Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ventricles, Meninges and CSF: Prepared By: Dr. Shilan H. Karim Assistant Professor of Anatomy & Histology
Uploaded by
lazo dara0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views65 pagesOriginal Title
6
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views65 pagesVentricles, Meninges and CSF: Prepared By: Dr. Shilan H. Karim Assistant Professor of Anatomy & Histology
Uploaded by
lazo daraCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 65
Ventricles, Meninges and CSF
Prepared by:
Dr. Shilan H. karim
Assistant Professor of Anatomy & histology
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
Ventricles, Meninges and CSF
Prepared by:
Dr. Shilan H. karim
Assistant Professor of Anatomy & histology
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
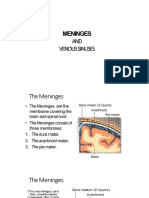
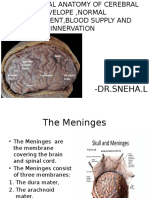
• The brain and the spinal cord are surrounded by three membranes or
meninges
• which are
• Dura
• Arachnoid
• Pia mater.
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
Dura mater
• The dura mater of the brain is conventionally described as two layers:
• the endosteal layer and the meningeal layer .
• These are closely united except along certain lines, where they
separate to form venous sinuses.
• The endosteal layer is nothing more than the periosteum covering
the inner surface of the skull bones. At the foramen magnum, it does
not become continuous with the dura mater of the spinal cord.
Around the margins of all the foramina in the skull, it becomes
continuous with the periosteum on the outside of the skull bones.
• It is most strongly adherent to the bones over the base of the skull.
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
• The meningeal layer is the dura mater proper.
• It is a dense, strong fibrous membrane covering the brain and is
continuous through the foramen magnum with the dura mater of the
spinal cord.
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
• The meningeal layer sends inward four septa, which
divide the cranial cavity into freely communicating
spaces that lodge the subdivisions of the brain .
• The function of these septa is to restrict the
displacement of the brain associated with
acceleration and deceleration, when the head is
moved.
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
• The falx cerebri is a sickle-shaped fold of dura mater that lies in the
midline between the two cerebral hemispheres.
• Its narrow anterior end is attached to the internal frontal crest and
the crista galli. Its broad posterior part blends in the midline with the
upper surface of the tentorium cerebelli. The superior sagittal sinus
runs in its upper fixed margin, the inferior sagittal sinus runs in its
lower concave free margin, and the straight sinus runs along its
attachment to the tentorium cerebelli.
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq 6
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq 7
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq 8
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq 9
The tentorium cerebelli
• is a crescent-shaped fold of dura mater that roofs
over the posterior cranial fossa .
• It covers the upper surface of the cerebellum and
supports the occipital lobes of the cerebral
hemispheres. In the anterior edge there is a gap, the
tentorial notch, for the passage of the midbrain,
which produces an inner free border and an outer
attached or fixed border.
• The fixed border is attached to the posterior clinoid
processes, the superior borders of the petrous bones,
and the margins of the grooves for the transverse
sinuses on the occipital bone.
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq 13
• The free border runs forward at its two ends, crosses the attached
border, and is affixed to the anterior clinoid process on each side..
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
• The falx cerebri and the falx cerebelli are attached to the upper and
lower surfaces of the tentorium, respectively.
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
• 3. Falx cerebelli is a small sickle –shaped fold of dura mater attached
to the
• internal occipital crest projects forward between the two cerebellar
• hemispheres .its posterior fixed margin contains the occipital sinus.
• 4. Diaphragma sellae is a small, circular fold of dura mater that
forms the
• roof for the sella turcica.
• A small opening in its center allows passage of the stalk of the
pituitary gland.
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
Dural venous sinuses
• The venous sinuses of the cranial cavity are situated
between the layers of the dura mater.
• Their main functions to receive blood from the brain
through the cerebral veins and the CSF from the
subarachnoid space through the arachnoid villi.
• The blood in the dural sinuses ultimately drains in to
the internal jugular veins in the neck.
• The dural sinuses have no valves ,Emissary veins
,which are also valveless ,connect the dural sinuses
with the diploic veins of the skull and with the veins
of the scalp.
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
Superior sagittal sinus
• Occupies the upper fixed border of the falx cerebri.it
begins anteriorly at the foramen cecum .
• It runs posteriorly grooving the vault of the skull ,and at
the internal occipital protuberance it deviates to one or
the other side (usually right) and becomes continuous
with the corresponding Transverse sinus ,the superior
sagittal sinus receives in its course the superior cerebral
veins.
• At the internal occipital protuberance it is dilated to form
the confluence of the sinuses. Here the superior sagittal
sinus usually becomes continuous with the right
transverse sinus,
• it is connected to the opposite transverse sinus and
receives the occipital sinus.
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
Saeed 22
The inferior sagittal sinus
• Occupies the free lower margin of the falx cecebri.
• it runs backward and joins the great cerebral vein at the free margin
of the tentorium cerebelli ,to form thes staright sinus.
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq 24
Straight sinus
• Occupies the line of junction of the falx cerebri with tentorium
cerebelli.It
• is formed by the union of the inferior sagittal sinus with the great
cerebral vein .
• It ends by turning to the left (sometimes to right) to form the
transverse sinus.
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
• The occipital sinus is a small sinus occupying the attached margin of
the falx cerebelli. It commences near the foramen magnum, where it
communicates with the vertebral veins and drains into the confluence
of sinuses.
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
The Transverse sinuses
• Are paired structures and they begin at the internal
occipital protuberance
• .the right is usually continuous with the superior
sagittal sinus ,and the left with the straight sinus.
• They receives the superior petrosal sinuses, the
inferior cerebral and cerebellar veins and the diploic
veins .they end by turning downward as the sigmoid
sinus.
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
• Sigmoid sinuses
• Are direct continuation of o the transverse sinuses.
• The sinus then turns forward and then inferiorly through the
posterior part of the jugular foramen to become continuous with the
superior bulb of the internal jugular vein.
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
The cavernous sinuses
• are situated in the middle cranial fossa on each side of the body of
the sphenoid bone .
• Numerous trabeculae cross their interior, giving them a spongy
appearance, hence the name.
• Each sinus extends from the superior orbital fissure in front to the
apex of the petrous part of the temporal bone behind.
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
• The internal carotid artery, surrounded by its sympathetic nerve
plexus, runs forward through the sinus .
• The abducent nerve also passes through the sinus.
• The third and fourth cranial nerves and the ophthalmic and maxillary
divisions of the trigeminal nerve run forward in the lateral wall of the
sinus .
• They lie between the endothelial lining and the dura mater. The
tributaries are the superior and inferior ophthalmic veins, the inferior
cerebral veins, the sphenoparietal sinus, and the central vein of the
retina.
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq 31
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq 32
• The sinus drains posteriorly into the superior and inferior petrosal
sinuses and inferiorly into the pterygoid venous plexus.
• The two sinuses communicate with each other by means of the
anterior and posterior intercavernous sinuses, which run in the
diaphragma sellae anterior and posterior to the stalk of the
hypophysis cerebri .
• Each sinus has an important communication with the facial vein
through the superior ophthalmic vein. (This is a route by which
infection can travel from the facial skin to the cavernous sinus.)
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
• The superior and inferior petrosal sinuses are small sinuses situated
on the superior and inferior borders of the petrous part of the
temporal bone on each side of the skull .
• Each superior sinus drains the cavernous sinus into the transverse
sinus, and each inferior sinus drains the cavernous sinus into the
internal jugular vein.
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
Arachnoid mater
• Is a delicate, impermeable membrane covering the brain and lying
between the pia mater internally and dura mater externally,
• it is separated from dura by Subdural space filled by a film of fluid
and separated from pia mater by Subarachnoid space which is filled
with CSF.
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
• In certain areas the arachnoid projects into the venous sinuses to
form arachnoid villi.
• The arachnoid villi are most numerous along the superior sagittal
sinus, aggregation of arachnoid villi are known as
• arachnoid granulations.
• CSF is absorbed by the arachnoid granulations to the blood stream.
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
• Structures passing to and from the brain to the skull or its foramina
must pass through the subarachnoid space.
• All the cerebral arteries and veins lie in the space, as do the cranial
nerves.
• In case of optic nerve, the arachnoid forms a sheath for the nerve
thus the subarachnoid space extends around the optic nerve as far as
the eye ball.
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
Saeed 41
Pia mater
• Is a vascular membrane covered by flattened
mesothelial cells.
• It closely invests the brain covering the gyri and
decending to deepest sulci.
• It extends over the cranial nerves.
• The cerebral arteries entering the substance of the
brain carry a sheath of pia with them.
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
The Ventricular System and the
Cerebrospinal Fluid
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
Ventricular System
• The ventricles are four fluid-filled cavities located within
the brain
• these are the two lateral ventricles, the third ventricle,
and the fourth ventricle.
• The two lateral ventricles communicate through the
interventricular foramina (of Monro) with the third
ventricle.
• The third ventricle is connected to the fourth ventricle by
the narrow cerebral aqueduct (aqueduct of Sylvius).
• The fourth ventricle, in turn, is continuous with the
narrow central canal of the spinal cord and, through the
three foramina in its roof, with the subarachnoid space.
• The central canal in the spinal cord has a small dilatation
at its inferior end, referred to as the terminal ventricle
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq 46
Lateral Ventricles
• There are two large lateral ventricles, and one is
present in each cerebral hemisphere.
• The ventricle is a roughly C-shaped cavity and may be
divided into a body, which occupies the parietal lobe
and from which anterior, posterior, and inferior horns
extend into the frontal, occipital, and temporal lobes,
respectively.
• The lateral ventricle communicates with the cavity of
the third ventricle through the interventricular
foramen
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
• The body of the lateral ventricle extends from the
interventricular foramen posteriorly as far as the
posterior end of the thalamus.
• The roof is formed by the undersurface of the corpus
callosum.
• The floor is formed by the body of the caudate
nucleus and the lateral margin of the thalamus.
• The medial wall is formed by the septum pellucidum.
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
• The anterior horn of the lateral ventricle extends forward into the
frontal lobe.
• The posterior horn of the lateral ventricle extends posteriorly into the
occipital lobe.
• The inferior horn of the lateral ventricle extends anteriorly into the
temporal lobe
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
Third Ventricle
• The third ventricle is a slitlike cleft between the two thalami.
• It communicates anteriorly with the lateral ventricles through the
interventricular foramina (of Monro) and posteriorly with the fourth
ventricle through the cerebral aqueduct (of Sylvius)
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
• The anterior wall is formed by a thin sheet of gray matter, the lamina
terminalis, across which runs the anterior commissure .
• The posterior wall is formed by the opening into the cerebral
aqueduct.
• The lateral wall is formed by the medial surface of the thalamus
superiorly and the hypothalamus inferiorly.
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
Cerebral Aqueduct
• The cerebral aqueduct (aqueduct of Sylvius), a
narrow channel about(1.8 cm) long, connects the
third ventricle with the fourth ventricle.
• It is lined with ependymal cells.
• The direction of flow of cerebrospinal fluid is from
the third to the fourth ventricle.
• There is no choroid plexus in the cerebral aqueduct.
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
Fourth Ventricle
• The fourth ventricle is a tent-shaped cavity filled with
cerebrospinal fluid.
• It is situated anterior to the cerebellum and posterior
to the pons and the superior half of the medulla
oblongata .
• It is lined with ependyma and is continuous above
with the cerebral aqueduct of the midbrain and below
with the central canal of the medulla oblongata and
the spinal cord .
• The fourth ventricle possesses lateral boundaries, a
roof, and a rhomboid-shaped floor.
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
Floor or Rhomboid Fossa
• The diamond-shaped floor is formed by the posterior
surface of the pons and the cranial half of the medulla
oblongata .
• The floor is divided into symmetrical halves by the
median sulcus.
• On each side of this sulcus, there is an elevation, the
medial eminence, which is the sulcus limitans.
• Lateral to the sulcus limitans, there is an area known
as the vestibular area .
• The vestibular nuclei lie beneath the vestibular area.
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
Subarachnoid Space
• The subarachnoid space is the interval between the arachnoid mater
and pia mater and, therefore, is present where these meninges
envelop the brain and spinal cord .
• The space is filled with cerebrospinal fluid and contains the large
blood vessels of the brain.
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq
Cerebrospinal fliud CSF
• CSF is formed in the choroid plexus by both filtration and
active transport.
• In normal adults, the CSF volume is 90 to 200 mL ,
approximately 20 percent of the CSF is contained in the
ventricles; the rest is contained in the subarachnoid space in
the cranium and spinal cord.
• The normal rate of CSF production is approximately 20 mL
per hour.
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq 63
Thanks
The First & The Only Franchise in the Iraq 64
You might also like
- The OrbitDocument115 pagesThe OrbitPhilip McNelson100% (1)
- 2-Meninges and SinusesDocument62 pages2-Meninges and SinusesMajd HallakNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Spinal CordDocument47 pagesAnatomy of Spinal CordmayseeNo ratings yet
- Summary of Head DR - Ihab - 3Document41 pagesSummary of Head DR - Ihab - 3ايمان عبد الشافىNo ratings yet
- Veins of H & NDocument92 pagesVeins of H & NHossam ThabetNo ratings yet
- The Face and ScalpDocument31 pagesThe Face and ScalpRobin TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Venous Drainage of Head and Neck RegionDocument76 pagesVenous Drainage of Head and Neck Regiondenis kurianNo ratings yet
- Brain CisternsDocument42 pagesBrain CisternsLepaca KliffothNo ratings yet
- Dura Mater & Cranial SinusDocument30 pagesDura Mater & Cranial SinusSadiq Wadood Siddiqui100% (1)
- Anatomy of Meninges Ventricles CerebrospinalfluidDocument120 pagesAnatomy of Meninges Ventricles CerebrospinalfluidSasikala MohanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Vestibular Organ and NeuralDocument56 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Vestibular Organ and Neuralvineet_ent100% (1)
- Opthalmology NotesDocument43 pagesOpthalmology NotesKashif Khan100% (2)
- External Carotic Artery LigationDocument67 pagesExternal Carotic Artery LigationErnesto Fer FdezNo ratings yet
- Master Radiology Notes NeuroDocument97 pagesMaster Radiology Notes NeuroSnezana MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- MCQ in OphthalmologyDocument108 pagesMCQ in OphthalmologySushi HtetNo ratings yet
- Osama’s Ophthalmology NotesDocument127 pagesOsama’s Ophthalmology NotesMd. Abdullah Rumman100% (1)
- HN-other-stxDocument232 pagesHN-other-stxJerlyns OmondiNo ratings yet
- Meninges: Dr. Katharina Kian R. Demerre - BacolodDocument78 pagesMeninges: Dr. Katharina Kian R. Demerre - BacolodCyril Jay G. OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Brain Dura Mater AnatomyDocument25 pagesBrain Dura Mater AnatomyVinus VaghelaNo ratings yet
- Meninges: Rabbia Yousaf (Pharm-D) Rashid Latif College of PharmacyDocument30 pagesMeninges: Rabbia Yousaf (Pharm-D) Rashid Latif College of PharmacyShafaqat Ghani Shafaqat GhaniNo ratings yet
- BrainDocument33 pagesBrainGeoffreyNo ratings yet
- Vertebral Column and Sinuses Handout DR Wael ElsaedDocument8 pagesVertebral Column and Sinuses Handout DR Wael Elsaedفراج - FarragNo ratings yet
- 7 The Meninges, CSFDocument22 pages7 The Meninges, CSFDavid KleinNo ratings yet
- Bau Dent2008 Meninges and Venous Sinuses 2023Document33 pagesBau Dent2008 Meninges and Venous Sinuses 2023rozhinajalili1381turkeyNo ratings yet
- Spinal CordDocument60 pagesSpinal CordPiyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Spinal CordDocument31 pagesSpinal CordMercy DakaNo ratings yet
- The Maxilla BoneDocument7 pagesThe Maxilla BoneAhmed OudahNo ratings yet
- MENINGES - Anatomy of Dura Matter, Pia MatterDocument34 pagesMENINGES - Anatomy of Dura Matter, Pia MatterfidhavfathimaNo ratings yet
- Operative Surgery 6Document21 pagesOperative Surgery 6tresfour2No ratings yet
- Anatomy of CVS: 4. Blood Vessels of The Head & NeckDocument37 pagesAnatomy of CVS: 4. Blood Vessels of The Head & Necksultan khabeebNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Hemispheres 2018 PDFDocument69 pagesCerebral Hemispheres 2018 PDFlailatul husnaNo ratings yet
- Scalp: Dr. ManuniDocument18 pagesScalp: Dr. ManuniVinus VaghelaNo ratings yet
- 1A Head and Neck IntroductionDocument17 pages1A Head and Neck IntroductionPataraza, Louis Joshua E.No ratings yet
- Inner Ear Vestibular SystemDocument44 pagesInner Ear Vestibular Systemdharmendra kirarNo ratings yet
- The Spinal CordDocument59 pagesThe Spinal CordbegeerizikNo ratings yet
- Intro Head and NeckDocument74 pagesIntro Head and NeckAuza Moses Ibrahim100% (2)
- Radiology MeningesDocument36 pagesRadiology MeningesSudhakarNo ratings yet
- Development of Nervous System by Dr Hemant JoshiDocument25 pagesDevelopment of Nervous System by Dr Hemant JoshiHemant JoshiNo ratings yet
- Presentation SHW 32oo, Isnin NiDocument23 pagesPresentation SHW 32oo, Isnin NiAmibella Amirah NabilahNo ratings yet
- 9d Orbit-Blood Vessels & Nerves-Dr-GosaiDocument8 pages9d Orbit-Blood Vessels & Nerves-Dr-GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- The Brain's Blood SupplyDocument41 pagesThe Brain's Blood SupplyRtvc RoldanNo ratings yet
- Scalp and OsteologyDocument116 pagesScalp and Osteologychynne ongNo ratings yet
- BRAIN pptDocument114 pagesBRAIN pptJaravuy JaravuyNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System: by Sunil KumarDocument61 pagesCentral Nervous System: by Sunil KumarSUNIL KUMARNo ratings yet
- Cerebral White MatterDocument32 pagesCerebral White MatterAbdullah UmarNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi Sistem PersyarafanDocument37 pagesAnatomi Dan Fisiologi Sistem PersyarafanAnonymous xfBKTQfNo ratings yet
- Cranial Fossae: Zara Denisse Garcia Ella Carmela Chavez Mae Nen Vedeja Mardred MarceloDocument40 pagesCranial Fossae: Zara Denisse Garcia Ella Carmela Chavez Mae Nen Vedeja Mardred MarceloZara Sebastianne GarciaNo ratings yet
- Skull Anatomy and MeningesDocument25 pagesSkull Anatomy and MeningesGeoffreyNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document53 pagesPresentation 1rgroup331No ratings yet
- Tentorial MeningiomasDocument42 pagesTentorial MeningiomasFaizyab AhmedNo ratings yet
- 11 - Head & Neck (Blood Vessels) (FF) - Part 2Document22 pages11 - Head & Neck (Blood Vessels) (FF) - Part 2checkmateNo ratings yet
- Brainstem Anatomy and FeaturesDocument12 pagesBrainstem Anatomy and FeatureslindaNo ratings yet
- Neuro AnatomyDocument191 pagesNeuro Anatomysirima makuraNo ratings yet
- The Meninges: Head & Neck Unit - Lecture 3 د - مسعلأا ليلج رديحDocument17 pagesThe Meninges: Head & Neck Unit - Lecture 3 د - مسعلأا ليلج رديحAnandyoSeptiawanNo ratings yet
- Inner Ear for UGDocument33 pagesInner Ear for UGdebdeepbhattacharya411No ratings yet
- Special Senses - II: DR Muhammad Ressam NazirDocument26 pagesSpecial Senses - II: DR Muhammad Ressam NazirRessam NazirNo ratings yet
- Anat of Meningeal (Me)Document17 pagesAnat of Meningeal (Me)farah fadzilNo ratings yet
- 10 - CN Iii, Iv, V1 & ViiDocument42 pages10 - CN Iii, Iv, V1 & ViiOlowooje AyomideNo ratings yet
- LG 1 (Half - The Salivary Glands)Document31 pagesLG 1 (Half - The Salivary Glands)allanNo ratings yet
- The Midbrain and Important ConnectionsDocument118 pagesThe Midbrain and Important ConnectionsBaguma MichaelNo ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy of The Kidney 2Document22 pagesGross Anatomy of The Kidney 2Precious JuliusNo ratings yet
- Dura Mater & Cranial SinusDocument30 pagesDura Mater & Cranial SinusSadiq Wadood SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Ul PDFDocument8 pagesUl PDFNourhan ShabanNo ratings yet
- NeckDocument215 pagesNeckpilot abdi baariNo ratings yet
- NEUROSCIENCE MeningesDocument6 pagesNEUROSCIENCE MeningesRoselle AbrazaldoNo ratings yet
- Dural Venous SinusDocument38 pagesDural Venous SinusChipego NyirendaNo ratings yet
- A Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)From EverandA Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)No ratings yet
- Skull, Cranial Cavity and Venous SinusesDocument30 pagesSkull, Cranial Cavity and Venous SinusesZobayer AhmedNo ratings yet
- AngiofibromaDocument7 pagesAngiofibromaPandu DiputraNo ratings yet
- Isolated Third Nerve PalsyDocument4 pagesIsolated Third Nerve PalsySora KerovaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Head and Neck, Nasal Concha - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument6 pagesAnatomy, Head and Neck, Nasal Concha - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelfabubakar rizviNo ratings yet
- Microsurgical Anatomy of the Abducens NerveDocument13 pagesMicrosurgical Anatomy of the Abducens Nerveelena morettiNo ratings yet
- Carotid Cavernous FistulaDocument3 pagesCarotid Cavernous FistulaSadia GullNo ratings yet
- Anatomy MnemonicsDocument11 pagesAnatomy MnemonicsJennifer CollinsNo ratings yet
- Anatomia FacialDocument10 pagesAnatomia FacialIgor NatanyoNo ratings yet
- Nasal Vestibular Furunculosis Presenting As The Rudolph SignDocument2 pagesNasal Vestibular Furunculosis Presenting As The Rudolph Signyeni novi yantiNo ratings yet
- Variant Anatomy in MR Venography of BrainDocument11 pagesVariant Anatomy in MR Venography of BrainIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Fascial SpacesDocument79 pagesFascial SpacesArun MamachanNo ratings yet
- Syndromes and DiseasespdfDocument17 pagesSyndromes and DiseasespdfnicewanNo ratings yet
- Dangerous Area of The FaceDocument6 pagesDangerous Area of The FaceterataktantiNo ratings yet
- Embolisation in ENTDocument9 pagesEmbolisation in ENTsudheer joelNo ratings yet
- A Case of Multiple Cranial Nerves Palsy Post ElectrocutionDocument4 pagesA Case of Multiple Cranial Nerves Palsy Post ElectrocutionEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Nasopharyngeal AngiofibromaDocument51 pagesNasopharyngeal Angiofibromakamal saudNo ratings yet
- Horner Syndrome: A Clinical Review: Timothy J. MartinDocument10 pagesHorner Syndrome: A Clinical Review: Timothy J. Martinpresentator dadakanNo ratings yet
- Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma Treatment OptionsDocument51 pagesNasopharyngeal Angiofibroma Treatment OptionsMiranda Yudhi CyubidubiduuNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument9 pagesAnatomyAnchal LohanaNo ratings yet
- 1st SeminarDocument85 pages1st SeminarVeena GoudNo ratings yet
- Abducent Nerve: DR. Nirmal Jayadev Final Year PG Student (MS Ophthalmology) MKCG Medical College Berhampur OdishaDocument58 pagesAbducent Nerve: DR. Nirmal Jayadev Final Year PG Student (MS Ophthalmology) MKCG Medical College Berhampur OdishaZeptalanNo ratings yet