Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organic Chemistry
Uploaded by
P. Phani prasadCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Organic Chemistry
Uploaded by
P. Phani prasadCopyright:
Available Formats
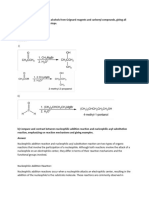
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY This reaction follows first order kinetics.
1. Predict the alkenes that would be formed in the SN1 reaction is two step mechanism
following reactions and identify the major alkene. (i) In 1st step alkyl halide undergo ionization and form
a carbocation.
(ii) In 2nd step the carbocation combine with
nucleophile gives product.
Ex:
Ans:
According to Saytzeff’s rule.
The order of reactivity of SN1 reaction is 30 > 20 >10
alkyl halides
(ii)
4. Explain the mechanism of Nucleophilic
bimolecular substitution SN2 reaction with one
example.
The rate of SN2 reaction depends upon the
concentration of both alkyl halide and nucleophile.
R α [R–X] [Nu–]
R = k [R–X] [Nu–]
This reaction follows second order kinetics.
SN2 mechanism is one step mechanism.
2. How will you carry out the following In these reactions a transition state formed. In
conversions? which both the reactant molecules are partially
1) Ethane to bromo ethene bonded to each other.
2) Toluene to benzyl alcohol
Ans:
1) Ethane to bromo ethene:
2) Toluene to benzyl alcohol:
The order of reactivity of SN2 reaction is 10 > 20
>30 alkyl halides
3. Explain the mechanism of Nucleophilic
unimolecular substitution SN1 reaction with one 5. Define the following (i) Racemic mixture
example. (ii) Retention of configuration (iii) Enantiomers
The rate of SN1 reaction depends only on the (i) Racemic mixture:
concentration of alkyl halide. The equimolar mixture (50:50) of dextro and laevo
R α [R–X] isomers is called Racemic mixture.
R = k [R–X]
Racemic mixture has zero optical rotation.
Ex: ( ) butan-2-ol
(ii) Retention of configuration:
The repetition in stereo chemistry of the reactant, in
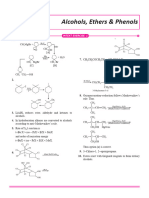
8. Write the equations for the preparation of
the product is known as Retention of configuration.
Phenol using benzene, conc.H2SO4 and NaOH.
If the product formed has configuration opposite to
that of the reactant then the reaction is said to be
inversion of configuration.
9. Explain the acidic nature of phenols and
compare with that of alcohols.
Phenols are acidic in nature because they produce
(iii) Enantiomers: proton and phenoxide ion. The formed phenoxide ion
The stereoisomers which are non super imposible is stabilized by resonance effect.
mirror images to each other are called enantiomers. More the stability of conjugate base more is acidic in
nature.
6. Write the reactions showing the major and The resonating structures of phenoxide ion
minor products when chlorobenzene is reacted
with CH3Cl and CH3COCl in presence of AlCl3.
(a) Friedel Craft’s alkylation:
Chlorobenzene reacts with CH3Cl in presence of
anhydrous AlCl3 to form 1-chloro-4-methyl benzene
(major) 1-chloro-2-methyl benzene (minor).
Comparision of acidic nature of Phenol and
ethanol:
(b) Friedel craft’s acylation: Phenol is more acidic than ethanol. This is
Chlorobenzene reacts with CH3COCl in presence of because phenoxide ion is more stable than
anhydrous AlCl3 to form 2-chloro acetophenone ethoxide ion due to resonance.
(minor) and 4-chloro acetophenone (major) Resonance is not possible in ethoxide ion hence it
is less stable.
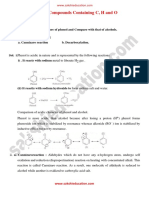
10. Write the products formed by the reduction
and oxidation of phenol.
Reduction: Phenol reacts with Zn dust gives benzene.
7. Give the preparation of phenol from cumene.
Cumene (isopropyl benzene) is oxidized in the
presences of air form cumene hydro peroxide which
on hydrolysis in acid medium gives phenol.
Oxidation: Phenol reacts with chromic acid gives Aldol condensation is carried out between two
benzoquinone. different aldehydes is called cross aldol condensation.
If both the aldehydes contain α – hydrogen, it gives a
mixture of four products. If only one aldehyde contain
α – hydrogen it gives one product.
(iv) Decarboxylation:
11. With a suitable example write equations for the Sodium salts of carboxylic acids heated with soda
following (i) Kolbe’s reaction (ii) Reimer- lime removal of carbon dioxide takes place in the
Tiemann reaction (iii) Wiliamsons ether synthesis. form of Na2CO3 is called decarboxylation reaction.
(i) Kolbe’s reaction: Phenol reacts with NaOH gives
sodium phenoxide. This reacts with CO2 in acid
medium forms salicylic acid.
13. Explain the following named reactions.
(i) Sandameyer’s reaction:
Aniline reacts with nitrous acid gives benzene
diazonium chloride which reacts with Cu2Cl2/HCl
(ii) Reimer – Tiemann reaction: Phenol reacts with gives chlorobenzene.
chloroform in presence of NaOH gives
salicylaldehyde.
(ii) Gatterman reaction:
Aniline reacts with nitrous acid gives benzene
diazonium chloride which reacts with Cu/HCl gives
(iii) Williamsons synthesis: Alkyl halides react with chlorobenzene.
sodium alkoxides to form ethers.
Ex: C2H5Cl + C2H5ONa C2H5–O–C2H5 + NaCl
Diethyl ether
12. Describe the following (i) Acetylation (ii)
Cannizaro reaction (iii) Cross aldol condensation 14. Compare the acidic strength of acetic acid,
(iv) Decorboxylation chloroacetic acid, benzoic acid and phenol.
(i) Acetylation: Anisole reacts with acetyl chloride in Ans:
presence of anhydrous AlCl3 gives oand p- methoxy chloroacetic acid > benzoic acid > acetic acid >
acetophenone. Phenol
15. How do you prepare ethyl cyanide and Ethyl
isocyanide from a common alkylhalide?
Ethyl chloride reacts with KCN gives ethyl cyanide as
major product.
CH3–CH2–Cl KCN CH3–CH2–CN+ CH3–CH2–NC
(ii) Cannizaro reaction: Ethyl cyanide (major) ethyl isocyanide
Aldehydes which have no α – hydrogen reacts with Ethyl chloride reacts with AgCN gives ethyl
concentrated alkali undergo self oxidation and isocyanide as major product.
reduction reaction. CH3–CH2–Cl KCN CH3–CH2–NC+ CH3–CH2–CN
HCHO + HCHO Conc.NaOH CH3OH + HCOONa ethyl isocyanide (major)
(iii) Cross aldol condensation:
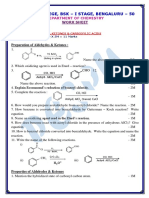
ORGANIC NAMED REACTIONS heating with KOH in presence of ethylene glycol gives
1. Finkelstein reaction: alkanes.
Alkyl chlorides/ bromides reacts with NaI in presence of
acetone gives alkyl iodides.
Ex: CH3Cl + NaI dry acetone CH3I + NaCl
10. Friedel craft’s Alkylation reaction:
2. Swarts reaction: Anisole reacts with methyl chloride in presence of
Alkyl chlorides/ bromides heated with metal fluorides anhydrous AlCl3 gives o – methoxy toluene and p –
such as AgF, Hg2F2, CoF2 or SbF3 gives alkyl fluorides. methoxy toluene.
Ex: CH3Br + AgF CH3F + AgBr
3. Wurtz – Fittig reaction:
A mixture of alkyl halide and aryl halide reacts with
sodium in presence of dry ether gives alkylarene.
11. Friedel craft’s acylation reaction:
Anisole reacts with acetyl chloride in presence of
anhydrous AlCl3 gives o – methoxy acetophenone and p
– methoxy acetophenone.
4. Fittig reaction:
Aryl halides treated with sodium in presence of dry ether
gives biphenyl.
12. Rosenmund reduction:
5. Kolbe’s reaction: Benzoyl chloride on reduction in presence of Pd –BaSO 4
Phenol reacts with NaOH gives sodium phenoxide. This gives Benzaldehyde.
reacts CO2 gives salicylic acid.
6. Reimer – Tiemann reaction: 13. Etard reaction:
Phenol reacts with chloroform in the presence of Toluene reacts with chromyl chloride gives chromium
NaOH/KOH gives Salicyladehyde. complex, which on hydrolysis gives benzaldehyde. This
reaction is called Etard reaction.
7. Williamson’s reaction:
Alkyl halides react with sodium alkoxides to form 14. Stephen reaction:
ethers. Nitriles are reduced with stannous chloride in the
Ex: Ethyl chloride reacts with sodium ethoxide gives presence of HCl gives imine, which on hydrolysis gives
diethyl ether aldehydes
C2H5Cl + C2H5ONa C2H5–O–C2H5 + NaCl RCN+SnCl2+HCl RCH=NH H3O+ RCHO
Diethyl ether
8. Clemmenson reduction: 15. Aldol condensation:
Aldehydes or ketones react with Zn – Hg and Conc. HCl Aldehydes which having α – hydrogen undergoes
gives alkanes. condensation in the presence of dil. NaOH to form β –
hydroxy aldehydes called aldol. Which loses water gives
α, β unsaturated product.
9. Wolf – kishner reduction:
Aldehydes or ketones react with hydrazine followed by
Aniline reacts with nitrous acid at 0 to 5oC gives
benzene diazonium chloride which reacts with Cu / HCl
gives chlorobenzene.
16. Cannizzaro reaction:
22. Decarboxylation reaction:
Aldehydes which have no α – hydrogen reacts with
Sodium salts of carboxylic acids heated with soda lime
concentrated alkali undergo self oxidation and reduction
removal of carbon dioxide takes place in the form of
reaction.
Na2CO3 is called decarboxylation reaction.
HCHO + HCHO Conc.NaOH CH3OH + HCOONa
17. Cross aldol condensation:
Aldol condensation is carried out between two different 23. Diazotization reaction:
aldehydes is called cross aldol condensation. If both the The conversion of primary aromatic amines into
aldehydes contain α -hydrogen, it gives a mixture of four diazonium salts is known as diazotization.
products. If only one aldehyde contain α – hydrogen it
gives one product.
18. Hell – volhard – zelensky reaction (HVZ):
Carboxylic acids having at least one α-hydrogen reacts
with X2 (Cl2/Br2) in presence of red phosphorus to give α
– halo acid. This reaction is called HVZ reaction.
EX: Chlorine reacts with acetic acid in the presence of
red Phosphorus to give trichloro acetic acid.
19. Carbylamine reaction or isocyanide test:
Aniline reacts with chloroform in presence of NaOH
gives phenyl isocyanide. This test used to detect primary
amines.
20. Sandmeyer’s reaction:
Aniline reacts with nitrous acid at 0 to 5oC gives
benzene diazonium chloride which reacts with
Cu2Cl2/HCl gives chlorobenzene.
21. Gatterman reaction:
You might also like
- 11 Alcohols Phenols and EthersDocument39 pages11 Alcohols Phenols and EthersAishwarya Naidu100% (1)
- JF PVQQ FRFFNC Eu HCMGAMDocument67 pagesJF PVQQ FRFFNC Eu HCMGAMelonmuskonmoonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper Pa1 Class 12Document6 pagesChemistry Paper Pa1 Class 12Prisha GuptaNo ratings yet
- ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Class NotesDocument19 pagesORGANIC CHEMISTRY Class NotesWolam guyNo ratings yet
- Enolates and CarbanionsDocument14 pagesEnolates and CarbanionsPatricia DinaNo ratings yet
- Halo AlkanesDocument92 pagesHalo AlkanesRaichal P BijuNo ratings yet
- Art Integrated Learning Project (Ritik Kumar)Document49 pagesArt Integrated Learning Project (Ritik Kumar)abhiabhishek6073No ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11 Alcohols Phenols and EthersDocument32 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11 Alcohols Phenols and EthersRiya NarangNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11 Alcohols Phenols and EthersDocument32 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11 Alcohols Phenols and EthersVIJAYNo ratings yet
- Reactions With BenzeneDocument25 pagesReactions With BenzeneVicky75% (4)
- 12 Chemistry Keypoints Revision Questions Chapter 10 PDFDocument13 pages12 Chemistry Keypoints Revision Questions Chapter 10 PDFSahil Kalra100% (1)
- Chemistry Study Material XII - Part 2 - 0Document91 pagesChemistry Study Material XII - Part 2 - 0krishnakumar01928374No ratings yet
- Note HaloalkanesDocument7 pagesNote HaloalkanesNabin JoshiNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Phenols EthersDocument31 pagesAlcohol Phenols Etherssyedasifbasha1990No ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument14 pagesHaloalkanes and HaloarenesHarshitha GowdaNo ratings yet
- Trinitrotoluene (TNT), A Pale Yellow, Solid Organic Nitrogen Compound Used Chiefly As An Explosive, Prepared by Stepwise Nitration of TolueneDocument76 pagesTrinitrotoluene (TNT), A Pale Yellow, Solid Organic Nitrogen Compound Used Chiefly As An Explosive, Prepared by Stepwise Nitration of TolueneVidhan PatniNo ratings yet
- Xii Ch10 Haloalkane and HaloarenesDocument4 pagesXii Ch10 Haloalkane and HaloarenesYash RajNo ratings yet
- Synthesis and Reactions of Cobalt Complexes PDFDocument3 pagesSynthesis and Reactions of Cobalt Complexes PDFRoberto SousaNo ratings yet
- STK 1233 Organic Chemistry 1: LU 5.2: Reactions of Aromatic CompoundsDocument63 pagesSTK 1233 Organic Chemistry 1: LU 5.2: Reactions of Aromatic CompoundsArllen Joy AlbertNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 12th Class 1Document22 pagesChapter 11 12th Class 1Nisha vankhadeNo ratings yet
- Test On Alcohols 2023Document2 pagesTest On Alcohols 2023pratibha atreyNo ratings yet
- The Reaction Gives Pure Alkyl HalidesDocument8 pagesThe Reaction Gives Pure Alkyl HalidesMohammed IliasNo ratings yet
- AminesDocument12 pagesAminesEmelda BanumathyNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Worksheet with AnswerDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Worksheet with AnswerAyush RajputNo ratings yet
- To Download Other Subject Question Bank Visit WWW - Eshaale.inDocument18 pagesTo Download Other Subject Question Bank Visit WWW - Eshaale.inSwetha RNNo ratings yet
- Unit 9: Arenes, Phenols and Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Recommended Prior KnowledgeDocument4 pagesUnit 9: Arenes, Phenols and Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Recommended Prior KnowledgeHubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- Alcohol, Phenol and EthersDocument28 pagesAlcohol, Phenol and EthersMohd ShareefNo ratings yet
- nabila qna xm 4 5Document4 pagesnabila qna xm 4 5skmahfuzahmed.bd3No ratings yet
- nabila qna xmDocument4 pagesnabila qna xmskmahfuzahmed.bd3No ratings yet
- II PUC Chemistry - SN1 and SN2 MechanismsDocument4 pagesII PUC Chemistry - SN1 and SN2 MechanismsShamanth MNo ratings yet
- Halo NewDocument10 pagesHalo NewMohammed IliasNo ratings yet
- Alcohols Q.A.Document41 pagesAlcohols Q.A.Abhinav BishtNo ratings yet
- Umyu CHM 4207Document14 pagesUmyu CHM 4207bangysmashiNo ratings yet
- Organohalides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and EliminationsDocument37 pagesOrganohalides: Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations민규강No ratings yet
- MS - Aldehyde Ketone Carboxylic AcidDocument11 pagesMS - Aldehyde Ketone Carboxylic AcidApeksha KumariNo ratings yet
- (Chem 31) LE2 Samplex + AnsKey (1-1920)Document10 pages(Chem 31) LE2 Samplex + AnsKey (1-1920)Glyzen GaleonNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes-Imp QNSDocument3 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes-Imp QNSjamesNo ratings yet
- Nucleophilic Substitution Questions - PKBDocument12 pagesNucleophilic Substitution Questions - PKBPawan BabelNo ratings yet
- Phenol Preparation and Chemical ReactionsDocument13 pagesPhenol Preparation and Chemical Reactions36 : Tushar RajguruNo ratings yet
- Alcohols Most Imp Questions With SolutionsDocument6 pagesAlcohols Most Imp Questions With Solutionsvishalkammar99No ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY OF ALIPHATIC HYDROCARBONSDocument8 pagesCHEMISTRY OF ALIPHATIC HYDROCARBONSHibba IsrarNo ratings yet
- 7 - Alcohols, Ethers - Phenols (Engg) Sol - FinalDocument20 pages7 - Alcohols, Ethers - Phenols (Engg) Sol - Finalarfaz13111No ratings yet
- An Overview of Sn1 and Sn2 ReactionsDocument35 pagesAn Overview of Sn1 and Sn2 ReactionsPedro Suyu100% (1)
- Chemistry Alcohols Phenols and Ethers PDFDocument37 pagesChemistry Alcohols Phenols and Ethers PDFMohammed RafiuddinNo ratings yet
- Anic Compounds Containing CHO PDFDocument12 pagesAnic Compounds Containing CHO PDFGunnu NarayanNo ratings yet
- 25717Document27 pages25717nandhakishore412No ratings yet
- Chemistry of Reactive Intermediate FinalDocument38 pagesChemistry of Reactive Intermediate FinalTefera100% (1)
- WK7 - Halogenated HCDocument10 pagesWK7 - Halogenated HCsam cuadraNo ratings yet
- Organic Named ReactionsDocument21 pagesOrganic Named ReactionsP. Phani prasadNo ratings yet
- II PUC Chem Worksheet - Aldehyde S and KetonesDocument3 pagesII PUC Chem Worksheet - Aldehyde S and KetonesMrinal DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl CompoundsDocument29 pagesCarbonyl CompoundsKarthik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl CompoundsDocument29 pagesCarbonyl CompoundsKarthik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Organic Reasoning NewDocument27 pagesOrganic Reasoning NewJeyanthiNo ratings yet
- Unit 11. Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers One Mark Questions: Ans: EthanolDocument10 pagesUnit 11. Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers One Mark Questions: Ans: EthanolDeva RajNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument99 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and EthersSanya VermaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Chemistry of BenzeneDocument22 pages2 - Chemistry of BenzeneGrgtNo ratings yet
- Nucleophilic Substitution ReactionsDocument41 pagesNucleophilic Substitution Reactionseva982205No ratings yet
- Hydroarbons: 1. Give The Different Confirmations of Ethane With Their Newman Projection FormulaDocument2 pagesHydroarbons: 1. Give The Different Confirmations of Ethane With Their Newman Projection FormulaAmogh SinghNo ratings yet
- Annual Reports in Organic Synthesis — 1971From EverandAnnual Reports in Organic Synthesis — 1971John McMurryNo ratings yet
- Us3479310 PDFDocument7 pagesUs3479310 PDFKhoi Nguyen DangNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Unit 1Document12 pagesModule 1 Unit 1Mia Lorena JandocNo ratings yet
- Freon 134a Si Thermodynamic PropertiesDocument52 pagesFreon 134a Si Thermodynamic PropertiesAyu LestariNo ratings yet
- RRLDocument3 pagesRRLArianne Rose TalledoNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates of Sub Bab 15Document8 pagesCarbohydrates of Sub Bab 15dilla daniahNo ratings yet
- Shell Tellus S2M68 Msds - 00107669Document7 pagesShell Tellus S2M68 Msds - 00107669Jasmine TsoNo ratings yet
- Anuj AgrawalDocument15 pagesAnuj AgrawalSAVITRI GURJARNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document160 pagesLecture 4Ahmed ShahabiNo ratings yet
- Choke Sizing CorrelationDocument6 pagesChoke Sizing CorrelationEnyerberht Castañeda BritoNo ratings yet
- Refraction WorksheetDocument2 pagesRefraction WorksheetRicardo Johnson0% (1)
- Physicochemical Properties and Sensory Evaluation of Jelly Candy Made From Different Ratio of K-Carrageenan and KonjacDocument10 pagesPhysicochemical Properties and Sensory Evaluation of Jelly Candy Made From Different Ratio of K-Carrageenan and Konjacarifrahmanh11No ratings yet
- ODU Chemistry Chapter 5.1-5.2 Thermodynamics and Energy ReviewDocument10 pagesODU Chemistry Chapter 5.1-5.2 Thermodynamics and Energy Reviewjarzola11No ratings yet
- Adhesion of Cells To Polystyrene SurfaceDocument7 pagesAdhesion of Cells To Polystyrene Surfacef20212314No ratings yet
- GenBio 1 - 2nd Quarter ReviewerDocument8 pagesGenBio 1 - 2nd Quarter Reviewerjoshua tejadaNo ratings yet
- Bio-Vision - SSLC Chemistry SmileDocument19 pagesBio-Vision - SSLC Chemistry SmilemujeebNo ratings yet
- Kathmandu Water Purification Filters TestDocument1 pageKathmandu Water Purification Filters TestManish ThapaNo ratings yet
- What Is X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRD) : Bragg's LawDocument8 pagesWhat Is X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRD) : Bragg's LawsafiNo ratings yet
- SS - AIATS - 01 (Adv) - P - 1 - A - 2020-06-21 - 2020 - QDocument23 pagesSS - AIATS - 01 (Adv) - P - 1 - A - 2020-06-21 - 2020 - Qyash chawliyaNo ratings yet
- Determinación de Acrilamida en Dieferentes MaterialesDocument88 pagesDeterminación de Acrilamida en Dieferentes MaterialesMarianella ZegarraNo ratings yet
- ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code Week: February 2023Document11 pagesASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code Week: February 2023Mark GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Fluorescence Spectroscopy: CHE5540 Lab Exercise 9Document10 pagesFluorescence Spectroscopy: CHE5540 Lab Exercise 9prakush_prakushNo ratings yet
- Dielectric Constant ValuesDocument42 pagesDielectric Constant ValuesocedwiputriNo ratings yet
- P40 - Spec SheetDocument8 pagesP40 - Spec Sheetpurin phokhunNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Calculations Ii (TKK 1319 - 2 SKS) : Meta Fitri Rizkiana, S.T., M.Sc. NRP. 760017111Document20 pagesChemical Engineering Calculations Ii (TKK 1319 - 2 SKS) : Meta Fitri Rizkiana, S.T., M.Sc. NRP. 760017111Riatus SNo ratings yet
- 09-08-15 SR - Iit-Iz-Co-Spark Jee Adv Rpta-2 (2013 p2) Q'paperDocument33 pages09-08-15 SR - Iit-Iz-Co-Spark Jee Adv Rpta-2 (2013 p2) Q'paperKumar Prasad100% (1)
- HabaCHIAN Slat Conveyor ChainsDocument128 pagesHabaCHIAN Slat Conveyor Chainsjunico76No ratings yet
- ControTrace Saves Customer $100KDocument4 pagesControTrace Saves Customer $100KmarraezNo ratings yet
- M Alkalinity and P AlkalinityDocument3 pagesM Alkalinity and P AlkalinityFA AyNo ratings yet
- A History of Thermo Jarrell Ash Corporation and Spectroscopist Richard F. JarrellDocument7 pagesA History of Thermo Jarrell Ash Corporation and Spectroscopist Richard F. Jarrelldusan.papez9216No ratings yet
- Science Lab ReportDocument8 pagesScience Lab Reportapi-452660914No ratings yet