0% found this document useful (0 votes)
93 views5 pagesMRI Machine Components and Enhancements
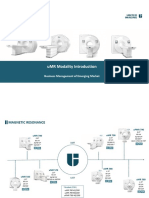
The document discusses the functions of various components of an MRI machine including the magnet, gradient coils, radio frequency coils, patient table, bore, operator console, computer, patient coil, power supply and shim system. It also summarizes five existing MRI products and specifies metrics for designing a new MRI system including bore size, weight, dimensions, lifespan and cost.
Uploaded by
Kwesi TreyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
93 views5 pagesMRI Machine Components and Enhancements
The document discusses the functions of various components of an MRI machine including the magnet, gradient coils, radio frequency coils, patient table, bore, operator console, computer, patient coil, power supply and shim system. It also summarizes five existing MRI products and specifies metrics for designing a new MRI system including bore size, weight, dimensions, lifespan and cost.
Uploaded by
Kwesi TreyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd