0% found this document useful (0 votes)
106 views3 pagesBinomial Theorem Guide
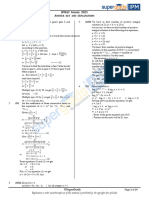
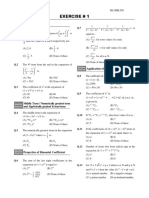
The document discusses the binomial theorem, which expresses the expansion of powers of binomial expressions. Some key points covered include:
1. The binomial theorem uses Pascal's triangle to determine the binomial coefficients in the expansion of terms like (a + b)n.
2. It provides formulas for the general term and sums of expansions of expressions like (a + x)n, (1 + x)n, and (1 - x)n.
3. Various forms and properties of the binomial expansion are discussed, including the middle term, differentiation, integration, and expressions with non-integer indices.
Uploaded by
SLCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
106 views3 pagesBinomial Theorem Guide
The document discusses the binomial theorem, which expresses the expansion of powers of binomial expressions. Some key points covered include:
1. The binomial theorem uses Pascal's triangle to determine the binomial coefficients in the expansion of terms like (a + b)n.
2. It provides formulas for the general term and sums of expansions of expressions like (a + x)n, (1 + x)n, and (1 - x)n.
3. Various forms and properties of the binomial expansion are discussed, including the middle term, differentiation, integration, and expressions with non-integer indices.
Uploaded by
SLCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd