Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mypchem Ch10answers
Uploaded by
PikunoShuousOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mypchem Ch10answers
Uploaded by
PikunoShuousCopyright:
Available Formats
Page 251 What does the reactivity series tell us?
Page 261 Experiment: What is the percentage of
1. a) Spontaneous oxygen in atmospheric air?
b) Spontaneous 4. 4Fe(s) + 3O2(g) → 2Fe2O3(s)
c) Non-spontaneous This is the simplified version of the chemical
d) Non-spontaneous equation of a series of more complex reactions.
e) Spontaneous 5. Elemental iron has undergone oxidation in the
presence of oxygen and water.
f) Spontaneous
2. Gold will not react with an acid such as
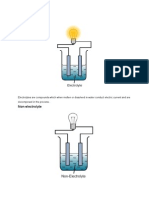
Page 264 Demonstration: Electrolysis of molten
hydrochloric acid as gold is the least reactive
metal in the series and will not displace hydrogen zinc chloride
ions from an acid. 1. Initially when the zinc chloride is a solid, the light-
bulb is not lit. As the zinc chloride begins to melt,
the lightbulb begins to flicker and eventually is
Page 255 Which species are capable of movement
fully lit. As solid ionic compounds, the ions in zinc
in a voltaic cell? chloride are unable to move between the
1. Anions from the salt bridge move into the anode electrodes to complete the circuit and therefore
cell to maintain charge balance as electrons are no electrons will flow in the external circuit. When
lost from the anode into the external circuit. zinc chloride is molten, the redox reactions at the
Cations from the salt bridge move into the cathode anode and cathode will proceed, ions in the
to counter balance the electrons that move into molten electrolyte can pass between the
the cathode from the external circuit. electrodes, electrodes will begin to flow from the
anode to the cathode and the bulb will be lit.
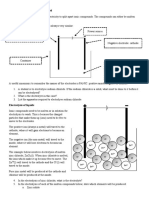
Page 255 Experiment: Investigating a voltaic cell 2. Anode: 2Cl–(l) → Cl2(g)+ 2e–
1. Identify the anode and cathode cell; identify the Cathode: Zn2+(l) + 2e– → Zn(s)
composition of the electrolyte in each cell and the Overall: 2Cl–(l) + Zn2+(l) → Cl2(g) + Zn(s)
molarity; label the polarity of the electrodes; draw
the symbol for a voltmeter in the external circuit; Page 265 How are sodium metal and chlorine gas
identify the direction of the electron flow in the produced commercially?
external circuit; nominate and name the electro-
lyte for the salt bridge and state its molarity. 1. Melting (or fusion); solid to liquid.
2. Half reactions should be charged balanced (states
of matter not required). Page 266 How are sodium metal and chlorine gas
produced commercially?
Page 261 Voltaic cells 1. Yellow-green vapor produced (chlorine gas).
1. a) Zn(s) + Pb2+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + Pb(s)
b) Fe(s) + 2Cu+(aq) → Fe2+(aq) + 2Cu(s) Page 269 Demonstration: The reaction between
c) Mg(s) + Sn2+(aq) → Mg2+(aq) + Sn(s) concentrated hydrochloric acid and ammonia
d) Ni(s) + Br2(l) → Ni2+(aq) + 2Br–(aq) 1. After a period of time, a ring of white smoke will
e) Na(s) + Ag+(aq) → Na+(aq) + Ag(s) appear inside the glass or plastic tubing.
2. The precipitate which forms is called ammonium
Page 261 Experiment: What is the percentage of chloride, NH4Cl(s).
3. The ammonium chloride forms closer to the end of
oxygen in atmospheric air?
the plastic tubing where the chlorine was
1. The steel wool will change color from gray to introduced. From this observation you can infer
red/brown.
that the ammonia molecules traveled at a faster
2. Approximate values of 16–20% should be rate than the chlorine molecules. This inference is
calculated.
supported by the fact that ammonia has a smaller
3. The value calculated experimentally maybe lower molar mass than chlorine and therefore the
than the percentage of oxygen in atmospheric air
molecules will have a larger kinetic energy at a
as the amount of steel wool used in experiments
given temperature.
may not have been sufficient to extract all of the
dissolved oxygen from the water during the
oxidation process.
© Oxford University Press 2018 1
Page 270 Demonstration: Reaction between
zinc and iodine and the diffusion of iodine gas
in the air
1. Zinc powder is gray in color and the iodine
crystals are a purple/black color.
2. The name of the salt formed in this reaction is zinc
iodide, ZnI2.
3. Iodine can undergo the process of sublimation,
where a solid changes state directly to a gas. This
process requires energy, which is derived from
the exothermic reaction between zinc and iodine.
Summative assessment
Electrochemical cells
1. There are six possible reactions. List the balanced half-cell reaction at both the
anode and cathode. For the mark, the equation that occurs at the anode must
have been reversed.
Anode half-equation Cathode half-equation Overall chemical reaction
Zn ↔ Zn2+ + 2e– Fe2+ + 2e– ↔ Fe Zn + Fe2+ → Zn2+ + Fe
Zn ↔ Zn2+ + 2e– Cu2+ + 2e– ↔ Cu Zn + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu
Zn ↔ Zn2+ + 2e– Ag+ + e– ↔ Ag Zn + 2Ag+ → Zn2+ + 2Ag
Fe ↔ Fe2+ + 2e– Cu2+ + 2e– ↔ Cu Fe + Cu2+ → Fe2+ + Cu
Fe ↔ Fe2+ + 2e– Ag+ + e– ↔ Ag Fe + 2Ag+ → Fe2+ + 2Ag
Cu ↔ Cu2+ + 2e– Ag+ + e– ↔ Ag Cu + 2Ag+ → Cu2+ + 2Ag
2. Zn + Fe2+ → Zn2+ + Fe Zinc is oxidized, iron is reduced.
Zn + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu Zinc is oxidized, copper is reduced.
Zn + 2Ag+ → Zn2+ + 2Ag Zinc is oxidized, silver is reduced.
Fe + Cu2+ → Fe2+ + Cu Iron is oxidized, copper is reduced.
Fe + 2Ag+ → Fe2+ + 2Ag Iron is oxidized, silver is reduced.
Cu + 2Ag+ → Cu2+ + 2Ag Copper is oxidized, silver is reduced.
3. i) Two separate cells that contain an electrolyte and an electrode; symbol for
voltmeter drawn in the external circuit; wires connecting the electrodes in
either cell; a salt bridge connecting the two separate cells; concentration of
electrolytes and the temperature of the system is at standard conditions
(see page 255 of MYP Chemistry for a labelled diagram).
ii) Cathode and anode labelled clearly.
iii) For example: Fe2+; Cu2+; H+; OH–.
iv) All nitrate salts are soluble so the presence of nitrate ions will not form
precipitates in the cells; sodium is a reactive metal and the sodium ion is
unlikely to undergo reduction.
v) The direction of the movement of electrons is from the anode to the cathode.
4. Tin is a less reactive metal when compared to the alkali metals such as sodium
and potassium. At the cathode, tin(II) ions from the aqueous solution will
undergo reduction forming elemental tin. A grey solid will begin to plate onto
the surface of the cathode:
Sn2+(aq) + 2e– → Sn(s)
At the anode, iodide ions will be preferentially oxidized:
2I–(aq) → I2(l) + 2e–
Identifying a reactivity series
5. The hypothesis should outline the relationship between copper, zinc and
magnesium in terms of the electrochemical series; and which of these species
will be preferentially oxidized or reduced.
2 © Oxford University Press 2018
6. Design should include clear statement of:
independent and dependent variables
rationale for the method and practical details, including
o correct names of apparatus used in your design
o amounts and concentration of chemicals being used
consideration of safety, ethical and environmental issues
description of the step-by-step methodology for the investigation, including
the construction of the voltaic cells
description of how qualitative observations will be recorded
identification of the quantitative data that will be recorded and the design of
data tables to present this information
Marks awarded on a scale from 0 marks for a completely inadequate design to 8
marks for an exemplary design.
Identifying a reactivity series – analysis and evaluation
7. Magnesium is able to displace copper ions from solution as it is higher in the
reactivity series and will preferentially undergo oxidation. Copper ions will be
reduced;
Zinc is able to displace copper ions from solution as it is higher in the reactivity
series and will preferentially undergo oxidation. Copper ions will be reduced;
Lead is able to displace copper ions from solution as it is higher in the reactivity
series and will preferentially undergo oxidation. Copper ions will be reduced;
Magnesium is able to displace lead ions from solution as it is higher in the
reactivity series and will preferentially undergo oxidation. Lead ions will be
reduced;
Zinc is able to displace lead ions from solution as it is higher in the reactivity
series and will preferentially undergo oxidation. Lead ions will be reduced;
Magnesium is able to displace zinc ions from solution as it is higher in the
reactivity series and will preferentially undergo oxidation. Zinc ions will be
reduced.
8. Suitable hypothesis is suggested; hypothesis is testable; hypothesis is based on
scientific reasoning; method for the investigation takes into consideration
significant factors that may influence the reliability of the data.
9. Any evaluation of the methodology should examine strengths; and weaknesses
that are realistic and relevant; extensions to the experiment should result in
new knowledge about the concept.
Chemistry throughout the centuries
10. Students may mention the following points in their response:
The change in appearance of the laboratories over time;
The clothes worn by the scientists in the different images;
The lack of electricity in the images when compared to a modern laboratory;
The agenda of the early scientists compared to the modern scientific
community.
© Oxford University Press 2018 3
You might also like
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: Redox Reactions, Cells, Batteries and ElectrolysisDocument5 pagesElectrochemistry: Redox Reactions, Cells, Batteries and ElectrolysisfelixNo ratings yet
- 2324 Level M (Gr11 UAE-Gulf) Chemistry Chapter 4 NotesDocument18 pages2324 Level M (Gr11 UAE-Gulf) Chemistry Chapter 4 Notesaminata13536No ratings yet
- Chemistry - Notes Icse 10Document25 pagesChemistry - Notes Icse 10Suneet MohanNo ratings yet
- REDOX REACTIONS STDocument11 pagesREDOX REACTIONS STirehan.saiyedNo ratings yet
- Freelancers - G10 - Chem - Metals and Non-Metals PDFDocument13 pagesFreelancers - G10 - Chem - Metals and Non-Metals PDFKodati Durga Prasad KodatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter: Redox Reactions: Oxidation and ReductionDocument9 pagesChapter: Redox Reactions: Oxidation and ReductionD Singal100% (1)
- Handout ElectroChemistry BY S.KDocument16 pagesHandout ElectroChemistry BY S.Katsats815No ratings yet
- The Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsDocument30 pagesThe Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsBayan O. Abu SaadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document11 pagesChapter 4J.K HomerNo ratings yet
- 2Document4 pages2mikeasmith404No ratings yet
- The Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsDocument35 pagesThe Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsZulaikha NurafifiNo ratings yet
- ELECTROLYSIS OF MOLTEN SALTDocument33 pagesELECTROLYSIS OF MOLTEN SALTTom TommmaNo ratings yet
- KimiaDocument46 pagesKimiaErvina RetnaningtyasNo ratings yet
- Chapter: Redox Reactions: Oxidation and ReductionDocument15 pagesChapter: Redox Reactions: Oxidation and ReductionVibhor KaushikNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis MasteryDocument8 pagesElectrolysis MasteryDonald ZhuoNo ratings yet
- CHM 114 Exp 10Document6 pagesCHM 114 Exp 10João Antonio BassettoNo ratings yet
- D-& F Block ElementsDocument46 pagesD-& F Block ElementsdetectionisimpressionNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry NotesDocument16 pagesElectrochemistry NotesHE HUA YIPNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis 090618180154 Phpapp01Document20 pagesElectrolysis 090618180154 Phpapp01jiivi87No ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT 3, OLeitch & JJarvis Mec 3206Document25 pagesASSIGNMENT 3, OLeitch & JJarvis Mec 3206Oneil Prettyboyswagg LeitchNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: Physical ChemistryDocument32 pagesElectrochemistry: Physical ChemistryDavidson ChanNo ratings yet
- 4.2 ElectrolysisDocument5 pages4.2 Electrolysis211273wNo ratings yet
- Electrochemsitry NotesDocument9 pagesElectrochemsitry NotesAhmad Shafiq ZiaNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis of molten lead bromideDocument38 pagesElectrolysis of molten lead bromidehemanth PNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis Mechanisms and ApplicationsDocument17 pagesElectrolysis Mechanisms and ApplicationsInnocent EbilNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry NotesDocument54 pagesElectrochemistry NotesAkash Roy67% (6)
- 12 TH V-I ModifiedDocument151 pages12 TH V-I ModifiedAkash VigneshwarNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis: Term MeaningDocument22 pagesElectrolysis: Term MeaningYeen ChengNo ratings yet
- s.4 Chem Notes On Electrlysis Corrected Copy.Document9 pagess.4 Chem Notes On Electrlysis Corrected Copy.Ronald RomNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument16 pagesElectrochemistryitsshaunboteNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Chemicals - AKHS Edition 2020 - Complete NotesDocument20 pagesElectricity and Chemicals - AKHS Edition 2020 - Complete NotesKim SewoonNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument38 pagesElectrochemistryShannon SmithNo ratings yet
- Ib Chemistry Answers S3Document14 pagesIb Chemistry Answers S3Carlos JesúsNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Copper Content in Coins Using Colorimetric and Volumetric MethodsDocument31 pagesAnalysis of Copper Content in Coins Using Colorimetric and Volumetric MethodsOctavianLars50% (6)
- LXL - Gr12PhysicalSciences - 27 - Redox Reactions - 02sep2014Document5 pagesLXL - Gr12PhysicalSciences - 27 - Redox Reactions - 02sep2014HNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 9th CLASS Long QuestionsDocument12 pagesCHAPTER 7 9th CLASS Long Questionssomerakhan2023No ratings yet
- Electrolytic CellsDocument32 pagesElectrolytic CellsHendi PratamaNo ratings yet
- Redox and Electrochem Review Multiple Choice Eboard AnswersDocument4 pagesRedox and Electrochem Review Multiple Choice Eboard AnswersKhaledEl-MaghallawyNo ratings yet
- C12 Electrochemistry IgcseDocument33 pagesC12 Electrochemistry IgcseAnna DixonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - ElectrolysisDocument51 pagesChemistry - Electrolysisjoannavera2020No ratings yet
- 1st Year Chemistry Notes Electrochemistry ExercisesDocument31 pages1st Year Chemistry Notes Electrochemistry ExercisesshahidkakaNo ratings yet
- 6A Electrochemistry - AnswerDocument6 pages6A Electrochemistry - AnswerWong Wai Lun100% (1)
- Mypchem Ch8answersDocument4 pagesMypchem Ch8answersPikunoShuousNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Reactions: + Battery - Salt BridgeDocument7 pagesElectrochemical Reactions: + Battery - Salt BridgewscienceNo ratings yet
- Ch-18 Electrochemistry CaabilDocument50 pagesCh-18 Electrochemistry CaabilAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: End of Year Exam RevisionDocument9 pagesChemistry: End of Year Exam Revisionapi-354037574No ratings yet
- Chapter 19: Electrochemistry: The Quest For Clean Energy: Problems: 19.2-19.3, 19.13-19.58, 19.69-19.72, 19.75-19.78Document24 pagesChapter 19: Electrochemistry: The Quest For Clean Energy: Problems: 19.2-19.3, 19.13-19.58, 19.69-19.72, 19.75-19.78Star LightNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 ElectrochemistryDocument11 pagesChapter 6 ElectrochemistryAshraf Shaharudin100% (1)
- UntitledDocument9 pagesUntitledemanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Redox ReactionsDocument23 pagesChapter 8 Redox Reactionsapi-19916399No ratings yet
- 10 Chapter Electrochemistry Text Book ExerciseDocument31 pages10 Chapter Electrochemistry Text Book ExerciseSajid AzeemNo ratings yet
- Form 4A Notes: Cations Migrate To The Cathode and Are Reduced by Gaining of ElectronsDocument9 pagesForm 4A Notes: Cations Migrate To The Cathode and Are Reduced by Gaining of ElectronsGono TakaduuNo ratings yet
- Notes PDFDocument91 pagesNotes PDFjoyce heahNo ratings yet
- Test4 Ch19 Electrochemistry Practice ProblemsDocument13 pagesTest4 Ch19 Electrochemistry Practice ProblemsPhysiochemo Chemical100% (1)
- Chemistry Teach Yourself Series - Topic 4 - RedoxDocument15 pagesChemistry Teach Yourself Series - Topic 4 - RedoxHenry PoetrodjojoNo ratings yet
- Class X ElectrolysisDocument4 pagesClass X ElectrolysisvartikasinghNo ratings yet
- Exam Chew 1Document7 pagesExam Chew 1ThilagaNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument65 pagesElectrochemistryLiam GalbanNo ratings yet
- Aluminized SteelDocument6 pagesAluminized SteelMamacintNo ratings yet
- Discussion of Extended Drucker-Prager Yield Criterion in Slope Stability AnalysisDocument4 pagesDiscussion of Extended Drucker-Prager Yield Criterion in Slope Stability AnalysisAbdelmoez ElgarfNo ratings yet
- Spring Back in Sheet Metal Bending-A Review: Gawade Sharad, Dr. V. M. NandedkarDocument4 pagesSpring Back in Sheet Metal Bending-A Review: Gawade Sharad, Dr. V. M. Nandedkarkhudhayer1970No ratings yet
- Past Papers:Unit OperationsDocument2 pagesPast Papers:Unit OperationsMalavikaNNo ratings yet
- Astm C335Document11 pagesAstm C335deivisbtsNo ratings yet
- Metals 1 PDFDocument17 pagesMetals 1 PDFhareshNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Mid ExamDocument5 pagesFluid Mechanics Mid ExamRalph CastilloNo ratings yet
- Jurnal ErielDocument5 pagesJurnal ErielPaste GigiNo ratings yet
- Bamboo+Alumina CompositeDocument5 pagesBamboo+Alumina CompositeAmmineni Syam PrasadNo ratings yet
- Crystal Structure - Delivery NotesDocument35 pagesCrystal Structure - Delivery NotesAninda LahiriNo ratings yet
- Deflection Calculation Sheet: Units ReferenceDocument4 pagesDeflection Calculation Sheet: Units Referenceabdul khaderNo ratings yet
- Quiz 5 Atoms, Atomic Theory, Atomic StructureDocument4 pagesQuiz 5 Atoms, Atomic Theory, Atomic StructureJoeylyn BalidioNo ratings yet
- Irfp 90N20DDocument10 pagesIrfp 90N20DF.da CostaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Different Cutting Milling Strateg - 2020 - Procedia ManuDocument8 pagesComparative Analysis of Different Cutting Milling Strateg - 2020 - Procedia Manumatheus soranzzoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Notes PDFDocument74 pagesFluid Mechanics Notes PDFvirendra100% (3)
- 2023 VCAA Physics Exam SolutionsDocument2 pages2023 VCAA Physics Exam SolutionsRobin MowlaNo ratings yet
- Tor Ferita 4C6 blf177 2Document2 pagesTor Ferita 4C6 blf177 2cana_robertNo ratings yet
- High Energy PMT TPMZ0003EDocument76 pagesHigh Energy PMT TPMZ0003Egoutu41No ratings yet
- United States Patent (191: Schweier Et A)Document5 pagesUnited States Patent (191: Schweier Et A)Maya RamlahNo ratings yet
- Tool Wear and FailureDocument65 pagesTool Wear and FailureBasarabeanuNo ratings yet
- TDS YIEH 6082 PlateDocument4 pagesTDS YIEH 6082 PlateSatendra ThakurNo ratings yet
- Interview QuestionsDocument1 pageInterview Questionslee2148No ratings yet
- Thermal Processing of MetalsDocument63 pagesThermal Processing of MetalsNagaVenkateshGNo ratings yet
- GKS-112 M Screw-in Test Probe DetailsDocument1 pageGKS-112 M Screw-in Test Probe DetailsCindy RiveraNo ratings yet
- Friction Stir Welding and ProcessingDocument9 pagesFriction Stir Welding and ProcessingPKNo ratings yet
- CSCE 613: Fundamentals of VLSI Chip Design: Instructor: Jason D. BakosDocument26 pagesCSCE 613: Fundamentals of VLSI Chip Design: Instructor: Jason D. BakosbhawnaNo ratings yet
- JOIST With Taper Flanges - BS4 Part 1993 ALL SECTION - DimensionsDocument1 pageJOIST With Taper Flanges - BS4 Part 1993 ALL SECTION - DimensionsAxiv The GreatNo ratings yet
- Amount of Wax or Alumimum Required To Absorb Backscattered Electron IIDocument2 pagesAmount of Wax or Alumimum Required To Absorb Backscattered Electron IIramramani1416No ratings yet
- Structural Analysis PetDocument125 pagesStructural Analysis PetGirish ChandranNo ratings yet
- T18 Full Bok Test PhysisDocument2 pagesT18 Full Bok Test Physisfarhanshoaib34No ratings yet