Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HW 6 - PalmaMariaDaniela - Ceramics
Uploaded by
MARIA DANIELA PALMA LOOROriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HW 6 - PalmaMariaDaniela - Ceramics
Uploaded by
MARIA DANIELA PALMA LOORCopyright:
Available Formats
4.
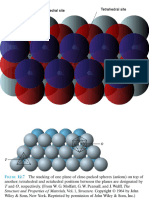
The zinc blende crystal structure is one that may be generated from close-packed planes
of anions.
Table 2: Summary of Some Common Ceramic Crystal Structures.
a) Will the stacking sequence for this structure be FCC or HCP? Why?
The stacking sequence of close-packed planes of anions for the zinc blende crystal structure will be
the same as FCC because the anion packing is FCC.
b) Will cations fill tetrahedral or octahedral positions? Why?
The cations will fill tetrahedral positions since the coordination number for cations is four.
c) What fraction of the positions will be occupied?
Only one-half of the tetrahedral positions will be occupied because there are two tetrahedral sites
per anion, and yet only one cation per anion.
Yachay Tech University 3
5. The corundum crystal structure, found for Al2 O3 , consists of an HCP arrangement of
O2- ions; the Al3+ ions occupy octahedral positions.
a) What fraction of the available octahedral positions are filled with Al3+ ions?
For this crystal structure, two-thirds of the octahedral positions will be filled with Al3+ ions since
there is one octahedral site per O2− ion, and the ratio of Al3+ to O2− ions is two-to-three.
b) Sketch two close-packed O2- planes stacked in an AB sequence, and note octahedral positions
that will be filled with the Al3+ ions.
Two close-packed O2− planes and the octahedral positions between these planes that will be filled
with Al3+ ions are sketched below.
Yachay Tech University 4
7. In terms of bonding, explain why silicate materials have relatively low densities.
The silicate materials have relatively low densities because the atomic bonds have a high degree of
covalency, and, therefore, are directional. This limits the packing efficiency of the atoms, and there-
fore, the magnitude of the density.
8. Would you expect Frenkel defects for anions to exist in ionic ceramics in relatively large
concentrations? Why or why not?
Frenkel defects for anions would not exist in appreciable concentrations because the anion (of an
anion vacancy-anion interstitial pair) is quite large and is highly unlikely to exist as an interstitial.
9. For the ZrO2 -CaO system (Figure 12.24, Callister, 9th ed.), write all eutectic and eutectoid
reactions for cooling.
Figure 1: A portion of the zirconia-calcia phase diagram; ss denotes solid solution. (Adapted from V. S. Stubican and S. P. Ray, ”Phase Equilibria and Ordering in the System ZrO2 − CaO,” J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 60[11-12] 535 (1977).
Reprinted by permission of the American Ceramic Society.)
There is only one eutectic for the portion of the ZrO2 − CaO system shown in Figure 12.24, which,
upon cooling, is:
Liquid → cubic ZrO2 + CaZrO3
There are two eutectoids, which reactions are as follows:
Tetragonal → monoclinic ZrO2 + cubic ZrO2
cubic → monoclinic ZrO2 + CaZr409
Yachay Tech University 7
You might also like
- Close-Packing and Interstitial SitesDocument3 pagesClose-Packing and Interstitial SitesBIBI HUDANo ratings yet
- 2023MSEII Handout8Document17 pages2023MSEII Handout8王竣右No ratings yet
- 02 - Bonding of CeramicsDocument23 pages02 - Bonding of CeramicsMd. Rafiqul IslamNo ratings yet
- Ionic Crystal StructuresDocument10 pagesIonic Crystal StructuresEhsaan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Structure of CeramicsDocument80 pagesStructure of CeramicsAmir Nazri KaibingNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Impq CH01 The Solid State 01 PDFDocument7 pages12 Chemistry Impq CH01 The Solid State 01 PDFVinay GaneshNo ratings yet
- MME365 Glass and Ceramics Engineering: Bonding in Ceramic MaterialsDocument31 pagesMME365 Glass and Ceramics Engineering: Bonding in Ceramic MaterialsZahir Rayhan JhonNo ratings yet
- Metallic and Ionic Solids (Autosaved)Document25 pagesMetallic and Ionic Solids (Autosaved)Asmaa HatemNo ratings yet
- MME 295 Lec 2 - 3Document41 pagesMME 295 Lec 2 - 3Alzeno DoeNo ratings yet
- Concept Check AnswersDocument64 pagesConcept Check AnswersAbhishek Yamini100% (1)
- 3.012 Problem Set 1 3.012Document4 pages3.012 Problem Set 1 3.012Alde AndroNo ratings yet
- Solid State - Structures1Document38 pagesSolid State - Structures1YuNeng KhongNo ratings yet
- SSP - 2Document21 pagesSSP - 2Reema KhanNo ratings yet
- Posiciones Picos DRXDocument14 pagesPosiciones Picos DRXfadarkNo ratings yet
- MSM SolutionDocument12 pagesMSM SolutionAnil ChauvanNo ratings yet
- Ncert PDF Notes Class 12 ChemistryDocument286 pagesNcert PDF Notes Class 12 ChemistryJígñésh Jáy PrákáshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Structural Imperfections Kingery Introducción A Los Materiales CerámicosDocument27 pagesChapter 4 - Structural Imperfections Kingery Introducción A Los Materiales CerámicosLaura BárbaroNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Structures of Metals and CeramicsDocument38 pagesLecture 3 - Structures of Metals and CeramicsDan CostelloNo ratings yet
- Stability of Crown Ether Complexes A Mo Theoretical StudyDocument8 pagesStability of Crown Ether Complexes A Mo Theoretical StudyArturoIvánPavónHernándezNo ratings yet
- Crystal Structure - 複本Document75 pagesCrystal Structure - 複本劉宇哲No ratings yet
- E Ffects of Magnesium Ions and Water Molecules On The Structure of Amorphous Calcium Carbonate: A Molecular Dynamics StudyDocument8 pagesE Ffects of Magnesium Ions and Water Molecules On The Structure of Amorphous Calcium Carbonate: A Molecular Dynamics StudySaeed AbdNo ratings yet
- CBSE Chemistry Class 12 Chapter 1-The Solid State - Important Questions With SolutionsDocument20 pagesCBSE Chemistry Class 12 Chapter 1-The Solid State - Important Questions With SolutionsZaidenNo ratings yet
- Unit I The Solid State: Points To RememberDocument12 pagesUnit I The Solid State: Points To RememberInquisitive Kid100% (1)
- 1 Solid State MLPDocument16 pages1 Solid State MLPRV SinghNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Density,: Cell Unit of Total Cell Unit in Atoms of MassDocument37 pagesTheoretical Density,: Cell Unit of Total Cell Unit in Atoms of MassSudhamsh KNo ratings yet
- CP5Document10 pagesCP5Aravind Raj-kuruviNo ratings yet
- Crystal StructuresDocument16 pagesCrystal StructuresNiken ApriliaNo ratings yet
- THE Solid State: Chapter - 1Document7 pagesTHE Solid State: Chapter - 1Mohamed YaseenNo ratings yet
- Concept Checkpoint AnswersDocument114 pagesConcept Checkpoint AnswersrrameshsmitNo ratings yet
- Minimum Learning MaterialDocument18 pagesMinimum Learning MaterialKshitiz GoelNo ratings yet
- Chepter Wise QuestionsDocument240 pagesChepter Wise QuestionsVinay Tyagi100% (1)
- Engineering Materials ME-221) : Instructor: Dr. Rafiq AhmadDocument32 pagesEngineering Materials ME-221) : Instructor: Dr. Rafiq AhmadAhmad NawazNo ratings yet
- Section 4D Bonding and Structure IV (Metallic Bonding)Document11 pagesSection 4D Bonding and Structure IV (Metallic Bonding)api-3734333No ratings yet
- Mse 351 Engineering Ceramics I: Anthony Andrews (PHD)Document24 pagesMse 351 Engineering Ceramics I: Anthony Andrews (PHD)Bernard YamoahNo ratings yet
- FFFFF 5Document15 pagesFFFFF 5nukenariNo ratings yet
- The Solid State: Unit-1Document7 pagesThe Solid State: Unit-1Rams ChanderNo ratings yet
- MTRLDocument35 pagesMTRLVictor Anthony CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument185 pagesChemistryAshutosh Shaw100% (1)
- Chemistry Study Material For CBSE Class-12Document246 pagesChemistry Study Material For CBSE Class-12Apex Institute75% (4)
- Chemistry Study Material - 2011-12Document246 pagesChemistry Study Material - 2011-12Harsh BhambhaniNo ratings yet
- Symmetry & Crystal StructuresDocument37 pagesSymmetry & Crystal StructuresNurnajihah Sukimi JiehaNo ratings yet
- Structure of Solids 1Document5 pagesStructure of Solids 1zakNo ratings yet
- Structures and Properties of CeramicsDocument38 pagesStructures and Properties of CeramicsArjayNo ratings yet
- Slides MLL100 4th WeekDocument62 pagesSlides MLL100 4th WeekTanishka GurjarNo ratings yet
- Materials Science and Engineering Concept Check Part3 PDFDocument26 pagesMaterials Science and Engineering Concept Check Part3 PDF李宛芸No ratings yet
- Chapter Outline:: CeramicsDocument24 pagesChapter Outline:: CeramicsSeptian Eka TruenoNo ratings yet
- 1 Crystal Defects - Ch04Document72 pages1 Crystal Defects - Ch04Kimberly Joy FerrerNo ratings yet
- Xii ChemistryDocument35 pagesXii ChemistryPratikNo ratings yet
- Chepter Wise QuestionsDocument513 pagesChepter Wise QuestionsAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Callister SolutionsDocument122 pagesCallister SolutionsJ.Srinivas RaoNo ratings yet
- CH 12Document19 pagesCH 12Suliman AlkabaeleNo ratings yet
- Type of Solid Intermolecular Forces Properties Examples: The Key Crystalline SolidsDocument18 pagesType of Solid Intermolecular Forces Properties Examples: The Key Crystalline SolidsSachin KumarNo ratings yet
- Sum Chapter 1Document4 pagesSum Chapter 1mdilshadshigri1000No ratings yet
- SEMICONDUCTORS: They Are Here, There, and EverywhereDocument47 pagesSEMICONDUCTORS: They Are Here, There, and EverywhereMess YeahNo ratings yet
- Solid State: Objective Type Questions Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument5 pagesSolid State: Objective Type Questions Multiple Choice QuestionsSnehashis BoseNo ratings yet
- Advances in Structure Research by Diffraction Methods: Fortschritte der Strukturforschung mit BeugungsmethodenFrom EverandAdvances in Structure Research by Diffraction Methods: Fortschritte der Strukturforschung mit BeugungsmethodenW. HoppeNo ratings yet
- Amorphous Semiconductors: Structural, Optical, and Electronic PropertiesFrom EverandAmorphous Semiconductors: Structural, Optical, and Electronic PropertiesNo ratings yet
- LuzuriagaKenia - PalmaMaría - POST Lab 6Document23 pagesLuzuriagaKenia - PalmaMaría - POST Lab 6MARIA DANIELA PALMA LOORNo ratings yet
- LuzuriagaKenia - PalmaMaría - Post - Practica 4Document20 pagesLuzuriagaKenia - PalmaMaría - Post - Practica 4MARIA DANIELA PALMA LOORNo ratings yet
- 1st Set Exercises - Ma Daniela Palma - CalificadoDocument11 pages1st Set Exercises - Ma Daniela Palma - CalificadoMARIA DANIELA PALMA LOORNo ratings yet
- HW 2 - PalmaMariaDaniela - CorrosionDocument6 pagesHW 2 - PalmaMariaDaniela - CorrosionMARIA DANIELA PALMA LOORNo ratings yet
- Column Check ListDocument2 pagesColumn Check ListMalaciucaTGVNo ratings yet
- 4/2 and 4/3 Directional Control Valve, Manually Operated: Size 04 (D 02) Q 30 L/min (8 GPM) P 320 Bar (4600 PSI)Document2 pages4/2 and 4/3 Directional Control Valve, Manually Operated: Size 04 (D 02) Q 30 L/min (8 GPM) P 320 Bar (4600 PSI)Vito LaudicinaNo ratings yet
- Boq National Library Timor LesteDocument24 pagesBoq National Library Timor Lestekrisna kingNo ratings yet
- VWR 1500 Series ManualDocument28 pagesVWR 1500 Series ManualDanielNo ratings yet
- F1 Flow Measurement in Closed ConduitDocument5 pagesF1 Flow Measurement in Closed ConduitSzeQiLungNo ratings yet
- 21 Weldability of SteelsDocument40 pages21 Weldability of Steelssaeidian100% (2)
- Ac Dur Sba G PDFDocument2 pagesAc Dur Sba G PDFbhagwatpatilNo ratings yet
- TRO CX7323 - E11 - Ad PDFDocument2 pagesTRO CX7323 - E11 - Ad PDFJosip DuvnjakNo ratings yet
- MCQ Thermal PDFDocument6 pagesMCQ Thermal PDFpriya dharshiniNo ratings yet
- Material Design of Aerated Concrete-An Optimum Performance DesignDocument6 pagesMaterial Design of Aerated Concrete-An Optimum Performance DesignYuliusRiefAlkhalyNo ratings yet
- Meyco Segment HR PDFDocument16 pagesMeyco Segment HR PDFFabioSoaresNo ratings yet
- Analysis of RateDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Ratehs_civilNo ratings yet
- Precedent Reliatel WiringDocument64 pagesPrecedent Reliatel WiringMihai IavorschiNo ratings yet
- CargotectureDocument5 pagesCargotecturefitsum tesfayeNo ratings yet
- SSE QC CIV 402 Rev0 PDFDocument2 pagesSSE QC CIV 402 Rev0 PDFBhalsingh JangraNo ratings yet
- Plasticity and Structure of SoilDocument28 pagesPlasticity and Structure of SoilJazmine ValenzonaNo ratings yet
- 2005 (A Colori) TAHER - Strenghtening of Critically Designed Girders With Dapped EndsDocument31 pages2005 (A Colori) TAHER - Strenghtening of Critically Designed Girders With Dapped EndsEleonora InghelleriNo ratings yet
- Marco Island Executive Airport Terminal Construction Change of Order #5 - 2021Document5 pagesMarco Island Executive Airport Terminal Construction Change of Order #5 - 2021Omar Rodriguez OrtizNo ratings yet
- Lubricated Plug Valves: Price List #3119 - Effective: 3/1/19Document16 pagesLubricated Plug Valves: Price List #3119 - Effective: 3/1/19nurhadiNo ratings yet
- 5.deflections Using Energy Methods PDFDocument47 pages5.deflections Using Energy Methods PDFking burgosNo ratings yet
- Hinge: Door HingesDocument4 pagesHinge: Door HingesWee Yong KeeNo ratings yet
- Pe Ball Valves: CertusDocument4 pagesPe Ball Valves: CertusheviNo ratings yet
- Mep ManualDocument108 pagesMep ManualNiyas TkNo ratings yet
- Burj KhalifaDocument12 pagesBurj KhalifaNishi KapadiaNo ratings yet
- CladdingDocument78 pagesCladdingRahul RaghavNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Alternative Composite Material For High Speed Precision Machine Tool Structures PDFDocument14 pagesAnalysis of Alternative Composite Material For High Speed Precision Machine Tool Structures PDFfunkyNo ratings yet
- Hardie Plank Installation GuideDocument1 pageHardie Plank Installation GuideBrandon VieceliNo ratings yet
- 100 Questions For IEEDocument18 pages100 Questions For IEEmusleh19No ratings yet
- Types of Steel BarsDocument6 pagesTypes of Steel BarsvitamkupaNo ratings yet
- Verification of Stress HypothesesDocument9 pagesVerification of Stress HypothesesAfifa AfifaNo ratings yet