Professional Documents
Culture Documents
13
Uploaded by
Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRao0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 page13
Uploaded by
Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
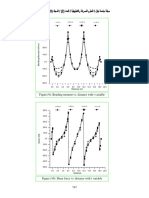
Figure 4.
by tunnelling.Int J Num Anal Meth Geomech, 29 (2005), pp.
REFERENCES 1485 1507
[1] BS 8102, Code of practice for protection of below grade structures [5] O. Reul, M.F. Randolph.Piled rafts in overconsolidated clay:
against water from the ground. British Standards Institution; 2009. comparison of in-situ measurements and numerical
analyses.Géotechnique, 53 (3) (2003), pp. 301 315
[2] Chew MYL, Nayanthara DS. Factors affecting water-tightness in
wet area of high-rise residential buildings. Archit Sci Rev [6] O.C. Zienkiewicz, R.L. Taylor, J.Z. Zhu.The finite element method
2002;45(4):375 83 its basis and fundamentals(6th ed.)Elsevier, London (2005)
[3] CIB, Building pathology: a state-of-the-art report. CIB Report [7] Varun, D. Assimaki, A. Shafieezadeh.Soil pile structure
Publication 155. CIB Working Commission W86. International interaction simulations in liquefiable soils via dynamic
Council for Building Research and Information, Holland; 1993. macroelements: formulation and validation.Soil Dyn Earthq Eng,
47 (2013), pp. 92 107
[4] P. Kitiyodom, T. Matsumoto, K. Kawaguchi.A simplified method
for piled raft foundations subjected to ground movements induced [8] H. Asega, T. Arai, K. Akira, J. Suzumura, K. Hanada, H.
Shiojuri, et al.A dynamic response analytical method of soil pile
56
You might also like
- EPRI Wet Chimney Design GuideDocument214 pagesEPRI Wet Chimney Design Guidegaurav_tank100% (2)
- An Explanatory Handbook To The Code of Practice For Foundations 2004Document5 pagesAn Explanatory Handbook To The Code of Practice For Foundations 2004tfvnjyNo ratings yet
- 1-Principles and Practice of Ground Improvement-Wiley (2015) - 31Document1 page1-Principles and Practice of Ground Improvement-Wiley (2015) - 31ksc6s9pphhNo ratings yet
- BS5930-2015 321Document1 pageBS5930-2015 321Ford cellNo ratings yet
- Shaffer 1999Document5 pagesShaffer 1999Ion AlbertoNo ratings yet
- ReferencesDocument4 pagesReferencesanasNo ratings yet
- Underground Structures During Earthquac Failure Mechanisms ofDocument13 pagesUnderground Structures During Earthquac Failure Mechanisms ofIntishar RahmanNo ratings yet
- Gold Film Surface Preparation For Self-Assembled Monolayer StudiesDocument8 pagesGold Film Surface Preparation For Self-Assembled Monolayer StudiesMarcelo Sebastian HerreraNo ratings yet
- A Comparison Between Rmse and Nsec Indexes Is Reported In: ReferencesDocument1 pageA Comparison Between Rmse and Nsec Indexes Is Reported In: ReferencesCovjece Ne Ljuti SeNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Conventional and Inverted Braced Excavations Using Subloading T ModelDocument16 pagesSimulation of Conventional and Inverted Braced Excavations Using Subloading T ModelbenjaminNo ratings yet
- 11 References PDFDocument7 pages11 References PDFKu SridevNo ratings yet
- SI Book References and StandardsDocument26 pagesSI Book References and StandardsIrsyadul FikriNo ratings yet
- Transparent Solid-State Lithiated Neutron Scintillators Based On Self-Assembly of Polystyrene-Block - Poly (Ethylene Oxide) Copolymer ArchitecturesDocument5 pagesTransparent Solid-State Lithiated Neutron Scintillators Based On Self-Assembly of Polystyrene-Block - Poly (Ethylene Oxide) Copolymer ArchitecturesMaheshNo ratings yet
- SMFE Bibliography PDFDocument8 pagesSMFE Bibliography PDFsamanta pandeyNo ratings yet
- Science 1213229Document5 pagesScience 12132291592162022No ratings yet
- Augmented Hydrogen Storage in Novel Nanoporous Carbon Based ArchitecturesDocument2 pagesAugmented Hydrogen Storage in Novel Nanoporous Carbon Based ArchitecturespantoleNo ratings yet
- Installation of Offshore Driven Piles - Regional Experience: View Publication Stats View Publication StatsDocument1 pageInstallation of Offshore Driven Piles - Regional Experience: View Publication Stats View Publication StatstehNo ratings yet
- Geofoam Blocks in Civil Engineering ApplicationsDocument1 pageGeofoam Blocks in Civil Engineering ApplicationsSemraaa 77No ratings yet
- Huang, Shenggen Feng, Yingtao Liu, Hao Wu, Wenbing Mei, GuoxiongDocument2 pagesHuang, Shenggen Feng, Yingtao Liu, Hao Wu, Wenbing Mei, GuoxiongHusein El MazloumNo ratings yet
- References KMRCLDocument3 pagesReferences KMRCLManisha YadavNo ratings yet
- Final Civil Engineering SyllabusDocument2 pagesFinal Civil Engineering SyllabusAbhishek MishraNo ratings yet
- Reference Books For SoilDocument5 pagesReference Books For SoilpooNo ratings yet
- Effect of Vertically Propagating Shear Waves On SeDocument12 pagesEffect of Vertically Propagating Shear Waves On SeIntishar RahmanNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka: Soil and Rock, PP 883-884Document1 pageDaftar Pustaka: Soil and Rock, PP 883-884Isran TomiaNo ratings yet
- Lierature Soil Cement MixDocument2 pagesLierature Soil Cement MixMichelfoersterNo ratings yet
- Contribution of Site Effects and Soil-Structure in PDFDocument9 pagesContribution of Site Effects and Soil-Structure in PDFricardomartinzevalloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (: 1. (Mulder 1991)Document3 pagesChapter 1 (: 1. (Mulder 1991)api-26678889No ratings yet
- References: Main Topics of Imret13Document1 pageReferences: Main Topics of Imret13Process LibraryNo ratings yet
- Chih Minlin2001Document9 pagesChih Minlin2001ahmadkhafanNo ratings yet
- Discussion of Dynamic Response of Arbitrarily Shaped Foundations Experimental VerificationDocument3 pagesDiscussion of Dynamic Response of Arbitrarily Shaped Foundations Experimental VerificationCarlosAlbertoBarriosnuevosPelaezNo ratings yet
- Scribd 4Document4 pagesScribd 4Assem HNo ratings yet
- Paper2-Full-Text-2018 (1) - 8Document1 pagePaper2-Full-Text-2018 (1) - 8hotch potchNo ratings yet
- Refs PDFDocument5 pagesRefs PDFVicky GothandNo ratings yet
- Science 2005 Nguyen 844 7Document5 pagesScience 2005 Nguyen 844 7Florin AndreiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Background ( (1-6) : Kober (1995) Binning Et Al. (1961)Document7 pagesChapter 1 Background ( (1-6) : Kober (1995) Binning Et Al. (1961)api-26678889No ratings yet
- Cracking in Drying SoilsDocument4 pagesCracking in Drying SoilsZdobniceNo ratings yet
- Studi Literatur Pendugaan Nilai Konduktivitas Hidraulik Dengan MenggunakanDocument11 pagesStudi Literatur Pendugaan Nilai Konduktivitas Hidraulik Dengan MenggunakanAlmar Reza MaulanaNo ratings yet
- List of ReferencesDocument9 pagesList of ReferencesOsama WahabNo ratings yet
- RefDocument13 pagesRefSri KrishnanNo ratings yet
- 7 A Review On The Pullout Capacity of An Anchor BlockDocument9 pages7 A Review On The Pullout Capacity of An Anchor BlockAna Sofía Arango BermúdezNo ratings yet
- Tai Leu Tham KhaoDocument5 pagesTai Leu Tham KhaoNakkolopNo ratings yet
- Nonlithographic Micro-And Nanopatterning of Tio Using Polymer Stamped Molecular TemplatesDocument6 pagesNonlithographic Micro-And Nanopatterning of Tio Using Polymer Stamped Molecular TemplatessachinbobadeNo ratings yet
- 4D Electron Tomography ScienceDocument6 pages4D Electron Tomography Sciencehappynewyear11No ratings yet
- Improved Oxygen Reduction Activity On Pt3Ni Via Increased Surface Site AvailabilityDocument6 pagesImproved Oxygen Reduction Activity On Pt3Ni Via Increased Surface Site AvailabilityARIADNANo ratings yet
- Communications: The Concept of Docking/Protecting Groups in BiohydroxylationDocument4 pagesCommunications: The Concept of Docking/Protecting Groups in BiohydroxylationPraveenNo ratings yet
- Jgein 2563 00061-14Document1 pageJgein 2563 00061-14nnibilpsofznmcmoygNo ratings yet
- References: Geotechnical and Geological Engineering, 23, 679-695Document4 pagesReferences: Geotechnical and Geological Engineering, 23, 679-695Darren ÐavençNo ratings yet
- Approaching Nanoxerography: The Use of Electrostatic Forces To Position Nanoparticles With 100 NM Scale ResolutionDocument5 pagesApproaching Nanoxerography: The Use of Electrostatic Forces To Position Nanoparticles With 100 NM Scale Resolutiong zero100% (2)
- Belgel 2Document6 pagesBelgel 2cenkNo ratings yet
- 2009 - Two-Dimensional Discrete Element Modeling of A Spherical Steel Media in ADocument8 pages2009 - Two-Dimensional Discrete Element Modeling of A Spherical Steel Media in AQADDAH BARAANo ratings yet
- Rereferral PresentationDocument2 pagesRereferral Presentationaks tripathiNo ratings yet
- Geotecnic Report Final 1 PDFDocument22 pagesGeotecnic Report Final 1 PDFyasir aliNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1359645422006061 Main 18 19Document2 pages1 s2.0 S1359645422006061 Main 18 19I BHARGAVNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant Design of Geotechnical Structures - Theory and PracticeDocument24 pagesEarthquake Resistant Design of Geotechnical Structures - Theory and Practicedhan singhNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanic0015Document1 pageSoil Mechanic0015jb.dqaNo ratings yet
- VOL3 - Ref Muros (GEORIO)Document3 pagesVOL3 - Ref Muros (GEORIO)thiago.vidalNo ratings yet
- Bibliographies StabilitédesolDocument12 pagesBibliographies StabilitédesolabdallahNo ratings yet
- RefDocument28 pagesRefAngNo ratings yet
- References On Reliability and Risk Analysis in Geotechnical EngineeringDocument31 pagesReferences On Reliability and Risk Analysis in Geotechnical EngineeringRuben FloresNo ratings yet
- 8de8.SCG BibliografiaDocument14 pages8de8.SCG BibliografiajoseNo ratings yet
- Proceedings of the International Symposium on Engineering in Complex Rock FormationsFrom EverandProceedings of the International Symposium on Engineering in Complex Rock FormationsLi ChengxiangNo ratings yet
- 16Document1 page16Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Concluding RemarksDocument1 pageConcluding RemarksArjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- 12Document1 page12Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- 14Document1 page14Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- 13Document1 page13Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Exhibit 5Document1 pageExhibit 5Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Exhibit 4Document1 pageExhibit 4Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Rigid 2Document1 pageRigid 2Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Exhibit 2Document1 pageExhibit 2Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Exhibit 3Document1 pageExhibit 3Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Rigid 4Document1 pageRigid 4Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Rigid 3Document1 pageRigid 3Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Exhibit 1Document1 pageExhibit 1Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Rigid 1Document1 pageRigid 1Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Dark Side of Thermal ProjectsDocument117 pagesDark Side of Thermal ProjectsArjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- APL - Cantilever SupportDocument11 pagesAPL - Cantilever SupportArjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Barto Thesis 2020Document34 pagesBarto Thesis 2020Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Lokfix E55 TDS 191018Document5 pagesLokfix E55 TDS 191018Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Eq - Madhya PradeshDocument1 pageEq - Madhya PradeshArjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Understanding GW Level TrendsDocument57 pagesUnderstanding GW Level TrendsArjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- SRAS ChemicalDocument22 pagesSRAS ChemicalArjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- ACI 351-A Fall 2021 AgendaDocument1 pageACI 351-A Fall 2021 AgendaArjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Agenda: Mission: Our Subcommittee Is Responsible For Maintaining and Updating The Report OnDocument2 pagesAgenda: Mission: Our Subcommittee Is Responsible For Maintaining and Updating The Report OnArjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- ACI 351-A Spring 2022 AgendaDocument1 pageACI 351-A Spring 2022 AgendaArjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- ACI 351 C Dynamic Fall AgendaDocument1 pageACI 351 C Dynamic Fall AgendaArjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- A New Approach To Predict Local Site Effects Related To Blast-Induced Ground VibrationsDocument8 pagesA New Approach To Predict Local Site Effects Related To Blast-Induced Ground VibrationsArjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Fly Ash Technical Note No. 6Document4 pagesFly Ash Technical Note No. 6Arjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Iscience: Systematic Characterization of Wing Mechanosensors That Monitor Airflow and Wing DeformationsDocument23 pagesIscience: Systematic Characterization of Wing Mechanosensors That Monitor Airflow and Wing DeformationsArjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Response of Concrete Frame Structure Under A Blasting Demolition EnvironmentDocument15 pagesDynamic Response of Concrete Frame Structure Under A Blasting Demolition EnvironmentArjun Chitradurga RamachandraRaoNo ratings yet