Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3rd Reviewer
3rd Reviewer
Uploaded by
Mercurio, Katrina Eunice0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesThis document provides a review for a science test covering living and nonliving things, microscopes, and cell structure. It includes:
1. An overview of branches of biology and characteristics of living things.
2. A description of microscopes, their inventor Anton Van Leeuwenhoek, and the main parts and functions of a microscope.
3. Details on the parts of the cell like the cell membrane, nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and differences between plant and animal cells.
Original Description:
Original Title
3rd-Reviewer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides a review for a science test covering living and nonliving things, microscopes, and cell structure. It includes:
1. An overview of branches of biology and characteristics of living things.
2. A description of microscopes, their inventor Anton Van Leeuwenhoek, and the main parts and functions of a microscope.
3. Details on the parts of the cell like the cell membrane, nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and differences between plant and animal cells.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pages3rd Reviewer
3rd Reviewer
Uploaded by
Mercurio, Katrina EuniceThis document provides a review for a science test covering living and nonliving things, microscopes, and cell structure. It includes:
1. An overview of branches of biology and characteristics of living things.
2. A description of microscopes, their inventor Anton Van Leeuwenhoek, and the main parts and functions of a microscope.
3. Details on the parts of the cell like the cell membrane, nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and differences between plant and animal cells.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Calayan Educational Foundation, Inc.
Basic Education Department – Junior High School Program
PACUCOA Accredited Level III
SCIENCE 7
Third Quarterly Assessment Test Reviewer
Coverage: Workbook p.64-77
I-LIVING & NONLIVING THINGS
BIOLOGY- Science of Life
Branches of Biology:
BOTANY- study of Plants ZOOLOGY- study of Animals
ORNITOLOGY- study of Birds CYTOLOGY-study of Cells
ANATOMY-study of internal structure HISTOLOGY-study of Tissues
ENTOMOLOGY-study of Insects HERPETOLOGY-study of Reptiles
MAMMOLOGY-study of mammals MYCOLOGY-study of Fungi
PALEOZOOLOGY-study of fossils of animals ICHTYOLOGY-study of Fishes
Characteristics of Living Things/ Signs of Life:
- Can move or transfer to other places
- Can reproduce
- Can respond to stimuli
- Can grow or increase its size
- Can think or give opinions
- Can act back or respond
- Can talk or reason out
- Breathing
II- MICROSCOPE-
- From Greek words mikros “small” and skopein ‘”look”
- An instrument or laboratory apparatus used to view microscopic specimens.
- Used to magnify objects too small to be seen by the naked eye.
- Microscopy- science of investigating objects under the microscope
Anton Van Leeuwenhoek – invented the microscope
Parts and Functions of Microscope:
1. Eyepiece/ Ocular / Lens- magnifies the image, 5X – 30X magnification
2. Body Tube- connects the eyepiece and the nosepiece.
3. Nosepiece- holds the objectives , can be revolved or rotated in choosing an objective
4. Objective lens- magnifies the image 4X-100X
5. Stage- holds the slide which contains the specimen,can move up and down.
6. Stage clips- holds the slide being observed
7. Coarse Adjustment Knob- moves the stage up and down to bring specimens on focus.
8. Fine Adjustment Knob- bring the specimen is sharp focus.
9. Mirror- the light source of a microscope
10. Arm- use for support or in holding the microscope
11. Diaphragm- controls the amount of light reaching the specimen
12. Base- supports the entire microscope
Calayan Educational Foundation, Inc.
Basic Education Department – Junior High School Program
PACUCOA Accredited Level III
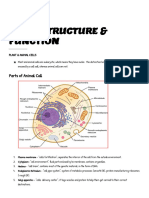
III CELL STRUCTURE:
Parts of the Cell:
1. Cell Membrane- it maintains the integrity of the cell and controls the passage of materials into and
out of the cell.
2. Cytoplasm- cytosol , is the liquid part of the cell
3. Nucleus- “control center/ brain of the cell”
- it controls all the cellular activities
4. Mitochondria- “power house of the cell”
-site of cellular respiration and photosynthesis in plant cell
ATP/ Adenosine Tri-Phosphate- “the energy currency of the cell”
5. Ribosomes- “site of Protein synthesis”
6. Endoplamic Reticulum(ER)- “Passage way of the cell/cell highway”
-transport the materials from ER
Smooth ER (SER)- without ribosomes
Rough ER (RER) – with ribosomes
7. Golgi Apparatus/ Bodies- “Packaging Counter of the Cell “
-modify the products of ER and manufactures polysaccharides
8. Lysosomes- “suicide bag of the cell”
-contains digestive enzymes that destroys foreign objects
9. Vacuoles- “storage sac of the cell”
-stores water or food ,larger and more abundant in plant cells
10. Chloroplast- “coloring pigment of the cell”
-produce Chlorophyll the gree pigment in plants used in food making
Photosybthesis- food making of plants using SOLAR energy
-products are sugar + water + oxygen
11. Cytoskeleton- “framework of the cell”
-gives shape and support
Difference between Plant and Animal Cells:
- Plant Cells have rigid Cell Wall containing Cellulose.
- Plant Cells have large Central Vacuole containing water.
- Plant Cells don’t have Lysosomes or Suicide bags
- Plant Cells have Chloroplast that produce Chlorophyll for Photosynthesis
- Plants Cells are boxed shape while Animal Cells have circular or irregular shapes
You might also like
- The Cellular Level of Organization - AnaphyDocument12 pagesThe Cellular Level of Organization - AnaphyJean Rose SalahayNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Cell PhysiologyDocument37 pagesCell Structure and Cell PhysiologyAliyu Aisha100% (1)
- O Level Biology NotesDocument547 pagesO Level Biology NotesSsonko Edrine100% (1)
- Bsczo 102 PDFDocument209 pagesBsczo 102 PDFajitha ajithNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Unit of Life: Cbse, Class Ix, BiologyDocument41 pagesFundamental Unit of Life: Cbse, Class Ix, BiologySmitha JayaprakashNo ratings yet
- 2 The Cell (PDFDrive)Document51 pages2 The Cell (PDFDrive)audiNo ratings yet
- Els Reviewer 2nd QuarterDocument8 pagesEls Reviewer 2nd QuarterKaezzy Yen RequermeNo ratings yet
- BIO 024 Session 1 7Document67 pagesBIO 024 Session 1 7Tracy DavidNo ratings yet
- QTR 2 Module 2 Plant and Animal CellsDocument16 pagesQTR 2 Module 2 Plant and Animal CellsNick Bantolo100% (7)
- 2nd Week IDEA GEN BIO 1Document5 pages2nd Week IDEA GEN BIO 1Cherrina AguilaNo ratings yet
- School Cell Analogy PpointDocument14 pagesSchool Cell Analogy Ppointapi-265180883No ratings yet
- P 75-92 QTR 2 TG Module 2 Plant and Animal CellsDocument18 pagesP 75-92 QTR 2 TG Module 2 Plant and Animal CellsJane Limsan PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- 2nd Reviewer ScienceDocument9 pages2nd Reviewer ScienceTristeine MorattiNo ratings yet
- Science Gen EdDocument17 pagesScience Gen EdDESSA EMBER ESPARESNo ratings yet
- Science General EducDocument24 pagesScience General EducDESSA EMBER ESPARESNo ratings yet
- Science 8 DLLDocument9 pagesScience 8 DLLKristin MejaritoNo ratings yet
- Cells Basic Function & StructureDocument2 pagesCells Basic Function & StructureEzel MayNo ratings yet
- Bio For Olevel PDFDocument422 pagesBio For Olevel PDFNalweyiso JoyceNo ratings yet
- MICROBIODocument24 pagesMICROBIOSnowNo ratings yet
- ProtistDocument5 pagesProtistGerald Agacid BangeroNo ratings yet
- Lp7-Plant and Animal CellsDocument4 pagesLp7-Plant and Animal CellsTeacher OliNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelle NotesDocument36 pagesCell Organelle NotesChoebe Khaye Shoebe100% (1)
- How To Focus A MicroscopeDocument31 pagesHow To Focus A Microscopekimsioco02No ratings yet
- Biology BookDocument51 pagesBiology BookRam NepaliNo ratings yet
- Cells: The Basis of Life: Mevan Siriwardane Mrs. Rolle's Biology - Barringer High School October 25, 2007Document14 pagesCells: The Basis of Life: Mevan Siriwardane Mrs. Rolle's Biology - Barringer High School October 25, 2007SAmi BalochNo ratings yet
- CellDocument30 pagesCellNovita SariNo ratings yet
- Lesson1 CellDocument3 pagesLesson1 CellClarisse De GuiaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Biology: Integrated Laboratory Science High SchoolDocument33 pagesGrade 7 Biology: Integrated Laboratory Science High SchoolLohaida MidtimbangNo ratings yet
- Genbio I ReviewerDocument12 pagesGenbio I Reviewerjustanony92No ratings yet
- Ii. Cellular Microbiology OutlineDocument8 pagesIi. Cellular Microbiology OutlineBABY NICOLE ARELLANONo ratings yet
- Cell Possible ActivitiesDocument21 pagesCell Possible ActivitiesPrincess JacintoNo ratings yet
- 7 Characteristics of Living Things: M R S G R E NDocument10 pages7 Characteristics of Living Things: M R S G R E Nmcda100% (1)
- Cell Theory ModuleDocument14 pagesCell Theory ModuleEunice Moureen Maravilla100% (2)
- 3.3 Difference Between Plant and Animal Cell Lesson PlanDocument6 pages3.3 Difference Between Plant and Animal Cell Lesson PlanJoana Mae IcoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Biology 1Document6 pagesReviewer in Biology 1CameronNo ratings yet
- GR 7 Module 2 For StudentsDocument16 pagesGR 7 Module 2 For StudentsPatricia Mae Rolls SantillanNo ratings yet
- Module 4 2ndqtDocument83 pagesModule 4 2ndqtJanelle RegachoNo ratings yet
- S.Y. 2021 - 2022 Teacher's Name: Norville Castillo Periña Quarter: 2 Grade: 7 Subject: SCIENCE/ Week 2 Time: T-TH 10:20-12:20 Date: Oct. 25-28Document2 pagesS.Y. 2021 - 2022 Teacher's Name: Norville Castillo Periña Quarter: 2 Grade: 7 Subject: SCIENCE/ Week 2 Time: T-TH 10:20-12:20 Date: Oct. 25-28Norville Castillo PeriñaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 2Document9 pagesLab Report 2Hannah Grace AquinoNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 - GenBio 1-Week 1 (23-24)Document41 pagesQuarter 1 - GenBio 1-Week 1 (23-24)Adrienne Skyle SibalaNo ratings yet
- Botany Notes Part 1Document22 pagesBotany Notes Part 1Rochenick MagoNo ratings yet
- BIOENERGETICSDocument7 pagesBIOENERGETICSReynald ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Biology ReviewerDocument11 pagesBiology ReviewerGia PuatoNo ratings yet
- Biology 1 Lab Report Edible CellDocument3 pagesBiology 1 Lab Report Edible CellLuisa SorianoNo ratings yet
- Biology Full NotesDocument259 pagesBiology Full NotesthaseiphologoNo ratings yet
- The Beginning of CellDocument4 pagesThe Beginning of CellTrishia Lynn MaldiaNo ratings yet
- Life Chap 1 Part1Document16 pagesLife Chap 1 Part1Elhade ElbakushNo ratings yet
- Exercise No. 3 The Plant CellDocument4 pagesExercise No. 3 The Plant CellMarielNo ratings yet
- Zoology Lesson 1 4Document9 pagesZoology Lesson 1 4Teodoro, Alexandra M.No ratings yet
- General Biology SLAS 2Document5 pagesGeneral Biology SLAS 2igotugirlalways143No ratings yet
- CHAPTER-1 - Experimental PsychologyDocument4 pagesCHAPTER-1 - Experimental PsychologysimonNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - Plant Structure and FunctionsDocument50 pagesWeek 4 - Plant Structure and FunctionsPrincess De LeonNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science ReviewerDocument11 pagesEarth and Life Science ReviewerVicente MarkNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument7 pagesBiologyConrado Juisan CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Biology 1 Lab Report Edible CellDocument3 pagesBiology 1 Lab Report Edible CellLuisa SorianoNo ratings yet
- 8 3+Patterns+in+NatureDocument24 pages8 3+Patterns+in+NatureSonny Hothi100% (1)
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDocument6 pagesCell Organelles WorksheetAndi ImanNo ratings yet
- Science Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesScience Lesson PlanAivan MulaNo ratings yet
- 12stem1g5-Lab 2 (Plant and Animal Cell)Document5 pages12stem1g5-Lab 2 (Plant and Animal Cell)Rea FrancineNo ratings yet
- What Is Science?: BiologyDocument9 pagesWhat Is Science?: Biologylordwill zaficoNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer q2Document7 pagesScience Reviewer q2Kathleen Joy PasionNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument39 pagesBiologyRizzuya UrakuwaNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument5 pagesScience Reviewerrinnxuxi12No ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting 1 - Revaluation Model - DiscussionDocument2 pagesIntermediate Accounting 1 - Revaluation Model - DiscussionMercurio, Katrina EuniceNo ratings yet
- Additional Problems in Impairment and Revaluation - DIYDocument6 pagesAdditional Problems in Impairment and Revaluation - DIYMercurio, Katrina EuniceNo ratings yet
- TAX-01 Chapter 1 - Introduction To TaxationDocument10 pagesTAX-01 Chapter 1 - Introduction To TaxationMercurio, Katrina EuniceNo ratings yet
- BANK RECONCILIATION - Addtl ProbsDocument1 pageBANK RECONCILIATION - Addtl ProbsMercurio, Katrina EuniceNo ratings yet
- Statement of Cash FlowsDocument2 pagesStatement of Cash FlowsMercurio, Katrina EuniceNo ratings yet
- SPM Biology F4C2 - Summary Notes 01Document9 pagesSPM Biology F4C2 - Summary Notes 01Daryl TanNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Unit 1 Cells and OrganellesDocument4 pagesGrade 7 Unit 1 Cells and OrganellesBramasta bumiNo ratings yet
- Science: (Q1) Following Figure Shows Three States of Matter and Its Interconversion. Which Process Display in A and B?Document70 pagesScience: (Q1) Following Figure Shows Three States of Matter and Its Interconversion. Which Process Display in A and B?RAJ KUMAR SINGHNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document4 pagesActivity 1sharksiedNo ratings yet
- proeukaryoticADMModule - Grade12 - Quarter1STEM - BIO12-Ia-c-3 DAN SIMON P. AQUINODocument26 pagesproeukaryoticADMModule - Grade12 - Quarter1STEM - BIO12-Ia-c-3 DAN SIMON P. AQUINOLyka Mae BenitoNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Life Science 2023 For RISODocument5 pagesFinal Exam Life Science 2023 For RISOJoderon NimesNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Reviewer 1Document17 pagesBIOLOGY Reviewer 1Jellanne CañezNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles ColoringDocument2 pagesCell Organelles ColoringThomas Neace-FranklinNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET 2.2 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesWORKSHEET 2.2 Cell Structure and FunctionasyuraNo ratings yet
- PRPM110L Module 3 & 4Document10 pagesPRPM110L Module 3 & 4CASSANDRA REIGN CONSTANTINONo ratings yet
- Module 2 Cell AnatomyDocument5 pagesModule 2 Cell Anatomy10. Briol AlvinNo ratings yet
- Exam Prep - Lec 1 - KEYDocument5 pagesExam Prep - Lec 1 - KEYAndrew ShiahNo ratings yet
- COT Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesCOT Lesson PlanJohn Carlo LucinoNo ratings yet
- Rajeem Outlaw Wright - Cell Organelle and Cell Theory QuizDocument2 pagesRajeem Outlaw Wright - Cell Organelle and Cell Theory QuizRajeem Outlaw WrightNo ratings yet
- Learn QR-ICSE Bio-9 (Binder)Document101 pagesLearn QR-ICSE Bio-9 (Binder)Eondongi Pong pongNo ratings yet
- Bab 3 f5 Dan Bab 2 f4Document43 pagesBab 3 f5 Dan Bab 2 f4Ismaliza IshakNo ratings yet
- Activity 14 - Cell Structure-PERALTADocument3 pagesActivity 14 - Cell Structure-PERALTACogie PeraltaNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument81 pagesBiochemistryGlorivy E. Mora GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell OrganellesDocument5 pagesAnimal Cell OrganellesakhileshmoneyNo ratings yet
- Biology: Pearson EdexcelDocument24 pagesBiology: Pearson EdexcelMahmoudAboAlSamenNo ratings yet
- 5) Cell Structure Summary - 9744 - 2022Document2 pages5) Cell Structure Summary - 9744 - 2022Faith GohNo ratings yet
- Errores Congenitos Del Metabolismo PDFDocument245 pagesErrores Congenitos Del Metabolismo PDFMarielaTessyGonzalesParedesNo ratings yet
- QB Biology Chapter 5Document19 pagesQB Biology Chapter 5Holda MohammedaliNo ratings yet