Chap 6Ariel Paulo G. TabangayNo ratings yet
- University of San Agustin Pre-Board Exam ReviewDocument8 pagesUniversity of San Agustin Pre-Board Exam ReviewRoyce SumagaysayNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY#3: Key Concepts of Power Electronics DevicesDocument3 pagesACTIVITY#3: Key Concepts of Power Electronics DevicesJhasper ManagyoNo ratings yet
- And NeetsDocument10 pagesAnd NeetsKier Jexter BagunuNo ratings yet
- Certcdavao: Instruction: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The FollowingDocument4 pagesCertcdavao: Instruction: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The FollowingJj JumawanNo ratings yet
- FET amplifier circuit guideDocument4 pagesFET amplifier circuit guideMansoor AslamNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Objective QuestionsDocument5 pagesUnit 4 Objective QuestionsRaviNo ratings yet
- Zener diode voltage regulator circuit problems and solutionsDocument5 pagesZener diode voltage regulator circuit problems and solutionsJonas ParreñoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 SCDocument37 pagesLecture 4 SCREMUEL JOHN ARELLANONo ratings yet
- Filter: All of TheseDocument24 pagesFilter: All of TheseMansoor AslamNo ratings yet
- 2.6power AmplifiersDocument9 pages2.6power AmplifiersChristine May CagaraNo ratings yet
- Analog ElectronicsDocument361 pagesAnalog ElectronicsVia Marie MesaNo ratings yet
- Review Questions Transistor and AmplifiersDocument2 pagesReview Questions Transistor and AmplifiersJohn PHilip MaramagNo ratings yet
- Ssc-Je-Electronic-Devices Electrical EngineeringDocument13 pagesSsc-Je-Electronic-Devices Electrical EngineeringPeerzada WahidNo ratings yet
- Jntu Online Examinations (Mid 2 - Eca) Cracked by Mr.20Document21 pagesJntu Online Examinations (Mid 2 - Eca) Cracked by Mr.20kattlaNo ratings yet
- Poweramplifiers 120119221518 Phpapp02Document32 pagesPoweramplifiers 120119221518 Phpapp02shankar1577100% (1)
- MME Electrical Session 1 Electrical FundamentalsDocument22 pagesMME Electrical Session 1 Electrical FundamentalsgpuonlineNo ratings yet
- IGCSE ElectricityDocument13 pagesIGCSE ElectricityHaider ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Class-B Power AmplifierDocument37 pagesClass-B Power AmplifiermesfinNo ratings yet
- QB ECC403 May 2022 Examination LIC SE EXTC Sem IV 2021-22Document9 pagesQB ECC403 May 2022 Examination LIC SE EXTC Sem IV 2021-22Dj RayNo ratings yet
- Jntu Online Examinations (Mid 2 - Eca)Document22 pagesJntu Online Examinations (Mid 2 - Eca)venkat gautam100% (2)
- Electronics ReviewerDocument2 pagesElectronics ReviewerroselleNo ratings yet
- Classification of Amplifiers Classification of Amplifiers 1. According To Frequency Capabilities. 1. According To Frequency CapabilitiesDocument31 pagesClassification of Amplifiers Classification of Amplifiers 1. According To Frequency Capabilities. 1. According To Frequency CapabilitiesAnaniah DuraiNo ratings yet
- AnalogEl-4-Power - Ampl-Part 1&2Document36 pagesAnalogEl-4-Power - Ampl-Part 1&2Albert GenceNo ratings yet
- Poweramps MCQ ReviewerDocument20 pagesPoweramps MCQ ReviewerJoecynnOycoNo ratings yet
- Mixed Quiz: Course-Wide ContentDocument2 pagesMixed Quiz: Course-Wide ContentHimanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- EX. NO: 1 Inverting, Non-Inverting Amplifiers and Differential Amplifier DateDocument125 pagesEX. NO: 1 Inverting, Non-Inverting Amplifiers and Differential Amplifier DateksrbalachandranNo ratings yet
- Power Amplifiers and ClassesDocument20 pagesPower Amplifiers and ClassesarunpatokarNo ratings yet
- ELectrician 4 Thsem NSQFDocument38 pagesELectrician 4 Thsem NSQFAbhimanyu Kilania100% (3)
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)No ratings yet
- EF900 Dissertation - Research TopicsDocument1 pageEF900 Dissertation - Research TopicsJayesh JoshiNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Microprocessor & Its Application - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument9 pagesUnit 4 - Microprocessor & Its Application - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inJayesh JoshiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Microprocessor & Its Application - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument10 pagesUnit 2 - Microprocessor & Its Application - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inJayesh JoshiNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Microprocessor & Its Application - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument9 pagesUnit 4 - Microprocessor & Its Application - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inJayesh JoshiNo ratings yet
- MPMC Unit 5Document62 pagesMPMC Unit 5ganeshNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 MCQDocument4 pagesUnit 3 MCQGEO MERINNo ratings yet
- Vaikom Muhammad Basheer Stories in Malayalam PDF FreeDocument5 pagesVaikom Muhammad Basheer Stories in Malayalam PDF FreekvharikeshNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Amplificador AudioDocument8 pagesData Sheet Amplificador AudiosebasvNo ratings yet
- Vacon NX OPTCI Modbus TCP Board User Manual DPD009Document32 pagesVacon NX OPTCI Modbus TCP Board User Manual DPD009TanuTiganuNo ratings yet
- User Manual of DCH-4000P-Ver DDocument17 pagesUser Manual of DCH-4000P-Ver DRobertNo ratings yet
- Principles of Operating Systems and Its ApplicationsDocument140 pagesPrinciples of Operating Systems and Its Applicationsray bryant100% (1)
- Cena de Los Filosofos en JavaDocument5 pagesCena de Los Filosofos en JavaCesar UlloaNo ratings yet
- XBox 360 Hardware DebugDocument36 pagesXBox 360 Hardware DebugAlexander Rivas Alpizar100% (1)
- Printlink5-ID - IV DICOM 3.0 Conformance StatementDocument20 pagesPrintlink5-ID - IV DICOM 3.0 Conformance StatementjamesNo ratings yet
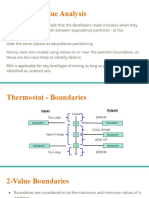
- Boundary Value AnalysisDocument9 pagesBoundary Value AnalysisChristien Froi FelicianoNo ratings yet
- JD Edwards Enterpriseone Tools: Form Design Aid Guide Release 9.1.XDocument530 pagesJD Edwards Enterpriseone Tools: Form Design Aid Guide Release 9.1.XGaurav SahuNo ratings yet
- CECS 277 Midterm Review Fa17Document12 pagesCECS 277 Midterm Review Fa17abdulbaset alselwiNo ratings yet
- Model830 FRU Replacement and Service PDFDocument857 pagesModel830 FRU Replacement and Service PDFVivian AspdinNo ratings yet
- Cse 1111Document4 pagesCse 1111Prudhvi AdapaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledndooraeNo ratings yet
- Project - Report - Rajni (200002065)Document32 pagesProject - Report - Rajni (200002065)Rajni SavaliyaNo ratings yet
- He - Full - Update - 11 99 99.00 RG U500 STD Hel 04Document3 pagesHe - Full - Update - 11 99 99.00 RG U500 STD Hel 04AndresGarcia AndreusDjPro0% (1)
- 7.5 A 250fps 124dB Dynamic-Range SPAD Image Sensor Stacked With Pixel-Parallel Photon Counter Employing Sub-Frame Extrapolating Architecture For Motion Artifact SuppressionDocument3 pages7.5 A 250fps 124dB Dynamic-Range SPAD Image Sensor Stacked With Pixel-Parallel Photon Counter Employing Sub-Frame Extrapolating Architecture For Motion Artifact SuppressionYung-Fu ChenNo ratings yet
- Digital VLSI Chip Design With Cadence and Synopsys Cad Tools Table of ContentsDocument5 pagesDigital VLSI Chip Design With Cadence and Synopsys Cad Tools Table of ContentsDarwinNo ratings yet
- Arduino LCD 16x2. Turn Single Screen Into Multiple Screens.: InstructablesDocument11 pagesArduino LCD 16x2. Turn Single Screen Into Multiple Screens.: InstructablesMohamed Tayeb AIBNo ratings yet
- Back-Office White-Label: O.K Sounds Great! What To Do Next?Document2 pagesBack-Office White-Label: O.K Sounds Great! What To Do Next?ahmedaisarrNo ratings yet
- Lec4 Se UmlDocument33 pagesLec4 Se UmljfzakiNo ratings yet
- Integrity Lifecycle Manager 12 Product Platforms PDFDocument3 pagesIntegrity Lifecycle Manager 12 Product Platforms PDFBinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Designing and Developing a Cloud-Based Container Management System for Maersk LineDocument38 pagesDesigning and Developing a Cloud-Based Container Management System for Maersk LineAlexNo ratings yet
- Basic Computer Literacy ExamDocument2 pagesBasic Computer Literacy ExamJames YaxNo ratings yet
- DG WLAN Secure Guest Access ArubaOS25Document43 pagesDG WLAN Secure Guest Access ArubaOS25luisNo ratings yet
- Nguyenvanthinh BKC13107 N01K13Document95 pagesNguyenvanthinh BKC13107 N01K13Nguyễn Văn ThịnhNo ratings yet
- IQ MK 3 Range Actuators - Module 6G (WIQ83017)Document3 pagesIQ MK 3 Range Actuators - Module 6G (WIQ83017)SuAnandNo ratings yet
- Hadoop Configuration and Single Node SetupDocument61 pagesHadoop Configuration and Single Node SetupParthNo ratings yet