Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assets Printing
Uploaded by
Irtiza AbbasCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assets Printing
Uploaded by
Irtiza AbbasCopyright:
Available Formats
Property, Plant & Equipment
(PPE): Definitions
PPE are (per IAS-16) IAS 16 –Additional
-tangible items that are Definitions
-held for use in the production or supply of goods or services, -Depreciation
for rental to others, or for administrative purposes; and -Depreciable amount
-are expected to be used during more than one period -Cost
where an asset is (per the framework): -Fair Value
-a resource -residual value
-controlled by an entity, -useful life
-as a result of past events, and -carrying amount
-from which future economic benefits are expected to flow to
the entity
Recognition criteria
-probable that future economic benefits will flow to the entity
-cost may be reliable measured
Initial Measurement
Initial costs Subsequent Costs
Cash Fair Value Capitalise only if:
-All costs necessarily Asset swaps: - -the recognition criteria are met
incurred in bringing FV of asset given up, unless (if not met, cost must be
the asset to a FV of asset received is more expensed)
location and putting clearly evident (or if it’s the
only FV available) Replacement of parts and repeat
it into a condition
-If no FV available, use major inspections: -
enabling it to be used
carrying amount of asset derecognise old carrying amount
as intended by
given up -capitalise new cost (generally as
management
a separate part)
Subsequent Measurement
In general Changes in accounting estimate
-The depreciable amount must be occur if any of the following are changed:
depreciated on a systematic basis over -the estimated useful life
the estimated useful life of the asset -the method of depreciation
-The method used should reflect the -the residual value
pattern in which economic benefits are -the estimated cost of dismantling,
expected to be generated from the asset removing or restoring items of PPE
–The depreciation charge is expensed
unless it is capitalised to another asset See IAS-8 for more details
Measurement Models
Cost Model Revaluation model:
Calculation of the carrying amount: Calculation of the carrying amount:
-cost -fair value on date of revaluation
-less accumulated depreciation -less subsequent accumulated depreciation
-less accumulated impairment losses -less subsequent accumulated impairment losses
The rule: an asset may be written down The rule: the asset may be valued at its fair value (if
below HCA, but may never be revalued greater/ less than its HCA)
above its HCA
Increase in value: debit: asset (FV-ACA); credit:
Increase in value: previous impairment income (to extent reverses previous decrease: HCA-
reversed debit: asset; credit: reversal of ACA); credit: revaluation surplus (FV-HCA)
impairment loss (Income)
-limited to the carrying amount that it Decrease in value: debit: RS (to the extent reverses
would have had had there never been an previous increases: ACA-HCA); debit: expense (HCA-
impairment loss (i.e. its historical FV) credit: asset (FV-ACA)
carrying amount) The revaluation surplus: -
Decrease in value: impairment transferred annually to retained earnings (amount
debit: Impairment loss (Expense); credit: transferred equals after tax effect on profits as a
asset result of increased depreciation) OR
-transferred to RE when asset is fully depreciated
OR
-transferred to RE when asset is disposed-off.
Disclosures
General Disclosures: SOFP related disclosures: Income statement related
Disclosures needed -Reconciliation between opening & closing disclosures:
for: balances -Depreciation
-break-down of these balances into gross -Profit or loss on disposals
-Depreciation methods
carrying amount and accumulated –Increase or decrease in
-Rates (or useful lives) depreciation & Impairment losses RS
-Cost or revaluation -Tax effect of creation or
method If revaluation model, also increase in RS
-carrying amount using cost model -Transfer from RS to RE
-basis used for revaluation -Any restriction on
- valuer independent distributions to
-Reversal of Revaluation Surplus (RS) shareholders
-Impairment loss expensed
- Increase in/creation of RS
- Reversal of impairment loss
If cost model used, also
-the FV
Inventory Valuation:
Lower of Cost or NRV
Cost Net realizable value:
Calculation technique Calculation:
-Actual -Estimated selling price
-Standard; or Less: estimated costs to complete
-Retail method Less: estimated selling costs
Includes Excludes
-the general rule: costs that are incurred -abnormal wastage; storage costs (unless
in order to bring the asset to its present necessary to the production process);
location and condition administrative expenses that do not
-examples include: raw materials; labour; contribute to the general rule; selling
variable manufacturing overheads; fixed costs; transport costs outwards;
manufacturing overheads; transport recoverable transaction taxed
costs inwards; non-refundable taxes
Measurement of Inventory Movements
If goods are similar: use either If goods are not similar: use
-Weighted Average (WA) method -Specific Identification (SI) method
-First-in-first-out (FIFO) method
Disclosures
General Disclosures: SOFP related disclosures: Income statement related
Disclosures needed for: -Carrying amount in each disclosures:
-Accounting policies category of inventory -Amount of inventory
(materials, WIP, finished recognized as an expense
applied
goods, production (usually cost of sales/cost
-Inventory remaining on supplies, merchandise) of goods sold)
statement of financial and in total -Amount of write-downs
position -Carrying amount of any to NRV or other losses
-Inventory costs inventory measured at fair -Amount of any write-
recognized in profit or loss value less costs to sell down reversals
-Carrying amount of -Circumstances that
inventory pledged as resulted in reversals
collateral for liabilities
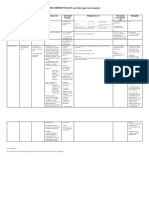
Property
Owner-occupied (Follow IAS-16) Investment Property (Follow IAS-40)
-Land/ building/ both -Land/ building/ both
-Held by owner or lessee under a finance -Held by owner or lessee under a finance
lease lease
-For use in supply of goods/ services or -To earn rentals or for capital
for admin purposes appreciation
Recognition Measurement
-Same as for PPE (IAS-16) -Initial measurement: cost
R -Definition & recognition criteria -Subsequent measurement: choose between 2 models
e must be met
-Subsequent expenditure: normal capitalization rules
c (IAS-16)
Initial Measurement -Transfer in/ out (5 possibilities)
o -Disposals/ purchases (IAS-16)
-Cost
g -Including transaction costs -Impairments (IAS 36)
n
i Subsequent Measurement
t -Cost model or fair value model
-You can choose any model; except IAS40.34: properties held under operating lease and
i classified as investment property must use fair value model (i.e. no choice)
o -All property to be measured using the same model
n
Cost model Fair Value model
-IFRS 5: if available for sale; or -Changes in FV to be recognized in P/L
-IAS 16: for all other assets -If FV becomes no longer available, then last
& known FV remains the CA until a new FV is
available
M Change in Use Situation Accounting
e From investment property (FVM) Owner occupies the Deemed cost in IAS 16 or IAS 2 is FV
to owner-occupied property or to property or begins to at the date of change in use
a inventory develop it for sale
s From owner-occupied property in End of owner-occupation Depreciation to the date of change;
IAS 16 to investment property the difference between carrying
u (FVM) in IAS 40 amount & FV is accounted for
r according to the revaluation in IAS
16
e
From inventory in IAS-2 to Owner enters into an Difference between IAS 2 carrying
m investment property (FVM) in IAS operating lease with a amount and IAS 40 FV is recognized
40 third party in P/L
e
In progress investment property Owner finish construction Difference between carrying
n (CM) in IAS 40 to investment or development amount & FV is recognized in P/L
t property (FVM) in IAS 40
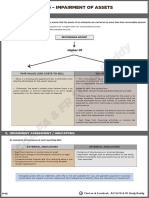
Impairment of Assets
There should be an annual ‘test of impairment’ with the purpose of identifying possible
impairments. Calculate the: carrying amount (CA) and recoverable amount (RA)
If the CA>RA = Impairment
Carrying amount Recoverable amount Impairment loss
per statement of Greater of: ACA-RA:
financial position: -value in use or -ACA>HCA: Debit RS
-cost or fair value -fair value less costs to sell -HCA>RA: debit IL
-less ‘accumulated
depreciation and Calculated if:
-test of impairment suggests impairment
impairment losses’
-intangible asset that:
- has indefinite useful life
-is not available for use
-is goodwill
Fair value less costs to sell Value in use
Amount obtainable in an arm’s length The present value of estimated future cash
transaction between knowledgeable, willing flows from:
parties -use and
Less -disposal at end of useful life
Disposal costs Exclude the following cash flows:
-Financing
-Tax
-Outflows in respect of obligations already
recognized as liabilities
Estimated future cash flows Appropriate discount rate
Use cash flows based on managements’ best -Pre-tax
estimated projections: -Market related risk free rate
- Short-term projections (less than 5 yrs): -Adjusted for risks specific to the asset
approved budgets only
-Long-term projections (beyond 5 years):
extrapolate the approved budget using a
justifiable growth rate (generally a stable/
declining growth rate)
Test of Impairment
External information Internal information
-Significant decrease in market value -Obsolescence
-Significant adverse current/ future changes -Physical damage
in the market in which the asset is used - Adverse current/ future changes in usage of the
-Increase in market interest rates (decreases asset
value in use) -Actual profits and/ or cash flows worse than
-Carrying amount of business net assets > budgeted
market capitalization etc. -Net cash outflows or losses becomes apparent
when looking at figures in aggregate (e.g. past +
current; current + future; past + current + future)
Recognition
Impairment loss Reversal of impairment loss
If cost model is used: If cost model is used:
debit: impairment loss (expense) debit: accumulated depreciation and impairment
credit: accumulated depreciation and losses
impairment losses credit: impairment loss (income)
Or Or
If revaluation model is used: If revaluation model is used:
where there is a revaluation surplus debit: up to HCA:
revaluation surplus (to the extent of the debit: accumulated depreciation & impairment
balance therein) and credit: cost losses and
credit: reversal of impairment loss (income)
If the drop in value exceeds the revaluation
surplus balance: debit: impairment loss for any amounts above HCA:
(expense) (with any excess) debit: cost and
credit: accumulated depreciation and credit: revaluation surplus
impairment losses
Depreciation thereafter: a new Depreciation thereafter: a new depreciable
depreciable amount is calculated (after amount is calculated (after deducting the
deducting the accumulated impairment remaining accumulated impairment loss)
loss) which should be depreciated over which should be depreciated over the
the remaining useful life of the asset. remaining useful life of the asset.
Inventory Valuation:
Lower of Cost or NRV
Cost Net realizable value:
Calculation technique Calculation:
-Actual -Estimated selling price
-Standard; or Less: estimated costs to complete
-Retail method Less: estimated selling costs
Includes Excludes
-the general rule: costs that are incurred -abnormal wastage; storage costs (unless
in order to bring the asset to its present necessary to the production process);
location and condition administrative expenses that do not
-examples include: raw materials; labour; contribute to the general rule; selling
variable manufacturing overheads; fixed costs; transport costs outwards;
manufacturing overheads; transport recoverable transaction taxed
costs inwards; non-refundable taxes
Measurement of Inventory Movements
If goods are similar: use either If goods are not similar: use
-Weighted Average (WA) method -Specific Identification (SI) method
-First-in-first-out (FIFO) method
Disclosures
General Disclosures: Balance sheet related Income statement related
Disclosures needed for: disclosures: disclosures:
-Accounting policies -Carrying amount in each -Amount of inventory
category of inventory recognized as an expense
applied
(materials, WIP, finished (usually cost of sales/cost
-Inventory remaining on goods, production of goods sold)
statement of financial supplies, merchandise) -Amount of write-downs
position and in total to NRV or other losses
-Inventory costs -Carrying amount of any -Amount of any write-
recognized in profit or loss inventory measured at fair down reversals
value less costs to sell -Circumstances that
-Carrying amount of resulted in reversals
inventory pledged as
collateral for liabilities
You might also like
- Pas 16 Property Plant and EquipmentDocument4 pagesPas 16 Property Plant and EquipmentKristalen ArmandoNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Theories ReviewerDocument18 pagesPart 1 Theories ReviewerNey Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Ind As - 16Document11 pagesInd As - 16OopsbymistakeNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Revaluation and ImpairmentDocument3 pagesReviewer Revaluation and ImpairmentMei Leen DanielesNo ratings yet
- Accounting Standard Summary Notes Group IDocument15 pagesAccounting Standard Summary Notes Group ISrinivasprasadNo ratings yet
- Subsequent Measurement of Property, Plant and Equipment: Cost ModelDocument6 pagesSubsequent Measurement of Property, Plant and Equipment: Cost ModelLorraine Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- PAS Recognition Measurement Increase in Carrying Amount Due To Revaluation Derecognition Presentation and DisclosureDocument3 pagesPAS Recognition Measurement Increase in Carrying Amount Due To Revaluation Derecognition Presentation and DisclosureTimothy james PalermoNo ratings yet
- Intangible AssetsDocument3 pagesIntangible Assetsgreat angelNo ratings yet
- AS 10 - Property Plant and Equipment: Recognition CriteriaDocument5 pagesAS 10 - Property Plant and Equipment: Recognition CriteriaAshutosh shriwasNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Theories ReviewerDocument19 pagesPart 1 Theories ReviewerNey Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12Document6 pagesLesson 12Jamaica bunielNo ratings yet
- FA2A SU3 Property Plant and EquipmentDocument3 pagesFA2A SU3 Property Plant and EquipmentHasan EvansNo ratings yet
- Fixed AssetDocument20 pagesFixed AssetMohamed Ahmed RammadanNo ratings yet
- Ppe Acctng203Document5 pagesPpe Acctng203PgumballNo ratings yet
- Comparison 7.5 ĐiểmDocument23 pagesComparison 7.5 Điểmtuân okNo ratings yet
- FA2A SU5 Impairment of AssetsDocument4 pagesFA2A SU5 Impairment of AssetsHasan EvansNo ratings yet
- Pas 36: Impairment of Assets: ObjectiveDocument6 pagesPas 36: Impairment of Assets: ObjectiveLEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- AFFS w3Document21 pagesAFFS w3Thi Kim Ngan TranNo ratings yet
- Fixed Assets IAS 16Document25 pagesFixed Assets IAS 16zulfi100% (2)
- Aud Application 2 - Handout 6 Revaluation (UST)Document5 pagesAud Application 2 - Handout 6 Revaluation (UST)RNo ratings yet
- Accountancy Review Center (ARC) of The Philippines Inc.: Student HandoutsDocument5 pagesAccountancy Review Center (ARC) of The Philippines Inc.: Student HandoutsRNo ratings yet
- Module 7 13 No 11Document6 pagesModule 7 13 No 11LEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Tangible and Intangible Non Current Assets Lecture NotesDocument20 pagesTangible and Intangible Non Current Assets Lecture NotesDivya NandiniNo ratings yet
- Reporting of Long-Lived Assets/PPE/Fixed AssetsDocument6 pagesReporting of Long-Lived Assets/PPE/Fixed AssetsAnishaSapraNo ratings yet
- Summary of IFRSDocument32 pagesSummary of IFRSFarwa Samreen67% (3)
- SBR - Chapter 4Document6 pagesSBR - Chapter 4Jason KumarNo ratings yet
- Week 9 Impairment of Non-Current Assets (MFRS 136) For StudentsDocument32 pagesWeek 9 Impairment of Non-Current Assets (MFRS 136) For StudentsAnselmNo ratings yet
- Property, Plant and Equipment (IAS 16) : Haroon Arshad Butt IcmapDocument16 pagesProperty, Plant and Equipment (IAS 16) : Haroon Arshad Butt IcmapHaroon A ButtNo ratings yet
- Property, Plant Equipment-IAS 16Document19 pagesProperty, Plant Equipment-IAS 16Taimur ShahidNo ratings yet
- 01 - Finacc - Property, Plant, and EquipmentDocument5 pages01 - Finacc - Property, Plant, and EquipmentAbigail PadillaNo ratings yet
- Mfrs 116: Property, Plant & Equipment: Prepared By: Mohd Sobre Bin IsmailDocument27 pagesMfrs 116: Property, Plant & Equipment: Prepared By: Mohd Sobre Bin IsmailBrenda JessNo ratings yet
- Pas 16Document20 pagesPas 16Princess Jullyn ClaudioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 IAS 36 Impairment of AssetsDocument13 pagesChapter 17 IAS 36 Impairment of AssetsKelvin Chu JYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document2 pagesChapter 4Azi LheyNo ratings yet
- Cfas Pas 1-16Document8 pagesCfas Pas 1-16Sagad KeithNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting & ControlDocument4 pagesCost Accounting & ControlQueeny CuraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - NotesDocument2 pagesChapter 4 - NotesLovely CabardoNo ratings yet
- ICAIEKM Material 180116Document57 pagesICAIEKM Material 180116INTER SMARTIANSNo ratings yet
- Impairment-Of-Assets by Adeeb HassanDocument24 pagesImpairment-Of-Assets by Adeeb HassanadeebNo ratings yet
- Acc470 Ias 36Document33 pagesAcc470 Ias 36Naji EssaNo ratings yet
- E-Portfolio: PAS 36 - Impairment of AssetsDocument3 pagesE-Portfolio: PAS 36 - Impairment of AssetsKaye NaranjoNo ratings yet
- TA.2011 - Revaluation & ImpairmentsDocument22 pagesTA.2011 - Revaluation & ImpairmentsJay-L TanNo ratings yet
- Property, Plant Equipment-IAS 16Document21 pagesProperty, Plant Equipment-IAS 16Shoaib SakhiNo ratings yet
- IAS 16 PPE - LectureDocument11 pagesIAS 16 PPE - LectureBeatrice Ella DomingoNo ratings yet
- Tudy Buddy: Ias 36 - Impairment of AssetsDocument2 pagesTudy Buddy: Ias 36 - Impairment of AssetsAbdullah Al Amin MubinNo ratings yet
- Ind AS 16 - RBM (WBS)Document7 pagesInd AS 16 - RBM (WBS)KRISHNENDU JASHNo ratings yet
- Summary - Ppe - ImpairmentDocument15 pagesSummary - Ppe - ImpairmentLorelie OrtegaNo ratings yet
- MEASUREMENT BASES and Other Important RemindersDocument2 pagesMEASUREMENT BASES and Other Important RemindersShaina Monique RangasanNo ratings yet
- MEASUREMENT BASES and Other Important RemindersDocument2 pagesMEASUREMENT BASES and Other Important RemindersShaina Monique RangasanNo ratings yet
- Accounting Standard 2Document12 pagesAccounting Standard 2Norfarah AzlieyanaNo ratings yet
- Fin Mar ReviewerDocument2 pagesFin Mar ReviewerPixie CanaveralNo ratings yet
- Impairment of Non Current Assets - Ias 36: - Impairment Is A Reduction To The Recoverable Amount of An Asset or ADocument89 pagesImpairment of Non Current Assets - Ias 36: - Impairment Is A Reduction To The Recoverable Amount of An Asset or ATram NguyenNo ratings yet
- Summary - IAS 36 by HKDocument3 pagesSummary - IAS 36 by HKaimanraees10No ratings yet
- Tax and Accounting 5Document2 pagesTax and Accounting 5Jerrom DuqueNo ratings yet
- Ifrs at A Glance: IAS 16 Property Plant and EquipmentDocument4 pagesIfrs at A Glance: IAS 16 Property Plant and EquipmentDimitris PapadopoulosNo ratings yet
- Ifrs Vs UsgaapDocument2 pagesIfrs Vs UsgaapPrachi JainNo ratings yet
- Ifrs at A Glance: IAS 16 Property Plant and EquipmentDocument4 pagesIfrs at A Glance: IAS 16 Property Plant and EquipmentRjan LGNo ratings yet
- 08 Ias 2Document3 pages08 Ias 2Irtiza AbbasNo ratings yet
- 06 Ifrs 5Document3 pages06 Ifrs 5Irtiza Abbas100% (1)
- 07 Segment Reporting 1Document4 pages07 Segment Reporting 1Irtiza AbbasNo ratings yet
- 07 Segment Reporting 1Document4 pages07 Segment Reporting 1Irtiza AbbasNo ratings yet
- 03 Ias 20Document3 pages03 Ias 20Irtiza AbbasNo ratings yet
- Title Name Corporate Governance, Business Laws & Ethics: Qaiser IqbalDocument12 pagesTitle Name Corporate Governance, Business Laws & Ethics: Qaiser IqbalMuzammil LiaquatNo ratings yet
- Industry and Community Project: Jacobs - Creating A Smart Systems Approach To Future Cities Project OutlineDocument14 pagesIndustry and Community Project: Jacobs - Creating A Smart Systems Approach To Future Cities Project OutlineCalebNo ratings yet
- Journal Articles: Types of JournalsDocument4 pagesJournal Articles: Types of JournalsOtieno SteveNo ratings yet
- O Repensar Da Fonoaudiologia Na Epistemologia CienDocument5 pagesO Repensar Da Fonoaudiologia Na Epistemologia CienClaudilla L.No ratings yet
- POLYTHEOREMSDocument32 pagesPOLYTHEOREMSYen LeeNo ratings yet
- 100 IdeasDocument21 pages100 IdeasNo ID100% (1)
- Line Integrals in The Plane: 4. 4A. Plane Vector FieldsDocument7 pagesLine Integrals in The Plane: 4. 4A. Plane Vector FieldsShaip DautiNo ratings yet
- 2018 H2 JC1 MSM Differential Equations (Solutions)Document31 pages2018 H2 JC1 MSM Differential Equations (Solutions)VincentNo ratings yet
- M.T Nautica Batu Pahat: Clean Product Tanker 4,497 BHPDocument1 pageM.T Nautica Batu Pahat: Clean Product Tanker 4,497 BHPSuper 247No ratings yet
- Singer 900 Series Service ManualDocument188 pagesSinger 900 Series Service ManualGinny RossNo ratings yet
- Basic Knowledge About WDM Principle ADocument92 pagesBasic Knowledge About WDM Principle AJosé LópezNo ratings yet
- Whitepaper ITES Industry PotentialDocument6 pagesWhitepaper ITES Industry PotentialsamuraiharryNo ratings yet
- Tugas Inggris Text - Kelas 9Document27 pagesTugas Inggris Text - Kelas 9salviane.theandra.jNo ratings yet
- Overview of Incorporation in CambodiaDocument3 pagesOverview of Incorporation in CambodiaDavid MNo ratings yet
- NSTP SlabDocument2 pagesNSTP SlabCherine Fates MangulabnanNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation Report For Practicum TraineesDocument2 pagesPerformance Evaluation Report For Practicum TraineesJ.S100% (3)
- Best of The Photo DetectiveDocument55 pagesBest of The Photo DetectiveSazeed Hossain100% (3)
- Menara PMB Assessment Criteria Score SummaryDocument2 pagesMenara PMB Assessment Criteria Score SummarySyerifaizal Hj. MustaphaNo ratings yet
- Fish Culture in Ponds: Extension Bulletin No. 103Document32 pagesFish Culture in Ponds: Extension Bulletin No. 103Bagas IndiantoNo ratings yet
- 1ST Term J1 Fine Art-1Document22 pages1ST Term J1 Fine Art-1Peter Omovigho Dugbo100% (1)
- Enhancing Guest Experience and Operational Efficiency in Hotels Through Robotic Technology-A Comprehensive Review.Document8 pagesEnhancing Guest Experience and Operational Efficiency in Hotels Through Robotic Technology-A Comprehensive Review.Chandigarh PhilosophersNo ratings yet
- SCC5-4000F Single ShaftDocument15 pagesSCC5-4000F Single ShaftudelmarkNo ratings yet
- Advanced Statistical Approaches To Quality: INSE 6220 - Week 4Document44 pagesAdvanced Statistical Approaches To Quality: INSE 6220 - Week 4picalaNo ratings yet
- A Vision System For Surface Roughness Characterization Using The Gray Level Co-Occurrence MatrixDocument12 pagesA Vision System For Surface Roughness Characterization Using The Gray Level Co-Occurrence MatrixPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Sco 8th Class Paper - B Jee-Main Wtm-15 Key&Solutions Exam DT 17-12-2022Document4 pagesSco 8th Class Paper - B Jee-Main Wtm-15 Key&Solutions Exam DT 17-12-2022Udaya PrathimaNo ratings yet
- Travelstart Ticket (ZA10477979) PDFDocument2 pagesTravelstart Ticket (ZA10477979) PDFMatthew PretoriusNo ratings yet
- E9 Đề khảo sát Trưng Vương 2022 ex No 1Document4 pagesE9 Đề khảo sát Trưng Vương 2022 ex No 1Minh TiếnNo ratings yet
- Wind Turbines - I. Al-BahadlyDocument664 pagesWind Turbines - I. Al-Bahadlykevin_leigh_1No ratings yet
- Amsterdam Pipe Museum - Snuff WorldwideDocument1 pageAmsterdam Pipe Museum - Snuff Worldwideevon1No ratings yet
- Datalogic tl46 A Manual - 230104 - 140343Document2 pagesDatalogic tl46 A Manual - 230104 - 140343Emmanuel Baldenegro PadillaNo ratings yet
- Elerick Ron Cynthia 1983 SouthAfricaDocument4 pagesElerick Ron Cynthia 1983 SouthAfricathe missions networkNo ratings yet