Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 2 - Heart
Uploaded by
Michelle Pandolfo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
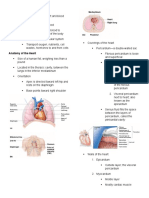
6 views1 page1) The heart is located in the mediastinum and is surrounded by membranes called the pericardium.
2) It has four chambers - two upper atria and two lower ventricles - separated by four valves that allow blood to flow in one direction.
3) The heart's conduction system controls the rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the heart muscles through a pacemaker and conduction pathways.
Original Description:
Resume Heart system
Original Title
Unit 2- Heart
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) The heart is located in the mediastinum and is surrounded by membranes called the pericardium.
2) It has four chambers - two upper atria and two lower ventricles - separated by four valves that allow blood to flow in one direction.
3) The heart's conduction system controls the rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the heart muscles through a pacemaker and conduction pathways.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageUnit 2 - Heart
Uploaded by
Michelle Pandolfo1) The heart is located in the mediastinum and is surrounded by membranes called the pericardium.
2) It has four chambers - two upper atria and two lower ventricles - separated by four valves that allow blood to flow in one direction.
3) The heart's conduction system controls the rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the heart muscles through a pacemaker and conduction pathways.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
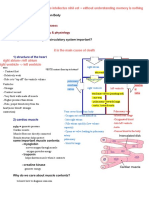
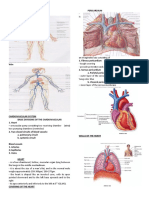
Location Heart
- Pericardial cavity btw the Conduction System of the Heart Beat
Mediastinum (area 4 HEART VALVES Heart
parietal & visceral layers of -Ventricles RELEXED: AV VALVES OPEN
from sternum to the the serous pericardium 1) Bicuspid/ Mitral Heart is a pump which -Rhythmical contraction &
to allow blood to flow from ATRIA into - Intercalated discs anchor cardiac
vertebral column & contains pericardial fluid (left Atrioventricular) circulates blood relaxation of the heart =
VENTRICLES cells together
btw the lungs) -Pericardial fluid reduces valve throughout the body CARDIAC CYCLE
(Papillary muscles are relaxed & chordae (myocardium behaves as a single unit)
Layers of the friction secreted into tendineae are slack) Each pumping action - One complete cycle of
2) Tricuspid (right - Heart muscle has fibers are SELF
Heart Wall pericardial cavity involves periods of contraction & relaxation of both
Atrioventricular) EXCITABLE ( generate action
1) Pericardium / - Ventricles CONTRACT: AV VALVES CLOSE potentials that trigger heart contraction (systole) atria alternating w/ contraction &
1) Fibrous pericardium( valve preventing backflow of blood into ATRIA
Epicardium(exter contractions) alternating w/ periods relaxation of both ventricles is a
nal layer) dense connec. tissue, (Papillary muscles contract and chordae of relaxation (diastole) heart beat (1sec.)
prevent. overstretching tendineae tighten) 2 Important functions:
- Surrounds & 2)Serous pericardium (thin 1) Act as PACEMAKER Pacemaker control of
protects the heart 3) Aortic - Prevent backflow of blood into the the heart beats DUBB” SOUND = SV CLOSED
delicate double membrane) 2) Form CONDUCTION SYSTEM
- Double lining of the semilunar valve VENTRICLES LUBB” SOUND = AV CLOSED
pericardial cavity - 95% of the heart is 4) Pulmonary - SL valves OPEN with VENTRICULAR
4 Conduction System of the
cardiac muscle (hard semilunar valve CONTRACTION 3 Mechanisms that Control Heart
2) Myocardium Heart
working, contracting) - Allows blood to flow into PULMONARY Rate
(cardiac muscle) - SL valves CLOSE TRUNK & AORTA 1) Sinoatrial node (SA node)
Inner myicardial surface - cluster of cells in wall of 1) Autonomic ( involuntary)
w/ VENTRICULAR (sound that you hear w/ stethoscope)
(chamber of heart & RIGHT ATRIUM Nervous System
3) Endocardium RELAXATION
valves) + continuous w/ -begins heart activity BOTH
(prevent blood - AV valve is OPEN SL valve is CLOSE Ex: change in blood pressure,
lining of large blood vessels ATRIA (pacemaker - Action
OBS: DUAL PATTERNS from returning to - SL valve is OPEN AV valve is CLOSE O2& CO2levels
OF CIRCULATION ( ventricles) Potential despolarization)
4 CHAMBERS OF THE Control is effected via a feed back
pulmonary & 4 •excitation spreads to AV
HEART loop (generally a negative)
systemic circuits) Double Circulation = one circulation btw node
- Receives blood from 3 sources: CORONARY HEART & LUNGS - other circulation btw 2) Atrioventricular node (AV node) Peacemaker is under control of
1) RIGHT SINUS (drains the heart), SUPERIOR( super. HEART & BROAD - In atrial septum the CARDIAC CENTERS
ATRIUM diaphragm: head, neck, upper limbs + - transmits signal to AV bundle
thoracic region) or INFERIOR (inf. CORONARY CIRCULATION Set ALL the OUTPUT to all teh
Receiving 3) AV bundle(bundle of His)
diaphragm: lower limbs & abdominopelvic effector to act on the regulate the
DEOXYGENATED - Circulation of blood in the -Connection btw ATRIA & VENTRICLES
region) VENA CAVA rate of heart (contraction &
blood from the ARTERIES & VEINS --> supply - divides into right/left bundle branches that
- Blood leaves through TRICUSPID VALVE relaxtion)
heart itself the heart muscle (myocardium) continue down septum
into RIGHT VENTRICLE
- GOES TO PURKINJE FIBERS Parasympathtic ( decrease rate)
- CORONARY ARTERIES supply
- RIGHT VENTRICLE receives blood from the oxygenated blood to the heart 4) Purkinje fibers Sympathetic (increased rate)
2) RIGHT RIGHT ATRIUM through the TRCUSPID muscle - large diameter fibers that conduct signals
VENTRICLE VALVE quickly from apex upward 2) Chemical regulation
OBS: consisting of - Each flap valve is attached to STRONG CARDIOMYOCYTE (cardiac
80% elastic fibres & connective tissue = CHORDAE TENDINEAE muscle cell) -- requires a reliable Variety of chemical compounds
endothelium - PAPILLARY MUSCLE is in the bootom of supply of oxygen, nutrients & a can affect heart rate: 2 ways
each VENTRICULE way to remove waste
- Interventricular septum: SEPARATE 1) Hormones
OBS: blood flows Coronary Circulation is NOT
ventricles - Chemical messengers produced by
higher press. to continuous; -- it cycles
- RIGHT VENTRICLE --> PULMONARY certain glands in the body function
lower press. areas --
SEMILUNAR VALVE --> PULMONARY TRUNK to stimulate various tissues and
> prevent any CORONARY VEINS drain the
--> LUNGS elicit a response
potential backflow, heart 3) Body temperature Ex: Adrenalin, Noradrenalin, Thyroid
the tricuspid valve - Elevated body temperature
- Receives blood from LUNGS - 4 pulmonary ARTERIA carry blood AWAY hormone (hormone do not decrease
veins from the HEART results in an increased heart heart rate)
3) LEFT ATRIUM - Blood leaves through the BICUSPID VEINS carry IT BACK TOWARDS rate
(MITRAL) VALVE into LEFT VENTRICLE the HEART - Lower body temperature 2) Ionic composition of blood
results in a decreased heart - Higher than normal levels of Na+ &
- BLOOD --> LEFT VENTRICLE --> AORTIC rate K+cause a decrease in heart rate
MYOCARDIAL THICKNESS
4) LEFT SEMILUNAR VALVE --> ASCENDING - There is obviously a limit to - Increased Ca2+ levels result in an
VENTRICLE AORTA --> BODY TISSUE - Right ventricle pumps blood to lungs the effect of both high & low increased heart rate
- Above the AORTIC SEMILUNAR ( Shorter distance, lower pressure, less temperature
VALVE are the openings to the resistance)
OBS: muscular layer CORONARY ARTERIES - Left ventricle pumps blood to body
is MUCH THICKER in (Longer distance, higher pressure,
OBS: ASCENDING AORTA: control the
the LEFT VENTRICLE more resistance)
amout of blood from the left
compared to the - LEFT VENTRICLE WORKS HARDER to
ventricule into the all body; 1st will be
RIGHT maintain same rate of blood flow as
delivery blood is the HEART
right ventricle
You might also like
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument25 pagesCardiovascular Systemangel_maui100% (22)
- Cardiovascular System Heart ReviewerDocument8 pagesCardiovascular System Heart ReviewerImmanuel Cris PalasigueNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Heart beats, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Heart beats, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Cardiovascular SystemDocument17 pagesThe Cardiovascular SystemChris Deinielle Marcoleta Sumaoang100% (1)
- Guyton Hall PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 9 PDFDocument8 pagesGuyton Hall PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 9 PDFOsman NazirNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY Final pt.1Document26 pagesANATOMY Final pt.1Gladys Mae S. BañesNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument8 pagesCardiovascular SystemHannah Grace CorveraNo ratings yet
- Management of Patients With Dysrhythmias and Conduction ProblemsDocument29 pagesManagement of Patients With Dysrhythmias and Conduction ProblemsYlanni Coritana100% (1)
- Lecture 3 Cardiovascular System 1Document54 pagesLecture 3 Cardiovascular System 1hafiz patah100% (1)
- CARDIOLOGYDocument15 pagesCARDIOLOGYPatty RomeroNo ratings yet
- CARDIODocument17 pagesCARDIORayana Ubas100% (1)
- 3 Cardiovascular PhysiologyDocument79 pages3 Cardiovascular PhysiologyJose Luna100% (2)
- Care of Clients With Problems in OxygenationDocument5 pagesCare of Clients With Problems in OxygenationSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Mammalian Heart PDFDocument5 pagesMammalian Heart PDFKhaled TurkNo ratings yet
- CH 21: Cardiovascular System - The HeartDocument21 pagesCH 21: Cardiovascular System - The HeartMadhuri DandamudiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 Heart Marie BDocument29 pagesChapter 19 Heart Marie BomarNo ratings yet
- Cardio 1Document7 pagesCardio 1Moon KillerNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 5Document13 pagesBiology Chapter 5Shahzaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Updated - CHAPTER 2 PART BDocument43 pagesUpdated - CHAPTER 2 PART Bdeela decemberNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CVS & Cardiac Muscles PropertiesDocument11 pagesIntroduction To CVS & Cardiac Muscles PropertiessadiqnawaabNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular ProblemsDocument15 pagesCardiovascular ProblemsMYLENE GRACE ELARCOSANo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Cardiovascular System Lecture Outline 1st PeriodDocument16 pagesKami Export - Cardiovascular System Lecture Outline 1st PeriodJada NovakNo ratings yet
- Modulo 1 - Estructura y FuncionDocument27 pagesModulo 1 - Estructura y FuncionYahn Carlos M MNo ratings yet
- CARDIO VASCULAR SYSTEM TransesDocument4 pagesCARDIO VASCULAR SYSTEM TransesBianca Paulyn CastilloNo ratings yet
- 1.08 - The Cardiovascular System, The Heart & The Blood VesselsDocument9 pages1.08 - The Cardiovascular System, The Heart & The Blood Vessels13PLAN, SENTH RUEN, ANo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart DiseasesDocument6 pagesCongenital Heart DiseasesMeryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesCirculatory SystemGiane MadrigalNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument4 pagesCardiovascular SystemPurple Ivy GuarraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: HEARTDocument2 pagesChapter 12: HEARTPrecious Faith RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument26 pagesCardiovascular SystemJenny Torreda100% (1)
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument57 pagesCardiovascular SystemSarah Shane Cortes CortesNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument10 pagesCirculatory SystemSheena PasionNo ratings yet
- CCN CardioDocument5 pagesCCN CardioSofia P. PanlilioNo ratings yet
- The Heart & Mediastinum: A Fixed Learning Module 2009 Compiled by Assoc Prof DR Hamiadji TanuseputroDocument40 pagesThe Heart & Mediastinum: A Fixed Learning Module 2009 Compiled by Assoc Prof DR Hamiadji TanuseputroQiqin DechrifentoNo ratings yet
- MD-7 HearttDocument28 pagesMD-7 HearttvincenzoNo ratings yet
- A18 BODY FLUIDS in Human BodyDocument1 pageA18 BODY FLUIDS in Human Bodyservoculus machatteNo ratings yet
- CIRCULATORY SYSTEM (Heart)Document4 pagesCIRCULATORY SYSTEM (Heart)Andrei NicoleNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument9 pagesCardiovascular SystemCrazy StrangerNo ratings yet
- Topic - 7 - Lec - Heart and Blood VesselsDocument10 pagesTopic - 7 - Lec - Heart and Blood Vesselsannamabalot3No ratings yet
- w2 Part 1Document30 pagesw2 Part 1farahafiqahNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular / Circulatory System: Upper Chambers or Receiving ChambersDocument2 pagesCardiovascular / Circulatory System: Upper Chambers or Receiving ChambersRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System - Deliver Oxygen and Nutrients - Carries Waste Products - Circulates Electrolytes (Na, K, Ca) andDocument4 pagesCirculatory System - Deliver Oxygen and Nutrients - Carries Waste Products - Circulates Electrolytes (Na, K, Ca) andyoonie catNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing: Anatomy HeartDocument8 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing: Anatomy HeartRoyce Vincent TizonNo ratings yet
- Circulation Lec 2 Part-2Document21 pagesCirculation Lec 2 Part-2Rudrapalash ChakrabartiNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System - Electrical SystemDocument5 pagesCardiovascular System - Electrical SystemRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System WordDocument18 pagesCardiovascular System WordLapitan Jared Anne S.No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System - The HeartDocument37 pagesCardiovascular System - The HeartCecil AlbaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular - SummaryDocument18 pagesCardiovascular - Summarys.tinaja.marieantonetteNo ratings yet
- Hap - Circulatory System HeartDocument13 pagesHap - Circulatory System HeartKyle LumingkitNo ratings yet
- 8.cardiovascular SystemDocument13 pages8.cardiovascular Systempodki gurungNo ratings yet
- Anaph111 - FinalsDocument7 pagesAnaph111 - FinalsUwen NalpNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Cardiac SystemDocument2 pagesChapter 8 Cardiac SystemGilianne Balatbat ManuelNo ratings yet
- Blood Vessels and Blood PressureDocument21 pagesBlood Vessels and Blood PressureIAhmad QasimNo ratings yet
- 013 Cardiovascular Physiology Blood Vessel CharacteristicsDocument3 pages013 Cardiovascular Physiology Blood Vessel CharacteristicsTtNo ratings yet
- A C.A.R. On P.B., 69 Y.O., Female, Diagnosed With Right Thalamic Infarction, and Hypertensive Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument8 pagesA C.A.R. On P.B., 69 Y.O., Female, Diagnosed With Right Thalamic Infarction, and Hypertensive Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseasefebie pachecoNo ratings yet
- #3 Cardiovascular SystemDocument18 pages#3 Cardiovascular SystemLapitan Jared Anne S.No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Med Physio (GP)Document14 pagesChapter 9 - Med Physio (GP)Ritch Jerielyn HaliliNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1: Cardiac Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesCHAPTER 1: Cardiac Anatomy and PhysiologyAlyssa BatasNo ratings yet
- Heart and Blood Vessel: Impulse Conducting System of The HeartDocument4 pagesHeart and Blood Vessel: Impulse Conducting System of The HeartCaperlac MarjorieNo ratings yet
- Heart and Blood Vessel: Impulse Conducting System of The HeartDocument4 pagesHeart and Blood Vessel: Impulse Conducting System of The HeartCaperlac MarjorieNo ratings yet