Professional Documents
Culture Documents
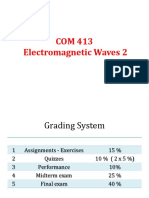
Electrical Requirements-13
Uploaded by
ayouta ademOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrical Requirements-13
Uploaded by
ayouta ademCopyright:
Available Formats
DEFINITIONS
(E)
Earth (ground)
The conductive mass of the earth whose electric potential at any point is
conventionally taken as equal to zero.
Earth electrode
One or more conductive parts embedded in the earth for the purpose of making
effective electrical contact with the general mass of earth. It can be conductive part,
which may be embedded in a specific conductive medium, e.g. concrete or coke, in
electric contact with earth.
Earth electrode resistance
The resistance of an earth electrode to earth.
Earth equipotential zone
A zone within which exposed conductive parts and extraneous conductive parts are
maintained at substantially the same potential by bonding such that, under fault
conditions, the difference in potential between simultaneously accessible exposed and
extraneous conductive parts will not cause electric shock.
Earth fault
A conductive part or a group of conductive parts in an intimate contact with and
providing an electrical connection with earth.
Earth fault loop impedance
The impedance of the earth fault current loop starting and ending at the point of earth
fault. This impedance is denoted by the symbol Z s .
Earthing
Connection of the exposed conductive parts of an installation to the main earthing
terminal of the installation.
Earthing arrangement
all the electric connections and devices involved in the earthing of a system, an
installation and equipment. This could be a locally limited arrangement of
interconnected earth electrodes on the high-voltage side.
Earthing conductor
A protective conductor connecting the main earthing terminal or bar to the earth
electrode.
Earthing Systems
An electrical system consisting of a single source of electrical energy and an
installation. For certain purposes, of the Regulations, types of systems are identified as
follows, depending upon the relationship of the source, and of exposed conductive
parts of the installation, to Earth:
TN system: a system having one or more points of the source of energy directly
earthed, the exposed conductive parts of the installation being connected to that
point by protective conductors.
TN-C system: a system in which the neutral and protective functions are
combined in a single conductor throughout the system.
SBC 401 2007 21/8
DEFINITIONS
TN-S system: a system having separate neutral and protective conductors
throughout the system.
TN-C-S system: a system in which neutral and protective functions are combined
in a single conductor in part of the system.
TT system: A system having one point of the source of energy directly earthed,
the exposed conductive parts of the installation being connected to earth electrodes
electrically independent of the earth electrodes of the source.
IT system: A system having no direct connection between live parts and Earth, the
exposed conductive parts of the electrical installation are being earthed.
Earth leakage current
A current, which flows to earth or to extraneous conductive parts in a circuit, which is
electrically sound. This current may have a capacitive component including that
resulting from the deliberate use of capacitor.
Earth-leakage protective device
Device which will remove the output power from one or more transformer(s), inverter(s) or
converter(s) in the event of a short-circuit between any relevant part of the output circuit and
earth.
Efficiency of a LPS
The ratio of the average annual number of direct lightning flashes which cannot cause
damage to the building to the direct lightning flash number to the building.
Electric circuit
An assembly of electrical equipment of the installation supplied from the same origin
and protected against overcurrent by the same protective devices.
Electric shock
Pathophysiological effect resulting from an electric current passing through a human
or animal body.
Electrical equipment
Any item used for such purposes as generation, conversion, transmission, distribution
or utilization of electrical energy, such as machines, transformers, apparatus,
measuring instruments, protective devices, equipment for wiring systems, appliances.
Electrical installation
An assembly of associated electrical equipment that fulfills a specific purpose or
purposes and having coordinated characteristics.
Electrical safety source
Source intended to maintain the supply to electrical equipment essential for the safety
services.
Electrically independent earth electrodes
Earth electrodes are located at such a distance from one another that the maximum
current likely to traverse one of them does not significantly affect the potential of the
others.
Electrically protective barrier
Part providing protection against direct contact from any usual direction of access.
SBC 401 2007 21/9
You might also like
- Grounding and EarthingDocument23 pagesGrounding and EarthingAmbika Jagmohansingh100% (2)
- Earthing HandoutDocument18 pagesEarthing Handoutjaffna100% (1)
- Electromagnetic Coil Gun - Construction and BasicDocument8 pagesElectromagnetic Coil Gun - Construction and BasicDaniel Pisau100% (1)
- Resonant GroundingDocument48 pagesResonant GroundingElectra GuunnNo ratings yet
- Earthing System: Presented By: Md. Noman Saber KhanDocument78 pagesEarthing System: Presented By: Md. Noman Saber Khansardarmkhan100% (2)
- Earthing PrimerDocument20 pagesEarthing PrimerSami DeorajNo ratings yet
- System Neutral EarthingDocument70 pagesSystem Neutral Earthingsorry2qazNo ratings yet
- EMC Coupling & Countermeasures GuideDocument5 pagesEMC Coupling & Countermeasures GuideVigneswaran VigneshNo ratings yet
- Neutral Earthing, Earthing Standards and Floating in LV NetworksDocument88 pagesNeutral Earthing, Earthing Standards and Floating in LV NetworksRajendra Prasad Shukla67% (3)
- Earthing SystemsDocument21 pagesEarthing SystemsGia BảoNo ratings yet
- Student Training Notes Floormap 3diDocument86 pagesStudent Training Notes Floormap 3diTechnical A-Star Testing & Inspection MalaysiaNo ratings yet
- Haris Linear AcceleratorDocument66 pagesHaris Linear AcceleratorHarisrahmanNo ratings yet
- EMI AnswersDocument16 pagesEMI AnswersMrinmayee DegaonkarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Grounding Systems ExplainedDocument5 pagesElectrical Grounding Systems ExplainedEri Febriansya100% (1)
- Question Bank For SEWA Electrical Engineer ExamDocument7 pagesQuestion Bank For SEWA Electrical Engineer ExamShahida Babeesh100% (2)
- Research and Thesis On Earthing System in LV NetworksDocument87 pagesResearch and Thesis On Earthing System in LV NetworksEngr Gulfam80% (5)
- EarthingDocument8 pagesEarthingSatyender Kumar Jain100% (1)
- Earthing system types and their characteristicsDocument8 pagesEarthing system types and their characteristicsTony KontisNo ratings yet
- Lecturer Note - Earthing SystemDocument31 pagesLecturer Note - Earthing SystemKelvin Lau100% (3)
- ERF and ELRDocument21 pagesERF and ELRChhinPiden100% (1)
- Earthing System: Eletrical Installation (EET0142)Document27 pagesEarthing System: Eletrical Installation (EET0142)Khalied HafeezNo ratings yet
- Electrical Requirements-12Document2 pagesElectrical Requirements-12ayouta ademNo ratings yet
- Earthing System: Objectives of Electrical EarthingDocument1 pageEarthing System: Objectives of Electrical EarthingredfordNo ratings yet
- Earthing SchemesDocument16 pagesEarthing SchemesKatik XalxoNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Earthing System: - June 10, 2010Document14 pagesInstrumentation Earthing System: - June 10, 2010indira_tungNo ratings yet
- Earthing SystemDocument14 pagesEarthing SystemNelson A. García RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Earthing SystemDocument9 pagesEarthing SystemmaheshshettymteducarNo ratings yet
- Earthing System - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument7 pagesEarthing System - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediagiriNo ratings yet
- Earthing Systems ExplainedDocument7 pagesEarthing Systems ExplainedNoor Zamri SudinNo ratings yet
- Earthing System - WikipediaDocument10 pagesEarthing System - WikipediaJay CaponponNo ratings yet
- T: Direct Connection of A With Earth Point (French: Terre)Document5 pagesT: Direct Connection of A With Earth Point (French: Terre)Rajendra Prasad ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Earthing System - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument7 pagesEarthing System - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSharaf Ali ZyoudNo ratings yet
- Earthing System - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesEarthing System - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaYuvaraj ChandrasekaranNo ratings yet
- ABUJA 5 Basics of Electrical GroundingDocument19 pagesABUJA 5 Basics of Electrical Groundingmuaz_aminu1422No ratings yet
- Earthing SystemDocument7 pagesEarthing SystemUvmnour BarwaryNo ratings yet
- Earthing SystemDocument8 pagesEarthing SystemMKNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Earthing Systems and Lightning ProtectionDocument7 pagesChapter Four Earthing Systems and Lightning Protectionyibelta abebeNo ratings yet
- Stray Voltages and Public Lighting InstallationsDocument23 pagesStray Voltages and Public Lighting InstallationsLourdhu Sagaya Jayakumar JNo ratings yet
- TN, TT, ItDocument14 pagesTN, TT, ItTuan Anh Le CongNo ratings yet
- Civil Grounding System ReportDocument10 pagesCivil Grounding System ReportMessi ArabNo ratings yet
- TT, TN, and IT Earthing Systems ExplainedDocument21 pagesTT, TN, and IT Earthing Systems ExplainedAamir AliNo ratings yet
- Silo - Tips Earthing System of Electrical CircuitDocument24 pagesSilo - Tips Earthing System of Electrical Circuitgerry jabinesNo ratings yet
- Definition of TermsDocument9 pagesDefinition of TermsKing DuqNo ratings yet
- Lightning Protection Systems ExplainedDocument45 pagesLightning Protection Systems ExplainedUdit NyatiNo ratings yet
- Barreto Electromagnetic InterferenceDocument6 pagesBarreto Electromagnetic InterferenceGiuseppe FerrariNo ratings yet
- Earthing Systems: Earthing or Earthing System Is The Total of All MeansDocument4 pagesEarthing Systems: Earthing or Earthing System Is The Total of All Meansrihatrivedi_069No ratings yet
- Electrical Requirements-11Document2 pagesElectrical Requirements-11ayouta ademNo ratings yet
- Basics of Earthing: Compiled By, Prof Shivam Shrivastava Ap-Ee, ItnuDocument19 pagesBasics of Earthing: Compiled By, Prof Shivam Shrivastava Ap-Ee, ItnuShivam ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Assigment Week 2 - Rizky Fajar A. H - 04211841000016 PDFDocument7 pagesAssigment Week 2 - Rizky Fajar A. H - 04211841000016 PDFRizky FajarNo ratings yet
- 02 - Smartscreen Handout 01 - Supplies & Earthing-1Document5 pages02 - Smartscreen Handout 01 - Supplies & Earthing-1Daniel HollandsNo ratings yet
- GroundingDocument56 pagesGroundingJawahar BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Hossam MohamedDocument7 pagesHossam MohamedAhmed FawzyNo ratings yet
- Cha 1Document40 pagesCha 1Yahya Faiez WaqqadNo ratings yet
- Earthing System: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesEarthing System: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAliq FazliNo ratings yet
- Need of Earthing or GroundingDocument2 pagesNeed of Earthing or GroundingShahida Babeesh0% (1)
- Earthing Purpose: Voltage, High Voltage and Buildings and Building Services Is Shown inDocument12 pagesEarthing Purpose: Voltage, High Voltage and Buildings and Building Services Is Shown inCESAR AREVALONo ratings yet
- Earthing SystemDocument15 pagesEarthing SystemTara CollierNo ratings yet
- GroundingDocument28 pagesGroundingDewanto WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- Methodology: Power Transformer GroundingDocument1 pageMethodology: Power Transformer Groundingirish sedilllNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Grounding System DesignDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Grounding System DesignRajendra Prasad ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Naming Electricity System Earthing ArrangementsDocument11 pagesNaming Electricity System Earthing ArrangementsRazek WardNo ratings yet
- International Diploma in Occupational Health and Safety PDFDocument48 pagesInternational Diploma in Occupational Health and Safety PDFadil khanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Requirements-18Document2 pagesElectrical Requirements-18ayouta ademNo ratings yet
- Electrical Requirements-19Document2 pagesElectrical Requirements-19ayouta ademNo ratings yet
- Electrical Requirements-16Document2 pagesElectrical Requirements-16ayouta ademNo ratings yet
- Electrical Requirements-11Document2 pagesElectrical Requirements-11ayouta ademNo ratings yet
- De Electrical - Requirements-10Document2 pagesDe Electrical - Requirements-10ayouta ademNo ratings yet
- Electrical Requirements-7Document2 pagesElectrical Requirements-7ayouta ademNo ratings yet
- Electrical Requirements-9Document2 pagesElectrical Requirements-9ayouta ademNo ratings yet
- Electrical Requirements-6Document2 pagesElectrical Requirements-6ayouta ademNo ratings yet
- Electrical Requirements-2Document2 pagesElectrical Requirements-2ayouta ademNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction Explained by The Wave and Particle Nature of LightDocument3 pagesReflection and Refraction Explained by The Wave and Particle Nature of LightRubin RubinNo ratings yet
- Advance Image Runner 6075Document96 pagesAdvance Image Runner 6075vishwajitNo ratings yet
- ABB TedDocument24 pagesABB TedLeonardoNo ratings yet
- Gea 18285 10 26 11Document10 pagesGea 18285 10 26 11zipotz3429No ratings yet
- Easy Altivar 310 - ATV310HD11N4EDocument6 pagesEasy Altivar 310 - ATV310HD11N4EPhaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document2 pagesChapter 6Monisha RNo ratings yet
- 02-CUMARK Inverter Application On Air CompressorDocument17 pages02-CUMARK Inverter Application On Air Compressorvictor riveroNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0925400522010334 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S0925400522010334 MainDibashkar biswasNo ratings yet
- CFE-SS Approach For Salient-Pole Synchronous Generators Under UnbalancesDocument21 pagesCFE-SS Approach For Salient-Pole Synchronous Generators Under UnbalancesMariem MakniNo ratings yet
- A General Approach of Space and Time Harmonics Interactions in Induction MotorsDocument3 pagesA General Approach of Space and Time Harmonics Interactions in Induction MotorsSudip MondalNo ratings yet
- Summative Science Test on AtomsDocument2 pagesSummative Science Test on AtomsAlvin GultiaNo ratings yet
- CUET UG Physics Notes Questionpaperdrive-minDocument41 pagesCUET UG Physics Notes Questionpaperdrive-minfriendshipisgreatmanNo ratings yet
- Kalpana - Viii Science 2021 - 2022Document11 pagesKalpana - Viii Science 2021 - 2022shindemrunali15No ratings yet
- Science Reviewer PhysicsDocument3 pagesScience Reviewer PhysicsZeus FrancisNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 Lab Report 4 (To Determine The Refractive Index of The Material of Prism by A Spectrometer) - Spring21-22 - Final Term - ACSDocument10 pagesPhysics 2 Lab Report 4 (To Determine The Refractive Index of The Material of Prism by A Spectrometer) - Spring21-22 - Final Term - ACSRafi IslamNo ratings yet
- Watt AC-DC Converters: FeaturesDocument3 pagesWatt AC-DC Converters: FeatureskofidNo ratings yet
- 6 To 7 Moving Scholarship Test 20-11-22Document14 pages6 To 7 Moving Scholarship Test 20-11-22ajay3518No ratings yet
- Wireless System: Online User Guide For Shure BLX Wireless System. Version: 4 (2019-H)Document28 pagesWireless System: Online User Guide For Shure BLX Wireless System. Version: 4 (2019-H)Anonymous EP0GKhfNo ratings yet
- 1X95 RM NYY (Test Report)Document4 pages1X95 RM NYY (Test Report)jamilNo ratings yet
- Base Si UnitsDocument10 pagesBase Si UnitsJehana NaolNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 0 - Course DescriptionDocument5 pagesLecture - 0 - Course DescriptionNour YehiaNo ratings yet
- Klim Ovzek - Unit Plan - Science 30 ElectromagneticDocument12 pagesKlim Ovzek - Unit Plan - Science 30 Electromagneticapi-463570013No ratings yet
- Types of Electrical Protection Relays or Protective RelaysDocument7 pagesTypes of Electrical Protection Relays or Protective RelaysTushar SinghNo ratings yet
- Nptel: NOC:Chemistry - I - Video CourseDocument3 pagesNptel: NOC:Chemistry - I - Video CourseAnu PriyaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Fiber OpticsDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Fiber OpticsNida AjrinaNo ratings yet
- Maxwell's Equations Tutorial for Time-Varying FieldsDocument9 pagesMaxwell's Equations Tutorial for Time-Varying FieldsNur Aqilah Abdullah HashimNo ratings yet
- Basic Physics and Imaging Characteristics of UltrasoundDocument9 pagesBasic Physics and Imaging Characteristics of UltrasoundAnucha MostafáNo ratings yet