Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Proteins Homework 231111 104935
Uploaded by
dongolsaleenCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Proteins Homework 231111 104935
Uploaded by
dongolsaleenCopyright:
Available Formats
Q2.
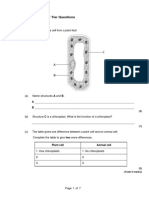
The diagram shows an epithelial cell from
the small intestine.
(a) (i) Name organelle Y.
______________________________________________________________
(1)
(ii) There are large numbers of organelle Y in this cell. Explain how these
organelles help the cell to absorb the products of digestion.
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
(2)
(c) Coeliac disease is a disease of the human digestive system. In coeliac disease,
the structures labelled Z are damaged.
Although people with coeliac disease can digest proteins they have low
concentrations of amino acids in their blood.
Explain why they have low concentrations of amino acids in their blood.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(2)
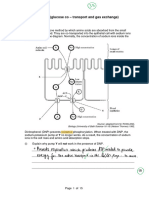
Q3. The diagram shows one method by which amino acids are absorbed from the small
intestine into the blood. They are co-transported into
the epithelial cell with sodium ions (Na+) at point X
on the diagram. Normally, the concentration of
sodium ions inside the epithelial cell is low.
Dinitrophenol (DNP) prevents respiration. When
treated with DNP, the sodium-potassium pump at Y
no longer works. As a result, the concentration of
sodium ions in the cell rises and amino acid
absorption stops.
(i) Explain why pump Y will not work in the
presence of DNP.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(2)
(ii) Explain why sodium ions and amino acids are not absorbed from the lumen of
the small intestine in the presence of DNP.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________(
2)
(iii) By what mechanism would amino acids leave the epithelial cell at point Z?
___________________________________________________________________
(1)
Q6. Trypsin is a protease. It is produced in an inactive form inside some of the cells of the
pancreas.
(a) Name the part of a pancreatic cell that produces the inactive form of trypsin.
___________________________________________________________________
(1)
(b) Suggest the advantage of producing trypsin in an inactive form inside cells in
the pancreas.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
(2)
(c) After the inactive form of trypsin enters the small intestine, another enzyme
removes a short chain of amino acids from the end of the inactive trypsin molecules.
This leads to the formation of the active form of trypsin.
(i) Name the type of bond hydrolysed when the short chain of amino acids is
removed.
______________________________________________________________
(1)
(ii) Sometimes trypsin can become activated inside a pancreatic cell. A competitive
inhibitor in the cell then binds to the trypsin and stops it working.
Explain how the competitive inhibitor stops trypsin working.
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________ (3)
You might also like
- Biotechnology PDFDocument28 pagesBiotechnology PDFCherry Lyn Belgira85% (13)
- Activators and Inhibitors (Enzyme)Document17 pagesActivators and Inhibitors (Enzyme)ronojoysengupta100% (2)
- High School Biology: Questions & Explanations for Cell & Molecular BiologyFrom EverandHigh School Biology: Questions & Explanations for Cell & Molecular BiologyNo ratings yet
- Transcription in EukaryotesDocument4 pagesTranscription in EukaryotesShaher Bano MirzaNo ratings yet
- MCQ MolecularDocument11 pagesMCQ MolecularMahmOod Gh100% (2)
- Immunology of The SkinDocument505 pagesImmunology of The SkinDan Stein100% (2)
- Pathoma Notes Part 1 - TPDocument50 pagesPathoma Notes Part 1 - TPluckyz89100% (1)
- Clinical and Basic Immunodermatology 2017Document889 pagesClinical and Basic Immunodermatology 2017Angelo BaezaNo ratings yet
- Lipids PpqsDocument29 pagesLipids PpqsTerreshaNo ratings yet
- Biomols Extra Qs and MS Incl Some EnzymesDocument19 pagesBiomols Extra Qs and MS Incl Some EnzymesKhushi ShahNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATION - classwork on anaerobic and aerobic (2)Document2 pagesRESPIRATION - classwork on anaerobic and aerobic (2)Mariah CampbellNo ratings yet
- Digestion and AbsorptionDocument69 pagesDigestion and Absorption/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- 5.1.1 and 5.1.2Document10 pages5.1.1 and 5.1.2Aamina HussainNo ratings yet
- Proteinsand Enzymes Part 2Document94 pagesProteinsand Enzymes Part 2dfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- Campylobacter jejuni causes diarrhoeaDocument5 pagesCampylobacter jejuni causes diarrhoeaBob yuNo ratings yet
- 4.1c Cell Biology HigherDocument64 pages4.1c Cell Biology HigherJayasri JeevaNo ratings yet
- Cape Biology Unit One Cells TutorialDocument10 pagesCape Biology Unit One Cells Tutorialakeisha kingNo ratings yet
- Mon Omers and Polymers a LevelDocument57 pagesMon Omers and Polymers a Leveldfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- 3.1.2 Carbohydrates EQDocument24 pages3.1.2 Carbohydrates EQteeb1826No ratings yet
- Week 5 Homework - 231012 - 184741Document15 pagesWeek 5 Homework - 231012 - 184741dongolsaleenNo ratings yet
- Membranes L3 MSDocument15 pagesMembranes L3 MSzaynabaziz52No ratings yet
- Application Questions Nx8jamDocument22 pagesApplication Questions Nx8jamdovidNo ratings yet
- .Archivetempt1 MOLECULES OF LIFE - Q Modul II (1-7)Document7 pages.Archivetempt1 MOLECULES OF LIFE - Q Modul II (1-7)Fatin HananiNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of CellsDocument29 pagesStructure and Functions of CellsKhushi ShahNo ratings yet
- A Level Biology Topic 1 AssessmentDocument15 pagesA Level Biology Topic 1 AssessmentgsapkaiteNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Homework - 231005 - 204804Document36 pagesWeek 4 Homework - 231005 - 204804dongolsaleenNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Biological MoleculesDocument3 pagesWorksheet Biological MoleculesJeon JungkookNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Mass Transport in Animals 2 - QuestionsDocument57 pages3.4 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Mass Transport in Animals 2 - QuestionsMaymunah HussainNo ratings yet
- Membranes L4 MSDocument19 pagesMembranes L4 MSzaynabaziz52No ratings yet
- Cell Membrane of Host CellDocument8 pagesCell Membrane of Host CellAshique FarhadNo ratings yet
- More Enzyme QuestionsDocument7 pagesMore Enzyme QuestionsAlNo ratings yet
- Set 5 Bioenergetics Grades 4 6Document17 pagesSet 5 Bioenergetics Grades 4 6Abir OmarNo ratings yet
- Biology Form IV Exam Guide and QuestionsDocument11 pagesBiology Form IV Exam Guide and Questionsmark smithNo ratings yet
- BiologyMock 2Document36 pagesBiologyMock 2backup14gNo ratings yet
- Mid Term f4 2008-Paper 2Document7 pagesMid Term f4 2008-Paper 2hamzah79No ratings yet
- Worksheet Biological MoleculesDocument5 pagesWorksheet Biological MoleculesNabeeha RaheelNo ratings yet
- 4 - Enzymes ExtendedDocument6 pages4 - Enzymes ExtendedYashodhaNo ratings yet
- Set 3 Cell Biology Grades 7 9Document17 pagesSet 3 Cell Biology Grades 7 9Abir OmarNo ratings yet
- HW BioDocument2 pagesHW BioRalph KingNo ratings yet
- Genetic Diversity and Adaptation Part 2Document88 pagesGenetic Diversity and Adaptation Part 2kafiazabit200No ratings yet
- Topic 5 NotesDocument8 pagesTopic 5 Notesdimitrap2024No ratings yet
- B Yr09 MQF Lev1to3 2023Document12 pagesB Yr09 MQF Lev1to3 2023AdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Digestion and Absorption QPDocument12 pages3.3 Digestion and Absorption QPHoyam ANo ratings yet
- ' GenetechnologiesPart2Document49 pages' GenetechnologiesPart2dfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- Biology Sixth Form TestDocument3 pagesBiology Sixth Form TestGeorge AshcroftNo ratings yet
- 0610/42 Biology: DC (ST/CT) 166141/1Document32 pages0610/42 Biology: DC (ST/CT) 166141/1Thapelo JeremiahNo ratings yet
- Organisation Foundation HigherDocument135 pagesOrganisation Foundation HigherSơnSơnNo ratings yet
- Latihan TopikalDocument39 pagesLatihan TopikalmazuraNo ratings yet
- P.6 SCIENCE HOLIDAY PACKAGE TERMDocument10 pagesP.6 SCIENCE HOLIDAY PACKAGE TERMshakiyonda256No ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 Exam OverviewDocument10 pagesBiology Form 4 Exam Overviewmark smithNo ratings yet
- B F3 Annual 2023Document18 pagesB F3 Annual 2023AdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- INSTRUCTIONDocument8 pagesINSTRUCTIONkelvinkaykatoyaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Functions ExplainedDocument6 pagesCell Structure and Functions ExplainedNilay SahNo ratings yet
- Academic Window BIOLOGY 7 PDFDocument15 pagesAcademic Window BIOLOGY 7 PDFsidharth balaji sridharanNo ratings yet
- Proteins and EnzymesDocument94 pagesProteins and Enzymesdfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- Organisation QP 2Document31 pagesOrganisation QP 2lizablatchfordNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Cell Structure and Microscopy QPDocument25 pages2.1 Cell Structure and Microscopy QPabdullahaltaccNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Enzymes - WorksheetDocument2 pagesChapter 4 Enzymes - Worksheetapi-372850850% (2)
- Practical Skills QuestionsDocument62 pagesPractical Skills QuestionshftuuNo ratings yet
- Examination Pack For Paper 2 (H)Document27 pagesExamination Pack For Paper 2 (H)Beth HampsonNo ratings yet
- Holiday Package Biology f4 2017Document2 pagesHoliday Package Biology f4 2017putri_latifahNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 NotesDocument6 pagesTopic 6 Notesdimitrap2024No ratings yet
- Year2guidedrevision Prac5and6Document19 pagesYear2guidedrevision Prac5and6alaynasharleezNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Plant NutritionDocument2 pagesGrade 8 Plant NutritionAmy BeacherNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Biological MoleculesDocument5 pagesWorksheet Biological MoleculesЕгор БиндерNo ratings yet
- 6.4 Homeostasis QPDocument4 pages6.4 Homeostasis QPChioma UchegbuNo ratings yet
- Blue Zone Higher Questions Lockdown WorkDocument7 pagesBlue Zone Higher Questions Lockdown WorkElllie TattersNo ratings yet
- Andrew Cannon - Enzyme Models & Factors Affecting Enzyme Action-LewisDocument4 pagesAndrew Cannon - Enzyme Models & Factors Affecting Enzyme Action-LewisAndrew CannonNo ratings yet
- 9 Mid Term Xam Paper 2020Document2 pages9 Mid Term Xam Paper 2020om guptaNo ratings yet
- Article 131Document9 pagesArticle 131Nikos HinasNo ratings yet
- ATP: The Cell's Energy CurrencyDocument4 pagesATP: The Cell's Energy CurrencyVignesh100% (1)
- FSC 111 Exam Past QuestionsDocument12 pagesFSC 111 Exam Past QuestionsAl-ameen OlawunmiNo ratings yet
- Introduction of PathophysiologyDocument32 pagesIntroduction of PathophysiologyOsama BakheetNo ratings yet
- GATE 2014: General Instructions During Examination: Common Data Button That Appears On The ScreenDocument31 pagesGATE 2014: General Instructions During Examination: Common Data Button That Appears On The ScreenSatish BojjawarNo ratings yet
- Taller Membrana CelularDocument1 pageTaller Membrana Celularvanessa ruizNo ratings yet
- Lipid Metabolism (II) - Fatty Acid Biosynthesis ExplainedDocument36 pagesLipid Metabolism (II) - Fatty Acid Biosynthesis Explainedlightning proNo ratings yet
- ProteomicsDocument24 pagesProteomicswatson191No ratings yet
- Chap 5 Reading WorksheetDocument3 pagesChap 5 Reading WorksheetSarahNo ratings yet
- Jawaban DK Herwandi - Pemicu 1 - Modul Hematologi Dan Onkologi - 2018Document5 pagesJawaban DK Herwandi - Pemicu 1 - Modul Hematologi Dan Onkologi - 2018HerwandiNo ratings yet
- Differential StainingDocument8 pagesDifferential Stainingabdullah albayatiNo ratings yet
- In Case of Appeal, Go To The Link: Final Result: 80.00 % M/qsy-Zagf-QqhDocument15 pagesIn Case of Appeal, Go To The Link: Final Result: 80.00 % M/qsy-Zagf-QqhnNo ratings yet
- PHR 308 - Part 6 - Anticancer Drugs - Pharmacology-III-3Document10 pagesPHR 308 - Part 6 - Anticancer Drugs - Pharmacology-III-3Abdur RaquibNo ratings yet
- Bio 1 Finals 11 STEMDocument3 pagesBio 1 Finals 11 STEMRosana De AsisNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle & Cancer Test Review Sheet: Name: DateDocument5 pagesCell Cycle & Cancer Test Review Sheet: Name: DateAnicia ToscanoNo ratings yet
- Classification and Function of Small Open Reading FramesDocument17 pagesClassification and Function of Small Open Reading FramesMandanirina RakotoarimananaNo ratings yet
- Eamcet 2.6.20Document201 pagesEamcet 2.6.20M JEEVARATHNAM NAIDUNo ratings yet
- Khannnn 2018Document91 pagesKhannnn 2018Sumant SainiNo ratings yet
- NFAT5 Amplifies Antipathogen Responses by Enhancing Chromatin Accessibility, H3K27 Demethylation, and Transcription Factor RecruitmentDocument17 pagesNFAT5 Amplifies Antipathogen Responses by Enhancing Chromatin Accessibility, H3K27 Demethylation, and Transcription Factor RecruitmentFernandoNo ratings yet
- Laguna University Midterm Exam in Natural Science IIDocument3 pagesLaguna University Midterm Exam in Natural Science IIVinlax ArguillesNo ratings yet
- Questions Bacterial Cell Structures An Introduction To The Bacterial CellDocument2 pagesQuestions Bacterial Cell Structures An Introduction To The Bacterial CellCarla May CaraNo ratings yet