Professional Documents
Culture Documents
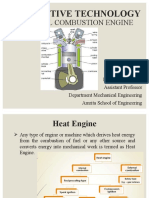
A Car Engine Generates Power From The Expansion of Compressed Air in A Contained Cylinder With The Help of Fuel That Is Why It
A Car Engine Generates Power From The Expansion of Compressed Air in A Contained Cylinder With The Help of Fuel That Is Why It
Uploaded by
21OT112- Huỳnh Gia KiệtOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A Car Engine Generates Power From The Expansion of Compressed Air in A Contained Cylinder With The Help of Fuel That Is Why It
A Car Engine Generates Power From The Expansion of Compressed Air in A Contained Cylinder With The Help of Fuel That Is Why It
Uploaded by
21OT112- Huỳnh Gia KiệtCopyright:
Available Formats
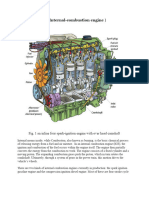
A car engine generates power from the expansion of compressed air in a contained
cylinder with the help of fuel that is why it's called as an internal combustion engine
before getting into the working let's see the main parts involved in the working of an
engine first the crankshaft this is the part which converts the linear motion of the piston to
a rotational force next the pistons and the piston rods the pistons will be pushed down by
the expansion of compressed air and turns the crankshaft and the valves which controls
the flow of air and fuel into the cylinders these vowels are driven by the intake camshaft
and the exhaust camshaft and the camshafts are driven by the crank itself using a timing
belt there will be idler pulleys and attention a pulley to hold.
The belt tight in place this here is the internal structure of a four-stroke inline 4-cylinder
dohc engine which is commonly found in most hatchback and sedan cars the four-stroke
engine should pass through four different strokes to complete one cycle to produce power
they are intake compression power and exhaust stroke the crank two camshaft ratio is 2 is
to 1 which means it will take to crank revolutions to complete one camshaft revolution
and the camshafts are designed in a responsive manner to open or closed based on the
corresponding strokes of each cylinder let's take a look at a single cylinder and see how a
four-stroke engine works.
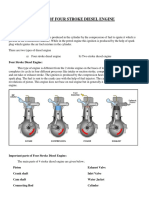
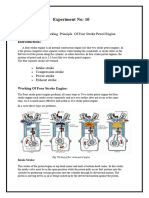
In detail in order to ignite the air fuel mixture a spark plug is used this will ignite the
compressed air fuel mixture with the help of an electrical spark we will take it down by
each stroke the intake stroke the inlet valve opens and the downward movement of the
piston creates a suction this pulls the air fuel mixture into the cylinder once the air fuel
mixture is in the cylinder compression stroke begins compressing the mixture at this time
both inlet and outlet valves stays closed at the end of compression stroke the air fuel
mixture is ignited by the spark plug the explosion exerts pressure and pushes the piston
down this is the power stroke.
Which produces power to the crank at the exhaust stroke the outlet valves opens and the
piston pushes out the burned gas the cycle starts again from intake stroke keeping the
engine running and produces power for a carburetor engine the air and fuel are mixed
inside the carburetor assembly and fed to the cylinders in the case of a fuel-injected
engine the fuel is injected into the intake manifold or directly into the cylinders since
only a power stroke produces power you may wonder how the engine turns continuously
well the answer is in the crank itself the flywheel and the crank counterweights provides
momentum which keeps the crankshaft from stopping immediately for a four-cylinder
engine considering any time instance one cylinder is always in power stroke which
produces more power and less vibrations comparing to a single cylinder engine and that
is how a car engine produces power and simple.
You might also like
- 2gnt 420a OverhaulDocument62 pages2gnt 420a OverhaulElsa Elizabeta Dekovic100% (1)
- Manual de Partes Motor John Deere 4024tDocument16 pagesManual de Partes Motor John Deere 4024tRobinson Guaneme60% (15)
- LV06 - Engines - Issue 1Document72 pagesLV06 - Engines - Issue 1Valentin Silvan Valentin SilvanNo ratings yet
- Two and Three Wheeler NotesDocument49 pagesTwo and Three Wheeler NotesAbishek AbhNo ratings yet
- (REHS0371) Installation and Initial Start Up Procedures For G3300 and G3400 EnginesDocument16 pages(REHS0371) Installation and Initial Start Up Procedures For G3300 and G3400 Enginesvictor.cipriani100% (1)
- Subaru Pinout ImprezaDocument4 pagesSubaru Pinout ImprezaWilliamZabaleta0% (1)
- ICE (Internal Combustion Engine)Document22 pagesICE (Internal Combustion Engine)johnlloydsantossssNo ratings yet
- Petrol EnginesoDocument7 pagesPetrol Enginesoapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Technical Description (Eport)Document4 pagesTechnical Description (Eport)api-284962336100% (1)
- Parts of An Automobile EngineDocument16 pagesParts of An Automobile EngineEric James CatanguiNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engine: Chapter Learning ObjectivesDocument17 pagesInternal Combustion Engine: Chapter Learning ObjectivesRahul KhatriNo ratings yet
- Ic EngineDocument27 pagesIc EngineSRL MECHNo ratings yet
- Essential For Engine OperationDocument13 pagesEssential For Engine OperationVõ Thanh LiêmNo ratings yet
- 1.FSAE Turbocharger Design and ImplementationDocument27 pages1.FSAE Turbocharger Design and ImplementationJoy NagNo ratings yet
- To: Mr. Tan Xiao Long, Technical Manager From: NG Hon Meng, Cadet Engineer Re: The Working of A Four-Stroke Engine Date: April, 8 2012Document1 pageTo: Mr. Tan Xiao Long, Technical Manager From: NG Hon Meng, Cadet Engineer Re: The Working of A Four-Stroke Engine Date: April, 8 2012Ng Hon MengNo ratings yet
- Engine Types and ClassificationsDocument16 pagesEngine Types and ClassificationsVõ Thanh Liêm100% (1)
- Basic Troubleshooting GuideDocument138 pagesBasic Troubleshooting GuideIrene J. HallNo ratings yet
- 2-Four and Two Stroke EnginesDocument27 pages2-Four and Two Stroke EnginesAHMADNo ratings yet
- Engine Part IDocument39 pagesEngine Part Iaashish koiralaNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 6Document5 pagesExperiment # 6Farhan AliNo ratings yet
- IC EnginesDocument8 pagesIC EnginesNo MINo ratings yet
- Assign#1 Thermo Lab. 2019p-ME-18Document8 pagesAssign#1 Thermo Lab. 2019p-ME-18Abdul Rasheed GhaziNo ratings yet
- Petrol Engine (Nehru Garden, JalandharDocument7 pagesPetrol Engine (Nehru Garden, Jalandharapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Experiment No 09Document3 pagesExperiment No 0920MCE 01 Mehwish KhanNo ratings yet
- Foro Adiciona YanacDocument6 pagesForo Adiciona Yanacdaniel yanacNo ratings yet
- IC EnginesDocument17 pagesIC EnginesS V Garata ReddyNo ratings yet
- Experiment - No.2: To Study The Parts and Working of Four Stroke Petrol EngineDocument6 pagesExperiment - No.2: To Study The Parts and Working of Four Stroke Petrol EngineHafeez AliNo ratings yet
- Gasoline EngineDocument6 pagesGasoline EngineJonan TutaanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Internal Combustion Engines.: Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics ME 1052Document7 pagesIntroduction To Internal Combustion Engines.: Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics ME 1052Supun AmarasingheNo ratings yet
- 4 Stroke Petrol EngineDocument9 pages4 Stroke Petrol EngineZahid MughalNo ratings yet
- LecturesDocument142 pagesLecturesMuhammad RazaNo ratings yet
- Ee Assignment 5Document7 pagesEe Assignment 5Himanshu AryaNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 3Document10 pagesExperiment # 3Farhan AliNo ratings yet
- Diesel EngineDocument20 pagesDiesel EngineProxima YusNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Engines BasicsDocument50 pagesModule 1 Engines Basicszaidkadiri9No ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Lab ReportDocument49 pagesThermodynamics Lab Reportjawad60% (5)
- Lect 2Document13 pagesLect 2khalid mustafaNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document10 pagesCH 1Anonymous 1aCZDEbMMNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 06: To Investigate The Operation 4 Stroke Diesel Engine For Power GenerationDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 06: To Investigate The Operation 4 Stroke Diesel Engine For Power GenerationAarizMalikNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentSahil KalaNo ratings yet
- What Is Engine Stroke?: Fuel Efficient Combustion ProcessDocument4 pagesWhat Is Engine Stroke?: Fuel Efficient Combustion ProcessYounis YaarubNo ratings yet
- Greater Noida Institute of Technology: 2-Stroke Petrol EngineDocument13 pagesGreater Noida Institute of Technology: 2-Stroke Petrol EngineEr Raghvendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Four Stroke EngineDocument5 pagesFour Stroke Enginemnoorulain80No ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document9 pagesExperiment 1Mehar HamzaNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermal Engineering: Prof. K. K.SHARMADocument69 pagesApplied Thermal Engineering: Prof. K. K.SHARMAKaran100% (1)
- Meec Prelim CompilationDocument16 pagesMeec Prelim CompilationBen Aldrian IbañezNo ratings yet
- Asi Unit 3Document21 pagesAsi Unit 3Raja RamNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument7 pagesLab Reportshah_gen89No ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument14 pages1 PDFinsanNo ratings yet
- Stroke and CyclesDocument6 pagesStroke and Cyclesjohn connoNo ratings yet
- Ic Engine: Kim.J.SeelanDocument41 pagesIc Engine: Kim.J.SeelanDrKim J SeelanNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion EngineDocument136 pagesInternal Combustion Enginepreethu02No ratings yet
- Four Stroke EngineDocument9 pagesFour Stroke Enginepawarsikander100% (3)
- IC EnginesDocument52 pagesIC EnginesSethu ramNo ratings yet
- Manual of Four Cylinder Four Stroke Petrol Engine Test RigDocument16 pagesManual of Four Cylinder Four Stroke Petrol Engine Test RigDhruv Patel100% (1)
- A A A AaaaaaaaaaaaaaaDocument2 pagesA A A AaaaaaaaaaaaaaaesakkimuthuNo ratings yet
- Diesel Automotive Engines: Energy and Power Technology TextbookDocument32 pagesDiesel Automotive Engines: Energy and Power Technology TextbookSrinivas EedaraNo ratings yet
- SUCTION STROKE Suction StrokeDocument5 pagesSUCTION STROKE Suction Strokeashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- 4 StrokeDocument2 pages4 StrokeFadh Zil IkramNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Internal CombussionDocument67 pagesLecture 2 - Internal Combussionchoongwenkang100% (2)
- Below Is An Overview of The Fuel System Intake OperationDocument8 pagesBelow Is An Overview of The Fuel System Intake OperationchigauNo ratings yet
- Petrol Engine1virkDocument3 pagesPetrol Engine1virkapi-3703711No ratings yet
- Honda Carburation ManualDocument20 pagesHonda Carburation ManualTõnisNo ratings yet
- Ju6h Nlkarg ProposalDocument9 pagesJu6h Nlkarg ProposalFerdinan Tulus Yones TobingNo ratings yet
- N45TM 1Document4 pagesN45TM 1Yew LimNo ratings yet
- Ransohoff RB Series 7 20Document2 pagesRansohoff RB Series 7 20jose guadalupe robles colinNo ratings yet
- Sample - ColinDocument9 pagesSample - ColinJesus Ocaña CalderónNo ratings yet
- Lubrication System (1Az-Fe) : On-Vehicle InspectionDocument32 pagesLubrication System (1Az-Fe) : On-Vehicle InspectionMusat Catalin-Marian100% (4)
- Rod Ratio KinematicsDocument6 pagesRod Ratio KinematicsJameel KhanNo ratings yet
- C161612 DiagDocument11 pagesC161612 DiagCarlos ReyesNo ratings yet
- D343, 346, 348, 349 Series: Clevite Heavy Duty Replacement Engine Parts For CaterpillarDocument2 pagesD343, 346, 348, 349 Series: Clevite Heavy Duty Replacement Engine Parts For CaterpillarMuhammad Fathin JuzarNo ratings yet
- Specifications KTA38 G-DRIVEDocument2 pagesSpecifications KTA38 G-DRIVEDouglas Moura100% (1)
- Ficha Tecnica Bomba Inyeccion MiniFlex EDocument1 pageFicha Tecnica Bomba Inyeccion MiniFlex Ejohn frader arrubla50% (2)
- 1989 Engine Performance On-Vehicle AdjustmentsDocument14 pages1989 Engine Performance On-Vehicle AdjustmentsJose PichinteNo ratings yet
- Valve Data Sheet: Operation and Maintenance ManualDocument3 pagesValve Data Sheet: Operation and Maintenance ManualVictor NunezNo ratings yet
- CH 06 - Aircraft SystemsDocument40 pagesCH 06 - Aircraft SystemsFahmi Prayogi100% (1)
- 7B - Scorecards - CFM Symposium 2017Document13 pages7B - Scorecards - CFM Symposium 2017aliNo ratings yet
- E450 Super Duty 6.8 2000-2001Document63 pagesE450 Super Duty 6.8 2000-2001Luis Ramon Arguello Real100% (1)
- Part Catalog B5.9-C152 462880088 IngersollrandDocument175 pagesPart Catalog B5.9-C152 462880088 IngersollrandIndra AremaNo ratings yet
- Obdii Code InfoDocument46 pagesObdii Code InfoPriyo Satriyo BudiharjoNo ratings yet
- Tag 1 ADocument46 pagesTag 1 ANOUR EDDINE ISSANo ratings yet
- 100 Series WMDocument144 pages100 Series WMAsif Mehmood100% (2)
- Fig. 1: Completed - The First Commercial ME EngineDocument4 pagesFig. 1: Completed - The First Commercial ME EngineAshutosh ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- OutboardSelectionChart ISSUE 10Document6 pagesOutboardSelectionChart ISSUE 103445121No ratings yet
- Intake and Exhaust: Autozine Technical SchoolDocument7 pagesIntake and Exhaust: Autozine Technical SchoolHenter TamásNo ratings yet
- N67te2a 193KW 1500RPMDocument3 pagesN67te2a 193KW 1500RPMsaiyedasadNo ratings yet
- Juntas ToyotaDocument78 pagesJuntas ToyotaHewa PCNo ratings yet
- 3a Prof Ata 71 Thru 80 Jt9dDocument88 pages3a Prof Ata 71 Thru 80 Jt9dDiego Ruddy Arcaine ZegarrundoNo ratings yet