Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BIO2102 - Microscopes 1x2OS 8Q7
Uploaded by
Prezy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesOriginal Title
BIO2102_microscopes 1x2OS 8Q7
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesBIO2102 - Microscopes 1x2OS 8Q7
Uploaded by
PrezyCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Name: Precy B.
Ramada Date: 09/13/2022
Course: BS Biology BIO 2102: Microbiology
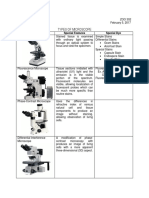
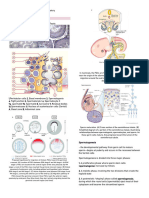
The Different Microscopes
Type of microscope Description Typical uses Sample image
Light microscopes Use visible light; shorter, blue wavelengths provide better resolution
Bright field Simple to use; To observe killed
relatively stained specimens
inexpensive; stained and naturally
specimens often colored live ones;
required also used to count
microorganisms
Dark field Uses a special filter To observe living,
in the condenser that colorless,
prevents light from unstained
directly passing organisms
through a specimen;
only light scattered
by the specimen is
visible
Phase contrast Uses a special To observe
condenser that splits internal structures
a polarized light of living microbes
beam into two
beams; contrast in
the image results
from the interactions
of the two beams
Differential Uses two separate To observe
interference beams instead of a internal structures
contrast (Nomarski) split beam; false of living microbes
color and a three-
dimensional effect
result from
interactions of light
beams and lenses; no
staining required
Fluorescence An ultraviolet light To localize
source causes specific chemicals
fluorescent natural or structures; used
chemicals or dyes to as an accurate and
emit visible light quick diagnostic
tool for detection
of pathogens
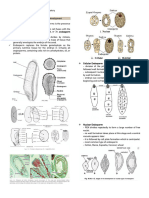
Electron Use electrons traveling as waves with short wavelengths: require
Microscopes specimens to be in a vacuum, cannot be used to examine living cells
Transmission Produces two- To observe
dimensional image internal
of ultrastructure of ultrastructural
cells detail of cells and
observation of
viruses and small
bacteria
Scanning Produces three- To observe the
dimensional view of surface details of
the surface of structures
microbes and cellular
structures
Probe Microscopes Uses microscopic probes that move over the surface of a specimen;
resolving power greater than electron microscopes
Scanning tunneling Measures the flow of To observe the
electrical current surface of objects;
between the tip of a provide extremely
probe and the fine detail, high
specimen to produce magnification, and
an image of the great resolution
surface at atomic
level
Atomic force Measures the To observe living
deflection of a laser specimens at the
beam aimed at the tip molecular and
of a probe that atomic levels
travels across the
surface of the
specimen
Sample image sources:
https://www.olympus-lifescience.com/en/microscope-resource/primer/anatomy/brightfieldgallery/
https://www.microscopeclub.com/dark-field-microscopy/
https://www.leica-microsystems.com/science-lab/phase-contrast/
https://www.microscopyu.com/galleries/dic-phase-contrast
https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/41334
https://www.ualberta.ca/biological-sciences/services/mf/galleries/index.html
http://nano.vub.ac.be/portfolio/scanning-probe-microscopy/
https://rsscience.com/bacteria/
You might also like
- MicroscopeDocument2 pagesMicroscopeHezekiah VillamorNo ratings yet
- Microscopy Techniques: The Instrument & Dyes and Staining Summary of Microscopic Instruments and Their CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesMicroscopy Techniques: The Instrument & Dyes and Staining Summary of Microscopic Instruments and Their Characteristicsthe someoneNo ratings yet
- Types of Microscope and Culture MediaDocument40 pagesTypes of Microscope and Culture MediaAsad ButtNo ratings yet
- ZOO302 HW1 Types of MicroscopeDocument3 pagesZOO302 HW1 Types of MicroscopeNini CioconNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus Aureus Escherichia Coli: Poliovirus (27 NM 0.027 M)Document15 pagesStaphylococcus Aureus Escherichia Coli: Poliovirus (27 NM 0.027 M)Sam DinhNo ratings yet
- Bacte Lec W2 Individual AssignmentDocument2 pagesBacte Lec W2 Individual AssignmentAkemi ParkNo ratings yet
- MICP LAB (WK - 1) Microscope, Other Equipment, Prokayyote, EukaryoteDocument10 pagesMICP LAB (WK - 1) Microscope, Other Equipment, Prokayyote, EukaryoteMia France SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Types of Microscope Description/ Uses: Light MicroscopesDocument3 pagesTypes of Microscope Description/ Uses: Light MicroscopesLea Chariza PagauisanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Microscopes Used in MicrobiologyDocument1 pageUnit 1: Microscopes Used in MicrobiologyMollyNo ratings yet
- CM Ass#3Document3 pagesCM Ass#3Bainasria MaligaNo ratings yet
- Histpath Lab Module 2Document7 pagesHistpath Lab Module 2Clair TugnaNo ratings yet
- Phase Contrast MicrosDocument7 pagesPhase Contrast MicrosRahul PalsNo ratings yet
- Minor Report Prashanth NanotechDocument13 pagesMinor Report Prashanth Nanotechprashanth 18ee029No ratings yet
- Microscope ModificationsDocument4 pagesMicroscope ModificationsJanno MallariNo ratings yet
- FHGJKJHGJKLJHGJKDocument9 pagesFHGJKJHGJKLJHGJKprashanth 18ee029No ratings yet
- Laboratory Techniques & EquipmentsDocument11 pagesLaboratory Techniques & EquipmentsambotNo ratings yet
- Different Kinds of Microscopes: Stereo MicroscopeDocument1 pageDifferent Kinds of Microscopes: Stereo MicroscopeJulian AlbaNo ratings yet
- Microscopy and The Discovery of The CellDocument35 pagesMicroscopy and The Discovery of The Cellmipan susuNo ratings yet
- What Is A Phase Contrast Microscope?Document10 pagesWhat Is A Phase Contrast Microscope?Alejandra NuñezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Microsopy and Preparation of SpecimenDocument63 pagesChapter 3 Microsopy and Preparation of SpecimenMARIAM AFIFAH NUBAHARINo ratings yet
- Systematic "A" Level Biology. Basic and Simplified Revision NotesDocument458 pagesSystematic "A" Level Biology. Basic and Simplified Revision NotesNelima Stella mercy100% (2)
- Tools in MicrobiologyDocument26 pagesTools in MicrobiologyMaria Gabriela Ycaza ZuritaNo ratings yet
- Struktur Sel Dan OrganelDocument33 pagesStruktur Sel Dan OrganelSeptian IksanNo ratings yet
- MicroscopeDocument24 pagesMicroscopeAnkur MishraNo ratings yet
- Caie As Biology 9700 Theory v4Document31 pagesCaie As Biology 9700 Theory v4USMAN JUNAID LAKHA NINo ratings yet
- Histology (p2) Introduction To Histology and Tissue ProcessingDocument7 pagesHistology (p2) Introduction To Histology and Tissue Processing2F - MACAO, KHALILANo ratings yet
- MICROSDocument5 pagesMICROSAlfNo ratings yet
- 2.1 The Properties of Light 2.3 Instruments of Microscopy: 70 2 - SummaryDocument3 pages2.1 The Properties of Light 2.3 Instruments of Microscopy: 70 2 - SummaryAna GrimaldoNo ratings yet
- wuolah-free-TOOLS IN CELL BIOLOGYDocument2 pageswuolah-free-TOOLS IN CELL BIOLOGYMARIA BERMUDEZ LOPEZNo ratings yet
- MicrosDocument35 pagesMicrosfaezeh zare karizakNo ratings yet
- La1 ReviewerDocument4 pagesLa1 ReviewerRhea Mae TabayagNo ratings yet
- Developments in MicrosDocument3 pagesDevelopments in MicrosТетяна ЧучукNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument154 pagesCell Structure and FunctionSatya NadellaNo ratings yet
- Tristan Scott - BIOL-1408-46440 - LAB 04 Microscopy and The Cell - MaymesterDocument9 pagesTristan Scott - BIOL-1408-46440 - LAB 04 Microscopy and The Cell - MaymesterTristan ScottNo ratings yet
- Microbio Act#1 (Baylon, Bunyi, Encarnacion, and Galera)Document8 pagesMicrobio Act#1 (Baylon, Bunyi, Encarnacion, and Galera)Samantha Nicole S. GaleraNo ratings yet
- BMMicrosDocument16 pagesBMMicrosYambanwan FinleyNo ratings yet
- Microscope Laboratory Activity 1Document4 pagesMicroscope Laboratory Activity 1Ambot sa ImoNo ratings yet
- MicrosDocument39 pagesMicrosKalyani GNo ratings yet
- Microscopy and StainingDocument14 pagesMicroscopy and StainingEJ BarnuevoNo ratings yet
- Biology Lab Activity 2Document6 pagesBiology Lab Activity 2Adrian Anthony Villaluz GasatayaNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 MicrosDocument8 pagesLab 1 MicrosAubrey Joie Esguerra FigueroaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Microscopic World: Course-Bio I Lab Session - Fall - 2021 Section - 001Document16 pagesIntroduction To Microscopic World: Course-Bio I Lab Session - Fall - 2021 Section - 001Satya NadellaNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument12 pagesThe CellEdrian MartinNo ratings yet
- Biochem WorksheetDocument4 pagesBiochem WorksheetAlpha KNo ratings yet
- Microscope: تايرصب لوا يرباجلا يداهلا دبع نسح D Lab 7 BiologyDocument3 pagesMicroscope: تايرصب لوا يرباجلا يداهلا دبع نسح D Lab 7 BiologyHassan AljaberiNo ratings yet
- Light Electron: Bright Field Virtual Fluorescence Phase-Contrast Confocal Polarizing Scanning TransmissionDocument3 pagesLight Electron: Bright Field Virtual Fluorescence Phase-Contrast Confocal Polarizing Scanning TransmissionMary Rose AllinegNo ratings yet
- ReviewDocument5 pagesReviewLea PadillaNo ratings yet
- Ch18 Methods Cell BiologyDocument34 pagesCh18 Methods Cell Biology周易No ratings yet
- Microscope Type Distinguishing Features Typical Image of Microbe Principal UsesDocument2 pagesMicroscope Type Distinguishing Features Typical Image of Microbe Principal UsesakljbdfioNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Microscope and Its UsageDocument5 pagesDifferent Types of Microscope and Its UsageKryle SevilleNo ratings yet
- Types of MicrosDocument30 pagesTypes of MicrosKarishma100% (1)
- 3-Techniques in Cell BiologyDocument15 pages3-Techniques in Cell Biologywhether913No ratings yet
- 1st Seminar Microscope EditedDocument36 pages1st Seminar Microscope EditedSharonNo ratings yet
- The Cell 1Document133 pagesThe Cell 1Laica BlazaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cell BiologyDocument1 pageIntroduction To Cell BiologyMc FNo ratings yet
- Bacterial IdentificationDocument18 pagesBacterial IdentificationPan YangNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument83 pagesCell Structure and FunctionKyza MondaloNo ratings yet
- La1 ReviewerDocument4 pagesLa1 ReviewerRhea Mae TabayagNo ratings yet
- Chemical Biology: Techniques and ApplicationsFrom EverandChemical Biology: Techniques and ApplicationsBanafshe LarijaniNo ratings yet
- Developmental Biology Notes 3Document26 pagesDevelopmental Biology Notes 3PrezyNo ratings yet
- Devbio 1Document10 pagesDevbio 1PrezyNo ratings yet
- Genetics CH 3-4Document19 pagesGenetics CH 3-4PrezyNo ratings yet
- Exercise 9 DevbiolabDocument4 pagesExercise 9 DevbiolabPrezyNo ratings yet
- MicrobioLec Q and A Notes ZMAzPDocument6 pagesMicrobioLec Q and A Notes ZMAzPPrezyNo ratings yet
- D-K For MicrofilariaeDocument1 pageD-K For MicrofilariaePrezyNo ratings yet
- D-K For PlasmodiaDocument2 pagesD-K For PlasmodiaPrezyNo ratings yet
- D-K For Amoebae and FlagellatesDocument2 pagesD-K For Amoebae and FlagellatesPrezyNo ratings yet
- D-K For Helminth EggsDocument2 pagesD-K For Helminth EggsPrezyNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 WebinarDocument1 pageActivity 3 WebinarPrezyNo ratings yet
- SDG 4Document43 pagesSDG 4PrezyNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Flake BehavioursDocument12 pagesHydrogen Flake BehavioursAlex AjuNo ratings yet
- Fournier1977 Geotermometer & Mixing PDFDocument10 pagesFournier1977 Geotermometer & Mixing PDFAnonymous FdickkSXcNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry SL Topic 5 Questions 1Document11 pagesIB Chemistry SL Topic 5 Questions 1Vibha RaviNo ratings yet
- Lab Report TLCDocument6 pagesLab Report TLCkashvinwarmaNo ratings yet
- JVCVReport1215 PDFDocument1 pageJVCVReport1215 PDFUlises BadilloNo ratings yet
- Q2 Science 9 - Module 1Document27 pagesQ2 Science 9 - Module 1Reynalyn asoyNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Coordination ChemistryDocument818 pagesComprehensive Coordination Chemistryrace egrNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9Document3 pagesMatter in Our Surroundings Class 9Pushpa Kumari89% (18)
- Manual Técnico de Despiece A.A. Serie MUZ-GEDocument12 pagesManual Técnico de Despiece A.A. Serie MUZ-GEesteban andres olivaNo ratings yet
- CH205 Lab - Corrosion (S11172685)Document6 pagesCH205 Lab - Corrosion (S11172685)Nitesh ChandNo ratings yet
- Law of Definite Composition - Answer SHeetDocument2 pagesLaw of Definite Composition - Answer SHeetFrank Anthony SanchezNo ratings yet
- CSB AminesDocument6 pagesCSB AminesShauryaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Aspirin Tablet PDFDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Aspirin Tablet PDFAnonymous TmwS3ZmseNo ratings yet
- Hess's Law (1.5.5) - CIE As Chemistry Revision Notes 2022 - Save My ExamsDocument9 pagesHess's Law (1.5.5) - CIE As Chemistry Revision Notes 2022 - Save My ExamsSahana KumarNo ratings yet
- Sequencing of Separation Columns: Direct Sequence Indirect SequenceDocument18 pagesSequencing of Separation Columns: Direct Sequence Indirect SequenceVidvendu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Biochar-Based Engineered Composites For Sorptive Decontamination of WaterDocument65 pagesBiochar-Based Engineered Composites For Sorptive Decontamination of WaterIssaoui MansourNo ratings yet
- PPE Problem Set 1Document128 pagesPPE Problem Set 1Gracee86% (14)
- Chap. 6Document23 pagesChap. 6Nadeem ShaukatNo ratings yet
- Steam Calculation On Basis of Flow-Temperature (1) 2222Document5 pagesSteam Calculation On Basis of Flow-Temperature (1) 2222hmaza shakeelNo ratings yet
- Atomic Physics Notes QuestionsDocument17 pagesAtomic Physics Notes QuestionsvijayaraghavanNo ratings yet
- Lecture Pt. 4Document35 pagesLecture Pt. 4zy- SBGNo ratings yet
- A Level Chemistry Paper 2 Exam 10Document4 pagesA Level Chemistry Paper 2 Exam 10Anthony AndyNo ratings yet
- Diplomarbeit A Versteegh MPI PP Berlin - Kugelblitz PDFDocument123 pagesDiplomarbeit A Versteegh MPI PP Berlin - Kugelblitz PDFtobit3000No ratings yet
- Polymer PhysicsDocument405 pagesPolymer PhysicsPurushothaman100% (6)
- SOx FGD LimestoneDocument30 pagesSOx FGD LimestonehafizdtomoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Journal: Contents Lists Available atDocument15 pagesChemical Engineering Journal: Contents Lists Available atSaikat SahaNo ratings yet
- E 204 - 98 R02 - Rtiwna - PDFDocument17 pagesE 204 - 98 R02 - Rtiwna - PDFpechugonisNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Closed System and Open SystemDocument2 pagesDifference Between Closed System and Open SystemSouroJeet100% (1)
- Alkyl Halide-Jeemain - Guru PDFDocument37 pagesAlkyl Halide-Jeemain - Guru PDFUma JadounNo ratings yet
- chl9 (Sem 1 Inorganic)Document24 pageschl9 (Sem 1 Inorganic)rodrigues flemeNo ratings yet