Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(August 24, 2021) Framework For Maternal and Child Nursing - NCM 33 Lecture
Uploaded by
Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
(August 24, 2021) Framework For Maternal and Child Nursing - NCM 33 Lecture
Uploaded by
Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoCopyright:
Available Formats
1
NCM 33 Lecture health supervision and efficient medical attention, and is taught the elements
Instructor: Barbara Lyn Galvez of healthy living (Reyala, 2000).
Transcribed by: Claire J. Tenaja
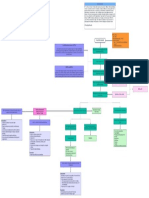
Philosophy of MCN
Framework for Maternal and Child Nursing
Is community-centered Protects the rights of all family members do a daily
Newborn - 0-28 days body scan
Infant - after 28 days
● Some books say they are both the same Is research-centered Use of existing knowledge in a new and creative
way so as to generate new concepts,
Childbirth is 50/50 methodologies, and understandings
● Mother dies child lives or vise versa
Is based on nursing Places importance on promotion of health
theory
Health of the Mother and Child:
● Involves the whole family, not just the mother or child
Is based on the belief Personal, cultural, and religious, attitudes and
● Doctor will first give the information, not the nurse (e.g. bleeding of the that pregnancies or beliefs influence the meaning of pregnancy for
mother) childhood illness are individuals and make each experience unique
stressful because they
What is the most critical year of a child’s life? 1st year are crises
→ immunizations are common (hepa B, BCG, polio, oral polio)
→ immunizations help protect babies from diseases Is a challenging for for Maternal-child nursing is family centered. The
the nurse and is a major father of the child is as important as the mother
factor in promoting high
When are the most vital moments of a pregnancy? 1st Trimester/First 3 months level wellness in
Framework for maternal and child health nursing families
- Provides guidance and direction to implementation of programs and research-centered
interventions in maternal/reproductive, newborn and child health
- A structure that facilitates implementation of child and maternal health Pregnancy, labor and
delivery and the
puerperium are part of
Obstetrics - Care of woman during childbirth; derived from Greek work “obstare” (to
the continuum of the
keep watch) total life cycle. Is based
on nursing theory.
Pediatrics - derived from Greek word, “pais” (child)
Postpartum - up to 6 weeks before involution
Focus on MCN (Maternal and Child Nursing) - Care of childbearing and
Involution - before uterus returns back to normal
childbearing families
Strategic Thrusts (2005-2010)
What is the difference between obstetrics and pediatrics?
Basic emergency obstetric care
● Launch and implement the Basic Emergency Obstetric Care strategy in
Primary goal of MCH - promotion and maintenance of optimum health of the mother
coordination with the DOH.
and newborn
● It entails the establishments of facilities that provide emergency obstetric
care for every 125,000 population and which are located strategically.
Goals of MCH (Maternal and Child Health)
Prenatal and postnatal care
1. To ensure that every expectant and nursing mother maintains good health,
● Improves the quality of prenatal and postnatal care
learns the art of child care, has normal delivery and bears healthy child
Women’s Health Risks and Reduction
2. That every child, wherever possible lives and grows up in a family unit with
love and security, in healthy surroundings, receives adequate nourishment,
TENAJA 2021 | NCM 33 Lecture
2
● Reduce women’s exposure to health risks through the institutionalization of b. Provision of warmth
responsible parenthood & provision of appropriate health care package to all c. Referral
women of reproductive age especially those who are less than 18 years old d. Blood transfusion: due to massive blood loss of mother
Health Advocation
● LGUs and NGOs and other stakeholders must advocate for health through
resource generation and allocation for health services to be provided for the
mother and the newborn
Maternal Neonatal and Child Health and Nutrition Strategy (MNCHN)
- It applies specific policies and actions for local health systems to
systematically address health risks that lead to maternal and especially
neonatal deaths which comprise half of the reported infant mortalities
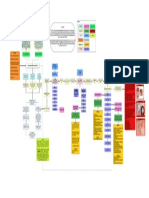
Basic Emergency Obstetrics and Newborn (BEMONC)
- Refers to lifesaving services for emergency maternal and newborn
condition/complications being provided by a health facility of professional
- Services include the following:
7 Signal Obstetric Functions
1. Parenteral antibiotics BeMONC shall operate within 24hours with 7 signal obstetric function. Shall have
- Injectable antibiotics due to complications relating to of access to communication and transportation facilities
infection to the mother Lying in Clinics → same service, lesser expenses
- If infection untreated, it would lead to sepsis
- Sepsis: generalized infection → can reach up to the brain Staff composition
2. Parenteral uterotonics ● Medical doctor
- Uterotonics: products that induce contractions ● Registered nurse
3. Parenteral anticonvulsants ● Registered midwife
- Given by injection to stop convulsive seizures to mothers
in labor Comprehensive Emergency Obstetrics and Newborn Care (CEMONC)
4. Manual removal of the placenta - Refers to lifesaving services for emergency maternal and newborn
- Retaining the placenta will cause infection to the mother condition/complications as in BeMONC plus the provision of surgical delivery
5. Removal of retained products of conception and blood bank services and other specialized obstetric interventions
6. Assisted vaginal delivery - BeMONC + surgical delivery + blood bank services
- Nurses assist doctors and midwives in delivering babies ● blood bank → blood donations for whenever the mother is bleeding
- 3 [student] nurses in delivery ● Vaginal birth → 500 mL of blood
● handle nurse → gets the baby ● Cesarian Birth → 1000mL of blood or more
● assisting nurse → cutting placenta
● initial care nurse → takes care of baby like Essential Health Services Available in the Health Care Facilities
resuscitation A. Antenatal Registration/Prenatal Care
7. Resuscitation of the newborn Objective: to reach all pregnant women, to give sufficient care to ensure a
healthy pregnancy and the birth of a full term healthy baby
- Available in all health facilities
Performance of Assisted Vaginal Deliveries - Not limited only for pregnant mothers:
- Removal of retained placental product it also includes neonatal interventions Normal Healthy instructions and counseling advice for
which include at the minimum: prompt prenatal care examination
a. Newborn resuscitation
TENAJA 2021 | NCM 33 Lecture
3
○ Dose: 60mg/400ug tablet
Mild complications: ● Thorough evaluation
○ Schedule: daily
● Will determine the frequency of follow-up
● Folic acid supplementation (very important)
of these cases by the rural health unit, city
○ prevents neurological conditions to the newborn
health clinic or puericulture center
○ If mothers don’t take this, there are cases where babies are born
without a skull (anencephaly) → will lead to death due to fragility
Potentially serious Referred to the most skilled source of medical and
complications hospital care (like NOPH)
Clean and Safe Delivery
Check for emergency signs (7 Danger signs of pregnancy)
- All RHUs and BHS should have a master list of pregnant women in their 1. Unconsciousness - May lead into seizures
respective catchment center 2. Vaginal bleeding - Not normal
- The Home Based Mother’s Record (HBMR) shall be used when rendering 3. Severe abdominal bleeding
prenatal care as a guide in the identification of risk factors, danger signs and - Might be ectopic pregnancy → embryo is not grown in the uterus,
to be able to do appropriate measures fallopian tube (not a nourishing environment, might burst)
- There should be at least 3 prenatal visits following the prescribed timing: 4. Looks very ill - A pregnant woman is not sick
3 Prenatal visits 5. Severe headache with visual disturbance - Not normal in pregnancy
6. Severe breathing difficulty - Gasping for breath is not normal
First Prenatal Visit Early in pregnancy as possible, during the first
(1-3 months) trimester 7. Severe vomiting - Vomiting is not normal in 2nd to 3rd trimester
Second Prenatal Second trimester B. Make woman comfortable
Visit (4-6 months) C. Assess the woman in labor
● LMP: Last Menstrual Period
Third and Third and subsequent visits during the third ● Number of pregnancy
Subsequent Visits trimester. More frequent visits should be done for ● Start of labor pains
(6-9months and those at risk or with complications. ● Age/height
beyond)
● 7 Danger signs of pregnancy
4th* - postpartum (uncommon though, usually until 3rd ra)
Idk ngano walay D
Tetanus Toxoid Immunization E. Decide if the woman can safely deliver
● Important for pregnant women and child bearing age women to protect them F. Give supportive care throughout labor - be with the woman at always
from the deadly disease TETANUS G. Monitor and manage labor - monitor signs and check for emergencies
○ 2 doses of tt vaccination received 1 month before delivery to H. Monitor closely after delivery - monitor signs and check for emergencies
protect baby from neonatal tetanus, and; I. Continue care for at least two hours postpartum - monitor signs and check for
○ 3 booster dose shots to complete the five doses following the emergencies
recommended schedule provides full protection J. Inform, counsel, and teach woman - teach how to hold, care, burp the baby; cord
*The mother is then called as a “fully immunized mother” (FIM) care
*Total of 5 doses
Micronutrient Supplementation Home Delivery
Is necessary to prevent anemia, vitamin A deficiency and other nutritional disorders - Is normal for pregnancies attended by licensed health personnel
● Vitamin A - Is discouraged if woman is able to go to the hospital
○ Dose: 10,000 iu - Trained hilots may be allowed to attend home deliveries only in the following
○ Given a week starting on the 4th month of pregnancy (do not give it circumstances
before the 4th month of pregnancy because it might cause a. Areas where there are no health personnel and maternal care
congenital problems in the baby) b. When, at the time of delivery, such personnel is not available
● Iron
TENAJA 2021 | NCM 33 Lecture
4
c. Actively practicing but untrained birth attendants, (hilots) should be ○ By doing NBS, metabolic disorders may be detected even before
identified, trained and supervised by a personnel of interest clinical signs and symptoms are present
BHS/RHU trained on Maternal Care ● This treatment can be given early to prevent consequences of untreated
The following are qualified for home delivery: conditions
● Full term - retained in the uterus for the normal period of gestation before
birth a full-term newborn Timing
● Less than 5 pregnancies ● Ideally done within 48-72hrs of life
● Cephalic position - head first ● May also be done after 24hrs of birth
● Without exiting diseases - like high blood, asthma, allergies - Blood is taken from heel of baby, then placed on a paper (or a
● No history of complications place to put the blood), and then screened by the laboratory
- Treatment can be done immediately
Home delivery kit
● 2 pairs of [sterile] clamps *Watch videos on newborn screening*
● Pair of scissors
● Antiseptice (may use 70% Povidone/Iodine) Government programs that provide a safe and healthy baby-mother
● Soap and hand brush relationship
● Clean towel/piece of cloth The rooming-in and Breastfeeding Act of 1992
● Flashlight - To encourage, protect, and support the practice of breastfeeding
● Sphygmomanometer, stethoscope - Creates an environment where basic physical, emotional, and psychological
● Clean hands, clean surface, and clean cord must be strictly followed to need of mothers and infants are fulfilled through the practice of rooming in
prevent infection and breastfeeding
● Provide a safe and healthy mother and baby relationship
Guide for Home Delivery ● For early attachment/ binding with the mother
For registered patients ● Colostrum: necessary nutrients the baby needs (in mother's milk)
- Time when regular pains started ● Before wheeling out from OR, start breastfeeding immediately
- Whether bag of water ruptured or not
- Presence or absence of vaginal discharge and bleeding, etc., Milk Code of 198 Safe and Adequate Nutrition for Infants
- Whether mother moved her bowels and has urinated - Aims to contribute the provision of safe and adequate nutrition of infants by
- Fetal movement felt by the mother or not unusual symptoms such as the protection and promotion of breastfeeding; and by ensuring the proper
bleeding, headache, spots before eyes use of breastmilk substitutes and supplements when these are necessary
*sports in the eyes are danger signs (indicator of high blood - Call of intensification of the dissemination of information on breastfeeding
pressure, arterial spasm) and proper nutrition, and the regulation of advertising, marketing and
distribution of breastmilk substitutes and other related products, including
For unregistered patients bottles and teats
- Get same information as for those registered patient ● Commercial milk is DISCOURAGED
- Get medical and obstetric history ● Mothers should breastfeed their babies
● Exclusive breastfeeding for babies
Newborn Screening (NBS)
- Is a public health program aimed at the early identification of infants who are Family planning counseling
affected by certain genetic/metabolic/infectious conditions - Support a woman and her partner in choosing the method of family planning
- Early identification and intervention can lead to significant reduction of that best suits them and to support them in solving any problems that may
morbidity, mortality, and associated disabilities in affected infant arise with the selected method
-
Significance of Newborn Screening Quiz - 25 August 2021, 7:30 am
● Most babies with metabolic disorders look “normal” at birth Class at 9am
TENAJA 2021 | NCM 33 Lecture
You might also like
- Infants and ToddlersDocument14 pagesInfants and ToddlersJosias Smith100% (1)
- Brigance Early Childhood Screen IIIDocument1 pageBrigance Early Childhood Screen IIISakura ResmiNo ratings yet
- Narrative Child Protection InsetDocument1 pageNarrative Child Protection Insetmichelle c lacad81% (16)
- Care of Mother Child, Adolescent (Well Clients)Document2 pagesCare of Mother Child, Adolescent (Well Clients)Shheeeeeshh100% (1)
- Educ 201 Child Ado ModuleDocument59 pagesEduc 201 Child Ado Modulecharmen rogandoNo ratings yet
- MCN MidtermsDocument48 pagesMCN MidtermsAng, Rico GabrielNo ratings yet
- NCM 33 Framework For Maternal and Child Health Nursing: ST ST RD ND TH TH RD TH TH THDocument5 pagesNCM 33 Framework For Maternal and Child Health Nursing: ST ST RD ND TH TH RD TH TH THSherika Mariz Moreno GuarinNo ratings yet
- NCM 107N - MaternalDocument46 pagesNCM 107N - MaternalNEIL NETTE S. REYNALDONo ratings yet
- NCM107 Prelim Lecture 1Document2 pagesNCM107 Prelim Lecture 1Sachi Reuel BernateNo ratings yet
- Care of Mother, Child, AdolescentsDocument38 pagesCare of Mother, Child, AdolescentsAN1 M3No ratings yet
- MCN Ii - 1 FrameworkDocument9 pagesMCN Ii - 1 FrameworkKathleen NocheNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Health - Maternal Care NursingDocument5 pagesReproductive Health - Maternal Care NursingMaria KawilanNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics: Framework For Maternal & Child Nursing NCM 107Document6 pagesObstetrics: Framework For Maternal & Child Nursing NCM 107Gen MatheNo ratings yet
- NCM 103 Week 1Document21 pagesNCM 103 Week 1Maria Theresa SalvillaNo ratings yet
- Frameworks MCHNDocument33 pagesFrameworks MCHNJerald FernandezNo ratings yet
- Framework of Maternal, Child Health Nursing Care: ObstareDocument40 pagesFramework of Maternal, Child Health Nursing Care: ObstareJohn CarloNo ratings yet
- W1. FrameworkDocument48 pagesW1. FrameworkZairene Jane del RosarioNo ratings yet
- MCN Finals NotesDocument287 pagesMCN Finals NotesbabyboyNo ratings yet
- Cmca Lec PrelimDocument22 pagesCmca Lec PrelimAnyrNo ratings yet
- Acta Paediatrica - 2021 - Klemming - Mother Newborn Couplet Care From Theory To Practice To Ensure Zero Separation For AllDocument7 pagesActa Paediatrica - 2021 - Klemming - Mother Newborn Couplet Care From Theory To Practice To Ensure Zero Separation For Allmels050895No ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing CompressDocument15 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing CompressRy Llanes100% (1)
- Maternal and Child Health NursingDocument9 pagesMaternal and Child Health NursingCassandra NicoleNo ratings yet
- Ncm107mch Module1 FrameworkDocument30 pagesNcm107mch Module1 FrameworkVenus Anne LamayoNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics 1Document35 pagesObstetrics 1HUTALLA CezanneNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Pregnancy and Prenatal CareDocument24 pagesLesson 5 - Pregnancy and Prenatal CareAPRIL ALAPNo ratings yet
- MCN II - NotesDocument8 pagesMCN II - NotesJoey VenegasNo ratings yet
- Prelim Care of Mother Child Adolescent Lec TransesDocument9 pagesPrelim Care of Mother Child Adolescent Lec TransesJay Estrella0% (1)
- Maternal LecDocument17 pagesMaternal Lecs2020106372No ratings yet
- Framework For Maternal and Child Health NursingDocument10 pagesFramework For Maternal and Child Health NursingSHERYL TEMPLANo ratings yet
- Mcn-Lec PrelimsDocument113 pagesMcn-Lec PrelimsYsabelle DamasoNo ratings yet
- Ncma 217 (Lec) - PrelimsDocument24 pagesNcma 217 (Lec) - PrelimsLou KristofferNo ratings yet
- NCM109 Prelim (First Notes)Document10 pagesNCM109 Prelim (First Notes)Mary Queenie Tulin100% (2)
- Introduction To MCN Prof. Dymphna Casquejo: Framework For Maternal and Child NursingDocument4 pagesIntroduction To MCN Prof. Dymphna Casquejo: Framework For Maternal and Child NursingLynnelljhyen MALUBAYNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health NursingDocument11 pagesMaternal and Child Health NursingNoelle FabrosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Introduction On MCHNDocument20 pagesLesson 1 Introduction On MCHNAPRIL ALAPNo ratings yet
- Community Medicine Presentation FINALDocument17 pagesCommunity Medicine Presentation FINALmomin.laangNo ratings yet
- Week 2-3 Part 1Document26 pagesWeek 2-3 Part 1EmpieNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health NursingDocument1 pageMaternal and Child Health NursinggreinabelNo ratings yet
- MCN ReviewerDocument31 pagesMCN ReviewerShania Karylle TanNo ratings yet
- MCN ReviewerDocument14 pagesMCN ReviewerMary Joy Teylan CalongoNo ratings yet
- MCN Reviewer Sa PrelimDocument22 pagesMCN Reviewer Sa PrelimMary Joy Teylan CalongoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mother and Child Health Nursing NCM 107Document8 pagesIntroduction To Mother and Child Health Nursing NCM 107Gen MatheNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child NursingDocument4 pagesMaternal and Child NursingZhoey ReyesNo ratings yet
- Framework For Maternal and Child Health NursingDocument18 pagesFramework For Maternal and Child Health NursingTrisha ApalisNo ratings yet
- MCNDocument47 pagesMCNSamantha DiegoNo ratings yet
- Introduction of New BornDocument7 pagesIntroduction of New BornAshish Gupta100% (1)
- Maternity Chapter 01 Framework For Maternal and Child Health Nursing PDFDocument9 pagesMaternity Chapter 01 Framework For Maternal and Child Health Nursing PDFChskNo ratings yet
- Learning Exercises - Framework For Maternal and Child Health NursingDocument4 pagesLearning Exercises - Framework For Maternal and Child Health NursingKilla BischeNo ratings yet
- A. Goals and Philosophies of Maternal and Child Health Nursing The 2020 National Health GoalsDocument3 pagesA. Goals and Philosophies of Maternal and Child Health Nursing The 2020 National Health GoalsJoymae Olivares TamayoNo ratings yet
- 9B. Effectiveness of Educational Intervention On Breastfeeding Among Primi Pregnant WomanDocument6 pages9B. Effectiveness of Educational Intervention On Breastfeeding Among Primi Pregnant Womanagaua16No ratings yet
- 5 Peripartum Breastfeeding ManagementDocument5 pages5 Peripartum Breastfeeding Managementhaviza nisaNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child PrelimDocument27 pagesMaternal and Child PrelimjadarcNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Framework For Maternal and Child NursingDocument2 pagesModule 1 Framework For Maternal and Child NursingJustine FloresNo ratings yet
- Local Media958922746168865631Document8 pagesLocal Media958922746168865631Kate Lawrence BitantosNo ratings yet
- MCHN 1ST&2ND LectDocument8 pagesMCHN 1ST&2ND LectZahNo ratings yet
- Chapter01 A Framework For Maternal and Child NursingDocument36 pagesChapter01 A Framework For Maternal and Child NursingJoebeth Competente100% (1)
- Maternal and Child NotesDocument26 pagesMaternal and Child NotesJann ericka JaoNo ratings yet
- MCHN Framework 2Document5 pagesMCHN Framework 2Lucyvelle DaramanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 MergedDocument212 pagesUnit 1 Mergedyokinosamaa2No ratings yet
- Family Centered Maternity Care PP2017Document5 pagesFamily Centered Maternity Care PP2017melaNo ratings yet
- Seminar On PRVNTV ObgDocument43 pagesSeminar On PRVNTV Obgraghuram reddyNo ratings yet
- Oxytocin IVDocument7 pagesOxytocin IVAnamika LinggaNo ratings yet
- 1.maternal and Child Health NursingDocument33 pages1.maternal and Child Health NursingBhie Bhie100% (1)
- NCP Part 1 Overview of NCPDocument23 pagesNCP Part 1 Overview of NCPMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Annotated Reading - DHF (Pedia)Document5 pagesAnnotated Reading - DHF (Pedia)Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- 7 Nurses Notes Charting FDAR PDocument2 pages7 Nurses Notes Charting FDAR PMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- FINAL MedsheetDocument1 pageFINAL MedsheetMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- 10 1016j Teln 2018 12 005Document6 pages10 1016j Teln 2018 12 005Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Passive Ent Pe2qDocument1 pagePassive Ent Pe2qMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- (August 25, 2021) Basic Concepts in Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocument3 pages(August 25, 2021) Basic Concepts in Nutrition and Diet TherapyMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- AKI vs. CKD FinalDocument1 pageAKI vs. CKD FinalMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis and Nursing Interventions For Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis and Nursing Interventions For Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- (REVISED) CRANIOTOMY-CmapDocument1 page(REVISED) CRANIOTOMY-CmapMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- D.S.E.B Patient's Initials Submitted By: Josiah David P. Maraat Kyrah Mae Nerez Submitted To: Asst. Prof. Zorrina Luague Date: 10/24/2022Document15 pagesD.S.E.B Patient's Initials Submitted By: Josiah David P. Maraat Kyrah Mae Nerez Submitted To: Asst. Prof. Zorrina Luague Date: 10/24/2022Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- FHP and NCPDocument12 pagesFHP and NCPMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Simulated Care (Bajado)Document6 pagesSimulated Care (Bajado)Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- FHP and NCP (Ravera)Document11 pagesFHP and NCP (Ravera)Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Simulated Care (Bajado)Document6 pagesSimulated Care (Bajado)Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Nursing-Care-Plan-J P VDocument8 pagesNursing-Care-Plan-J P VMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Prostate Cancer - Group 12Document1 pageProstate Cancer - Group 12Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Bajado - Annotated Reading (CHN RLE)Document8 pagesBajado - Annotated Reading (CHN RLE)Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- PDF 1Document101 pagesPDF 1Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- World Psychiatry - 2016 - Maslach - Understanding The Burnout Experience Recent Research and Its Implications ForDocument9 pagesWorld Psychiatry - 2016 - Maslach - Understanding The Burnout Experience Recent Research and Its Implications ForMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Orthopaedic Surgery - Pre and Post Operative Management in AdultsDocument30 pagesOrthopaedic Surgery - Pre and Post Operative Management in AdultsMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Fractures - LeafletDocument2 pagesFractures - LeafletMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Black and Brown Business BrochureDocument2 pagesBlack and Brown Business BrochureMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Prostate CancerDocument39 pagesProstate CancerMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Survey Questionnaire B. Socio-Economic DataDocument5 pagesSurvey Questionnaire B. Socio-Economic DataMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Care of Postcraniotomy Patients Leaflet 3Document2 pagesCare of Postcraniotomy Patients Leaflet 3Ma. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On Nursing Management of Fluid Electrolyte and Acid Base ImbalancesDocument3 pagesWorksheet On Nursing Management of Fluid Electrolyte and Acid Base ImbalancesMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- NCP Cholecystectomy RevisedDocument7 pagesNCP Cholecystectomy RevisedMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- HIV - AIDSDocument1 pageHIV - AIDSMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Family Tree ExerciseDocument2 pagesFamily Tree ExerciseMelissa Torres OsorioNo ratings yet
- Adhd For CounselorsDocument7 pagesAdhd For CounselorsEdl ZsuzsiNo ratings yet
- A Teenage Life - SpeechDocument2 pagesA Teenage Life - Speechjennamaemusni_55810486% (36)
- Autotelic Personality QuestionnaireDocument15 pagesAutotelic Personality QuestionnaireRuqayya OmarNo ratings yet
- Mapsy-603 PyqDocument4 pagesMapsy-603 PyqprakharcoolsNo ratings yet
- Hutt Families For Midwives Evidence PaperDocument12 pagesHutt Families For Midwives Evidence PaperStuff NewsroomNo ratings yet
- Child Psychology Research PaperDocument7 pagesChild Psychology Research PaperJamal DeNo ratings yet
- SF2 August 11 Humss Ngilay SHSDocument3 pagesSF2 August 11 Humss Ngilay SHSTaj NgilayNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Lesson 19 Too EarlyDocument44 pagesUnit 3 Lesson 19 Too EarlyAbigail Sarmiento0% (1)
- How The Child Welfare System Works: Factsheet - October 2020Document8 pagesHow The Child Welfare System Works: Factsheet - October 2020Cosby BlackNo ratings yet
- Effects of Birth Order On PersonalityDocument7 pagesEffects of Birth Order On Personalitymary louise maganaNo ratings yet
- Sas #20 - Edu 537Document6 pagesSas #20 - Edu 537Divine Joy Atractivo PinedaNo ratings yet
- ASPERGER'SDocument4 pagesASPERGER'SJohana NyagayaNo ratings yet
- VED04 COURSE OUTLINE PSYCHOLOGICAL THEORIES OF VALUES EDUCATIONDocument4 pagesVED04 COURSE OUTLINE PSYCHOLOGICAL THEORIES OF VALUES EDUCATIONANJANETT BUENAVENTURANo ratings yet
- Cup FeedingDocument2 pagesCup FeedingEaster Soma HageNo ratings yet
- Hypoglycemia in Exclusively Breastfed High-Risk Neonates - A Hospital-Based StudyDocument7 pagesHypoglycemia in Exclusively Breastfed High-Risk Neonates - A Hospital-Based StudyNeta Aza MaineztNo ratings yet
- Maternal, Labor, Delivery, and Perinatal Outcomes Associated With Placental Abruption: A Systematic ReviewDocument23 pagesMaternal, Labor, Delivery, and Perinatal Outcomes Associated With Placental Abruption: A Systematic ReviewasfwegereNo ratings yet
- Laporan Rak NarkotikaDocument18 pagesLaporan Rak NarkotikaaliyahNo ratings yet
- Psychological Changes in PregnancyDocument8 pagesPsychological Changes in PregnancyMaria Ivy Rochelle TanNo ratings yet
- Activity 2222Document2 pagesActivity 2222Rheeanne AmilasanNo ratings yet
- Adhd Presentation 1Document8 pagesAdhd Presentation 1api-314230015No ratings yet
- V. Naegels Rule Calculating EDD, AOG, OB ScoreDocument15 pagesV. Naegels Rule Calculating EDD, AOG, OB ScoreSophia LayugNo ratings yet
- Case Study of A ChildDocument27 pagesCase Study of A Childapi-534836842No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Physical Growth Sexual DevelopmentDocument38 pagesLecture 1 Physical Growth Sexual Developmentjaish8904No ratings yet
- Models of Maternity CareDocument2 pagesModels of Maternity CareFerry FernandoNo ratings yet
- Child Abuse 1Document3 pagesChild Abuse 1api-285958901No ratings yet