Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Behavioural Mechanism and Neural Control
Behavioural Mechanism and Neural Control
Uploaded by
DrMumtaz F Musaliar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
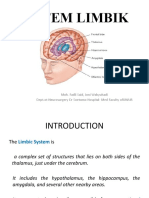
3 views14 pagesThe hypothalamus controls homeostatic mechanisms and is connected to the pituitary gland, regulating hunger, emotion, and autonomic functions. The limbic system includes the amygdala for identifying danger and emotions, hippocampus for long term memory, and cingulate gyrus for pain response. Different areas of the cerebral cortex control emotional behaviors through connections with the limbic system and hypothalamus.
Original Description:
Original Title
BEHAVIOURAL MECHANISM AND NEURAL CONTROL
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe hypothalamus controls homeostatic mechanisms and is connected to the pituitary gland, regulating hunger, emotion, and autonomic functions. The limbic system includes the amygdala for identifying danger and emotions, hippocampus for long term memory, and cingulate gyrus for pain response. Different areas of the cerebral cortex control emotional behaviors through connections with the limbic system and hypothalamus.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views14 pagesBehavioural Mechanism and Neural Control
Behavioural Mechanism and Neural Control
Uploaded by
DrMumtaz F MusaliarThe hypothalamus controls homeostatic mechanisms and is connected to the pituitary gland, regulating hunger, emotion, and autonomic functions. The limbic system includes the amygdala for identifying danger and emotions, hippocampus for long term memory, and cingulate gyrus for pain response. Different areas of the cerebral cortex control emotional behaviors through connections with the limbic system and hypothalamus.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
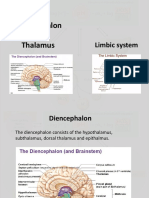
BRAIN- Seat of consciousness.
HYPOTHALAMUS- Highly vascular., Controls
homeostatic mechanism.
PITUTARY GLAND- Infundibulum connects the
hypothalamus to pituitary
It contains both nerves and blood vessels.
❑Satiation centre/ Hunger Centre
❖Regulate hunger
❖Located in the ventro-median part of
the hypothalamus.
❖Satiation centre monitors the
quantity of food
Stimulation of hypothalamic nuclei
produces various emotions such as fear,
pleasure etc.
Some functions are under the control of
autonomic nervous system that are
influenced by emotions.
It is controlled by the anterior part of
the hypothalamus and the neighboring
septal region.
Hormonal stimulation.
CEREBRAL CORTEX – Controls
emotional behavior.
NEOPALLIUM-Arousal of aggressive
behavior.
PALAEOPALLIUM- Placid behavior.
In 1878,the French neurologist Paul
broca-limbic lobe(limbic system)
1)AMYGDALA- Identification of danger ,self
protection, fear, love, friendship etc.
2)HIPPOCAMPUS- Long term memory
3)HYPOTHALAMUS-Motivated behavior,
thermoregulation, sexuality, hunger, thirst.
4)CINGULATE GYRUS-Emotional reaction
to pain, regulation of aggressive behavior
5)PRE-FRONTAL AREA- It comprises the
entire non-motor anterior region of frontal
lobe
The manifestation and regulation of
several behavior and motivational drives.
1. What are the components that make up the limbic
system?
2. What are the main output centers for the effects of the
limbic system?
3. What is the relationship between the olfactory system
and the limbic system?
4. What are the connections and functions of the
amygdala?
5. How does "emotional memory" function in the
amygdala?
6. What is the role of the prefrontal cortex in emotions?
You might also like
- CHEMOLITHOTROPHSDocument26 pagesCHEMOLITHOTROPHSDrMumtaz F MusaliarNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia Case StudyDocument8 pagesSchizophrenia Case Studyaira2350% (2)
- The Limbic System: Presented by Lam Yee LeeDocument17 pagesThe Limbic System: Presented by Lam Yee LeeLylee LamNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Regulation of Internal EnvironmentDocument17 pagesModule 5 Regulation of Internal EnvironmentSakshi Jauhari100% (1)
- Limbic SystemDocument49 pagesLimbic SystemBaishali DebNo ratings yet
- Limbic SystemDocument14 pagesLimbic SystemTAMIL100% (1)
- Brain Long QuestionDocument4 pagesBrain Long QuestionHasnain AsifNo ratings yet
- Bios252carsonexam2studyguide 2Document17 pagesBios252carsonexam2studyguide 2MARY NERI100% (1)
- Limbic LECTUREDocument34 pagesLimbic LECTURESohira QaziNo ratings yet
- PhysiologyDocument15 pagesPhysiology221618No ratings yet
- Emotions: Rishikulya.A Student Counsellor Department of Clinical Psychology SriherDocument33 pagesEmotions: Rishikulya.A Student Counsellor Department of Clinical Psychology SrihervedhikaNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Quarter 3Document10 pagesScience 10 Quarter 3Kine HenituseNo ratings yet
- Asd NotesDocument9 pagesAsd NotesZosmita Shane GalgaoNo ratings yet
- The Limbic SystemDocument5 pagesThe Limbic SystemAhmad Badius ZamanNo ratings yet
- Neurological DevelopmentDocument22 pagesNeurological DevelopmentFritz LumasagNo ratings yet
- Sistem Limbik: Moh. Fadli Said, Joni Wahyuhadi Dept - Ot Neurosurgery DR Soetomo Hospital-Med Faculty OfunairDocument13 pagesSistem Limbik: Moh. Fadli Said, Joni Wahyuhadi Dept - Ot Neurosurgery DR Soetomo Hospital-Med Faculty OfunairspiritNo ratings yet
- CHP 3 PSYCHDocument8 pagesCHP 3 PSYCHEmma Mahoney100% (1)
- Sem IV Unit IV Study NoteDocument5 pagesSem IV Unit IV Study NoteSafaa FaizalNo ratings yet
- Brain & Cranial Nervous SystemDocument74 pagesBrain & Cranial Nervous SystemMAHARANINo ratings yet
- Diencephalon and Its FunctionsDocument11 pagesDiencephalon and Its FunctionsAgnes MumiraNo ratings yet
- Otak Dan NN CranialisDocument74 pagesOtak Dan NN CranialisDebri ErwendiNo ratings yet
- Psych 100 Physiological Basis of BehaviorDocument3 pagesPsych 100 Physiological Basis of BehaviorEissel PaparonNo ratings yet
- What Is HypothalamusDocument15 pagesWhat Is HypothalamusyogieNo ratings yet
- Group 4 DiencephalonDocument23 pagesGroup 4 Diencephalonkqnvhmwx9dNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Structure and Function of The Nervous System I. StructuresDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Structure and Function of The Nervous System I. StructuresChielo ZartigaNo ratings yet
- The Autonomic Motor System: HypothalamusDocument10 pagesThe Autonomic Motor System: HypothalamusThe Panda EntertainerNo ratings yet
- MODULE 6 Lesson 6: The Power of The MindDocument4 pagesMODULE 6 Lesson 6: The Power of The MindEterna LokiNo ratings yet
- Midterm Psych Module 7Document14 pagesMidterm Psych Module 7Ladybelle GototosNo ratings yet
- Objectives For Hypothalamus I & Ii: Reading Assignment: Hypothalamus 1 & II "Handouts" Mason's Medical NeurobiologyDocument153 pagesObjectives For Hypothalamus I & Ii: Reading Assignment: Hypothalamus 1 & II "Handouts" Mason's Medical NeurobiologyNargiz KutliyarovaNo ratings yet
- Diencephalon Thalamus: Limbic SystemDocument18 pagesDiencephalon Thalamus: Limbic SystemОксана КрасильниковаNo ratings yet
- Wa0010.Document23 pagesWa0010.fh9455038No ratings yet
- HypothalamusDocument47 pagesHypothalamusHira SultanNo ratings yet
- Areas of The BrainDocument18 pagesAreas of The Brainjmie18No ratings yet
- The Human BrainDocument17 pagesThe Human BrainSadiq Abdo92No ratings yet
- Lec 6b Nervous SystemDocument21 pagesLec 6b Nervous Systemfarhatshoaib19No ratings yet
- Limbic SystemDocument18 pagesLimbic SystemJessy OnahNo ratings yet
- Anfis Sistem NeuroBehaviourDocument37 pagesAnfis Sistem NeuroBehaviourDediSunartoNo ratings yet
- Lobes of The BRAIN: Right Hemisphere Left HemisphereDocument9 pagesLobes of The BRAIN: Right Hemisphere Left HemisphereAsniah Hadjiadatu AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesNervous SystemMARIE ERICKA ARONANo ratings yet
- Lecture 2. The Hypothalamus and Its Connections WI24 BIOL 4840Document17 pagesLecture 2. The Hypothalamus and Its Connections WI24 BIOL 4840nitaediNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System.: Anatomy & Physiology ofDocument79 pagesThe Nervous System.: Anatomy & Physiology offlex gyNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Group 9Document77 pagesEndocrine System Group 9Jei SanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - 6 Reviewer For Science (3Q)Document19 pagesLesson 1 - 6 Reviewer For Science (3Q)maryayahdeleonNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Summary NotesDocument4 pagesNervous System Summary NotesIrish Buaya Gementiza100% (1)
- I. Illustrate and Give The Parts and Functions of The BrainDocument9 pagesI. Illustrate and Give The Parts and Functions of The BrainBrian Jhones Chan AbundoNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Nervous System2Document20 pagesDisorders of The Nervous System2Ian Rizavi Villamor AntopinaNo ratings yet
- Coordination and Control HsDocument11 pagesCoordination and Control Hsmalindabissoon312No ratings yet
- Biopsychology Assignment: Biology of EmotionsDocument11 pagesBiopsychology Assignment: Biology of EmotionsIris HerondaleNo ratings yet
- HypothalamusDocument9 pagesHypothalamussnowNo ratings yet
- Lecture (Endocrine System)Document15 pagesLecture (Endocrine System)GerofeNo ratings yet
- Intro To Psych L2Document13 pagesIntro To Psych L2Abigail MorfeNo ratings yet
- Forebrain: Anatomy of Human BrainDocument9 pagesForebrain: Anatomy of Human BrainStuti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Autonomic NotesDocument4 pagesAutonomic NotesYeyeth Jabaybay TabolongNo ratings yet
- The Central Nervous System (CNS)Document13 pagesThe Central Nervous System (CNS)DishuNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument18 pagesReportrtvb77smjhNo ratings yet
- Emotional Network in The BrainDocument11 pagesEmotional Network in The BrainDolly GuptaNo ratings yet
- CognitiveDocument6 pagesCognitivesanika kadamNo ratings yet
- MHNDocument26 pagesMHNGopika SNo ratings yet
- Psychology PresentationDocument16 pagesPsychology PresentationFasih RehmanNo ratings yet
- The Limbic SystemDocument7 pagesThe Limbic Systemkerima juliaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: A Tutorial Study GuideFrom EverandNervous System: A Tutorial Study GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- ETHOLOGYDocument16 pagesETHOLOGYDrMumtaz F MusaliarNo ratings yet
- Documentationonbiodiversity 170224160020Document23 pagesDocumentationonbiodiversity 170224160020DrMumtaz F MusaliarNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Cell - StructureDocument32 pagesBacterial Cell - StructureDrMumtaz F MusaliarNo ratings yet
- Dna ReplicationDocument145 pagesDna ReplicationDrMumtaz F MusaliarNo ratings yet
- DR Mumthas YahiyaDocument38 pagesDR Mumthas YahiyaDrMumtaz F MusaliarNo ratings yet
- Marine BenthosDocument23 pagesMarine BenthosDrMumtaz F MusaliarNo ratings yet
- Gene Transfer TechniquesDocument36 pagesGene Transfer TechniquesDrMumtaz F MusaliarNo ratings yet