Professional Documents
Culture Documents
8th Science STAAR Cheat Sheet
8th Science STAAR Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
Jahir Sanchez BarahonaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
8th Science STAAR Cheat Sheet
8th Science STAAR Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
Jahir Sanchez BarahonaCopyright:
Available Formats
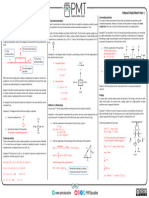
8th Grade Science STAAR Review
Cheat Sheet
Matter & Energy Force, Motion, & Energy
Subatomic Particles Groups Periods
1. Same # of valence 1. Same # of Newton’s 3 Laws of Motion
Protons Neutrons Electrons electrons electron shells
1. Inertia- An object at rest stays at rest
Positive Neutral Negative 2. Similar chemical 2. Similar atomic
and physical mass and an object in motion stays in
properties motion unless acted on by an
1 AMU 1 AMU 0 AMU
unbalanced force.
Nucleus Nucleus Electron Cloud 2. Force & Acceleration- The more mass
an object has the more force needed to
A=P=E accelerate it. F=MA
Atomic Number=12
3. Action-Reaction- For every action there
Protons = 12 is an equal and opposite reaction.
Electrons = 12
Balanced:
M-A=N
Mass= 24 Net Force= 0
No movement
Atomic Number = 12
24-12= 12 NEUTRONS
Unbalanced:
Subtract opposing forces
Magnesium is found in group 2, period Moves in the direction of the
greater force
3 so that means it will have 2 Valence
Electrons and 3 Electron Shells. Speed- The distance and object travels in a
certain amount of time.
2 Valence Electrons will make it very reactive.
Velocity- Speed in a certain direction.
Groups 1 & 7 Highest Reactivity
Acceleration- When an object, speeds up, slows
Group 8 Unreactive down, or changes direction. (A change in
velocity).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Distance-Time Velocity-Time
C3H8 + 502 4H20 + 3CO2
Atoms= Subscripts (The small number to the right of the Stopped Constant
element) Example: 3 atoms of Carbon or 10 atoms of
Oxygen. Hint- Don’t forget to multiply the coefficient
and subscript when they belong to the same element.
Elements= Capital Letters Example: 3 Elements on the
Reactant Side. (Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen)
Metals- good conductors, solid, Formula Triangles
Molecules = Coefficients in front of compounds (The big
malleable, luster. d W
number) Example: 1 molecule of C3H8 and 4 molecules of Speed Work
Nonmetals- not good conductors, liquids t s F d
H2O
or gases.
Compounds= Two or more CAPITAL LETTERS together
M
Example: H2O and CO2 Metalloids- share properties of both F
Force Density
metals and nonmetals M A D V
8th Grade Science STAAR Review
Cheat Sheet
Earth & Space
Spring Tides: Occur at the New Moon and Full Cold Front
Moon phases. “Spring into action”, this is the
most drastic difference between high and low
tides. The S for Spring think S for Sideways.
Warm Front
Neap Tides: Occur at the First Quarter and
Third Quarter moon phases. Not a big difference
between high and low tides. The N for Neap High Pressure
think N for North.
Clear skies
and fair
Convergent Divergent Transform weather
Topographic Map Low Pressure
Alfred Wegner Clouds,
precipitation
Contour Interval:
Mountains Valleys Faults and storms
Subtract lowest elevation Continental Drift
from highest elevation.
developed into
H-R
X= Peak of mountain Plate Tectonics
Rotation- Spinning in place, 24 hours, day-night
Diagram
cycle.
Revolution- Traveling around another object, 365
days/1 year.
Axial Tilt- 23.5 degrees, why we have seasons,
everything is the exact opposite in the Southern
Brightness Temperature is NOT Surface Temperature
Hemisphere.
related to Brightness!
Absolute Magnitude: Size Our Sun is a middle-age,
average sized, yellow, main-
Spectral Class: Color sequence star.
Organisms & Environment Marine (Ocean) Freshwater (Lake) Terrestrial
Producer/Consumer Predator/Prey Parasite/Host (Land)
A plant being eaten by An animal hunting, An organism that uses
an animal for energy. killing and eating another living
another animal. organism as a feeding
source, a place to lay
eggs and a habitat.
Biotic- Any living organism in an Artificial Reefs are made to Natural Selection: The process that allows
ecosystem. replace destroyed coral organisms with stronger genetic traits to live and
pass those traits on to their offspring.
(Plants & Animals)
reefs.
Biodiversity: The variety of species in an area and
Abiotic- Nonliving resources in an Ways that we affect our the genetic variation within those species.
ecosystem that help the biotic ocean systems: pollution,
Ecological Succession: A predictable and slow
factors survive. oil spills, overharvesting.
process of the rebuilding of an ecosystem.
(Sunlight, soil, rocks, water, and air)
You might also like
- Reviewer in Science1Document6 pagesReviewer in Science1Cailin Loraine VibarNo ratings yet
- Ch11 - Part1B+Kinetics of Particle Newtons LawDocument51 pagesCh11 - Part1B+Kinetics of Particle Newtons LawSutapa NaskarNo ratings yet
- Physics A LevelDocument38 pagesPhysics A LevelThoon Nadi NaiNo ratings yet
- 01.1 RelativityUnits v3Document14 pages01.1 RelativityUnits v3alguNo ratings yet
- Checklist m2Document3 pagesChecklist m2Arwa HamdiNo ratings yet
- Hand Out DYNAMICSDocument11 pagesHand Out DYNAMICSBry RamosNo ratings yet
- 7.3 Structure of Atom QuarksDocument3 pages7.3 Structure of Atom QuarksEjaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Nmat ReviewerDocument8 pagesChemistry Nmat ReviewerAlec Jasper U. Villamayor100% (7)
- Ch.10 Forces and MotionDocument1 pageCh.10 Forces and Motionkhadijah aliNo ratings yet
- Physics - Electricity & Magnetism CompendiumDocument27 pagesPhysics - Electricity & Magnetism CompendiumHedrene TolentinoNo ratings yet
- A Level Mechanics 3 Forces and MotionDocument1 pageA Level Mechanics 3 Forces and MotionHANSNo ratings yet
- STPM Chemistry Notes Ch1-Ch5Document8 pagesSTPM Chemistry Notes Ch1-Ch5Pang Wei Na100% (3)
- A Level Physics NotesDocument92 pagesA Level Physics NotesMuhammad MalikNo ratings yet
- MRI Lecture NotesDocument33 pagesMRI Lecture NotesArungoud PoshalaNo ratings yet
- PHYS101 Lecture 12Document21 pagesPHYS101 Lecture 12Eren CengizNo ratings yet
- MECH 2 Module 3 Unit 1 Newton's Second Law of MotionDocument19 pagesMECH 2 Module 3 Unit 1 Newton's Second Law of MotionIya AsperinNo ratings yet
- CHAP12 Kinetics of Particles Newtons2Law PDFDocument38 pagesCHAP12 Kinetics of Particles Newtons2Law PDFwahidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1&2Document48 pagesChapter 1&2John HeriniNo ratings yet
- New Formula of Nuclear Force PDFDocument7 pagesNew Formula of Nuclear Force PDFSURESH SURAGANINo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 (.2) - The Particle ZooDocument19 pagesLesson 7 (.2) - The Particle Zooharold hargridNo ratings yet
- From A Fren - / Stay Alive: ND ST RDDocument7 pagesFrom A Fren - / Stay Alive: ND ST RDdan anna stylesNo ratings yet
- FM1 Chp4 ElasticCollisionsInOneDimensionDocument27 pagesFM1 Chp4 ElasticCollisionsInOneDimensionBharathi SelvamNo ratings yet
- PhyPartChap1 2012 2013Document40 pagesPhyPartChap1 2012 2013mathieu.hernandez360No ratings yet
- Scienceclinic Smartprep GR10 Dbe Eng 2023 V4.1Document54 pagesScienceclinic Smartprep GR10 Dbe Eng 2023 V4.1RetuNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula SheetDocument12 pagesPhysics Formula SheetGiulia CostantiniNo ratings yet
- 03 - Particle Equilibrium 20-21Document59 pages03 - Particle Equilibrium 20-21Ahmed AbdelmaksoudNo ratings yet
- Data and Formula BookletDocument5 pagesData and Formula Booklet王涛No ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2nd Monthly Examinations ReviewerDocument7 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2nd Monthly Examinations ReviewerRoldan AlcazarNo ratings yet
- IJSO Stage-I & II - Chemistry Sheet-2017-18Document23 pagesIJSO Stage-I & II - Chemistry Sheet-2017-18Himanshu ThakurNo ratings yet
- Resumo Física Nuclear e de PartículasDocument83 pagesResumo Física Nuclear e de PartículasVictor qsxasdasdNo ratings yet
- 14 Particle PhysicsDocument4 pages14 Particle PhysicsOmgalevels12345100% (1)
- Mithun's Physics Revision Notes (Unit 1)Document6 pagesMithun's Physics Revision Notes (Unit 1)Mithun Dev SabaratnamNo ratings yet
- Core Course: What You Should KnowDocument4 pagesCore Course: What You Should KnowjalajsinghNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Engineering NotesDocument36 pagesNuclear Engineering NotesMatthew CurmiNo ratings yet
- MOMENTUM IMPULSE and COLLISIONDocument2 pagesMOMENTUM IMPULSE and COLLISIONRALPH ANDREW ESPERONNo ratings yet
- Physics Deleted and Added PortionDocument2 pagesPhysics Deleted and Added PortionOfficially MedicoNo ratings yet
- Barandes On Magnetic Forces and WorkDocument7 pagesBarandes On Magnetic Forces and Workdavid zilbermanNo ratings yet
- Aqm Lecture 8Document12 pagesAqm Lecture 8sayandatta1No ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument29 pagesPhysics NotesAlicia TanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Electronic Structure of AtomsDocument6 pagesChapter 1 Electronic Structure of AtomsHong Hong WongNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Particles NotesDocument15 pagesFundamental Particles NotesanushaapNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Electrostatic Forces and The Structure of Matter: No Terms ExplanationDocument22 pagesUnit 1 Electrostatic Forces and The Structure of Matter: No Terms ExplanationPhạm Thành ĐạtNo ratings yet
- A Level Physics NotesDocument80 pagesA Level Physics NotesAsghar Abbas100% (3)
- Chapter 2: Matter: Temperature, CDocument1 pageChapter 2: Matter: Temperature, Cteoh6234No ratings yet
- Lecture 02 - Electric Force and Electric FieldDocument33 pagesLecture 02 - Electric Force and Electric FieldRei RamirezNo ratings yet
- Physics Cheat SheetDocument21 pagesPhysics Cheat SheetDinu PereraNo ratings yet
- 1Document30 pages1sabasharifNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 1Document7 pagesChemistry Unit 1Natasha Liliane LootNo ratings yet
- General Inorganic Chemistry Presentation For BSU Compre Handout 2Document118 pagesGeneral Inorganic Chemistry Presentation For BSU Compre Handout 2Ahe BeongNo ratings yet
- Physics Unit 4Document13 pagesPhysics Unit 4ua785100% (1)
- Physics GlossaryDocument21 pagesPhysics GlossaryKing VaibhavNo ratings yet
- Bloch Electrons in SSPDocument6 pagesBloch Electrons in SSPThushanan AnanthalingamNo ratings yet
- Chem101 Ho5Document5 pagesChem101 Ho5nairbatnabamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Modern Theory of PolarizationDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Modern Theory of PolarizationBilal HaiderNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument188 pagesChemistryCricwiz 10No ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Newton's LawsDocument35 pagesTopic 2 - Newton's LawsMay AuditorNo ratings yet
- (Gs Material Science) : Structure of Atom and Interatomic BondingDocument23 pages(Gs Material Science) : Structure of Atom and Interatomic BondingramlakhanNo ratings yet
- Im 1482154379 PDFDocument23 pagesIm 1482154379 PDFramlakhanNo ratings yet
- Negative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 6: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #6From EverandNegative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 6: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #6No ratings yet
- Y10 May 2021 GL PrepDocument52 pagesY10 May 2021 GL PrepFatma SharifNo ratings yet
- Sugar Mill SettingsDocument2 pagesSugar Mill Settingssalahuddin1960100% (3)
- Ethers and Their Relatives: Based On Mcmurry, Organic Chemistry, Chapter 18, 6Th Edition, (C) 2003 2Document10 pagesEthers and Their Relatives: Based On Mcmurry, Organic Chemistry, Chapter 18, 6Th Edition, (C) 2003 2Camila FlorezNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Practice Set BDocument4 pagesChemistry Practice Set BYash PawarNo ratings yet
- 72-1065E RevA MM FL23PDocument145 pages72-1065E RevA MM FL23PmarloztasNo ratings yet
- A1018 10Document8 pagesA1018 10jagarcik5No ratings yet
- AntidotesDocument34 pagesAntidotesDivithNo ratings yet
- Vapor Pressure and Raoult's Law University of The Philippines DilimanDocument3 pagesVapor Pressure and Raoult's Law University of The Philippines DilimanAcademicBMNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 Summary For AsDocument11 pagesPaper 1 Summary For AsElastic FantasticNo ratings yet
- RRB NTPC - Chemistry - Acid-Bases and Salts-TeluguDocument6 pagesRRB NTPC - Chemistry - Acid-Bases and Salts-TeluguRUPA DEVINo ratings yet
- Workability, Strength, and Shrinkage of Ultra-Highperformance Seawater, Sea Sand Concrete WithDocument23 pagesWorkability, Strength, and Shrinkage of Ultra-Highperformance Seawater, Sea Sand Concrete WithGerad ValdezNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note Solution ChemistryDocument6 pagesLecture Note Solution ChemistryAdelia SetianingsihNo ratings yet
- CH 4250: Process Engineering: Assignment 3 Name: - Roll NoDocument2 pagesCH 4250: Process Engineering: Assignment 3 Name: - Roll NoJanani MNo ratings yet
- Modified Waste Egg Shell Derived Bifunctional Catalyst For Biodiesel Production From High FFA Waste Cooking Oil. A ReviewDocument12 pagesModified Waste Egg Shell Derived Bifunctional Catalyst For Biodiesel Production From High FFA Waste Cooking Oil. A ReviewFarah TalibNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of Mould Powders For Slab CastingDocument10 pagesPhysical Properties of Mould Powders For Slab CastingAmir GorjiNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Inorganic Analysis)Document4 pagesQualitative Inorganic Analysis)himanshumallikaNo ratings yet
- MCAT Student Guide Rev Jan 2013 Finalv2Document16 pagesMCAT Student Guide Rev Jan 2013 Finalv2NatalieNo ratings yet
- Self Compacting ConcreteDocument46 pagesSelf Compacting ConcreteJeet Pawar80% (5)
- BA322e Glasslined Outlet Valves AMA-BT-APA-BT 80-50-150-100Document14 pagesBA322e Glasslined Outlet Valves AMA-BT-APA-BT 80-50-150-100qbalangeNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: COMPLIES WITH 29 CFR 1910.1200. Osha Hazard Communication RuleDocument3 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: COMPLIES WITH 29 CFR 1910.1200. Osha Hazard Communication Ruleeti apriyantiNo ratings yet
- Crystal GrowthDocument20 pagesCrystal GrowthAniket SujayNo ratings yet
- 3 Chapter 6 Treatment of Water b2 25Document31 pages3 Chapter 6 Treatment of Water b2 25Ambu DeviNo ratings yet
- Exam Sci 101Document36 pagesExam Sci 101Xenia Mae FloresNo ratings yet
- A1c Prestige 24iDocument1 pageA1c Prestige 24imrashrafiNo ratings yet
- Cooling and Sealing Air SystemsDocument4 pagesCooling and Sealing Air SystemsEDGARNo ratings yet
- Molecular ElectronicsDocument20 pagesMolecular ElectronicsArvind KumarNo ratings yet
- Karnataka Common Entrance Test: Question With Solutions of Chemistry, Physics, Mathematics and BiologyDocument55 pagesKarnataka Common Entrance Test: Question With Solutions of Chemistry, Physics, Mathematics and BiologyVikashNo ratings yet
- Determination of Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) Concentration in Some of Commercial Products, by Redox TitrationDocument9 pagesDetermination of Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) Concentration in Some of Commercial Products, by Redox Titration하은No ratings yet
- Agbami Crude Oil Assay: Far East CutpointsDocument4 pagesAgbami Crude Oil Assay: Far East Cutpointsdassi99No ratings yet
- Iso 05061-2002Document12 pagesIso 05061-2002Simon sunNo ratings yet