Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Certcdavao: Instruction: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The Following
Uploaded by
Jj JumawanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Certcdavao: Instruction: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The Following
Uploaded by
Jj JumawanCopyright:
Available Formats
CERTCDAVAO WEEKLY EXAM 8 Elecs
Electronic Engineering
Instruction: Select the correct answer for each of the following a. Av=gmRd c. Av=(g_m R_s)/(1+g_m R_s )*
questions. Mark only one answer for each item by shading the box b. Av=gmRs d. Av=(g_m R_d)/(1+g_m R_d )
corresponding to the letter of your choice on the answer sheet provided.
12. The capacitor that produces an ac ground is called a(n)
Strictly no erasures allowed. Use pencil no. 1 only.
a. coupling capacitor c. bypass capacitor*
NOTE: Whenever you come across a caret (^) sign, it means
b. dc open d. ac open
exponentiation.
1. Consider the following statements for a metal oxide semiconductor 13. In a class B push-pull amplifier, the transistors are biased slightly
field effect transistor above cutoff to avoid
(MOSFET): a. crossover distortion* c. negative feedback
P: As channel length reduces, OFF-state current increases. b. unusually high efficiency d. a low input impedance
Q: As channel length reduces, output resistance increases.
R: As channel length reduces, threshold voltage remains constant. 14. Three different points are shown on a dc load line. The upper point
S: As channel length reduces, ON current increases. represents the
Which of the above statements are INCORRECT? a. minimum current gain c. saturation point*
(A) P and Q (C) Q and R* b. quiescent point d. cutoff point
(B) P and S (D) R and S
15. Which of the following conditions are needed to properly bias an
2. The Ebers-Moll model of a BJT is valid npn transistor amplifier?
(A) only in active mode a. forward bias the base/emitter junction and reverse bias the
(B) only in active and saturation modes base/collector junction.
(C) only in active and cut-off modes b. forward bias the collector/base junction and reverse bias the
(D) in active, saturation and cut-off modes* emitter/base junction.
c. apply a positive voltage on the n-type material and a negative
3. A long-channel NMOS transistor is biased in the linear region with voltage on the p-type material.
𝑉𝐷𝑆=50 mV and is used as a resistance. Which one of the following d. apply a large voltage on the base.
statements is NOT correct?
(A) If the device width 𝑊 is increased, the resistance decreases. 16. Determine the gm of a source-follower network given IDSS=16mA,
(B) If the threshold voltage is reduced, the resistance decreases. Vp=4V, VGSQ=2.86V and IDQ=4.56mA.
(C) If the device length 𝑊 is increased, the resistance increases. a. 32.31ms b. 2.22ms c. 2.28ms* d. 3.22ms
(D) If 𝑊𝑊𝑊 is increased, the resistance increases.*
17. Determine the dynamic resistance of a voltage-divider Depletion
4. Which one of the following statements is correct about an ac- Type MOSFET with IDSS=6mA, Vp=-3. gos=10uS.
coupled common-emitter amplifieroperating in the mid-band region? a. 32.31ms b. 2.22ms c. 100k Ω* d. 231k Ω
(A) The device parasitic capacitances behave like open circuits,
whereas coupling and bypasscapacitances behave like short 18. If the value of resistor Rf in an averaging amplifier circuit is equal to
circuits.* the value of one input resistor divided by the number of inputs, the
(B) The device parasitic capacitances, coupling capacitances and output will be equal to
bypass capacitances behave likeopen circuits. a. the average of the individual inputs
(C) The device parasitic capacitances, coupling capacitances and b. the inverted sum of the individual inputs
bypass capacitances behave likeshort circuits. c. the sum of the individual inputs
(D) The device parasitic capacitances behave like short circuits, d. the inverted average of the individual inputs*
whereas coupling and bypasscapacitances behave like open
circuits. 19. If the input to a comparator is a sine wave, the output is a
a .ramp voltage c. rectangular wave*
5. A differential amplifier has an open-loop voltage gain of 120. The
b. sine wave d. sawtooth wave
input signals are 2.45V and 2.35V. Calculate the output voltage of
the amplifier. 20. To get a negative gate-source voltage in a self-biased JFET circuit,
A. 12 V * B. 14 V C. 16 V D. 10 V you must use a
a. voltage divider c. ground
6. A differential amplifier has an open-loop voltage gain of 150 and a b. source resistor* d. negative gate supply voltage
common input signal of 4.0 V to both terminals. An output signal of
15 mV results. Determine the common-mode gain and the CMRR. 21. In the constant-current region, how will the IDS change in an n-
A. 91.16 dB B. 89.76 dB C. 90.40 dB D. 92.04 dB * channel JFET?
a. as vgs decreases id decreases*
7. A good transimpedance amplifier has b. as vgs increases id increases
(a) Low input impedance and high output impedance c. as vgs decreases id remains constant
(b) High input impedance and high output impedance. d. as vgs increases id remains constant
(c) High input impedance and low output impedance
(d) Low input impedance and low output impedance* 22. IDSS can be defined as:
a. the minimum possible drain current
b. the maximum possible current with vgs held at –4 v
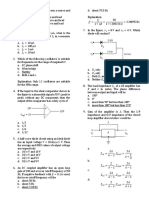
8. How many op-amps are required to implement this equation
c. the maximum possible current with vgs held at 0 v*
d. the maximum drain current with the source shorted
23. What is the input impedance of a common-gate configured JFET?
a. very low* c. high
A. 2 B. 3 C. 4 D. 1* b. low d. very high
9. In a CE germanium transistor amplifier, self-bias is used. The 24. With the E-MOSFET, when gate input voltage is zero, drain current
various parameters are: Vcc=16V, Rc=3k Ω, RE=2k Ω, R1=56k Ω, is:
R2=20k Ω and α=0.985. Determine the operating point. a. at saturation c. idss
b. zero* d. widening the channel
a.7.33V,1.88mA c. 3.22V, 1.55mA
b. 6.225V, 1.955mA* d. 7.87V, 1.623mA
25. With a 30-volt VDD, and an 8-kilohm drain resistor, what is the E-
10. 1The primary function of the bias circuit is to MOSFET Q point voltage, with ID = 3 mA?
a. hold the circuit stable at VCC a. 6 V* c. 24 V
b. hold the circuit stable at vin b. 10 V d. 30 V
d. hold the circuit stable at the designed Q-point*
26. When an input signal reduces the channel size, the process is
11. A source follower has a voltage gain (Av) of called:
CERTC Review Center : MANILA-CEBU-BAGUIO-DAVAO(09323288053) Page 1
CERTCDAVAO WEEKLY EXAM 8 Elecs
Electronic Engineering
a. enhancement c. gate charge b. integration or differentiation* d. addition or subtraction
b. substrate connecting d. depletion*
41. In an open-loop op-amp circuit, whenever the inverting input (–) is
27. In an n-channel JFET, what will happen at the pinch-off voltage? negative relative to the noninverting input (+), the output will:
a. the value of VDS at which further increases in VDS will cause a. swing negative c. be balanced
no further increase in ID* b. close the loop d. swing positive*
b. the value of VGS at which further decreases in VGS will cause
no further increases in ID 42. With a differential gain of 50,000 and a common-mode gain of 2,
c. the value of VDG at which further decreases in VDG will cause what is the common-mode rejection ratio?
no further increases in ID
a. –87.9 Db c. 43.9 dB
d. the value of VDS at which further increases in VGS will cause
b. –43.9 Db d. 87.9 dB*
no further increases in ID
43. The major difference between ground and virtual ground is that
28. The common-source JFET amplifier has:
virtual ground is only a:
a. a very high input impedance and a relatively low voltage gain*
b. a high input impedance and a very high voltage gain a. voltage reference* c. power reference
c. a high input impedance and a voltage gain less than 1 b. current reference d. difference reference
d. no voltage gain
44. If the gain of a closed-loop inverting amplifier is 3.9, with an input
29. The overall input capacitance of a dual-gate D-MOSFET is lower resistor value of 1.6 kilohms, what value of feedback resistor is
because the devices are usually connected: necessary?
a. in parallel c. with separate inputs a. 6240 ohms* c. 410 ohms
b. with separate insulation d. in series* b. 2.4 kilohms d. 0.62 kilohms
30. A field effect transistor operates with a drain current of 100 mA and 45. All of the following are basic op-amp input modes of operation
a gate source bias of −1 V. The device has agfs value of 0.25. If the EXCEPT
bias voltage decreases to−1.1 V, determine the change in drain a. inverting mode* c. double-ended
current b. common-mode d. single-ended
a.-7.8mA c. -25mA*
46. A circuit whose output is proportional to the difference between the
b. 25mA d. 7.8mA
input signals is considered to be which type of amplifier?
31. If the per unit value of electrons which leave the emitter and pass to a. common-mode c. differential*
the collector is 0.9 in an n-p-n transistor and the emitter current is 4 b. darlington d. operational
mA, then
47. If ground is applied to the (+) terminal of an inverting op-amp, the (–
a. the base current is approximately 4.4 mA
) terminal will:
b. the collector current is approximately 3.6 mA*
c the collector current is approximately 4.4 mA a. not need an input resistor c. have high reverse current
d. the base current is approximately 3.6 mA b. be virtual ground* d. not invert the signal
32. An ideal operational amplifier has 48. A noninverting closed-loop op-amp circuit generally has a gain
a. infinite output impedance c. infinite bandwidth* factor:
b. zero input impedance d. all of the above a. less than one c. of zero
b. greater than one* d. equal to one
33. Another name for a unity gain amplifier is:
a. difference amplifier c. single ended 49. If the Op – Amp in the figure has an input offset voltage of 5 mV and
b. comparator d. voltage follower* an open-loop voltage gain of 10,000 then V0 will be
34. A differential amplifier has a common-mode gain of 0.2 and a
common-mode rejection ratio of 3250. What would the output
voltage be if the single-ended input voltage was 7 mV rms?
a. 1.4 mV rms c.4.55 V rms*
b. 650 mV rmS d. 0.455 V rms A. 0 V C. + 15 V or -15 V*
B. 5 mV D. +50 V or -50 V
35. What is the difference between common-mode and differential-
mode input signals? 50. This circuit is an example of a(n)________.
a. phase relationship* c. current
b. voltage d. apparent power
36. The input offset current equals the
a. average of two base currents
b. collector current divided by the current gain
c. difference between two base-emitter voltages
d. difference between two base currents*
37. The common-mode voltage gain is A. dc voltmeter C. instrumentation amplifier*
a. smaller than differential voltage gain* B. display driver D. None of the above
b. equal to voltage gain
c. greater than differential voltage gain 51. Calculate the output voltage if V1 = –3.3 V and V2 = 0.8 V.
d. none of the above
38. An ideal amplifier should have:
a. high input current c. high output impedance
b. zero offset* d. moderate gain
39. If an op-amp has one input grounded and the other input has a
signal feed to it, then it is operating as what?
a. common-mode c. double-ended
b. single-ended* d. noninverting mode A. 0 V B. 6.6 V*
40. When a capacitor is used in place of a resistor in an op-amp C. –4 V D. 2 V
network, its placement determines:
a. open- or closed-loop gain c. saturation or cutoff
CERTC Review Center : MANILA-CEBU-BAGUIO-DAVAO(09323288053) Page 2
CERTCDAVAO WEEKLY EXAM 8 Elecs
Electronic Engineering
52. Determine the output voltage for this circuit with a sinusoidal input B. 16.7 mA D. 20 mA
of 2.5 mV.
A. –0.25 V 67. The principal advantage(s) of MOSFETs over BJTs is (are)
B. –0.125 V* A. their biasing networks are simpler.
C. 0.25 V B. their drive requirements are simpler.
D. 0.125 V C. they can be connected in parallel for added drive capability.
D. all of the above*
53. Whattype of biasing circuit is shown in the figure?
68. An op-amp integrator has a square-wave input. The output should
be
A. a sine wave. C. a triangle wave.*
B. a square wave. D. pure DC.
69. How many op amps does window comparator require?
A. 1 C. 2*
B. 3 D. 4
70. A transistor acts as __ when saturated.
A. open circuit C. variable resistance
A. Gate bias C. Gate feedback bias B. very low resistance* D. very high resistance
B. Self-bias* D. Emitter bias
71. For a fixed bias configuration, calculate the output impedance if
54. Which JFET amplifier would be used to couple a low-impedance RB=330kΩ, RC=2.7 kΩ, hfe=120, hie=1.175kΩ and hoe=20μA/V.
voltage source to a higher-impedance load? A. 1.171 kΩ C. 50 kΩ
A. The common-source amplifier C. The common-drain amplifier B. 2.56 kΩ* D. 2.7 kΩ
B. The common-gate amplifier* D. Depends upon the situation
72. An E-MOSFET with its gate connected to its drain is an example of
55. What is re′ equal to in terms of h parameters? A. A three-terminal device C. An active load*
A. hre / hoe* C. (hre + 1) / hoe B. A passive load D. A switching device
B. hie – (hre / hoe)(1 + hfe) D. hfe
73. Which of the following does not affect the junction capacitance of a
diode?
56. On the drain characteristic curve of a JFET for VGS = 0, the pinch-off A. the cross-sectional area of the P-N junction
voltage is B. the width of the depletion region
A. below the ohmic area. C. the phase of an applied ac signal*
B. between the ohmic area and the constant current area.* D. the reverse-bias voltage
C.between the constant current area and the breakdown region.
D. above the breakdown region. 74. In a P-channel JFET, the gate-source voltage must be connected so
that the positive polarity is applied to the _________terminal of the
JFET and the negative polarity is applied to the _______terminal.
57. A JFET data sheet specifies VGS(off) = –6 V and IDSS = 8 mA. Find the A. gate, source * C. drain, source
value of ID when VGS = –3 V. B. source, gate D. source, drain
A. 2 mA* C. 4 mA
B. 8 mA D. none of these 75. Determine the circuit shown in figure 13.
58. A class B amplifier operates in the linear region for
A. slightly more than 180° of the input cycle.
B. 360° of the input cycle.
C. slightly less than 180° of the input cycle.*
D. much less than 180° of the input cycle.
59. The IGBT has which three terminals?
A. anode, cathode, and gate C. emitter, collector, and gate*
B. source, drain, and gate D. emitter, collector, and base
60. A comparator with hysteresis is sometimes known as a(n)
A. integrator. C. differentiator.
B. Schmitt trigger.* D. none of the above
A. Voltage-divider bias IGFET
61. For an op-amp having a slew rate of 2 V/μs, what is the maximum B. Voltage-divider bias JFET
closed-loop voltage gain that can be used when the input signal C. Voltage-divider bias D-MOSFET
varies by 0.5 V in 10μs? D. Voltage-divider bias E-MOSFET*
A. 30 C. 40*
B. 50 D. 60 76. For a n-channel JFET with r0 = 10 kW, (VGS= 0 V, VP = - 6 V)the drain
62. The current gain of a pnp transistor is resistance rd at VGS= - 3 V is given by
A. the negative of the npn current gain A. 40 kΩ* B. 4.44 kW C. 2.5 kΩ D. 120 kW
B. the collector current divided by the emitter current
77. What does a voltage-divider bias provide?
C. near zero A. an unstable Q point
D. the ratio of collector current to base current* B. a stable Q point *
C. a Q point that is stable and easily varies with changes in the
63. An opamp comparator circuit employs transistor’s current gain
A. no feedback* C. -ve feedback D. a Q point that easily varies with changes in the transistor's current
B. +ve feedback D. both B and C gain
64. Which transistor bias circuit arrangement provides good Q-point 78. Referring to this transfer curve shown in figure 5, determine I D at VGS = 2
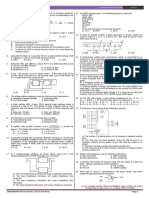
stability, but requires both positive and negative supply voltages? V.
A. base bias C. collector bias
B. voltage-divider bias D. emitter bias*
65. Which FET amplifier(s) has (have) a phase inversion between input
and output signals?
A. common-gate C. common-drain
B. common-source* D. all of the above
66. A class A amplifier with RC = 3.3 kΩ and RE = 1.2 kΩ has a VCC = 20
V. Find IC(sat)
A. 0.444 mA* C. 1.333 mA
A. 4.4 mA* C. 6.1 mA
B. 0.111 mA D. 4.444 mA
CERTC Review Center : MANILA-CEBU-BAGUIO-DAVAO(09323288053) Page 3
CERTCDAVAO WEEKLY EXAM 8 Elecs
Electronic Engineering
A. both the base-emitter and base-collector junctions are reverse
79. In figure 7, Calculate βdc at VCE = 15 V and IB = 30 μA. biased
B. the base-emitter junction is reverse biased, and the base-collector
junction is forward biased
C. the base-emitter junction is forward biased, and the base collector
junction is reverse biased
D. both the base-emitter and base-collector junctions are forward
biased*
92. Which biasing method is the most unstable?
A. Self bias C. Fixed bias *
B. Combination bias D. Emitter stabilized bias
93. The ______ stage provides a moderate voltage gain, a moderate input
impedance, and a moderate output impedance.
A. 100 B. 50 C. 116 D. 110* A. common-drain C. common-base
B. common-collector D. common-emmiter*
80. Introducing a resistor in the emitter of a common amplifier stabilizes the
dc operating point against variations in 94. For an n channel enhancement MOSFET with threshold voltage of 2.5
A. only the temperature C. only the β of the transistor V, determine the current at gate source voltage of 6 V.
B. both temperature and β* D. none of the above A. 0.675 mA C. 1.675 mA
B. 3.675 mA* D. 2.675 mA
81. Compared to a CE stage, a swamped amplifier has an input impedance
that is 95. Calculate the stability factor due to the variation of ICBO from 1 nA to 21
nA when the temperature changes from room temperature to 100 ˚C.
A. smaller B. equal C. larger* D. zero The change in collector-current due to the change of ICBO was found to
be 0.5 µA.
82. If βDC is increased by 10%, the collector-to-emitter voltage drop A. 5 C. 25*
A. increases by less than or equal to 10% B. 15 D. 35
B. decreases by less than or equal to 10%*
C. increase by more than 10% 96. If the capacitor from emitter to ground in a common emitter amplifier is
D. decreases by more than 10% removed, the voltage gain
A. increases C. decreases *
83. In a transistor amplifier, the reverse saturation current ICO
B. becomes erratic D. remains the same
A. double for every 10° rise in temperature*
B. doubles for every 1° rise in temperature
C. increase linearly with the temperature 97. What is true about the of a BJT?
D. doubles for every 5° rise in temperature A. lesser than 1* C. greater than 1
B. unity D. infinity
84. When the gate-to-source voltage (VGS) of a MOSFET with threshold
voltage of 400 mV, working in saturation is 900 mV, the drain current is 98. Why is the common – emitter amplifier the most widely used transistor
observed to be 1 mA. Neglecting the channel width modulation effect amplification configuration?
and assuming that the MOSFET is operating at saturation, what is the A. it provides voltage gain C. it provides high power gain
drain current for an applied VGS of 1400 mV? B. it provides current gain D. all of the above *
A. 0.5 mA B. 3.5 mA C. 2.0 mA D. 4.0 mA*
99. A JFET might work better than a bipolar transistor in
85. In the amplifier circuit shown in the figure, the values of R1 and R2 are
such that the transistor is operating at VCE = 3V and IC = 1.5 mA when
A. a high-voltage rectifier C. a weak-signal RF amplifier *
its â is 150. What is the operating point (VCE, IC) for a transistor with â B. a power-supply filter D. a power transformer
of 200.
100. An op-amp can be considered as an ideal
A. Voltage controlled current source
B. Current controlled current source
C. Voltage controlled voltage source *
D. Current controlled voltage source
GODBLESS AND MORE POWERS!
CERTC
A. 2V, 2mA* B. 4V, 2mA C. 3V, 2mA D. 4V, 1 mA
86. For normal operation of a pnp BJT, the base must be ___ with respect
to the emitter and ___ with respect to the collector.
A. positive, negative C. positive, positive
B. negative, positive* D. negative, negative
87. The current gain of a pnp transistor is
A. the negative of the npn current gain
B. the collector current divided by the emitter current
C. near zero
D. the ratio of collector current to base current*
88. The drain current of MOSFET in saturation is given by ID = K(VGS -
VT)2 where K is a constant. What is the magnitude of the
transconductance gm?
A. K(VGS - VT)2/VDS C. 2K(VGS - VT)*
B. ID/(VGS – VDS) D. K(VGS - VT)2/VGS
89. A common-emitter amplifier has (_____) voltage gain, (_____) current
gain, (_____) power gain, and (_____) input impedance.
A. high, low, high, low C. high, high, high, low*
B. high, high, high, high D. low, low, low, high
90. Which of the following is referred to as the reverse transfer voltage
ratio?
A. hi C. hr*
B. hf D. ho
91. A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is used as a power control switch
by biasing it in the cut-off region (OFF state) or in the saturation region
(ON state). In the ON state, for the BJT
CERTC Review Center : MANILA-CEBU-BAGUIO-DAVAO(09323288053) Page 4
You might also like
- Electrical Engineering DictionaryDocument60 pagesElectrical Engineering DictionaryMuhammadHaris67% (3)
- QSC RMX Series 805 1450 2450Document42 pagesQSC RMX Series 805 1450 2450naughtybigboy100% (5)
- Powerline Pre Board Ree Sept 2010Document15 pagesPowerline Pre Board Ree Sept 2010Junnar Jay AbañoNo ratings yet
- Question Bank 2Document7 pagesQuestion Bank 2Misis AdaNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Strength of Materials 5691845f3ea8eDocument13 pagesDokumen - Tips Strength of Materials 5691845f3ea8eJay GeeNo ratings yet
- AC Circuit 2 (Three-Phase)Document2 pagesAC Circuit 2 (Three-Phase)marlon desaculaNo ratings yet
- Half Range Fourier SeriesDocument18 pagesHalf Range Fourier SeriesVictor DoyoganNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument3 pagesExamMaria Deborah Vivas BaluranNo ratings yet
- Certc - Davao Diagnostic Exam: Instruction: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The FollowingDocument4 pagesCertc - Davao Diagnostic Exam: Instruction: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The FollowingJj JumawanNo ratings yet
- Certc - Davao Diagnostic Exam: Instruction: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The FollowingDocument4 pagesCertc - Davao Diagnostic Exam: Instruction: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The FollowingJj JumawanNo ratings yet
- Certc - Davao Diagnostic Exam: Instruction: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The FollowingDocument4 pagesCertc - Davao Diagnostic Exam: Instruction: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The FollowingJj JumawanNo ratings yet
- Certc: Instruction: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The Following QuestionsDocument4 pagesCertc: Instruction: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The Following QuestionsArnel Pamaos Lopiba MontañezNo ratings yet
- Advance Mathematics - ECEDocument10 pagesAdvance Mathematics - ECErachelle rivadullaNo ratings yet
- Algebra 1: Multiple ChoiceDocument1 pageAlgebra 1: Multiple ChoiceTrina Ritchell AquinoNo ratings yet
- MAN B&W Diesel A/S: Instruction Book For 35-42 MC Engines Volume I: 'Operation'Document3 pagesMAN B&W Diesel A/S: Instruction Book For 35-42 MC Engines Volume I: 'Operation'Jose Carlos Castellanos PerezNo ratings yet
- Iecep Elecs 2Document10 pagesIecep Elecs 2Rick SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson 1 Laplace TransformDocument13 pagesModule 1 Lesson 1 Laplace TransformVictor DoyoganNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Practice ProblemsDocument4 pagesElectrical Engineering Practice ProblemsJj JumawanNo ratings yet
- Mesl Set 1Document8 pagesMesl Set 1RENE JOSHUA PECASONo ratings yet
- Certcdavao: Electronics EngineeringDocument4 pagesCertcdavao: Electronics EngineeringJj JumawanNo ratings yet
- Fourier Series AnalysisDocument23 pagesFourier Series AnalysisVictor DoyoganNo ratings yet
- Advance Review Weekly Exam 2 BacolodDocument4 pagesAdvance Review Weekly Exam 2 BacolodgiophilipNo ratings yet
- Exam DC1 and 2Document2 pagesExam DC1 and 2Jj JumawanNo ratings yet
- Certcdavao: Instruction: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The FollowingDocument4 pagesCertcdavao: Instruction: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The FollowingJj JumawanNo ratings yet
- Indiabix With ExplanationsDocument46 pagesIndiabix With ExplanationsJustin ConsonNo ratings yet
- IndiaBIX - Analog Electronics - Section 1Document6 pagesIndiaBIX - Analog Electronics - Section 1Mikaela VillalunaNo ratings yet
- Calculator TechniquesDocument23 pagesCalculator TechniquesVilly Joe CamayraNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Geas 2016 2ndsemDocument4 pagesDiagnostic Geas 2016 2ndsemjj012586No ratings yet
- CE ElexDocument4 pagesCE Elexjj012586No ratings yet
- 1.basic Coms Noise - 2018rgs PDFDocument4 pages1.basic Coms Noise - 2018rgs PDFJefrilAmboyNo ratings yet
- MCQ Elex-BoylestadDocument216 pagesMCQ Elex-BoylestadJj JumawanNo ratings yet
- Algebra 1 - Number Theory PDFDocument5 pagesAlgebra 1 - Number Theory PDFJj JumawanNo ratings yet
- Algebra 1 - Number Theory PDFDocument5 pagesAlgebra 1 - Number Theory PDFJj JumawanNo ratings yet
- Electronics MCQDocument4 pagesElectronics MCQHary KrizNo ratings yet
- ElecDocument4 pagesElecJj JumawanNo ratings yet
- ECE Materials and Components Section 1Document9 pagesECE Materials and Components Section 1MoneyNo ratings yet
- Solid State DevicesDocument79 pagesSolid State Devicesjj0125860% (2)
- DE Ee1Document4 pagesDE Ee1Jj JumawanNo ratings yet
- WE1 EceDocument1 pageWE1 EceJj JumawanNo ratings yet
- Day 01 - Algebra 1Document19 pagesDay 01 - Algebra 1Ironfalcon101No ratings yet
- Answer:: Y Abc + A + B + CDocument10 pagesAnswer:: Y Abc + A + B + CKarumon UtsumiNo ratings yet
- Aces Review Center: Ree Online Review Refresher Esas 7B by Engr. Jimmy L. Ocampo 0920 - 644 - 6246Document5 pagesAces Review Center: Ree Online Review Refresher Esas 7B by Engr. Jimmy L. Ocampo 0920 - 644 - 6246Jr TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Aces Review Center: Ree Online Review Refresher Math 10 by Engr. Jimmy L. Ocampo 0920 - 644 - 6246Document3 pagesAces Review Center: Ree Online Review Refresher Math 10 by Engr. Jimmy L. Ocampo 0920 - 644 - 6246Jr TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Basic Questions Related To Thermal EngineeringDocument16 pagesBasic Questions Related To Thermal EngineeringfarukhaliNo ratings yet
- Aces Review Center: Ree Online Review Math Related Terms by Engr. Jimmy L. Ocampo 0920 - 644 - 6246Document5 pagesAces Review Center: Ree Online Review Math Related Terms by Engr. Jimmy L. Ocampo 0920 - 644 - 6246Jr TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Coaching Exam No. 2 PECDocument3 pagesCoaching Exam No. 2 PECJoel JusayNo ratings yet
- Coaching Set 1 Pink PDFDocument8 pagesCoaching Set 1 Pink PDFVictor John PingkianNo ratings yet
- B " - Sin-: SinxDocument7 pagesB " - Sin-: Sinxjohn benedict orbeNo ratings yet
- Answers Self Test Grob's Basic Electronics-11edDocument6 pagesAnswers Self Test Grob's Basic Electronics-11edTaufiq Fahlifi YfzerobrrNo ratings yet
- Crc-Plane TrigometryDocument8 pagesCrc-Plane TrigometryJevan A. CalaqueNo ratings yet
- DynamicsDocument3 pagesDynamicsjj012586No ratings yet
- Westmead International SchoolDocument7 pagesWestmead International SchoolEugene ColleraNo ratings yet
- Rme April 2019 Exam 1 Key PDFDocument7 pagesRme April 2019 Exam 1 Key PDFJevan CalaqueNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits 2: Review Guide Series Review Guide SeriesDocument2 pagesAC Circuits 2: Review Guide Series Review Guide SeriesKylaNo ratings yet
- New Coaching 2Document11 pagesNew Coaching 2jj012586No ratings yet
- Miscellaneous ElementsDocument314 pagesMiscellaneous ElementsOnline EducatorNo ratings yet
- RF Review Center Weekly Exam 1Document2 pagesRF Review Center Weekly Exam 1Hary KrizNo ratings yet
- Transmission LinesDocument2 pagesTransmission LinesGlazylynCortezPalo100% (1)
- Chapter 6 Taylor and Maclaurin SeriesDocument22 pagesChapter 6 Taylor and Maclaurin SeriesStelios KondosNo ratings yet
- Esas Refresher 1 2022 JMQDocument4 pagesEsas Refresher 1 2022 JMQKylaNo ratings yet
- Draft of October 2015 Electronics Engineering Board Exam Questions and ConceptsDocument5 pagesDraft of October 2015 Electronics Engineering Board Exam Questions and ConceptsAyel Cejas Costiniano100% (1)
- Math12-1 - Lesson 9 - Spherical TrigonometryDocument15 pagesMath12-1 - Lesson 9 - Spherical TrigonometryKobe MartinezNo ratings yet
- Cmos QuestionsDocument10 pagesCmos Questionsmeenakshimani996No ratings yet
- ECE Mock Board Exam April 2022 ElectronicsDocument7 pagesECE Mock Board Exam April 2022 Electronicsx8t2w5ngjcNo ratings yet
- Ec 18Document11 pagesEc 18Darshan NakawalaNo ratings yet
- MME Electrical Session 1 Electrical FundamentalsDocument22 pagesMME Electrical Session 1 Electrical FundamentalsgpuonlineNo ratings yet
- ME1Document5 pagesME1jj012586No ratings yet
- ElectronicsDocument45 pagesElectronicsNorman OcoNo ratings yet
- Op AmpDocument3 pagesOp AmpAhnNo ratings yet
- GC-8 Basic ElectronicsDocument5 pagesGC-8 Basic ElectronicsyihesakNo ratings yet
- Certcdavao: Weekly Exam MathDocument2 pagesCertcdavao: Weekly Exam MathJj JumawanNo ratings yet
- WE2 EceDocument2 pagesWE2 EceJj JumawanNo ratings yet
- MTE 506.curriculum and Instructional Materials DevelopmentDocument2 pagesMTE 506.curriculum and Instructional Materials DevelopmentJj JumawanNo ratings yet
- Certcdavao: Probability Trigonometry Plane Geometry Solid GeometryDocument1 pageCertcdavao: Probability Trigonometry Plane Geometry Solid GeometryJj JumawanNo ratings yet
- We 2Document2 pagesWe 2Jj JumawanNo ratings yet
- We 2Document2 pagesWe 2Jj JumawanNo ratings yet
- We 3Document3 pagesWe 3Jj JumawanNo ratings yet
- 10dc GeneratorDocument6 pages10dc GeneratorJj JumawanNo ratings yet
- Powermos Transistor Buk104-50L/S Logic Level Topfet Buk104-50Lp/SpDocument14 pagesPowermos Transistor Buk104-50L/S Logic Level Topfet Buk104-50Lp/SpWallyWallysNo ratings yet
- VLSI DESIGN Question Bank: Unit 1Document12 pagesVLSI DESIGN Question Bank: Unit 1Babu GundlapallyNo ratings yet
- Load-: Circuit Is Minimum at ResonanceDocument11 pagesLoad-: Circuit Is Minimum at ResonanceNeeraj PatelNo ratings yet
- Sic 634Document17 pagesSic 634Tri Nguyen Real EstateNo ratings yet
- Micro-Cap 9: Electronic Circuit Analysis Program Reference ManualDocument916 pagesMicro-Cap 9: Electronic Circuit Analysis Program Reference Manualabc_axgaxgNo ratings yet
- Pe Tutorial 1Document8 pagesPe Tutorial 1kibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument16 pagesPDFCristian BandilaNo ratings yet
- U440/441 - Matched N Channel JFET PairsDocument7 pagesU440/441 - Matched N Channel JFET PairsGuillermo HernandezNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Braking Resistor Chopper CircuitDocument5 pagesDynamic Braking Resistor Chopper CircuitAri SutejoNo ratings yet
- BLHeli Programming by TX SiLabs Rev10.xDocument21 pagesBLHeli Programming by TX SiLabs Rev10.xTitiNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument76 pagesThesisSayantan Sinha100% (1)
- 10CS33 Logic Design NotesDocument14 pages10CS33 Logic Design Notesjgssb85No ratings yet
- EDCDocument1 pageEDClakshmipoNo ratings yet
- Glosario ArduinoDocument16 pagesGlosario ArduinoGustavo Adolfo Peña MarínNo ratings yet
- Park College of Engineering and Technology Kaniyur, Coimbatore - 641 659Document2 pagesPark College of Engineering and Technology Kaniyur, Coimbatore - 641 659Jeeva RathnamNo ratings yet
- Active RF and Microwave DevicesDocument4 pagesActive RF and Microwave DevicesCamsia Minaga100% (1)
- Sony KDL - 32EX305 Chasis AZ1 - L PDFDocument51 pagesSony KDL - 32EX305 Chasis AZ1 - L PDFRichard Jaca100% (1)
- ThesisDocument128 pagesThesisAvtar SinghNo ratings yet
- Linear Circuits Lab (2) - Electronic Circuits Lab: SpecificationsDocument4 pagesLinear Circuits Lab (2) - Electronic Circuits Lab: SpecificationsAlwi PutraNo ratings yet
- SMD Type Mosfet: N-Channel MOSFET AO4704Document4 pagesSMD Type Mosfet: N-Channel MOSFET AO4704toto totoNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics ApplicationDocument5 pagesPower Electronics Applicationrosy01710No ratings yet
- Electrical Power Steering Design Guide TEXASDocument18 pagesElectrical Power Steering Design Guide TEXASacmilan4eva1899100% (1)
- KTH ThesisDocument137 pagesKTH Thesisvarun hemanthNo ratings yet
- Opamp - Lf155 Lf156 Lf157 - NatsemDocument19 pagesOpamp - Lf155 Lf156 Lf157 - NatsemLudwig SchmidtNo ratings yet
- Series 9180/ 9270 Power AmplifierDocument20 pagesSeries 9180/ 9270 Power AmplifierCouger ForuNo ratings yet
- Audio Mixer Project ReportDocument7 pagesAudio Mixer Project ReportArslanNo ratings yet