Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 3 Msbte Asked Questions
Uploaded by
rutu surve (Ru.)Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 3 Msbte Asked Questions
Uploaded by
rutu surve (Ru.)Copyright:
Available Formats
EOE (22213) FY EE
Chapter 3
Q1 State relation between emitter current (IE), Base current (IB) • and collector current
(Ic) of BJT.
ANS- IE = Ic + IB (2 Marks)
IE = (1+β) IB
Q2 Compare BJT common base configuration with common collector configuration on the
basis of (i) Current gain (ii) Voltage gain (iii) Input impedance (iv) Output impedance
Q3 State condition for both junctions to operate BJT in cut off state, Active state and
saturation state.
DKTE, YCP ICHALKARANJI Page 1
EOE (22213) FY EE
Q4 In a common base configuration, the emitter current is 1 mA. If the emitter circuit is
open, the collector current is 50 micro A. Find total collector current. Assume a (Alpha) =
0.92.
ANS- ( 4 Marks)
Given Data : IE= 1mA
ICBO=50 μA,
α= 0.92
Using Equation: IC = α IE+ICBO
IC = (0.92 × 1mA ) + 0.05 mA.
IC = 0.97 mA.
Q5 A transistor is connected in common emitter (CE) configuration with collector supply
Vcc of 8V. Voltage drop across resistance RC connected in series with collector is 0.5 V.
The value of RC is 800 ohm. If alpha (α ) equal to 0.96, calculate : (i) Collector-emitter
voltage (ii) Collector current (iii) Base current
DKTE, YCP ICHALKARANJI Page 2
EOE (22213) FY EE
Q6 For common emitter configuration sketch input Characteristics for two different values
of VcE and output characteristics for two different values of IB. Write formula for input
resistance and output resistance.
Q7 List configurations of BJT.
Ans
Configurations of BJT : (2 Marks)
1) Common Base (CB) configuration
2) Common Emitter (CE) configuration
3) Common Collector (CC) configuration
Q8 In a common base connection, current amplification factor (a) is 0.9. If the emitter
current is 1 mA, determine the value of base current.
Ans: ( Equation 2 Marks & Answer 2 Marks)
Given data : α = 0.9 IE = 1mA
Αs α= IC /IE.
Therefore IC = 0.9mA
IE = IC +IB ……(Assume ICBO = 0)
DKTE, YCP ICHALKARANJI Page 3
EOE (22213) FY EE
IB = 0.1mA
OR
IB = (1- α) IE
IB = 0.1Ma
Q9 Identify type of BJT configuration having following features:
(i) BJT configuration having the least current gain.
(ii) KIT configuration called as voltage follower.
(iii) BJT configuration having current gain less than one.
(iv) BJT configuration suitable for impedance matching.
(v) BIT configuration suitable for voltage amplification.
(vi) BJT configuration having the least output impedance.
Ans: (Each 1 Mark)
(i) BJT configuration having the least current gain : Common Base Configuration
(ii) KIT configuration called as voltage follower: Common Collector Configuration
(iii) BJT configuration having current gain less than one : Common Base Configuration
(iv) BJT configuration suitable for impedance matching: Common Collector Configuration
(v) BIT configuration suitable for voltage amplification: Common Emitter Configuration
(vi) BJT configuration having the least output impedance: Common Collector Configuration
Q10 Draw output characteristics of common emitter [CE] configuration and explain active,
saturation and cut-off regions in detail.
Explanation : (3 Marks)
(1) Active Region:
In this region collector junction is reverse biased and emitter junction is forward biased. It is the
area to the right of VCE = 0.5 V and above IB= 0. In this region transistor current responds most
sensitively to IB. If transistor is to be used as an amplifier, it must operate in this region.
DKTE, YCP ICHALKARANJI Page 4
EOE (22213) FY EE
(2) Cut Off:
In this region collector junction is reverse biased and emitter junction is reverse biased
Cut off in a transistor is given by IB = 0, IC= ICO.
(3) Saturation Region:
In this region both junctions are forward biased. Since the voltage VBE and VBC
across a forward is approximately 0.7 V therefore, VCE = VCB + VBE = - VBC + VBE is
also few tenths of volts. In this region the transistor collector current is approximately given
by VCC / RC and independent of base current.
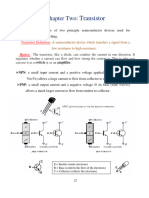
Q11 Draw symbol of NPN and PNP transistors.
Q12 Compare CB, CE, CC configuration of BJT with respect to following points:
(i) Input impedance (ii) Output impedance (iii) Current gain (iv) Voltage gain
Ans-
Parameter CB CE CC
Input impedance Very Low(less than Low(less than 1K) Very High(750K)
100 ohm)
Output impedance Very High High Low
Current gain Less than 1 High Very high
Voltage gain Greater than CC but Highest Lowest(less than 1)
less than CE
Q13 State need of biasing of BJT. List types of biasing.
Ans-
Need of biasing : (2marks for need of biasing)
The basic need of transistor biasing is to keep the base – emitter (BE) junction properly forward
biased and the collector – emitter (CE) junction properly reverse biased during the application of
AC signal.
This type of transistor biasing is necessary for normal and proper operation of transistor to be
used for amplification.
DKTE, YCP ICHALKARANJI Page 5
EOE (22213) FY EE
Types of biasing (2marks for Types of biasing )
1. Fixed bias.
2. Collector-to-base bias.
3. Fixed bias with emitter resistor.
4. Voltage divider bias or potential divider.
5. Emitter bias
Q14 In a common base configuration, current amplification factor is 0.8. If current is 2mA,
determine the value of base current.
Q15 Explain with circuit diagram operation of zener diode as a voltage regulator.
DKTE, YCP ICHALKARANJI Page 6
EOE (22213) FY EE
Working: (2 Mark)
Zener Diodes are widely used as Shunt Voltage Regulators to regulate voltage across small
loads. Zener Diodes have a sharp reverse breakdown voltage and breakdown voltage will be
constant for a wide range of currents. Thus we will connect the zener diode parallel to the load
such that the applied voltage will reverse bias it. Thus if the reverse bias voltage across the zener
diode exceeds the knee voltage, the voltage across the load will be constant.
Q16 Describe the operation of NPN transistor with neat diagram.
ANS
N-p-n transistor is made by sandwiching thin layer of p-type semiconductor between two layers
of n-type semiconductor. It has three terminals - Emitter, Base and collector. The npn transistor
has two supplies, one is connected through the emitter base and one through the collector base.
The supply is connected such that emitter-base are forward biased and collector base are reverse
biased. It means, Base has to be more positive than the emitter and in turn, the collector must be
more positive than the base. The current flow in this type of transistor is carried through
movement of electrons. Emitter emits electrons which are pulled by the base as it is more
positive. This end up in the collector as it is more positive. In this way, current flows in the
transistor.
DKTE, YCP ICHALKARANJI Page 7
EOE (22213) FY EE
Q17 Describe transistor as a switch with neat sketch.
ANS-
Working : ( Diagram 2 Marks Explanation 2 Marks)
From the circuit we can see that the control input Vin is given to base through a current limiting
resistor Rb and Rc is the collector resistor which limits the current through the transistor
When a sufficient voltage V is given to input, transistor becomes ON & it goes into saturation.
During this condition the Collector Emitter voltage Vce will be approximately equal to zero, ie
the transistor acts as a short circuit & Vo = 0.
When input voltage V=0, transistor becomes OFF & it goes into cutoff. The transistor acts as an
open circuit. During this condition the Collector Emitter voltage Vce=Vcc. Therefore Vo = Vcc.
DKTE, YCP ICHALKARANJI Page 8
EOE (22213) FY EE
Q18 Find out the input voltage of the zener regulator shown in Fig. 2. Assume Rs = 200 Ω
and 1Z (max) = 25 mA.
Q19 Define transistor. Explain how transistor works as a switch with input and output
waveforms.
ANS-
Definition of transistor: A semiconductor device with three connections, capable of amplification
in addition to rectification.
Working: Control input Vin is given to base through a current limiting resistor RB and Rc is the
collector resistor which limits the current through the transistor .When a sufficient voltage V is
given to input, transistor becomes ON & it goes into saturation. During this condition the
Collector Emitter voltage VCE will be approximately equal to zero, ie the transistor acts as a short
circuit & Vo = 0. When input voltage V=0, transistor becomes OFF & it goes into cutoff. The
transistor acts as an open circuit. During this condition the Collector Emitter voltage VCE=Vcc.
Therefore Vo = Vcc.
DKTE, YCP ICHALKARANJI Page 9
EOE (22213) FY EE
Q20 Draw circuit of zener diode as a voltage regulator.
DKTE, YCP ICHALKARANJI Page 10
You might also like
- BJT Written Report Group 8Document11 pagesBJT Written Report Group 8Jayvee GusenalemNo ratings yet
- 3a BJT IntroductionDocument20 pages3a BJT IntroductionSyahmi AkmalNo ratings yet
- Analogue Electronic Design Module E EEE2039 / EEE2026 / EEE2042Document36 pagesAnalogue Electronic Design Module E EEE2039 / EEE2026 / EEE2042Arvish RamseebaluckNo ratings yet
- Experiment 11: NPN BJT Common Emitter CharacteristicsDocument7 pagesExperiment 11: NPN BJT Common Emitter CharacteristicsMalikAlrahabiNo ratings yet
- 3.1 BJTransistors pt1 Rev2.3 LectDocument37 pages3.1 BJTransistors pt1 Rev2.3 LectShudermawan JarumanNo ratings yet
- EN564 Analogue Electronics and InstrumentationDocument46 pagesEN564 Analogue Electronics and InstrumentationAl AidenNo ratings yet
- 20013122-034-EDC Lab Manual#10Document7 pages20013122-034-EDC Lab Manual#10Usama MughalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics محاضراتDocument159 pagesPower Electronics محاضراتHasan Al-asadiNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics:: AssignmentDocument15 pagesAnalog Electronics:: AssignmentRenuka SarmishtaNo ratings yet
- I. Basic BJT Application & DC BiasingDocument20 pagesI. Basic BJT Application & DC BiasingNaim NizamNo ratings yet
- ClassDocument35 pagesClassSrikkanth RamachandranNo ratings yet
- 4 - BJTsDocument15 pages4 - BJTsSethiSheikhNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorsDocument38 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorsMuhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Bee C4Document15 pagesBee C4ruchitaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - BJTDocument102 pagesChapter 3 - BJTFarish IskandarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5Document5 pagesExperiment 5dummy008No ratings yet
- Electronics II - Transistor1Document58 pagesElectronics II - Transistor1Kareem AhmedNo ratings yet
- 4 A) Application of BJT As AmplifierDocument12 pages4 A) Application of BJT As AmplifierDharshan kumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 BJTDocument45 pagesChapter 3 BJTLuongtam LuongNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document25 pagesCH 3avishek aviNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistors - Study NotesDocument11 pagesBipolar Junction Transistors - Study NotesNagalingNo ratings yet
- Slide 4 - Electronics (Transistors)Document48 pagesSlide 4 - Electronics (Transistors)Priyatharshan ViswanathanNo ratings yet
- Theory For BJTDocument7 pagesTheory For BJTBenita AgbagwaraNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Transistor Biasing PDFDocument11 pagesBipolar Transistor Biasing PDFAliza TariqNo ratings yet
- 8 - Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument38 pages8 - Bipolar Junction TransistorShahnail MemonNo ratings yet
- EC6304 Electronic Circuits I Question BankDocument10 pagesEC6304 Electronic Circuits I Question BankAnonymous kQZgP8No ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistor - BJTDocument40 pagesBipolar Junction Transistor - BJTMathSolo Nam XBNo ratings yet
- Module 4 NotesDocument19 pagesModule 4 Notes4JN20ME039 - Sindhu H KNo ratings yet
- ET 212 Electronics: Bipolar Junction TransistorsDocument29 pagesET 212 Electronics: Bipolar Junction TransistorsPaula JaneNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument115 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorVince Silva100% (1)
- VTU Notes Basic ElectronicsDocument22 pagesVTU Notes Basic ElectronicsCicira BNo ratings yet
- الفصل 2tDocument23 pagesالفصل 2tmustafaasaad020No ratings yet
- AP Lab 12Document7 pagesAP Lab 12muhammad arslanNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorsDocument26 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorsEng Abdulkadir MahamedNo ratings yet
- Dept - 35 Chap17 PDFDocument33 pagesDept - 35 Chap17 PDFcrystyNo ratings yet
- Taylor & Francis TemplateDocument25 pagesTaylor & Francis TemplateOlatomide OlaosebikanNo ratings yet
- Analog Lab ManualDocument57 pagesAnalog Lab ManualMukesh Sahu100% (1)
- Experiment 3: Common Emitter CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesExperiment 3: Common Emitter CharacteristicsAhmed SalehNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - BJTDocument17 pagesLesson 5 - BJTPavan G MNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument93 pagesTransistorIbnu Zaqi Firdaus100% (2)
- Common Emitter AmplifierDocument12 pagesCommon Emitter AmplifierAffo AlexNo ratings yet
- Solid States Final TestDocument7 pagesSolid States Final TestRickel RoweNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Part 2Document9 pagesLab Manual Part 2Mm MNo ratings yet
- BJT TouhidDocument38 pagesBJT TouhidA.K.M.TOUHIDUR RAHMANNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 10:: Biploar TransistorDocument21 pagesLecture - 10:: Biploar TransistorGEORGENo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document45 pagesChapter 4api-394738731No ratings yet
- Transistor ManualDocument13 pagesTransistor ManualSURESH SURAGANINo ratings yet
- LAB 3-PE-LabDocument8 pagesLAB 3-PE-LabLovely JuttNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 BJTTransistorsDocument15 pagesLesson 7 BJTTransistorsBlueprint MihNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 (BJTand FET) - NewDocument32 pagesUnit-2 (BJTand FET) - NewdevanshhubNo ratings yet
- Common Emitter AmplifierDocument11 pagesCommon Emitter AmplifierZnevba Quintano100% (1)
- EdcDocument21 pagesEdcThiaga RajanNo ratings yet
- CH 03 TransistorDocument26 pagesCH 03 TransistorHatem DheerNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Short Answer Questions BJTDocument3 pagesUnit 3 Short Answer Questions BJTJSSNo ratings yet
- Module2a BEEDocument16 pagesModule2a BEEmd hasanNo ratings yet
- Word Bipolar TransistorDocument9 pagesWord Bipolar TransistorAliza TariqNo ratings yet
- The Common Emitter Amplifier Circuit: Bipolar TransistorDocument10 pagesThe Common Emitter Amplifier Circuit: Bipolar Transistorjain_arvind20027119No ratings yet
- ELL 100 Introduction To Electrical Engineering:: B J T (BJT)Document68 pagesELL 100 Introduction To Electrical Engineering:: B J T (BJT)vineetha nagahageNo ratings yet
- Financial and Economic Texts' Translation - 2 PGDocument2 pagesFinancial and Economic Texts' Translation - 2 PGbia1209No ratings yet
- Diode Equivalent ModelsDocument9 pagesDiode Equivalent ModelsJay Ey0% (1)
- Transitive & Intransitive Verbs: Grammar PracticeDocument5 pagesTransitive & Intransitive Verbs: Grammar PracticeSzeman YipNo ratings yet
- 8 GraphsFundamentalsDocument28 pages8 GraphsFundamentalsguptharishNo ratings yet
- Reference Book 2014 05 19Document84 pagesReference Book 2014 05 19leoNo ratings yet
- Ii Week 12 (Seminar)Document30 pagesIi Week 12 (Seminar)ccNo ratings yet
- Samgroup: Unli Vocab Now LearningDocument20 pagesSamgroup: Unli Vocab Now LearningBrixter MangalindanNo ratings yet
- Service Manual Omoda 5 Part4Document2,081 pagesService Manual Omoda 5 Part4Sina ArsaniNo ratings yet
- Maintain Training Facilities: Michigan English Assessments Inc. CBLM On Cookery NC Ii Date Developed: February 2017Document8 pagesMaintain Training Facilities: Michigan English Assessments Inc. CBLM On Cookery NC Ii Date Developed: February 2017Joebie delos reyesNo ratings yet
- SSP700ADocument4 pagesSSP700AKanwar Bir SinghNo ratings yet
- Purple Futuristic Pitch Deck PresentationDocument10 pagesPurple Futuristic Pitch Deck PresentationRidzki F.RNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics DPPDocument10 pagesElectrostatics DPPhimesh2006hNo ratings yet
- Attach Request: RRC Connection Setup Complete RRC Connection Setup CompleteDocument8 pagesAttach Request: RRC Connection Setup Complete RRC Connection Setup CompleteVusal SuleymanovNo ratings yet
- OPC Functional SpecificationsDocument30 pagesOPC Functional SpecificationselectedwessNo ratings yet
- Teach Yourself Complete Vietnamese (PDFDrive)Document383 pagesTeach Yourself Complete Vietnamese (PDFDrive)Djfrost 888No ratings yet
- Final CDP MuzaffarpurDocument224 pagesFinal CDP MuzaffarpurVivek Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- 03 Vertical Pump Test ANSI HI 2.6 2000Document48 pages03 Vertical Pump Test ANSI HI 2.6 2000Benny RivasNo ratings yet
- Discussion: Lesson 1. Emergence of The Social Science DisciplinesDocument8 pagesDiscussion: Lesson 1. Emergence of The Social Science Disciplinesrio mae carangaNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report: Gubat National High SchoolDocument2 pagesAccomplishment Report: Gubat National High SchoolSheila Divinagracia - EscobedoNo ratings yet
- lmp91000 PDFDocument31 pageslmp91000 PDFJoão CostaNo ratings yet
- ISO-TC309-Draft ISO 37000 - Governance of Organisations For Comment June 2020 - WFEODocument44 pagesISO-TC309-Draft ISO 37000 - Governance of Organisations For Comment June 2020 - WFEOJAVIER100% (1)
- APA Style Student Report Template 7th EditionDocument5 pagesAPA Style Student Report Template 7th EditionMartin Zarate AzorsaNo ratings yet
- Improving Orientation With Yoked PrismDocument2 pagesImproving Orientation With Yoked PrismAlexsandro HelenoNo ratings yet
- Transportation Research Part C: Xiaojie Luan, Francesco Corman, Lingyun MengDocument27 pagesTransportation Research Part C: Xiaojie Luan, Francesco Corman, Lingyun MengImags GamiNo ratings yet
- 312 Full-3Document8 pages312 Full-3Le TrungNo ratings yet
- Mud Motor DV826Document1 pageMud Motor DV826CAMILO ALFONSO VIVEROS BRICEÑONo ratings yet
- Tapiwa Steve Mandaa - 165070 - Assignsubmission - File - Innovation Management Paper DraftDocument7 pagesTapiwa Steve Mandaa - 165070 - Assignsubmission - File - Innovation Management Paper DraftTapiwaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3: Illumination Design of Dental Clinic: B. Lighting StandardDocument16 pagesExperiment 3: Illumination Design of Dental Clinic: B. Lighting StandarderizaNo ratings yet
- Phe Manual 1000e GB tcm11-7539Document36 pagesPhe Manual 1000e GB tcm11-7539iwan kurniawanNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris Teknik Individual Assignment 3Document5 pagesBahasa Inggris Teknik Individual Assignment 3Khaiza SyNo ratings yet