Professional Documents
Culture Documents
9 MTH Ix 202122
Uploaded by
zeeshankaizer0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views7 pagesOriginal Title
9_MTH_IX_202122 (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views7 pages9 MTH Ix 202122
Uploaded by
zeeshankaizerCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
MATHEMATICS
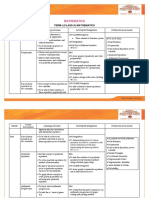
TERM-I (CLASS-IX) MATHEMATICS
Course
Month Learning Outcomes Activity/Art integration Portion for assessment
description
April Number • Representation of Natural numbers, MA
System Integers, rational Numbers on • To find the value of using circular objects.
number line. PT-I (17.07.2021)
• To represent an irrational number on number
• Representation of terminating/non- line. • Number System
terminating recurring decimals on a • Polynomials
number line.
AV CLASS/Geogebra: • Coordinate
• Operations on real numbers.
• Number system Geometry
• Existence of irrational numbers and
their representation on a number line. • Herons Formula
ART INTEGRATION
• nth root of a real number.
• To make beautiful sketch of flower or tree or any
• Rationalization of real numbers. Syllabus for PT-II
creature from nature using square root spiral.
• Rational exponents with positive real (4.1.1.3). • Number System
bases.
• Linear Equations In
Polynomials • To differentiate polynomials from MA Two Variables
other algebraic expression, • To interpret geometrically the factors of a
• Lines and Angles
• To find coefficients, terms, degree quadratic expression of the type x2+bx+c using
and zeros of polynomials. square grids, stripes and paper slips. • Triangles
• Constant, linear, quadratic and cubic
polynomials. Monomials, binomials
and trinomials.
• Factors and multiple.
June Polynomials • To know Zeros of polynomials. AV Class/ Geogebra
Course
Month Learning Outcomes Activity/Art integration Portion for assessment
description
• To learn about remainder and factor • To draw graph of polynomials and identifying
Syllabus for Term-I
theorems p(x)=q(x)s(x)+r(x), deg r(x) zeroes of a polynomial (Quadratic)
<deg q(x) • Number System
• To identify equations and Identities. ART INTEGRATION • Linear Equations In
Identities are true for all defined • Making small cubes with clay to show cubic Two Variables
values. identities.(4.1.2.1) • Coordinate
• To know Cartesian plane, coordinates MA Geometry
Coordinate
geometry of a point, names and terms • To obtain the mirror image of a given • Lines and Angles
associated with the coordinate plane, geometrical figure w .r .t. the x-axis and the y- • Triangles
notations, plotting points in the plane. axis.
• Heron’s Formula
Euclid’s • To know point, line, ray, angle, AV Class/ Geogebra
axioms, postulates theorems of Euclid • Statistics
geometry • Euclid and his work.
Geometry.
• Heron’s formula OUTDOOR ACTIVITY:
July Heron’s
• To find the area of field using Heron’s formula.
formula • Area of triangle =
ART INTEGRATION
• Using Heron's formula, find the area of a triangle
formed by three important places of a state:
Students will be asked to identify three
important locations/places of their choice (non-
collinear places so that a triangle is formed) and
find the distances among these places. Now,
using Heron's formula, find the area of that
triangle formed. (4.1.1.1.7).
• Basic terms and definitions. MA
Lines &
• To prove that sum of interior angles of a triangle
angles
is 180° (by paper cutting and pasting)
Course
Month Learning Outcomes Activity/Art integration Portion for assessment
description
• To know intersecting lines & Parallel • To prove that exterior angle of a triangle is equal
lines. Intersecting lines have distance to the sum of two opposite interior angles of the
0. Parallel lines have equal distance triangle (by paper cutting and pasting)
between them throughout. ART INTEGRATION
• The relation between angles when • To make a wall decorative piece using curve
two parallel lines are intersected by stitching. (4.1.5.1)
any transversal. AV Class/ Geogebra
• To show the relation between vertically opposite
• Angle Sum property of a Triangle.
angles.
• Exterior angle of a triangle is equal to • To find the relation between different pair of
sum of interior opposite angles. angles when a transversal intersects two parallel
lines.
• To prove that sum of interior angles of a triangle
is 180°.
• To prove exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the
sum of two opposite interior angles of the
triangle.
August Triangles • To know triangles as three MA
intersecting lines, three vertices, three • To find the centroid of a triangle using paper
angles, three sides. folding method.
• To differentiate congruency & • To find the orthocenter of a triangle using paper
similarity.
folding method.
• To learn different criteria for AV Class/ Geogebra
congruency of triangles.
• To show that angle opposite to the greater side of
• The angles opposite to equal sides of a triangle is greater.
a triangle are equal.
Course
Month Learning Outcomes Activity/Art integration Portion for assessment
description
• To locate centroid, orthocentre, incentre and
circumcentre of a triangle and hence to draw
incircle or circumcircle.
ART INTEGRATION
• Making a tourist brochure of famous buildings
known for their mathematical architecture.
(4.1.4.4)
Linear • To know linear equation in two MA
equation in variables, ax + by + c = 0. • To represent two linear equations geometrically
two Variables
• To Identify ordered pair of real on graph sheet and locate the point of
numbers satisfying the linear intersection.
equation. Plotting these points & ART INTEGRATION
joining them to show that they lie on
a line. • To make the picture of a bird or animal on a
graph paper by joining dots .(4.1.1.3)
Statistics • To know basic use of statistics in day MA
to day life and so in mathematics • To prepare the histogram/ frequency polygon
• To interpret & draw tables, charts, for the given case study.
data, bar graphs and histogram. ART INTEGRATION
• To represent data & its significance in • To make chart tabulation of music, costume ,
day to day life. language of a region etc.(4.5.3.2)
September Revision Entire Syllabus of PT-II
October Revision Entire Syllabus of TERM-I
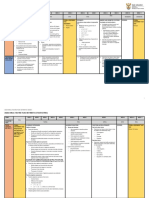
TERM-II (CLASS-IX) MATHEMATICS
Course
Month Learning Outcomes Activity/Art integration Portion for assessment
description
November Quadrilaterals • To learn quadrilateral as four MA
intersecting line segments. Syllabus for PT-III
• To verify the midpoint theorem for a triangle
• Quadrilaterals
• To know types of quadrilaterals like by paper folding, cutting and pasting method.
• Circles
Parallelogram, Rectangle, Square, AV CLASS/ Geogebra • Constructions
Trapezium, Rhombus and Kite. • To verify the midpoint theorem for a triangle. • Surface Area and
• To recall the properties of Volume
• To verify that the quadrilateral formed by
parallelogram related to sides, angles Syllabus for Term-II
joining the mid points of the sides of a
• Quadrilaterals
and diagonals. quadrilateral taken in order, is a parallelogram.
• Circles
• To learn the properties of • Constructions
Parallelogram, Rectangle, Square and • Surface Area and
Rhombus. Volume
• To learn mid-point theorem & its • Polynomials
application. • Probability
• Application of converse of midpoint
theorem.
Circles • To define and draw circle, radius of AV Class/ Geogebra
circle, centre, diameter.
• To prove the results related to chords, angle at
• To learn chord, arc, secant, sector, the centre and perpendicular from centre to a
segment of circles. chord etc.
• To prove various theorems and learn MA
different properties of circles.
Course
Month Learning Outcomes Activity/Art integration Portion for assessment
description
• To do the problems based on various • To prove by paper folding method that the
theorems of circles. angles in the same segment of a circle are
equal.
• To know cyclic quadrilateral, as all
vertices are on the same circle. • To prove by paper folding that angle
subtended by a chord on the centre is twice of
• Opposite angles of a cyclic
the angle subtended by the same chord on the
quadrilateral are supplementary.
remaining part of the circle.
ART INTEGRATION
• To make a mandala art painting. (4.1.1.9)
December December 22 -as National Mathematics Day – Inside/Outside Activities to be carried out.
Constructions • To construct bisectors of line
segments and angles of measure 60°,
90°, 45° etc.
• To develop skill to construct
different types of triangles
• To construct a triangle given its base,
sum/difference of the other two sides
and one base angle.
Surface area • To understand area and volume of MA
and volume different geometrical shapes, area as
• Model making of solid shapes and determine
a surface and volume as space
their LSA/TSA/Volume etc.
occupied by the body.
• To derive formula for CSA of a cone and
cylinder.
Course
Month Learning Outcomes Activity/Art integration Portion for assessment
description
• To know surface area of cuboids, OUTDOOR ACTIVITY:
cube, cylinder, cone, sphere
• To compare the Volume of a cone and a right
(including hemispheres).
circular cylinder of same radius and height.
• Volume of cuboids, cubes, cones, ART INTEGRATION
cylinders and spheres (including
hemispheres). • Story telling activity: A real-life situation can
be given. Based on that, various conceptual
questions can be asked based on the concept: A
situation can be told as a short story where the
different shapes are being used. Students
would be then asked to answer different
questions from that real life situation. (4.1.4.4)
January Probability • Expectation from different events. MA
• To understand probability - an • To find the probability of getting a head or tail
experimental approach. when two coins are tossed simultaneously.
• To find empirical probability of an
event from day to day life. ART INTEGRATED PROJECT
Polynomials • Revision
Revision for PT-III
February Revision • Entire Syllabus of Term-II
You might also like
- Mathematics: Term-I (Class-X) MathematicsDocument8 pagesMathematics: Term-I (Class-X) MathematicsNamish MainiNo ratings yet
- Math HL baseline test syllabus overviewDocument9 pagesMath HL baseline test syllabus overviewNoyonika DeyNo ratings yet
- CLMC (Africa) 2022: Curriculum Guide: July 14 2021Document4 pagesCLMC (Africa) 2022: Curriculum Guide: July 14 2021Onyinyechi SamuelNo ratings yet
- U017 Edexcel GCSE Maths Chart P2Document1 pageU017 Edexcel GCSE Maths Chart P2al-gazNo ratings yet
- Wced English Mathematics - 2024 Weekly Teaching Plan - Grade 9Document6 pagesWced English Mathematics - 2024 Weekly Teaching Plan - Grade 9carlabeukes1No ratings yet
- Numerical and Abstract Reasoning: Mathematics GuideDocument17 pagesNumerical and Abstract Reasoning: Mathematics GuideKazi Ayman RAHMANNo ratings yet
- Class-6 Maths WorkbookDocument12 pagesClass-6 Maths Workbookneomatrix70No ratings yet
- Ralli International School X MATHEMATICS (041/241) Yearly Planner & Assessment Syllabus (2022-23) Total Chapters: 14 Book: Ncert Text BookDocument6 pagesRalli International School X MATHEMATICS (041/241) Yearly Planner & Assessment Syllabus (2022-23) Total Chapters: 14 Book: Ncert Text BookTanmay AryaNo ratings yet
- PEDAGOGICAL PLAN FOR Mathematics (2020-21) CLASS – IXDocument5 pagesPEDAGOGICAL PLAN FOR Mathematics (2020-21) CLASS – IXAnnanya YaduvanshiNo ratings yet
- LISA Topics For Entering Grade 11 (Year 7)Document2 pagesLISA Topics For Entering Grade 11 (Year 7)peter.trubinNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Further Pure Mathematics Term 1 GFSDocument1 pageEdexcel Further Pure Mathematics Term 1 GFSMohammed Aayan PathanNo ratings yet
- Math Answers Lesson 2Document3 pagesMath Answers Lesson 2Maria Victoria Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Math 1 CompetenciesDocument3 pagesMath 1 CompetenciesRey Almodiel SolitarioNo ratings yet
- Mathematics (51) : AimsDocument10 pagesMathematics (51) : Aims28 Keshav Raj VII CNo ratings yet
- 1.210 ATP 2023-24 GR 9 Maths FinalDocument6 pages1.210 ATP 2023-24 GR 9 Maths FinalDirk SwanepoelNo ratings yet
- FunctionsDocument29 pagesFunctionsmartinajoan1No ratings yet
- Santos, John Albert M. - Cee2 Activity No.3Document2 pagesSantos, John Albert M. - Cee2 Activity No.3John Albert SantosNo ratings yet
- Physics Syl Lab UsDocument8 pagesPhysics Syl Lab UsABHINAV KUMAR SHUKLANo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument15 pagesSyllabusvedantacharya1829No ratings yet
- Maths Curriculum Yr 8Document1 pageMaths Curriculum Yr 8Heba HebaNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Curriculum Coverage For Year End 2022-23Document12 pagesYear 10 Curriculum Coverage For Year End 2022-23Romesa ZahraNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Atp 2023-24 Mathematics With DatesDocument4 pagesGrade 9 Atp 2023-24 Mathematics With Datesnare50% (2)
- y9 Math WorksheetDocument111 pagesy9 Math Worksheetanita_83No ratings yet
- Silibus Math OlympiadDocument1 pageSilibus Math OlympiadRudy HidayatNo ratings yet
- Maths IGCSE Scheme of Work 0580 - 2010Document6 pagesMaths IGCSE Scheme of Work 0580 - 2010Yenny TigaNo ratings yet
- NIMCET Syllabus 2020: List of Subjects Subject List of TopicsDocument3 pagesNIMCET Syllabus 2020: List of Subjects Subject List of TopicsJalaj PandeyNo ratings yet
- I-EMC Syllabus Junior: Subject Topic Subtopic ExplanationDocument1 pageI-EMC Syllabus Junior: Subject Topic Subtopic ExplanationHerwansyahNo ratings yet
- Topic 1)Document2 pagesTopic 1)api-63318741No ratings yet
- Here are the answers to the direct proportion questions:1. A = 2B2. 1. V = 4M 2. T = 5S 3. Y = 17X 4. H = 12M 5. N = 2P 3. 1. C = 1.5B 2. B = 18Document112 pagesHere are the answers to the direct proportion questions:1. A = 2B2. 1. V = 4M 2. T = 5S 3. Y = 17X 4. H = 12M 5. N = 2P 3. 1. C = 1.5B 2. B = 18Tanvir ButaNo ratings yet
- Math textbook contents and chapter overviewDocument15 pagesMath textbook contents and chapter overviewJ SoujanyaNo ratings yet
- Math 110 Syllabus Term 2 Functions Limits DerivativesDocument4 pagesMath 110 Syllabus Term 2 Functions Limits DerivativesMạnh QuangNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Math+110.docx.-3Document4 pagesSyllabus Math+110.docx.-3هبوب الريحNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem Syllabus (Math Ed 415 Mathematics)Document6 pages1st Sem Syllabus (Math Ed 415 Mathematics)graman65No ratings yet
- Exam Topics To Focus On Grade Ten 1793Document2 pagesExam Topics To Focus On Grade Ten 1793lerafi1309No ratings yet
- Extended Learner GuideDocument30 pagesExtended Learner GuideArminda Sofia AzevedoNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Math (India) : Con Nue Number SystemsDocument2 pagesClass 9 Math (India) : Con Nue Number Systemsavijitcu2007No ratings yet
- Maths Igcse Scheme of Work 0580 - 2010Document6 pagesMaths Igcse Scheme of Work 0580 - 2010Yenny Tiga100% (2)
- MYP G9 Syllabus 2019-20 - MathematicsDocument3 pagesMYP G9 Syllabus 2019-20 - MathematicsLlama jennerNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Coverage Mathematics 2022-23Document3 pagesSyllabus Coverage Mathematics 2022-23Ayyan NomanNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Lower Secondary Long Term Plan MathsDocument4 pagesYear 8 Lower Secondary Long Term Plan MathsMahamed AbusnenaNo ratings yet
- AQA C1 ChecklistDocument2 pagesAQA C1 Checklist965161191No ratings yet
- Handout CS F222 2018Document3 pagesHandout CS F222 2018Tussank GuptaNo ratings yet
- Differential Geometry: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument12 pagesDifferential Geometry: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchrachitNo ratings yet
- 3rd Form Scheme of Work Topic GuideDocument5 pages3rd Form Scheme of Work Topic GuideEustace DavorenNo ratings yet
- NATA SYLLABUSDocument3 pagesNATA SYLLABUSPhanindra B RNo ratings yet
- Revision Checklist For o Level Mathematics 4024 FinalDocument15 pagesRevision Checklist For o Level Mathematics 4024 FinalHussain TafazzulNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Schemes of Work Form Two 2021: New General Mathematics Book 2Document9 pagesMathematics Schemes of Work Form Two 2021: New General Mathematics Book 2Praise MafusireNo ratings yet
- Compare Mathematics Curricula of 4 Countries in 40 CharactersDocument5 pagesCompare Mathematics Curricula of 4 Countries in 40 CharactersJoyce May MendezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 PDFDocument44 pagesChapter 01 PDFKanishka SINGHNo ratings yet
- Pre Calculus TopicsDocument2 pagesPre Calculus TopicsAbheeshekNo ratings yet
- The Thinking Classroom PPT NewDocument45 pagesThe Thinking Classroom PPT NewAnonymous JzEb8CXErNo ratings yet
- BS Maths (Sem7)Document5 pagesBS Maths (Sem7)abdullahnasir22004No ratings yet
- Territorial Army SyllabusDocument2 pagesTerritorial Army Syllabusऋषभ यादवNo ratings yet
- 200+ Maths Exploration IdeasDocument2 pages200+ Maths Exploration IdeasShruti KabraNo ratings yet
- ATP 2023-24 GR 8 Maths FinalDocument6 pagesATP 2023-24 GR 8 Maths FinalJabulane SitholeNo ratings yet
- Term - Wise Syllabus Session-2019-20 Class-VIII Subject: MathematicsDocument53 pagesTerm - Wise Syllabus Session-2019-20 Class-VIII Subject: MathematicsDebayan MitraNo ratings yet
- QCDocument136 pagesQCpostscriptNo ratings yet
- Geometry PDFDocument14 pagesGeometry PDFgladys manaliliNo ratings yet
- 8th Maths Unit 1 Lesson Plan by Ravi SankarDocument7 pages8th Maths Unit 1 Lesson Plan by Ravi SankarPayal Rajat SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Objective Physics For NEET Vol 1 2022 - NodrmDocument897 pagesObjective Physics For NEET Vol 1 2022 - NodrmDhreeti Jain100% (1)
- Citibank IndiaDocument2 pagesCitibank IndiamukeshNo ratings yet
- AzureDocument58 pagesAzurezeeshankaizerNo ratings yet
- 9 Ca Ix 202122Document11 pages9 Ca Ix 202122zeeshankaizerNo ratings yet
- Phylum PriferaDocument3 pagesPhylum PriferazeeshankaizerNo ratings yet
- The Handbook of English For Specific Purposes: Edited by Brian Paltridge and Sue StarfieldDocument50 pagesThe Handbook of English For Specific Purposes: Edited by Brian Paltridge and Sue StarfieldEmiliano AcevedoNo ratings yet
- Bio205 2015spring Fry 1 - Bio 205 Syllabus Evolution 2015Document4 pagesBio205 2015spring Fry 1 - Bio 205 Syllabus Evolution 2015api-283084607No ratings yet
- Oet Reading Part A Additional - GlucomaDocument8 pagesOet Reading Part A Additional - Glucomaafacean25% (8)
- MPEGRepair HDDocument173 pagesMPEGRepair HDMAHTorresNo ratings yet
- 3rd Periodical Exam Math 9Document1 page3rd Periodical Exam Math 9DhangManongas-LlaboreVete100% (2)
- Leyte Department of Education Personal Development DocumentDocument2 pagesLeyte Department of Education Personal Development DocumentMaricar Cesista NicartNo ratings yet
- Review On Internal Combustion Engine Vibrations and MountingsDocument12 pagesReview On Internal Combustion Engine Vibrations and MountingsSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Developing Managers and LeadersDocument48 pagesDeveloping Managers and LeadersMazen AlbsharaNo ratings yet
- Uworld 2Document3 pagesUworld 2samNo ratings yet
- Born 1925 EngDocument30 pagesBorn 1925 EngFranz SchindlerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Logics and Critical Thinking SlidesDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Logics and Critical Thinking SlidesMKNo ratings yet
- Sample Reflective SummaryDocument3 pagesSample Reflective SummaryRicksen TamNo ratings yet
- Rufino Luna, Et - Al V CA, Et - Al (G.R. No. 100374-75)Document3 pagesRufino Luna, Et - Al V CA, Et - Al (G.R. No. 100374-75)Alainah ChuaNo ratings yet
- Lo Visual en YourcenarDocument272 pagesLo Visual en YourcenarJosé Ignacio Herrera LamasNo ratings yet
- History of Anglo Saxon Literature English Assignment NUML National University of Modern LanguagesDocument15 pagesHistory of Anglo Saxon Literature English Assignment NUML National University of Modern LanguagesMaanNo ratings yet
- Lana Del Rey - Born To Die AnalysisDocument3 pagesLana Del Rey - Born To Die AnalysisNajat HachemNo ratings yet
- Rule MiningDocument2 pagesRule Miningravi ramaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Balance of PaymentsDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Balance of PaymentsMurtaza JamaliNo ratings yet
- Full Test Bank For Industrial Organizational Psychology An Applied Approach 8Th Edition Michael G Aamodt 2 PDF Docx Full Chapter ChapterDocument33 pagesFull Test Bank For Industrial Organizational Psychology An Applied Approach 8Th Edition Michael G Aamodt 2 PDF Docx Full Chapter Chapterbumbardisospore.reejvz100% (12)
- Curcuma y MetforminaDocument8 pagesCurcuma y MetforminaJorge Luis Plasencia CubaNo ratings yet
- University of Waterloo Thesis RepositoryDocument5 pagesUniversity of Waterloo Thesis Repositoryafknkzkkb100% (2)
- The New McGuffey Fourth Reader by VariousDocument128 pagesThe New McGuffey Fourth Reader by VariousGutenberg.orgNo ratings yet
- Political Science Paper Analyzes Society and Polity in IndiaDocument231 pagesPolitical Science Paper Analyzes Society and Polity in IndiaAhmed0% (1)
- Introduction to Accounting BasicsDocument14 pagesIntroduction to Accounting BasicsJunaid IslamNo ratings yet
- Nmat Test Result-1017051213Document1 pageNmat Test Result-1017051213Dushyant SarvaiyaNo ratings yet
- Right Triangle Activity For Quiz #2 - RetakeDocument4 pagesRight Triangle Activity For Quiz #2 - Retakeapi-16147700No ratings yet
- BCOM SyllabusDocument67 pagesBCOM SyllabusvjayarajuNo ratings yet
- Case Study Walking The WalkDocument3 pagesCase Study Walking The Walk9899 Mariam Akter Marketing100% (1)
- CDN ED Psychology Themes and Variations 3rd Edition Weiten Solutions Manual 1Document35 pagesCDN ED Psychology Themes and Variations 3rd Edition Weiten Solutions Manual 1beverly100% (37)
- Scada/Ems/Dms: Electric Utilities Networks & MarketsDocument12 pagesScada/Ems/Dms: Electric Utilities Networks & MarketsdoquocdangNo ratings yet