Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aphy 101
Aphy 101
Uploaded by
Nalicia0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesThis document summarizes key cellular structures and organelles. It defines the cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, cytosol, and organelles. It describes the functions of the ribosome, smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, lysosomes, peroxisomes, and centrosome. The cell membrane regulates material transport in and out of the cell. The ribosome provides structural support and enzymatic activity for protein synthesis. The rough endoplasmic reticulum is involved in protein folding, sorting, and transport.
Original Description:
Science
Original Title
APHY 101
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes key cellular structures and organelles. It defines the cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, cytosol, and organelles. It describes the functions of the ribosome, smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, lysosomes, peroxisomes, and centrosome. The cell membrane regulates material transport in and out of the cell. The ribosome provides structural support and enzymatic activity for protein synthesis. The rough endoplasmic reticulum is involved in protein folding, sorting, and transport.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesAphy 101
Aphy 101
Uploaded by
NaliciaThis document summarizes key cellular structures and organelles. It defines the cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, cytosol, and organelles. It describes the functions of the ribosome, smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, lysosomes, peroxisomes, and centrosome. The cell membrane regulates material transport in and out of the cell. The ribosome provides structural support and enzymatic activity for protein synthesis. The rough endoplasmic reticulum is involved in protein folding, sorting, and transport.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
1.
Chapter 3 Cells
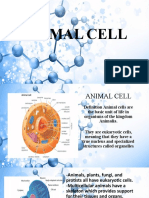
1. Cell membrane-the semipermeable membrane surrounding
the cytoplasm of a cell.
Nucleus-the membrane-enclosed organelle within a cell that
contains the chromosome.
Cytoplasm-provides a platform upon which other organelles can
operate within the cell.
Cytosol-the "soup" within which all of the cell's organelles reside
Fluid portion in the cytoplasm.
Organelles- Any of the Structures in cells that has a specialized
function.
2. regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell
3. The selectively permeable outer boundary of a cell consisting of a
phospholipid bilayer embedded with proteins.
4.
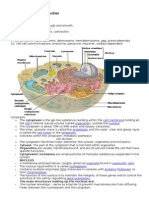
1. Ribosome-(ri′bo-sōm) Organelle composed of RNA and protein that
provides structural support and enzymatic activity for protein
synthesis.
2. Smooth E R (SER)- is associated with the production and
metabolism of fats and steroid hormones. It is 'smooth' because
it is not studded with ribosomes and is associated with smooth
slippery fats.
3. The rough endoplasmic reticulum or rER is vital for protein
synthesis that the cell uses for proper functioning. The rER is a
stack of membranous organelle that is embedded with
ribosomes. It functions in protein folding, sorting, and
transporting the proteins outside the cell to their proper
destinations.
4. Golgi apparatus
(gol′jē ap″ah-ra′tus) Organelle that prepares and modifies cellular
products for secretion.
Mitochondria- Mitochondria are tiny organelles inside cells that are
involved in releasing energy from food. This process is known as
cellular respiration. It is for this reason that mitochondria are often
referred to as the powerhouses of the cell
Lysosome- (li′so-sōm) Organelle that contains digestive enzymes.
Peroxisomes- (pĕ-roks′ĭ-sōm) Membranous cytoplasmic vesicle that
contains enzymes that catalyze reactions that produce and decompose
hydrogen peroxide.
Centrosome- Cellular organelle consisting of two centrioles.
You might also like
- Animal Cell Parts and Functions - Summary TableDocument16 pagesAnimal Cell Parts and Functions - Summary TableAnnie Lyn Villamor100% (1)
- Animal Cell Parts and FunctionsDocument8 pagesAnimal Cell Parts and FunctionsKarren Ferrer-Mora Handayan100% (1)
- Human Cell Diagram and Sickle CellDocument11 pagesHuman Cell Diagram and Sickle Cellaryaa2020No ratings yet
- BiotechDocument2 pagesBiotechKristel Faye Cortez SubiaNo ratings yet
- بايو م 2Document7 pagesبايو م 2alidoctor678No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument38 pagesCell Structure and FunctionHyacinth RaeNo ratings yet
- Mapa Mental. Human Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument2 pagesMapa Mental. Human Cell Structure and FunctionsLiselimrz MrzNo ratings yet
- Cell Intro InfoDocument12 pagesCell Intro Infoapi-237058097No ratings yet
- Pro and EuDocument15 pagesPro and EuCy BathanNo ratings yet
- ASDFASDFASDocument17 pagesASDFASDFASChristian Cyril RoldanNo ratings yet
- General Biology ReviewerDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerBaby AleiraNo ratings yet
- By: Tom Anthony A. Tonguia, RMT: Eukaryotic CellDocument9 pagesBy: Tom Anthony A. Tonguia, RMT: Eukaryotic CellTom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- Module For Anaphy CellDocument11 pagesModule For Anaphy CellBJ Bernardo IlNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell DefinitionDocument10 pagesAnimal Cell DefinitionAngelique VeteNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument2 pagesCell OrganellesSurminie Muksin100% (1)
- Biology Lab 4 The CellDocument7 pagesBiology Lab 4 The Cellrkfw7nq7xrNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biochemical Aspects) : Dr. Abid AliDocument49 pagesCell (Biochemical Aspects) : Dr. Abid AliShahzad MazharNo ratings yet
- Topic 2-Parts and Functions of The CellDocument45 pagesTopic 2-Parts and Functions of The CellDe Guia, Yuan Loriene Nina100% (1)
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesCell Structure and FunctionYeshua Dan BigasaNo ratings yet
- AP Cell Structure and Function Copy IpadDocument25 pagesAP Cell Structure and Function Copy IpadEbtisam AlmenhaliNo ratings yet
- 2 Cell and TissueDocument45 pages2 Cell and Tissuemandefro2No ratings yet
- Science PROKARYOTICEUKARYOTICDocument8 pagesScience PROKARYOTICEUKARYOTICsecurity securedNo ratings yet
- Cell Basics by MuneebDocument45 pagesCell Basics by MuneebMuneeb Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology DR Intesat M.el WahishyDocument30 pagesPathophysiology DR Intesat M.el Wahishyفافي الترهونيNo ratings yet
- Lec-8,9 CellsDocument30 pagesLec-8,9 CellsAbdullah-Al-mehedi HiraNo ratings yet
- g11 Els OrganellesDocument3 pagesg11 Els OrganellesJarod PeñaflorNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument70 pagesFunctional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsTrixie De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Cytoplasm 2.: Cell OrganellesDocument6 pagesCytoplasm 2.: Cell OrganellesSai Deekshita VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Sir Syed University of Engineering and Technology: Assignment No 1Document10 pagesSir Syed University of Engineering and Technology: Assignment No 1Ali InamNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument21 pagesAnimal CellGuzago, Reina Jane O.No ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellsDocument14 pagesAnimal and Plant Cellslea a delgadoNo ratings yet
- The Basic of LifeDocument21 pagesThe Basic of LifeJALAL JAMINo ratings yet
- Bio Final AssignmentDocument47 pagesBio Final AssignmentmikhailNo ratings yet
- Phospholipids (Fats With Phosphorous Attached), Which at Body Temperature AreDocument7 pagesPhospholipids (Fats With Phosphorous Attached), Which at Body Temperature AreCmae VidadNo ratings yet
- JetDocument14 pagesJetAnnie Lyn VillamorNo ratings yet
- The Cytoplasm: CytosolDocument5 pagesThe Cytoplasm: CytosolHariniNo ratings yet
- Human Biology: Dr. Safa Amer AliDocument20 pagesHuman Biology: Dr. Safa Amer AlikmoNo ratings yet
- By Muhammad SalmanDocument37 pagesBy Muhammad SalmanAmber ZahidNo ratings yet
- CellDocument37 pagesCellAmber ZahidNo ratings yet
- Cell The Basic Unit of Life 1Document22 pagesCell The Basic Unit of Life 1Matt Andrei AmorosoNo ratings yet
- Kingdom: Animal CellDocument8 pagesKingdom: Animal CellShaila IvoryNo ratings yet
- Cytoplasm and OrganellesDocument15 pagesCytoplasm and OrganellesAndrew MahilumNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 The CellDocument2 pagesChapter 2 The CellGela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The CellDocument43 pagesStructure and Function of The CellElvie Gutierrez100% (1)
- Plant Cell - LayoutDocument3 pagesPlant Cell - LayoutMahiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Cell Structure & FunctionDocument27 pagesLecture 3 - Cell Structure & Functionlazysadoon09No ratings yet
- Gen BioCell TheoryDocument18 pagesGen BioCell TheoryBernadeth CayaosNo ratings yet
- APP P3 The CellDocument6 pagesAPP P3 The CellZach TurnoNo ratings yet
- Animal Physiology Theory Lec1Document24 pagesAnimal Physiology Theory Lec1ao868598No ratings yet
- Lecture Last-Cell Organelles.Document3 pagesLecture Last-Cell Organelles.OnSolomonNo ratings yet
- Ans 201 Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsDocument33 pagesAns 201 Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsAdewaleNo ratings yet
- General Medical Biology: Lecture 3: Cell Structure and FunctionDocument24 pagesGeneral Medical Biology: Lecture 3: Cell Structure and FunctionRasan QadrNo ratings yet
- Unit II: Cell, Tissues, Glands, and MembranesDocument10 pagesUnit II: Cell, Tissues, Glands, and MembranesEds BernardoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure Function and PropertiesDocument10 pagesCell Structure Function and PropertiesWanda JohnNo ratings yet
- General Physiology: First YearDocument67 pagesGeneral Physiology: First YearGo HellNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument6 pagesCell Biologyakash kumarNo ratings yet
- Ploginpartpppppp: Parts of Animal CellsDocument2 pagesPloginpartpppppp: Parts of Animal CellsNelson De LimaNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Biology Chapter 8 - Revision NotesDocument10 pagesClass 11 Biology Chapter 8 - Revision NotesHARKIRIT KAUR100% (1)
- Ch. 3 Cell ReviewDocument5 pagesCh. 3 Cell ReviewDivine GelasiusNo ratings yet