Professional Documents
Culture Documents
W9 - Epidemiology and Antibiotic Resistance
W9 - Epidemiology and Antibiotic Resistance
Uploaded by
Zelle Da ReyesOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
W9 - Epidemiology and Antibiotic Resistance
W9 - Epidemiology and Antibiotic Resistance
Uploaded by
Zelle Da ReyesCopyright:
Available Formats
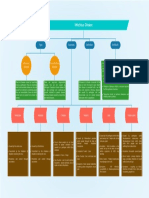
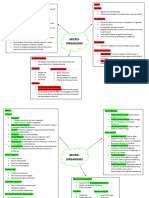
Epidemiology and Antibiotic Resistance Fomites
Portals of Entry
Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease
Modes of Transmission
● Direct person-to-person contact
● Direct mucus membrane to mucus membrane
● Indirect by air droplets or dust
● Indirect contamination of food and water
● Blood contamination by vectors
● Mechanical transmission - arthropod carries pathogen on its feet
● Biological transmission - pathogen reproduces in the vector;
transmitted via bites or feces
Portals of Exit
Question: What type of host is the most susceptible to infection?
Extent of Host Involvement
Vectors vs. Reservoirs
I. ACCORDING TO AREA OF INVASION
● Reservoirs are the natural hosts of pathogenic organisms and
- Localized, Systemic, Focal, Latent
are usually unaffected by any diseases associated with the
pathogen that they host (i.e. bats are natural reservoirs for Ebola
and SARS-CoV-like viruses). They do not actively transmit these
pathogens to other hosts.
● Vectors are organisms that actively infect other organisms with
the pathogens they carry (i.e. mosquitos are vectors of malaria
and dengue virus).
II. ACCORDING TO SEVERITY Epidemiology
● Science that deals with the frequency and distribution of disease
and the factors that contributes to their spread.
Herd Immunity
Epidemiology and Statistics
Blood Infections
● Sepsis: toxic inflammatory condition arising from the spread of
microbes, especially bacteria or their toxins, from a focus of infection
● Bacteremia: bacteria in the blood
● Septicemia: also known as blood poisoning; growth of bacteria in the
blood
● Toxemia: toxins in the blood
● Viremia: viruses in the blood
Primary vs. Opportunistic Infections
● Primary infection: acute infection that causes the initial illness.
● Secondary infection: opportunistic infection after a primary
(predisposing) infection.
III. ACCORDING TO THE MANNER IT REACHES THE BODY
● Communicable vs. Non-communicable diseases
Controlling the Growth of Microbes in Vivo
● Antimicrobial agents/drugs can be used to inhibit or control the growth
of microbes within the body.
● The goal is to create treatments that only target pathogenic and
organisms but do not harm human body cells.
Characteristics of Antimicrobial Agents
● Kill or inhibit the growth of pathogens
● Cause no damage to the host
● Cause no allergic reaction in the host
● Be stable when stored in solid or liquid form
● Remain in specific tissues in the body long enough to be effective
● Kill the pathogens before they mutate and become resistant to it
Drug Resistance
Mechanisms for Drug Resistance
Bactericidal vs. Bacteriostatic
● Bactericidal – Kills bacteria
● Bacteriostatic – Suppresses bacterial growth
Beta-Lactams
● Beta-Lactams inhibit bacteria by binding covalently to PBPs
(Penicillin-Building Proteins) in the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane.
● PBPs are essential in the process of cell wall Biosynthesis
You might also like
- Clinical BacteriologyDocument123 pagesClinical Bacteriologykurotsukki todoroki100% (1)
- Crane LoadingsDocument2 pagesCrane Loadingsmoseslugtu632470% (10)
- Economics Desire IAS MindmapDocument115 pagesEconomics Desire IAS MindmapShimla95% (21)
- Core Values and Formalization As Determinants of Individual Behavior in An Organization A Managerial PerspectiveDocument14 pagesCore Values and Formalization As Determinants of Individual Behavior in An Organization A Managerial PerspectiveMonica PalaciosNo ratings yet
- TOEFL Diagnostic TestDocument47 pagesTOEFL Diagnostic TestLilian G. Romero L.No ratings yet
- Host Pathogen Interaction FinalDocument37 pagesHost Pathogen Interaction FinalSrijan BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- Host Pathogen Interaction FinalDocument37 pagesHost Pathogen Interaction FinalSrijan BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- FUNDA SLE - AsepsisDocument8 pagesFUNDA SLE - Asepsisprincessdiane.agripaNo ratings yet
- Classifications of Pathogenic MicroorganismsDocument5 pagesClassifications of Pathogenic Microorganismsjasonenmanuel10No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing Practice - MidtermDocument24 pagesFundamentals of Nursing Practice - MidtermShene Claire VigillaNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases Handouts)Document15 pagesCommunicable Diseases Handouts)snpjavierNo ratings yet
- Notes - Infection Control 1Document7 pagesNotes - Infection Control 1matingin.aileen11No ratings yet
- Introducing Communicable DiseasesDocument2 pagesIntroducing Communicable DiseasesSulaimaan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Med Dia Lec Oct. 26Document15 pagesMed Dia Lec Oct. 26Enha PenNo ratings yet
- NCMC103 Prelims ReviewerDocument13 pagesNCMC103 Prelims ReviewerVeronica ShaneNo ratings yet
- Infection and ContaminationDocument60 pagesInfection and ContaminationNur SetsuNo ratings yet
- Host-Parasite Relationship: Yuyun Kusnaningrum Pembimbing DR - Dewi Retnoningsih, SPMKDocument38 pagesHost-Parasite Relationship: Yuyun Kusnaningrum Pembimbing DR - Dewi Retnoningsih, SPMKBagus Ramanto SaputraNo ratings yet
- MLSP2 Module 1 Infection ControlDocument5 pagesMLSP2 Module 1 Infection Controleumhir7No ratings yet
- MICROPARA - Topic 7 - Bacteria and DiseaseDocument45 pagesMICROPARA - Topic 7 - Bacteria and DiseaseREGINA MAE JUNIONo ratings yet
- Chapter01 ThebasicsofMicrobiologyDocument14 pagesChapter01 ThebasicsofMicrobiologyFarooq SyedNo ratings yet
- Makerere University Year 2 Bacterial PathogenesisDocument14 pagesMakerere University Year 2 Bacterial Pathogenesiswilgus barazaNo ratings yet
- 3 Antimicrobial AgentDocument36 pages3 Antimicrobial AgentTariku AbebeNo ratings yet
- Immunology 1Document8 pagesImmunology 1zaina.malikNo ratings yet
- 2.3 PathogenesisDocument27 pages2.3 PathogenesisTobio KunnyNo ratings yet
- Lezon 1Document2 pagesLezon 1Idk UlitNo ratings yet
- Reviewer On Microbiology RleDocument10 pagesReviewer On Microbiology RleHernandez NicoleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Immunity Grade 10Document36 pagesChapter 10 Immunity Grade 10gabiplayz47No ratings yet
- NCM 112-Mod5Document6 pagesNCM 112-Mod5Samantha BolanteNo ratings yet
- Mekanisme Penyakit InfeksiDocument35 pagesMekanisme Penyakit InfeksiNur FaidahNo ratings yet
- Parasitology ReviewerDocument7 pagesParasitology ReviewerSandra Mhay RodilloNo ratings yet
- MicrobioDocument34 pagesMicrobiodead yrroehNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Parasitologi PPT BMD 21-22Document31 pagesIntroduction To Parasitologi PPT BMD 21-22NURFADILLAH HRNo ratings yet
- Infectious Disease XI312 RAMADocument1 pageInfectious Disease XI312 RAMAMuhammad NaufalNo ratings yet
- Lect 5 Bacterial PathogenicityDocument49 pagesLect 5 Bacterial PathogenicitySuha AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Infectious Disease Study NotesDocument56 pagesInfectious Disease Study NotesPierre BenardNo ratings yet
- Infection and Infectious ProcessDocument44 pagesInfection and Infectious Processpandey omkarNo ratings yet
- 4 - Host Microbe Interaction - 5nov2021Document50 pages4 - Host Microbe Interaction - 5nov2021haiqalfariq07No ratings yet
- First Sem NotesDocument37 pagesFirst Sem NotesRose Anne AbivaNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 Part 1Document43 pagesLec 2 Part 1Ahmed JamalNo ratings yet
- Host-Microbe Interactions - PoctDocument20 pagesHost-Microbe Interactions - PoctHUỲNH QUỐC KHÁNHNo ratings yet
- An To Infectious Diseases: Shira Shafir, PHD, MPH 24 January 2008Document50 pagesAn To Infectious Diseases: Shira Shafir, PHD, MPH 24 January 2008YL Slalu BahagieaNo ratings yet
- Infectious ProcessDocument69 pagesInfectious ProcessJR Rolf NeuqeletNo ratings yet
- Lec 4 Cviruses CorrectDocument28 pagesLec 4 Cviruses Correctchansadavid52No ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases: Dr. Wael H. Mansy, MD Edited by Willy ChouDocument32 pagesInfectious Diseases: Dr. Wael H. Mansy, MD Edited by Willy Chouwildan mullerNo ratings yet
- W1 Antimicrobial DrugsDocument8 pagesW1 Antimicrobial Drugsseanne kskwkwkaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Immunology BensonDocument9 pagesMicrobiology Immunology Bensonco230351No ratings yet
- Infectious DiseasesDocument6 pagesInfectious DiseasesAlexa QuizomNo ratings yet
- HandSC Level 2 Textbook Sample Chapters PDFDocument26 pagesHandSC Level 2 Textbook Sample Chapters PDFLiza GomezNo ratings yet
- Micropara Chap 3Document7 pagesMicropara Chap 3htagulao.nsgNo ratings yet
- Infectious Disease 1Document1 pageInfectious Disease 1Josie Jones BercesNo ratings yet
- Lecture (1) Odontogenic Infections of The Head 0 NeckDocument60 pagesLecture (1) Odontogenic Infections of The Head 0 Neckomar.alzaity.3000No ratings yet
- Antimicrobials ReviewerDocument7 pagesAntimicrobials ReviewerKeziah PepitoNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 Prefinal LectureDocument11 pagesNCM 112 Prefinal LectureRheeanne AmilasanNo ratings yet
- Molecular Pathogenesis of Infection (Khusus Palangkaraya 2011), Bahan Ujian SajaDocument27 pagesMolecular Pathogenesis of Infection (Khusus Palangkaraya 2011), Bahan Ujian SajaeciNo ratings yet
- Control of Communicable DiseaseDocument4 pagesControl of Communicable DiseaseBianca CordovaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Normal Flora..Document15 pages2 - Normal Flora..Arshad AbbasNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 Disease ProcessDocument30 pagesCHAPTER 5 Disease ProcessDanica DaniotNo ratings yet
- 8 - Bacteria and DiseaseDocument8 pages8 - Bacteria and DiseaseGlaiza BesarioNo ratings yet
- Micro OrganismsDocument5 pagesMicro Organismsnikitaria1603No ratings yet
- 7-Micro 2016Document19 pages7-Micro 2016Hakim SimonNo ratings yet
- CH 9 Physical and Chemical Control of Microbes-1Document10 pagesCH 9 Physical and Chemical Control of Microbes-1Karl Francis GarciaNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseasesDocument19 pagesCommunicable Diseasesriamanabat100% (5)
- Communicable DiseasesDocument1 pageCommunicable DiseasesthomasNo ratings yet
- W8 - Normal Human Microbiota and Nosocomial InfectionDocument3 pagesW8 - Normal Human Microbiota and Nosocomial InfectionZelle Da ReyesNo ratings yet
- Moments of Triumphs and Defeat in Parmenie and Final Days in RouenDocument8 pagesMoments of Triumphs and Defeat in Parmenie and Final Days in RouenZelle Da ReyesNo ratings yet
- Non-Nursing TheoriesDocument3 pagesNon-Nursing TheoriesZelle Da ReyesNo ratings yet
- Tessellations and FractalsDocument69 pagesTessellations and FractalsZelle Da ReyesNo ratings yet
- Summary, Conclusion, and RecommendationDocument3 pagesSummary, Conclusion, and RecommendationZelle Da ReyesNo ratings yet
- Autolight IP 16 17Document24 pagesAutolight IP 16 17Zelle Da ReyesNo ratings yet
- Clap Fan - Chapter 1Document6 pagesClap Fan - Chapter 1Zelle Da ReyesNo ratings yet
- Case Digest of Landmark CasesDocument3 pagesCase Digest of Landmark CasesJeslene CuadraNo ratings yet
- Template For Request To Additional Shs Program OfferingDocument7 pagesTemplate For Request To Additional Shs Program OfferingJerome BelangoNo ratings yet
- B. Philippine Airlines Inc. vs. CADocument15 pagesB. Philippine Airlines Inc. vs. CAKaloi GarciaNo ratings yet
- Observations in The Art of English Poesie (1602) of Certain Kinds of Musical Poetry, Especially 'OfDocument3 pagesObservations in The Art of English Poesie (1602) of Certain Kinds of Musical Poetry, Especially 'OfLee SenNo ratings yet
- Seven Chakras and Its CharacteristicsDocument1 pageSeven Chakras and Its Characteristicsapi-3722436No ratings yet
- LESSONDocument18 pagesLESSONViệt AnhNo ratings yet
- Vu Re Lecture 16Document28 pagesVu Re Lecture 16ubaid ullahNo ratings yet
- Assgnmnt Equity 2Document17 pagesAssgnmnt Equity 2Khazatul NaimaNo ratings yet
- PAPER PHYSICS (Kelompok 21 )Document4 pagesPAPER PHYSICS (Kelompok 21 )magfirahNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Thermal PhysicsDocument10 pages3.1 Thermal Physicsmardel11No ratings yet
- Functionality Test CasesDocument20 pagesFunctionality Test CasesNitin PatelNo ratings yet
- English Practice Book 4Document19 pagesEnglish Practice Book 4akilasrivatsavNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument63 pagesPeptic Ulcer DiseaseAli100% (1)
- 109 God The Jehovah JirehDocument132 pages109 God The Jehovah JirehKevin Reeve100% (1)
- Initial Diagnosis and Management of ComaDocument17 pagesInitial Diagnosis and Management of Comaguugle gogleNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Leadership Style On Employee Satisfaction andDocument9 pagesThe Effect of Leadership Style On Employee Satisfaction andjrdon123No ratings yet
- CACCIATORE, Et Al v. COUNTY OF BERGEN, Et Al - Document No. 31Document26 pagesCACCIATORE, Et Al v. COUNTY OF BERGEN, Et Al - Document No. 31Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Format Incident Report New 2019Document2 pagesFormat Incident Report New 2019Meliza RollanNo ratings yet
- Jarrett Graff - PD Reference Letter Spring 2021Document1 pageJarrett Graff - PD Reference Letter Spring 2021api-453380215No ratings yet
- Jency Dalphy: in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements For The Degree ofDocument25 pagesJency Dalphy: in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements For The Degree ofjency dalfyNo ratings yet
- Munasque vs. CADocument2 pagesMunasque vs. CASam FajardoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 English Unit PlanDocument8 pagesAssignment 3 English Unit Planapi-626567329No ratings yet
- Bagua Zhuan Huan ZhangDocument6 pagesBagua Zhuan Huan Zhangjilongfeng666No ratings yet
- Centre of Gravity: 3.1 Coplanar Parallel ForcesDocument14 pagesCentre of Gravity: 3.1 Coplanar Parallel ForcesSpidy MoveNo ratings yet
- Sonnet 54Document7 pagesSonnet 54api-272948113No ratings yet
- Basic Suturing and Wound Management: Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas DiponegoroDocument77 pagesBasic Suturing and Wound Management: Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Diponegoropranoto jaconNo ratings yet