Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Coloured Part of The Eye
Uploaded by
ANSH xD0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesThe document discusses various aspects of vision and optics. It addresses topics like the parts of the eye, how vision occurs via the retina, refraction through the cornea and lens, properties of light dispersion through prisms, and the formation of rainbows through refraction and total internal reflection in water droplets. Key points covered include that maximum refraction occurs at the cornea, the retina contains light-sensitive cells enabling vision, the vitreous humour fills the eye chamber between the lens and retina, and rainbows form when sunlight refracts and reflects off raindrops in the atmosphere.
Original Description:
Original Title
Coloured part of the eye
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses various aspects of vision and optics. It addresses topics like the parts of the eye, how vision occurs via the retina, refraction through the cornea and lens, properties of light dispersion through prisms, and the formation of rainbows through refraction and total internal reflection in water droplets. Key points covered include that maximum refraction occurs at the cornea, the retina contains light-sensitive cells enabling vision, the vitreous humour fills the eye chamber between the lens and retina, and rainbows form when sunlight refracts and reflects off raindrops in the atmosphere.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesColoured Part of The Eye
Uploaded by
ANSH xDThe document discusses various aspects of vision and optics. It addresses topics like the parts of the eye, how vision occurs via the retina, refraction through the cornea and lens, properties of light dispersion through prisms, and the formation of rainbows through refraction and total internal reflection in water droplets. Key points covered include that maximum refraction occurs at the cornea, the retina contains light-sensitive cells enabling vision, the vitreous humour fills the eye chamber between the lens and retina, and rainbows form when sunlight refracts and reflects off raindrops in the atmosphere.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
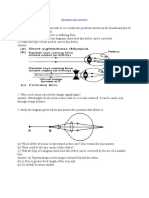
1.
Coloured part of the eye
a) Pupil
b) Iris
c) Cornea
d) Sclera
2. Maximum refraction occurs at which point of the eye?
a) Cornea
b) Eye lens
c) Pupil
d) Retina
3. How does image formation at retina help in vision?
a) Due to presence of blind spot
b) Due to presence of light sensitive cells
c) Due to less thickness of retina
d) All of the above
4. Fluid chamber between eye lens and retina is filled with
a) Aqueous humour
b) Vitreous humour
c) Fats
d) All of the above
5. How is it possible for an image to be formed always on retina?
a) Due to ciliary muscles
b) Due to flexibility of retina
c) Due to flexibility of eyeball
d) Due to fluid nature of vitreous humour
6. What happens to eye lens when ciliary muscles are relaxed?
a) Stretched and thick
b) Stretched and thin
c) Compressed and thick
d) Compressed and thin
7. When a person is not be able to see distant objects, he is suffering from ____
a) Presbyopia
b) Myopia
c) Hypermetropia
d) Both b and c
8. What is dispersion?
a) Scattering of white light into constituent of colours.
b) Splitting of white light into only 7 colours
c) Splitting of white light into its 7 constituent colours
d) Both a and c
9. What is the R.I of glass prism for different colours of light?
a) Same of all
b) Same for violet and blue coloured light.
c) Different for all.
d) Same for red and orange coloured light.
10. State the relation between refraction and wavelength of light.
a) Refraction is proportional to lambda
b) Refraction is inversely proportional to lambda
c) Both
d) None of the above.
11. What is angle of deviation?
a) Angle between normal and emergent ray.
b) Angle between incident ray and emergent ray
c) Angle between two lateral surfaces of prism
d) Both b and c
12. Small droplets in atmosphere behave as-
a) Small plane mirror
b) Small concave mirror
c) Small convex mirror
d) Small prism
13. Sunlight is –
a) Blue light
b) White light
c) Yellow light
d) Red light
14. How rainbow formation takes place?
a) Reflection – TIR – refraction
b) Refraction -TIR – refraction
c) Refraction – TIR – reflection
d) TIR – refraction – reflection
You might also like
- Chapter # 10 Geometrical OpticsDocument6 pagesChapter # 10 Geometrical OpticsSIR USMAN KHAN100% (3)
- Class Xii - CH-9 - Ray Optics and Optical Instruments (Competency - Based Test Items) Marks WiseDocument37 pagesClass Xii - CH-9 - Ray Optics and Optical Instruments (Competency - Based Test Items) Marks Wisesamaran270s100% (1)
- Comprhensive Exam Queations PDFDocument27 pagesComprhensive Exam Queations PDFhenok birukNo ratings yet
- BVOPT 601 Mcq'sDocument12 pagesBVOPT 601 Mcq'sShivani Yadav100% (9)
- Exam - OpticsDocument6 pagesExam - OpticsMahbubur Bhuiyan100% (1)
- MCQ - Human EyeDocument7 pagesMCQ - Human EyeThangaVelu100% (2)
- MCQ Type QuestionsDocument2 pagesMCQ Type QuestionsAnonymous rn5Te9MwkNo ratings yet
- MCQS On EyeDocument71 pagesMCQS On EyeFareed KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - HUMAN EYE and COLOURFUL WORLD-1Document23 pagesChapter 11 - HUMAN EYE and COLOURFUL WORLD-1Sriramulu JaichandarNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science (Physics) MCQs Chapter 11 QuestionsDocument28 pagesClass 10 Science (Physics) MCQs Chapter 11 QuestionsKSA TEXTILENo ratings yet
- Wave Optics MCQDocument8 pagesWave Optics MCQGuru ki physicsNo ratings yet
- EN1 Us 8 CM 9 D5 WLL2 R RfytDocument18 pagesEN1 Us 8 CM 9 D5 WLL2 R RfytMohammed IliasNo ratings yet
- Testpaper 1027016Document6 pagesTestpaper 1027016dreamlandpreschool2No ratings yet
- Braveheart Academy Science Test - Reflection and RefractionDocument1 pageBraveheart Academy Science Test - Reflection and RefractionAshwani PathakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document5 pagesChapter 2RanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful WorldDocument15 pagesChapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful WorldAdityaNo ratings yet
- OPHTHALMOLOGYDocument69 pagesOPHTHALMOLOGYcollinsmagNo ratings yet
- Class Test 10 (RRH)Document3 pagesClass Test 10 (RRH)Jeevanshu SoniNo ratings yet
- Human Eye WorksheetDocument3 pagesHuman Eye Worksheetcartooncompany73No ratings yet
- Lighttestclass 10Document4 pagesLighttestclass 10Anmol TwickleyNo ratings yet
- Winter Break Holiday Home Work Class-10Document4 pagesWinter Break Holiday Home Work Class-10api-326046013No ratings yet
- Human Eye and The Colorfull WorldDocument16 pagesHuman Eye and The Colorfull Worldanushanashi362No ratings yet
- Work Sheet Chapter 15 LightDocument2 pagesWork Sheet Chapter 15 Lightmadhav tomarNo ratings yet
- Half Yearly Revision Assignment For Grade X 2022Document7 pagesHalf Yearly Revision Assignment For Grade X 2022Anabella NavisNo ratings yet
- Science Worksheet - Light: Q1: Choose The Correct OptionDocument2 pagesScience Worksheet - Light: Q1: Choose The Correct OptionSarika AhujaNo ratings yet
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 6Document6 pagesMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 6Jagpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Te-Human Eye Final Revisor (2022-23)Document59 pagesTe-Human Eye Final Revisor (2022-23)Gautam SharrmaNo ratings yet
- Physics Books Pradeep Physics (Hinglish) The Human Eye and Colourful WorldDocument120 pagesPhysics Books Pradeep Physics (Hinglish) The Human Eye and Colourful WorldRoushan2104No ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-05 11 Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument7 pagesCbse Test Paper-05 11 Human Eye and The Colourful WorldTanmay KatyalNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-01 11 Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument5 pagesCbse Test Paper-01 11 Human Eye and The Colourful WorldTanmay KatyalNo ratings yet
- Human Eye and The Colorful World - MCQDocument4 pagesHuman Eye and The Colorful World - MCQGowri Venkat0% (1)
- MCQ Ray OpticsDocument4 pagesMCQ Ray OpticsDikshant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Jeep 111Document4 pagesJeep 111ShubhamNo ratings yet
- Vision and World of ColoursDocument6 pagesVision and World of ColoursAsish ThampiNo ratings yet
- Human Eye SpiralDocument9 pagesHuman Eye SpiralPravind KumarNo ratings yet
- Microbiology An Introduction 10th Edition Tortora Test BankDocument35 pagesMicrobiology An Introduction 10th Edition Tortora Test Bankbegravebasnetvp8su100% (32)
- 10 Science TP 11 1Document5 pages10 Science TP 11 1Ananaya BansalNo ratings yet
- Basic Physiological OpticsDocument16 pagesBasic Physiological OpticsAntwi EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Light: Year 9 Science Semester RevisionDocument4 pagesLight: Year 9 Science Semester Revisionapi-32133818No ratings yet
- Ophth TestsDocument48 pagesOphth TestsAkakpo ReindolfNo ratings yet
- 7 Human Eye and Colourful WorldDocument2 pages7 Human Eye and Colourful Worldvr techy factsNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper 10 McqsDocument3 pagesPhysics Paper 10 McqsShah Farman RathoreNo ratings yet
- Ch-10 Science PYQsDocument10 pagesCh-10 Science PYQsglusac261No ratings yet
- 10 Sci The Human Eye and The Colourful World NotesDocument15 pages10 Sci The Human Eye and The Colourful World Notestaiyab nurainNo ratings yet
- Colouful World MCQs PadhleDocument9 pagesColouful World MCQs PadhleALISHBA SARWARNo ratings yet
- MCQs - LightDocument9 pagesMCQs - Lightdeepak.idea84No ratings yet
- Anatomy Test Lesson 4Document3 pagesAnatomy Test Lesson 4Mary Rose BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Knowledge, F: Unit 3 Test OUTCOME 1 (11 Points)Document7 pagesKnowledge, F: Unit 3 Test OUTCOME 1 (11 Points)api-535415281No ratings yet
- CH 11Document11 pagesCH 11ojha.ramNo ratings yet
- Light MCQs PadhleDocument19 pagesLight MCQs Padhlesinghatharva2367No ratings yet
- Optometric OpticsDocument3 pagesOptometric OpticslakshmiamruthabhuvanagiriNo ratings yet
- 1628598558881SYBSC Physics Paper 2 - Optics MCQs With AnswersDocument27 pages1628598558881SYBSC Physics Paper 2 - Optics MCQs With AnswersShivam VermaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-11 Human Eye and Colourful World MCQsDocument15 pagesChapter-11 Human Eye and Colourful World MCQsSiddhantNo ratings yet
- Human Eye and Colourful World QuestionsDocument12 pagesHuman Eye and Colourful World QuestionsSahishna SurapaneniNo ratings yet
- New-DLP Phase2 Assignment-3 Module-B Final-9.8.18Document6 pagesNew-DLP Phase2 Assignment-3 Module-B Final-9.8.18PNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science HOTs Question Human Eye and Colourful WorldDocument18 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science HOTs Question Human Eye and Colourful WorldAadi PunjabiNo ratings yet
- OpthamologyDocument12 pagesOpthamologyRayyanNo ratings yet