Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Step 1 Express 2019-Gastrointestinal
Uploaded by
araine humesOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Step 1 Express 2019-Gastrointestinal
Uploaded by
araine humesCopyright:
Available Formats
First Aid Express 2019 workbook: GASTROINTESTINAL page 1
Gastrointestinal
Questions
EMBRYOLOGY
1. What are the critical weeks of midgut development? (p 352)_______________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
2. Describe the major differences between gastroschisis and omphalocele. (p 352) ______________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
3. A newborn is noted to choke and vomit immediately after first feeding. The mother had
polyhydramnios during pregnancy, and abdominal x-ray shows large amounts of air throughout the
bowel. What is the most likely diagnosis? (p 353) _______________________________________
4. Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis leads to what problem? (p 353) _____________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
5. What is the treatment for hypertrophic pyloric stenosis? (p 353) ___________________________
6. The head of the pancreas is derived from the _______________ (ventral/dorsal) pancreatic bud, the
body is derived from the _______________ (ventral/dorsal) pancreatic bud, and the tail is derived
from the _______________ (ventral/dorsal) pancreatic bud. (p 354)
Copyright © 2019 by ScholarRx All rights reserved v1.0
page 2 First Aid Express 2019 workbook: GASTROINTESTINAL
ANATOMY
7. Which GI ligament can be incised to access the lesser sac and which cannot? Why? (p 355) ____
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
8. Name the four histologic layers of the GI tract, from inside to out. (p 356) ____________________
______________________________________________________________________________
9. What histologic feature distinguishes the duodenum from any other part of the GI tract? What is the
purpose of this feature? (p 356, 366) _________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
10. What are the three branches of the celiac trunk? (p 358) _________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
11. Portal hypertension can lead to varices of which three structures? (p 359) ___________________
______________________________________________________________________________
12. Which type of hemorrhoid is painful? Why? (p 360) _____________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
13. Which zone of the liver is most sensitive to ischemic injury? (p 362) ________________________
14. What is the order of major structures that pass through the femoral region from lateral to medial.
(p 362) ________________________________________________________________________
15. The gastroesophageal junction is displaced in ______________________ hernias, whereas it is
undisturbed in ______________________ hernias. (p 364)
Copyright © 2019 by ScholarRx All rights reserved v1.0
First Aid Express 2019 workbook: GASTROINTESTINAL page 3
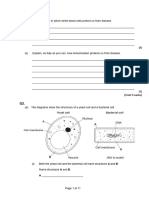
16. In the image below, identify the inguinal (Hesselbach) triangle and the three structures that define
this triangle. For each of the three regions (in blue), what type of hernia can occur at that location?
(p 364)
17. How does the course of a direct inguinal hernia differ from that of an indirect inguinal hernia?
(p 364) ________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
PHYSIOLOGY
18. Which cells are responsible for secreting cholecystokinin (CCK)? What are the effects of CCK
secretion? (p 365) _______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
19. What cells are responsible for producing gastric acid? What hormones act on them to cause
secretion? (p 366) _______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
20. Where in the GI tract is iron absorbed? Vitamin B12? Folate? Which requires cofactors to facilitate
absorption? (p 368) ______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
Copyright © 2019 by ScholarRx All rights reserved v1.0
page 4 First Aid Express 2019 workbook: GASTROINTESTINAL
21. Peyer patches contain B cells, which primarily secrete which class of immunoglobulin? (p 368)
______________________________________________________________________________
22. What is the composition of bile? (p 368) ______________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
23. Direct bilirubin is _______________ (conjugated/unconjugated) with glucuronic acid and is
_______________ (soluble/insoluble) in water. Indirect bilirubin is _______________ (conjugated/
unconjugated) and is _______________ (soluble/insoluble) in water. (p 369)
24. How is urobilinogen removed from the body? (p 369) ____________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
PATHOLOGY
25. What are two causes of sialolithiasis? (p 370) __________________________________________
26. How do the symptoms of achalasia differ from those of esophageal obstruction? (p 370) ________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
27. What is the characteristic imaging finding in a patient with achalasia? (p 370) _________________
28. What are the symptoms of Plummer-Vinson syndrome? (p 371) ___________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
29. What is a more common type of esophageal cancer in the United States? Worldwide? Why?
(p 372) ________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
30. What is a risk factor for acute gastritis? For chronic gastritis? (p 373) _______________________
______________________________________________________________________________
Copyright © 2019 by ScholarRx All rights reserved v1.0
First Aid Express 2019 workbook: GASTROINTESTINAL page 5
31. What are the five major risk factors for stomach cancer? (p 373) ___________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
32. What are four common stomach cancer metastases? (p 373) _____________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
33. The pain of gastric ulcers is _______________ (increased/decreased) with meals, whereas the pain
of duodenal ulcers is ________________ (increased/decreased) with meals. (p 374)
34. Name the five symptoms common to all malabsorption syndromes. (p 375) __________________
______________________________________________________________________________
35. What are three causes of pancreatic insufficiency? What is a major consequence? (p 375) ______
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
36. Celiac disease is characterized by antibodies to _____________, ___________________, and
_____________________, and is associated with a skin condition called ____________________.
(p 375)
37. Compare and contrast the characteristics of Crohn disease and ulcerative colitis. (p 376)
Characteristic Crohn Disease Ulcerative Colitis
Associated with colorectal
cancer?
Gross morphology
Depth of inflammation
Distinguishing complications
Granulomas?
Location
Rectal involvement
Copyright © 2019 by ScholarRx All rights reserved v1.0
page 6 First Aid Express 2019 workbook: GASTROINTESTINAL
38. How is the McBurney point used to diagnose appendicitis? (p 377) _________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
39. An older man presents with subacute onset of left lower quadrant pain. He has a fever. He reports a
typical American diet without much fiber. What is the most likely diagnosis? (p 377) ____________
______________________________________________________________________________
40. What is the difference between a false diverticulum and a true diverticulum? (p 377) ___________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
41. ____________________ (Intussusception/Volvulus) occurs when a portion of the bowel twists
around its mesentery; ___________________ (intussusception/volvulus) occurs when a proximal
bowel segment telescopes into a distal segment. (p 379-380)
42. What surgical complication is this a common cause of small bowel obstruction? (p 380) _________
______________________________________________________________________________
43. A 55-year-old woman presents with colicky pain. Results of a fecal occult blood test are positive.
Colonoscopy reveals thousands of polyps in the colon and rectum. What is the most likely diagnosis?
What if the patient also has osteosarcoma? What if, instead, she has a CNS glioma?
(p 381) ________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
44. What is the first mutational event typically associated with colorectal cancer? (p 383) ___________
______________________________________________________________________________
45. What are the signs and symptoms of cirrhosis and portal hypertension? (p 383) _______________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
46. In alcoholic hepatitis, the AST level is _______________ (greater than/less than) the ALT level; in
viral hepatitis, the AST level is _________________ (greater than/less than) the ALT level. (p 384)
Copyright © 2019 by ScholarRx All rights reserved v1.0
First Aid Express 2019 workbook: GASTROINTESTINAL page 7
47. Match the type of liver disease with its notable characteristic(s) (pp 385-386)
_____ A. α1-Antitrypsin deficiency 1. Causes panacinar emphysema
_____ B. Alcoholic cirrhosis 2. Thrombosis or compression of hepatic veins
_____ C. Alcoholic hepatitis 3. Fatty changes in macrovesicles; reversible
_____ D. Budd-Chiari syndrome 4. Mallory bodies
_____ E. Hepatic steatosis 5. Portal hypertension
_____ F. Hepatocellular carcinoma 6. Primary malignant liver tumor in adults
48. A newborn presents with persistent jaundice after two weeks of life, darkening urine, acholic
stools, and hepatomegaly. The labs indicate high direct bilirubin and GGT. What is the likely
diagnosis? (p 387) _________________________________________________________
49. Compare and contrast the characteristics of the hereditary hyperbilirubinemias. (p 388)
Crigler-Najjar Dubin-Johnson
Characteristic Gilbert Syndrome
Syndrome Syndrome
Impairment
Course of disease
Symptoms
50. What molecule accumulates to cause Wilson disease? What molecule is not made (tests show low
levels) because of this accumulation? What is the treatment? (p 389) _______________________
______________________________________________________________________________
51. What causes the classic triad of: cirrhosis, diabetes mellitus, and “bronze diabetes”? (p 389)
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
52. List three extrahepatic causes of biliary obstruction. (p 389) ______________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
53. List two intrahepatic causes of biliary obstruction. (p 389) ________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
Copyright © 2019 by ScholarRx All rights reserved v1.0
page 8 First Aid Express 2019 workbook: GASTROINTESTINAL
54. Match the term with its definition. (p 390)
_____ A. Ascending cholangitis 1. Gallstones
_____ B. Cholecystitis 2. Infection of biliary tree
_____ C. Cholelithiasis 3. Inflammation of the gallbladder
55. What enzymes are elevated in acute pancreatitis? (p 391) _______________________________
56. Name one common cause of chronic pancreatitis (p 391) ________________________________
PHARMACOLOGY
57. List the most common histamine-2 blockers for the GI tract. Which histamine receptor do they affect?
(p 392) ________________________________________________________________________
58. What are the proton pump inhibitors? Why are they such effective drugs? (p 392) _____________
______________________________________________________________________________
59. How is misoprostol most commonly used as a GI agent? (p 393) __________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
60. What is the most dangerous adverse effect of all antacids? (p 393) _________________________
61. What powerful medicine is used to control vomiting and nausea after surgery? What receptor does
it target? (p 394) _________________________________________________________________
62. What drug can be used to treat gastroparesis? What is a worrisome adverse effect? (p 394) _____
______________________________________________________________________________
63. What is the most common side effect of orlistat? What enzymes does it inhibit? (p 394) _________
______________________________________________________________________________
Copyright © 2019 by ScholarRx All rights reserved v1.0
First Aid Express 2019 workbook: GASTROINTESTINAL page 9
Answers
EMBRYOLOGY
1. Week 6: midgut herniates through umbilical ring
Week 10: returns to abdominal cavity, rotates around SMA 270 degrees.
2. Gastroschisis: Caused by failure of lateral fold closure, abdominal contents herniate lateral to
umbilicus; abdominal contents NOT covered in peritoneum or amnion; is not associated with
chromosome abnormalities. Omphalocele: Caused by failure of lateral walls to migrate at umbilical
ring, persistent midline herniation of abdominal contents into umbilical cord; abdominal contents ARE
surrounded by peritoneum; associated with congenital anomalies (eg, trisomies 13 and 18, Beckwith-
Wiedemann syndrome) and other structural abnormalities.
3. Esophageal atresia with tracheoesophageal fistula.
4. Gastric outlet obstruction. (A classic sign is nonbilious projectile vomiting.)
5. Surgical incision to relax the pyloric muscle (pyloromyotomy).
6. Ventral AND dorsal (ventral = uncinate process); dorsal; dorsal.
ANATOMY
7. The gastrohepatic ligament may be cut during surgery to access the lesser sac because there is a
thin minimally vascular portion that does not require violating the gastric arteries. The
hepatoduodenal ligament may NOT be incised, as the portal triad runs longitudinally through this
ligament.
8. Mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, and serosa (when intraperitoneal), adventitia (when
retroperitoneal). Remember MSMS.
9. Brunner’s glands; these glands secrete bicarbonate solution to neutralize acidic chyme that leaves
the stomach before it can reach the rest of the intestines.
10. Left gastric artery, splenic artery, and common hepatic artery.
11. Esophageal varices, Caput medusae (umbilicus), and anorectal varices.
Copyright © 2019 by ScholarRx All rights reserved v1.0
page 10 First Aid Express 2019 workbook: GASTROINTESTINAL
12. External hemorrhoids are painful because they receive somatic innervation.
13. Zone III (centrilobular zone).
14. Femoral nerve, femoral artery, femoral vein, lymphatics (femoral canal). Remember: You go from
lateral to medial to find your NAVeL.
15. sliding hiatal hernias; paraesophageal hiatal hernias.
16.
17. A direct inguinal hernia protrudes through the inguinal (Hesselbach) triangle (medial to inferior
epigastric vessels), whereas an indirect inguinal hernia goes through the internal inguinal ring,
external inguinal ring, and into the scrotum (lateral to inferior epigastric vessels).
PHYSIOLOGY
18. CCK is released by the I cells in the duodenum and jejunum. It acts on the neural muscarinic
pathways to cause pancreatic secretion and relaxation of the sphincter of Oddi. It also results in
increased gallbladder contraction and decreased gastric emptying.
19. Parietal cells. Histamine, acetylcholine and gastrin contribute to acid secretion.
20. Iron is absorbed in the duodenum, vitamin B12 is absorbed in the ileum; and folate is absorbed in the
small bowel. Vitamin B12 absorption requires a cofactor (intrinsic factor), whereas iron and folate
absorption do not.
21. Peyer patches contain B cells that differentiate into IgA-secreting plasma cells, which combat
intraluminal antigens.
Copyright © 2019 by ScholarRx All rights reserved v1.0
First Aid Express 2019 workbook: GASTROINTESTINAL page 11
22. Bile salts, phospholipids, cholesterol, bilirubin, water, and ions.
23. Conjugated; soluble; unconjugated; insoluble.
24. About 80% is excreted as stercobilin in the feces; of the other 20%, about 10% is excreted in the
urine as urobilin and about 90% returns to the liver via enterohepatic circulation.
PATHOLOGY
25. Dehydration or trauma.
26. Esophageal obstruction causes dysphagia with solids, whereas achalasia causes dysphagia with
both solids and liquids.
27. A “bird’s beak,” or dilated esophagus with an area of distal stenosis.
28. Dysphagia, iron deficiency anemia, and esophageal webs; may be associated with glossitis.
29. More common in America: adenocarcinoma; worldwide: squamous cell carcinoma. GERD is
common in the U.S. and can result in Barrett esophagus, which in turn can lead to adenocarcinoma.
30. Daily NSAID use; Helicobacter (H) pylori infection.
31. H pylori infection, diet high in smoked foods (nitrosamines), tobacco smoking, achlorhydria, and
chronic gastritis.
32. Virchow node (involvement of left supraclavicular node), Krukenberg tumor (bilateral metastases to
ovaries), Sister Mary Joseph nodule (subcutaneous periumbilical metastasis), and Blumer shelf
(metastasis to pouch of Douglas).
33. Increased; decreased.
34. Diarrhea, steatorrhea, weight loss, weakness, and vitamin and mineral deficiencies.
35. Cystic fibrosis, obstructing cancer, and chronic pancreatitis. A major consequence is deficiency in
the fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K) as well as B12 due to malabsorption of these vitamins.
36. anti-endomysial, anti-deamidated gliadin peptide antibodies; IgA anti-tissue transglutaminase;
dermatitis herpetiformis.
Copyright © 2019 by ScholarRx All rights reserved v1.0
page 12 First Aid Express 2019 workbook: GASTROINTESTINAL
37.
Characteristic Crohn Disease Ulcerative Colitis
Associated with colorectal
Yes Yes
cancer?
cobblestone mucosa,
Friable mucosa with superficial
creeping fat, bowel wall
Gross morphology and/or deep ulcerations. Loss
thickening, linear ulcers,
of haustra
fissures
Depth of inflammation Transmural Mucosal and submucosal only
Fistulas,
phlegmon/abscess, Fulminant colitis, toxic
Distinguishing complications
strictures, perianal megacolon, perforation
disease
Granulomas? Yes No
Any part of GI tract,
Location typically terminal ileum, Colon
then colon
Rectal involvement Usually rectal sparing Always involves rectum
38. McBurney point is one-third the distance from the right anterior superior iliac spine to the umbilicus;
pain localized to McBurney point (RLQ) is pathognomonic for appendicitis.
39. This is a typical presentation of diverticulosis, which can present with painless hematochezia.
40. In a false diverticulum, only the mucosa and submucosa outpouch; in a true diverticulum, all three
gut wall layers outpouch.
41. Volvulus; intussusception.
42. Adhesions; this is the most common cause of small bowel obstruction.
43. Familial adenomatous polyposis; Gardner syndrome; Turcot syndrome.
44. Loss of APC gene, which is associated with decreased intracellular adhesion and greater
proliferation.
45. Portal hypertension can cause hematemesis (esophageal varices), melena (gastric varices), caput
medusa, ascites, and hemorrhoids (anorectal varices). Cirrhosis can cause coma, scleral icterus,
fetor hepaticus, spider nevi, gynecomastia, jaundice, testicular atrophy, asterixis, bleeding tendency,
anemia, and ankle edema.
46. Greater than; less than.
Copyright © 2019 by ScholarRx All rights reserved v1.0
First Aid Express 2019 workbook: GASTROINTESTINAL page 13
47. A-1, B-5, C-4, D-2, E-3, F-6.
48. Biliary atresia
49.
Crigler-Najjar Dubin-Johnson
Characteristic Gilbert Syndrome
Syndrome, type I Syndrome
↑ unconjugated Conjugated
Impairment Bilirubin uptake
Bilirubin hyperbilirubinemia
Symptomatic; cure is
Course of disease Benign Benign
liver transplant
Jaundice Asymptomatic or
Symptoms Jaundice
Kernicterus mild jaundice
50. Copper; serum ceruloplasmin; chelation with penicillamine or trientine, oral zinc. Liver transplant in
acute liver failure related to Wilson disease.
51. Hemochromatosis. Iron deposits in the liver can cause cirrhosis, iron in the pancreas can lead to
DM, and deposition of hemosiderin in the skin will lead to the hyperpigmentation.
52. Gallstones, biliary strictures, and pancreatic carcinoma.
53. Primary biliary cholangitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis.
54. A-2, B-3, C-1.
55. Serum amylase or lipase.
56. Alcohol abuse.
PHARMACOLOGY
57. Cimetidine, ranitidine, famotidine, nizatidine. These are H2 receptor blockers.
58. Omeprazole, lansoprazole, esomeprazole, pantoprazole, and dexlansoprazole. PPIs are very
effective because they irreversibly inhibit H+/K+ ATPase, instead of blocking just one of several
stimulatory receptors.
59. Preventing NSAID-induced peptic ulcers.
Copyright © 2019 by ScholarRx All rights reserved v1.0
page 14 First Aid Express 2019 workbook: GASTROINTESTINAL
60. Hypokalemia.
61. Ondansetron; 5-HT3 antagonist.
62. Metoclopramide; parkinsonian effects (because it is a D2 receptor antagonist).
63. Orlistat inhibits gastric and pancreatic lipase, which results in decreased absorption of dietary fats.
Common side effects are: abdominal pain, flatulence, steatorrhea, and decreased absorption of fat-
soluble vitamins.
Copyright © 2019 by ScholarRx All rights reserved v1.0
You might also like
- Virtual Frog Dissection Pre-LabDocument2 pagesVirtual Frog Dissection Pre-LabLance ZambranoNo ratings yet
- 68 Genetic Engineering WebquestDocument2 pages68 Genetic Engineering Webquestapi-262586446No ratings yet
- The American Dream As The Theme in Buried Child SamDocument4 pagesThe American Dream As The Theme in Buried Child Sambeckmanb100% (3)
- ReproductiveDocument16 pagesReproductiveCarla CentenoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine: How To Use The Workbook With The VideosDocument11 pagesEndocrine: How To Use The Workbook With The VideosJustin CharlesNo ratings yet
- Step 1 Express 2018-RenalDocument14 pagesStep 1 Express 2018-RenalPratik JadhavNo ratings yet
- Step 1 Express 2018-ReproductiveDocument13 pagesStep 1 Express 2018-ReproductivePratik JadhavNo ratings yet
- InfectionandResponseHT (Copy)Document13 pagesInfectionandResponseHT (Copy)jane byersNo ratings yet
- Step 1 Express 2018-BiochemistryDocument26 pagesStep 1 Express 2018-BiochemistryPratik JadhavNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: QuestionsDocument26 pagesBiochemistry: QuestionsWendy MaeNo ratings yet
- Renal: QuestionsDocument15 pagesRenal: QuestionsMedStudent MedStudentNo ratings yet
- P.6 SCIENCE HOLIDAY PACKAGE TERMDocument10 pagesP.6 SCIENCE HOLIDAY PACKAGE TERMshakiyonda256No ratings yet
- Biochemistry AtfDocument26 pagesBiochemistry AtfDanielchowdary GarapatiNo ratings yet
- 001 SciDocument15 pages001 ScikatyNo ratings yet
- P6 End of Term I Science 2023Document6 pagesP6 End of Term I Science 2023Kinsambwe Noah100% (1)
- Biology Sixth Form TestDocument3 pagesBiology Sixth Form TestGeorge AshcroftNo ratings yet
- SS12510 07Document7 pagesSS12510 07Renuka SilvaNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument8 pagesEndocrineMedSchoolStuffNo ratings yet
- Mention The Process, Organ or Nutrient According To The Function in Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesMention The Process, Organ or Nutrient According To The Function in Digestive SystemRida Fatima Azhar - 74894/TCHR/BARNo ratings yet
- Set 3 Cell Biology Grades 7 9Document17 pagesSet 3 Cell Biology Grades 7 9Abir OmarNo ratings yet
- DA (SA) Past Papers - 2019 1st SemesterDocument77 pagesDA (SA) Past Papers - 2019 1st SemesterYudhika NaidooNo ratings yet
- Hematology I Lecture Assignment Chapter 20: Anemias Caused by Defects of Dna MetabolismDocument6 pagesHematology I Lecture Assignment Chapter 20: Anemias Caused by Defects of Dna MetabolismAujade Lozada PaNielNo ratings yet
- Amity International School, Noida Biology, Class Ix Chapter-5 The Fundamental Unit of Life Resource Sheet 1 (MLP 1)Document4 pagesAmity International School, Noida Biology, Class Ix Chapter-5 The Fundamental Unit of Life Resource Sheet 1 (MLP 1)Shubham SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Yr 8 HPE - Closing the Gap in Indigenous HealthDocument13 pagesYr 8 HPE - Closing the Gap in Indigenous HealthRyan SharmaNo ratings yet
- 5.1.1 and 5.1.2Document10 pages5.1.1 and 5.1.2Aamina HussainNo ratings yet
- B5 Bitesize RevisionDocument3 pagesB5 Bitesize Revisionlaura martinez lunaNo ratings yet
- Kabojja Junior School: P. 6 Term I Revision Test 2020 (Set II) Integrated ScienceDocument41 pagesKabojja Junior School: P. 6 Term I Revision Test 2020 (Set II) Integrated SciencejusttheyboyNo ratings yet
- Pathology: How To Use The Workbook With The VideosDocument8 pagesPathology: How To Use The Workbook With The VideosDinhLinhNo ratings yet
- MYP Biology 10 Worksheet: Diet, Insulin and Blood GlucoseDocument3 pagesMYP Biology 10 Worksheet: Diet, Insulin and Blood GlucoseLizzy AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Digestion and AbsorptionDocument69 pagesDigestion and Absorption/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- Topic 8 Assessment BookletDocument32 pagesTopic 8 Assessment BookletjingNo ratings yet
- FCA (SA) Part I Past Papers - 2019 2nd Semester 25 1 2024Document81 pagesFCA (SA) Part I Past Papers - 2019 2nd Semester 25 1 2024ModoroNo ratings yet
- Homesostasis and Repsonse HigherDocument70 pagesHomesostasis and Repsonse Highermohammed fayedNo ratings yet
- Biomols Extra Qs and MS Incl Some EnzymesDocument19 pagesBiomols Extra Qs and MS Incl Some EnzymesKhushi ShahNo ratings yet
- A03 Data AnalysisDocument19 pagesA03 Data Analysisleocarlton0700No ratings yet
- Mitosis WorksheetDocument9 pagesMitosis WorksheetBts/ ArmyNo ratings yet
- ReproductiveDocument8 pagesReproductiveMedSchoolStuffNo ratings yet
- P.4 Revision BookDocument125 pagesP.4 Revision Bookmuwanguzi rafiq100% (1)
- 3.8.2 Gene Expression - 26 MarksDocument8 pages3.8.2 Gene Expression - 26 MarksalaynasharleezNo ratings yet
- 2021 Biochem Activity 18 Biochemistry of AgingDocument4 pages2021 Biochem Activity 18 Biochemistry of AgingRaymark Flores EllamilNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering Webquest 5 16 17Document2 pagesGenetic Engineering Webquest 5 16 17api-262586446No ratings yet
- P.5 Sci Revision BookletDocument139 pagesP.5 Sci Revision BookletBosco KyakulagaNo ratings yet
- 6.4 Homeostasis QPDocument4 pages6.4 Homeostasis QPChioma UchegbuNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology WORKSHEETDocument7 pagesCSEC Biology WORKSHEETAnderson Michelle100% (1)
- SuperSizeMeVideo PDFDocument7 pagesSuperSizeMeVideo PDFcherholNo ratings yet
- Workbook of BiochemDocument22 pagesWorkbook of BiochemMedStudent MedStudentNo ratings yet
- paper-1-longer-answer-questionsDocument26 pagespaper-1-longer-answer-questionsaadilmiah2019No ratings yet
- A Level Biology Topic 1 AssessmentDocument15 pagesA Level Biology Topic 1 AssessmentgsapkaiteNo ratings yet
- Proteins Homework 231111 104935Document5 pagesProteins Homework 231111 104935dongolsaleenNo ratings yet
- RAMP EQsDocument11 pagesRAMP EQsalma.khaleefaNo ratings yet
- 4 - Enzymes ExtendedDocument6 pages4 - Enzymes ExtendedYashodhaNo ratings yet
- 3.46B1 Blood Worksheet 1Document4 pages3.46B1 Blood Worksheet 1Nakeisha Joseph100% (1)
- Name - Period - AP Biology Date - Raven Chapter 44 Guided Notes: Circulation & Respiration CirculationDocument8 pagesName - Period - AP Biology Date - Raven Chapter 44 Guided Notes: Circulation & Respiration CirculationDBQNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction WorksheetDocument3 pagesHuman Reproduction WorksheetDEEBAN0% (1)
- Biology Form 4 Exam OverviewDocument10 pagesBiology Form 4 Exam Overviewmark smithNo ratings yet
- Campylobacter jejuni causes diarrhoeaDocument5 pagesCampylobacter jejuni causes diarrhoeaBob yuNo ratings yet
- Step 1 Express 2018-Hematology and OncologyDocument12 pagesStep 1 Express 2018-Hematology and OncologyPratik JadhavNo ratings yet
- Organisation Foundation HigherDocument135 pagesOrganisation Foundation HigherSơnSơnNo ratings yet
- Edgcse Aap sb5 Eout High 0430Document7 pagesEdgcse Aap sb5 Eout High 0430Faiar Rob Year 9No ratings yet
- Basic Science Work Book 1Document64 pagesBasic Science Work Book 1Arezoo ZargollNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Decoded: Master Orgo with Step-by-Step SolutionsFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry Decoded: Master Orgo with Step-by-Step SolutionsNo ratings yet
- PICO School WorkDocument1 pagePICO School Workaraine humesNo ratings yet
- BLZ Ccs 2023 2027Document54 pagesBLZ Ccs 2023 2027araine humesNo ratings yet
- Marinedrugs 15 00072 v2 PDFDocument41 pagesMarinedrugs 15 00072 v2 PDFRose Ann BetonNo ratings yet
- Marinedrugs 15 00072 v2 PDFDocument41 pagesMarinedrugs 15 00072 v2 PDFRose Ann BetonNo ratings yet
- BPHA4552 Toxicology Lecture I. Intro To Toxic PeopleDocument56 pagesBPHA4552 Toxicology Lecture I. Intro To Toxic Peoplearaine humesNo ratings yet
- Intro To ToxicologyDocument20 pagesIntro To Toxicologyaraine humesNo ratings yet
- American Folk Song Lesson PlanDocument1 pageAmerican Folk Song Lesson Planapi-2844060150% (1)
- Guide 2017Document48 pagesGuide 2017Kleberson MeirelesNo ratings yet
- English Language Communication Skills Lab Manual: Name Roll No. Branch SectionDocument39 pagesEnglish Language Communication Skills Lab Manual: Name Roll No. Branch SectionSurendrakumar ThotaNo ratings yet
- 07Document30 pages07David MontoyaNo ratings yet
- 2608 Mathematics Paper With Solution MorningDocument9 pages2608 Mathematics Paper With Solution MorningTheManASHNo ratings yet
- Oxford Quantum Theory Lecture NotesDocument92 pagesOxford Quantum Theory Lecture Notest ElderNo ratings yet
- Julie Craven ResumeDocument3 pagesJulie Craven Resumeapi-469430606No ratings yet
- 7 Books You Must Have.Document3 pages7 Books You Must Have.Utkarsh PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- RelativeResourceManager PDFDocument113 pagesRelativeResourceManager PDFMuhammad Irfan SalahuddinNo ratings yet
- Guia de Instrucciones para Piloto - Garmin 1000Document57 pagesGuia de Instrucciones para Piloto - Garmin 1000Cesar Gaspar BaltazarNo ratings yet
- The Madhya Pradesh Public Trusts Act 1951Document13 pagesThe Madhya Pradesh Public Trusts Act 1951Zenith ChhablaniNo ratings yet
- Plotting and Model Building in MATLABDocument30 pagesPlotting and Model Building in MATLABMuhammad Shehzad KamalNo ratings yet
- Batra, Kanika - Kipps, Belsey, and Jegede - Cosmopolitanism, Transnationalism, and Black Studies in Zadie Smith's On BeautyDocument15 pagesBatra, Kanika - Kipps, Belsey, and Jegede - Cosmopolitanism, Transnationalism, and Black Studies in Zadie Smith's On Beautyjen-leeNo ratings yet
- NSTP 2 Community ServiceDocument19 pagesNSTP 2 Community ServiceTessia EralithNo ratings yet
- Radiohead - The King of LimbsDocument2 pagesRadiohead - The King of LimbsOsmar LaraNo ratings yet
- High risk patient dental questionsDocument3 pagesHigh risk patient dental questionsFoysal SirazeeNo ratings yet
- Connectors of Addition and ContrastDocument2 pagesConnectors of Addition and Contrastmmaarr100% (2)
- O & M of DC & UPS SystemsDocument65 pagesO & M of DC & UPS SystemshajimakNo ratings yet
- Sept 2013 NewsletterDocument6 pagesSept 2013 NewsletterBKU1965No ratings yet
- Beyond The Wall - The Village Hero Character PlaybookDocument4 pagesBeyond The Wall - The Village Hero Character Playbookmagic_fyodorNo ratings yet
- Target Mature Men with Luxury Watch MarketingDocument13 pagesTarget Mature Men with Luxury Watch MarketingAndriDwisondiNo ratings yet
- Kertas Kerja Projek Inovasi IPGDocument10 pagesKertas Kerja Projek Inovasi IPGTESL1-0619 Rasheed Muhammad Raffeeq Bin RizalNo ratings yet
- History PPT 1Document24 pagesHistory PPT 1Akash SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fire Protection Focus for TunnelsDocument12 pagesFire Protection Focus for Tunnelsfrank100% (1)
- UConn Criminal Information SummaryDocument2 pagesUConn Criminal Information SummaryEllyn SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Acefyl SPP - 03 Dec 2010Document54 pagesAcefyl SPP - 03 Dec 2010maliakbar111No ratings yet
- Supreme Court Ruling on Missing Court RecordsDocument7 pagesSupreme Court Ruling on Missing Court RecordsApr CelestialNo ratings yet
- 4 Strategies To Unlock Performance Management Constraints HFMDocument6 pages4 Strategies To Unlock Performance Management Constraints HFMajay kumarNo ratings yet
- 1988 Ojhri Camp Disaster in PakistanDocument3 pages1988 Ojhri Camp Disaster in PakistanranasohailiqbalNo ratings yet