Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Problems 4.2-Bjt-Amplifying & Switch
Uploaded by
[C3B] Aqilah HusnaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Problems 4.2-Bjt-Amplifying & Switch
Uploaded by
[C3B] Aqilah HusnaCopyright:
Available Formats
PS 4.
2 be/problem/ch4/bjt-amp&switch
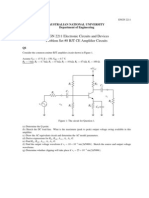
PROBLEMS 4.2-BJT: BJT-AMPLIFYING AND SWITCHING [Answer: A v =56 , V out =2.8 V ]
**Part A: Transistor as an Amplifier.
**Part B: Transistor as a Switching.
Q1. What is amplification?
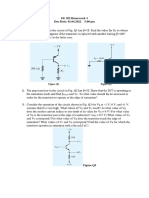
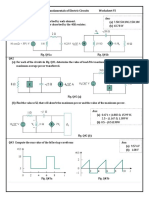
Q10. For the transistor circuit in Figure 4.2.2,
Q2. Define the voltage gain. a) What is the V CE whenV ¿ =0 V ?
b) What minimum value of I B is required to saturated this transistor if
Q3. Name two factors that determine the voltage gain of an amplifier.
β=200 ? Neglected V CE(sat)
Q4. A transistor has a voltage gain of 50. What is the output voltage when the c) Calculate the maximum value of R B whenV ¿ =5 V ?
input voltage is 100 mV?
[Answer: 5 V]
Q5. To achieve an output of 10 V with an input of 300 mW, what the voltage gain
is required?
[Answer: 33.33]
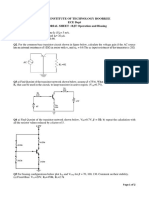
Q6. Determine the voltage gain and the ac output voltage in Figure 4.2.1 if
r 'e =50 Ω.
Figure 4.2.2
[Answer: a) 10 V, b) 50 A , c ¿ 86 k ]
Q11. Determine the minimum value of I B required to saturate the transistor in
Figure4.2.2 if β=125 and V CE(sat) =0.2 V
Figure 4.2.1 [Answer: 78.4 A]
[Answer: A v =20 ,V out =2 V ]
Q7. Related to figure 4.2.1, what the value of RC if it will take to have a voltage
gain of 50.
[Answer: 2.5k]
'
Q8. A transistor connected as in figure 4.2.1 has r e =20 Ω. If RC =1200 Ω, what
is the voltage gain? Calculate the ac output voltage.
[Answer: A v =60 ,V out =6 V ]
Q9. A 50 mV signal is applied to the base of biased transistor with r e '=10 Ω and
RC =560 Ω. Determine the signal voltage at collector.
1
You might also like
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 4 BJT OPN and BiasingDocument2 pagesTutorial Sheet 4 BJT OPN and BiasingSakshi GargNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Problems - 1 - Feb - 2018Document3 pagesTutorial Problems - 1 - Feb - 2018Animesh PariharNo ratings yet
- Wa0002.Document1 pageWa0002.GauravNo ratings yet
- 4d8f8analog 1, Tut SheetDocument19 pages4d8f8analog 1, Tut SheetmntykrNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 (Transistors)Document9 pagesAssignment 5 (Transistors)Rajesh PathakNo ratings yet
- EE 202 Homework3Document2 pagesEE 202 Homework3Garip KontNo ratings yet
- Eee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits (15ee34) - AssignmentDocument6 pagesEee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits (15ee34) - AssignmentchaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6: 1 2 C CE BEDocument4 pagesTutorial 6: 1 2 C CE BEAadarshPotluruNo ratings yet
- Sheet 4 Electronics - AnswerDocument7 pagesSheet 4 Electronics - AnswerOla Samir100% (1)
- BJT DC AnalysisDocument11 pagesBJT DC AnalysisShamganth KumarapandianNo ratings yet
- Sheet 4 ElectronicsDocument4 pagesSheet 4 ElectronicsAhmed Abo nNo ratings yet
- Final Question - ECE1312 - Sem1 - 14-15Document9 pagesFinal Question - ECE1312 - Sem1 - 14-15FARAZ ABDUL BASITNo ratings yet
- QUIZ 3-NOV23 - CH-1-2-3 - Feb22Document10 pagesQUIZ 3-NOV23 - CH-1-2-3 - Feb22MUHAMMAD NUR AMNI KHARIMANNo ratings yet
- Ec-101 - Final PDFDocument2 pagesEc-101 - Final PDFarjunv_14No ratings yet
- Tsheet1 EEDocument2 pagesTsheet1 EEHeena FarooqNo ratings yet
- 02 BJTs & BJT Amplifiers-ProblemsDocument4 pages02 BJTs & BJT Amplifiers-ProblemsntldvlaiNo ratings yet
- Anna Ec-IDocument3 pagesAnna Ec-Ikrishna_ScrbidNo ratings yet
- B1 Ece2002 50030 50290 50369Document4 pagesB1 Ece2002 50030 50290 50369NanduNo ratings yet
- 19 15ee201 A2 PDFDocument2 pages19 15ee201 A2 PDFYadhuvanth kumarNo ratings yet
- Homework#5 For Microelectronics (I)Document12 pagesHomework#5 For Microelectronics (I)Bruno IensenNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics Practice QuestionsDocument19 pagesAnalog Electronics Practice Questionssharma_rockstarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet: = 10 Ω and V = 0.7 V. The load /N = 10/1. If the primary isDocument3 pagesTutorial Sheet: = 10 Ω and V = 0.7 V. The load /N = 10/1. If the primary isDaniel EkassiNo ratings yet
- Assignment BJTDocument4 pagesAssignment BJTRamNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Summative 202 SaturdayDocument3 pagesPower Electronics Summative 202 SaturdayTấn Long Đoàn NguyễnNo ratings yet
- 131101-2 Gtu 3rd Sem PaperDocument4 pages131101-2 Gtu 3rd Sem PaperShailesh SankdasariyaNo ratings yet
- SheetDocument4 pagesSheetb5fc94cdd3No ratings yet
- Tutorial C4 SEEU2012Document4 pagesTutorial C4 SEEU2012dukeNo ratings yet
- Questions Edc Set3Document2 pagesQuestions Edc Set3Severus SnapeNo ratings yet
- Bogotá, D.C., 20 de Noviembre de 2019 Problemas Ela1 Problemas Propuestos: 1. in The Circuit of Figure A, The Diode Is IdealDocument6 pagesBogotá, D.C., 20 de Noviembre de 2019 Problemas Ela1 Problemas Propuestos: 1. in The Circuit of Figure A, The Diode Is IdealFelipe GuzmánNo ratings yet
- Assignment-II, Basic Electronics 1. The Circuit Shown Uses A Silicon Transistor HavingDocument4 pagesAssignment-II, Basic Electronics 1. The Circuit Shown Uses A Silicon Transistor HavingRanit NathNo ratings yet
- C1EC01-C1405 - ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS & DESIGN MergedDocument18 pagesC1EC01-C1405 - ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS & DESIGN Mergedchini_naniNo ratings yet
- Sem 3 Module 3Document5 pagesSem 3 Module 3Joshua HernandezNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics Circuit (ECE - 2101) (Make Up) RCSDocument2 pagesAnalog Electronics Circuit (ECE - 2101) (Make Up) RCSdeevNo ratings yet
- Solutionassignment Ent 162 ch456Document9 pagesSolutionassignment Ent 162 ch456Ken Argil GriñoNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems On Transistor Biasing Excellent StuffDocument15 pagesSolved Problems On Transistor Biasing Excellent StuffStudent HelperNo ratings yet
- EEC110A Win 2010 Final Exam: Name: ID #Document35 pagesEEC110A Win 2010 Final Exam: Name: ID #Zoro ZhaoNo ratings yet
- BJTAmplifierCircuits SolDocument9 pagesBJTAmplifierCircuits SolAristotle Atijera AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Sheet #3Document4 pagesSheet #3ABDONo ratings yet
- EE311 Analog Electronics Final Q1) (15 PTS.) A Class-A Emitter Follower Biased With A Constant Current Source Is Given in TheDocument6 pagesEE311 Analog Electronics Final Q1) (15 PTS.) A Class-A Emitter Follower Biased With A Constant Current Source Is Given in TheburakNo ratings yet
- 12-RC Phase Shift OscillatorDocument5 pages12-RC Phase Shift OscillatorA054 Shubham fundayNo ratings yet
- 12-RC Phase Shift OscillatorDocument5 pages12-RC Phase Shift OscillatorBanty BabliNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Question Bank 3 PDFDocument3 pagesBasic Electronics Question Bank 3 PDFPRAVEEN YADAWNo ratings yet
- Information About The Transistor and Its Bias State. AlsoDocument1 pageInformation About The Transistor and Its Bias State. AlsoGovind SharmaNo ratings yet
- EG1108 Tutorial 5: Transformers & Rectifier Circuits - Part 1 EG1108 Tutorial 5: Transformers & Rectifier Circuits - Part 1Document12 pagesEG1108 Tutorial 5: Transformers & Rectifier Circuits - Part 1 EG1108 Tutorial 5: Transformers & Rectifier Circuits - Part 1Leong ssNo ratings yet
- 7c634fcdEndSem 2022Document3 pages7c634fcdEndSem 2022biggusdiggus38No ratings yet
- Problems-Chapter-4 - ContentsDocument7 pagesProblems-Chapter-4 - ContentsThiện NguyễnNo ratings yet
- ECEG-2121 Workshhet VIDocument3 pagesECEG-2121 Workshhet VIXesoNo ratings yet
- Core-Iii-558-32511301 - Oc-Electronic Circuits-17-12-2020Document2 pagesCore-Iii-558-32511301 - Oc-Electronic Circuits-17-12-2020Sachin KumarNo ratings yet
- 9A02405 Analog Electronic CircuitsDocument4 pages9A02405 Analog Electronic CircuitssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- BL1125 - Test1C 2223 v1Document8 pagesBL1125 - Test1C 2223 v1Samz AdrianNo ratings yet
- Tugas 2Document2 pagesTugas 2shoffi arifin100% (2)
- Tutorial Problems: Bipolar Junction Transistor (Basic BJT Amplifiers)Document23 pagesTutorial Problems: Bipolar Junction Transistor (Basic BJT Amplifiers)vineetha nagahageNo ratings yet
- Ee-210 Analog Digital Electronics Final Examination Q No.1Document3 pagesEe-210 Analog Digital Electronics Final Examination Q No.1madihaNo ratings yet
- Assign 1Document3 pagesAssign 1anij9825No ratings yet
- 50+ Most Expected Question Part-3Document28 pages50+ Most Expected Question Part-3rishavrk692No ratings yet
- Assign 1 PDFDocument3 pagesAssign 1 PDFtanishk jainNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Honeywell CK65Document2 pagesDatasheet Honeywell CK65John VenturaNo ratings yet
- Deadlock in Distributed EnviornmentDocument31 pagesDeadlock in Distributed Enviornmenttarun_1992_sharma_20130% (1)
- FPT University Undergraduate Program Syllabus: (Under Decision No.1040/QĐ-ĐHFPT Dated 10/8/2018)Document18 pagesFPT University Undergraduate Program Syllabus: (Under Decision No.1040/QĐ-ĐHFPT Dated 10/8/2018)Chi TuyếtNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting The PXE Service Point and WDS in Configuration Manager 2007Document17 pagesTroubleshooting The PXE Service Point and WDS in Configuration Manager 2007Sunil KumarNo ratings yet
- Flexible Time Triggered Protocol For CANDocument8 pagesFlexible Time Triggered Protocol For CANAriana Ribeiro LameirinhasNo ratings yet
- Dining Philosopher: ProblemDocument9 pagesDining Philosopher: ProblemAastha SinghNo ratings yet
- Printed Circuit Boards Designing and Its Fabrication MethodsDocument54 pagesPrinted Circuit Boards Designing and Its Fabrication MethodsZaryab QaziNo ratings yet
- GalaxyEthernetModule E080 PDFDocument20 pagesGalaxyEthernetModule E080 PDFIvan VillapolNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 NetworkingDocument21 pagesChapter 2 Networkingvibz99No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Process Models: 1. Waterfall Model (Classic Life Cycle)Document57 pagesChapter 3 - Process Models: 1. Waterfall Model (Classic Life Cycle)AnggardaNo ratings yet
- Flexmodule: 8X Ge Poe+ Module (Exm-8C)Document4 pagesFlexmodule: 8X Ge Poe+ Module (Exm-8C)StartNo ratings yet
- Datasheet PDFDocument15 pagesDatasheet PDFNatali Lorena Félix MeirelesNo ratings yet
- OpenNebula-Open Cloud Reference Architecture Rev1.6 20190301Document10 pagesOpenNebula-Open Cloud Reference Architecture Rev1.6 20190301gopalshyambabu767No ratings yet
- SNMP TutorialDocument6 pagesSNMP TutorialantonioNo ratings yet
- Expt 03Document3 pagesExpt 03jk arnabNo ratings yet
- A Broker For Cost-Efficient QoS Aware Resource Allocation in EC2Document134 pagesA Broker For Cost-Efficient QoS Aware Resource Allocation in EC2kurt_vermeerschNo ratings yet
- ECE 445 - Fall 2020 - Lecture 4 - MIPS Machine Language and Program ExecutionDocument23 pagesECE 445 - Fall 2020 - Lecture 4 - MIPS Machine Language and Program Execution陳柏鈞No ratings yet
- Introduction To API TestingDocument3 pagesIntroduction To API Testingsulagna100% (8)
- Verilog Interview Questions Part 1Document7 pagesVerilog Interview Questions Part 1radhakodirekka8732No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 (Input and Output)Document55 pagesChapter 7 (Input and Output)Mocmoc SalihNo ratings yet
- Omicron ProtectionDocument176 pagesOmicron ProtectionWrya SaeedNo ratings yet
- SRS DemoDocument11 pagesSRS DemoTiasha DuttaNo ratings yet
- Sistem Informasi Geografis Fasilitas Kesehatan Bpjs Di Kota Palangka Raya Berbasis AndroidDocument10 pagesSistem Informasi Geografis Fasilitas Kesehatan Bpjs Di Kota Palangka Raya Berbasis AndroidIsabellaNo ratings yet
- 1 - MIT - Coimbatore ProspectusDocument43 pages1 - MIT - Coimbatore Prospectussangeethathangavel91No ratings yet
- TPCA8109Document8 pagesTPCA8109Servis AccuNo ratings yet
- TalendEnterprise ESB IG 50b enDocument58 pagesTalendEnterprise ESB IG 50b enNguyen Anh NguyenNo ratings yet
- CORE IMS Passive-Monitoring-solutionDocument24 pagesCORE IMS Passive-Monitoring-solutionRamon CuevasNo ratings yet
- FSDL0365RN, FSDM0365RN: Green Mode Fairchild Power Switch (FPS)Document20 pagesFSDL0365RN, FSDM0365RN: Green Mode Fairchild Power Switch (FPS)Andi Awal JanwarNo ratings yet
- LA4525Document8 pagesLA4525Antonieta Cano CruzNo ratings yet
- Computer Vision Lab Manual 2023Document63 pagesComputer Vision Lab Manual 2023VivekSinh RajputNo ratings yet