Professional Documents
Culture Documents
T6 Acne, Scabies, Eczema
Uploaded by
tarsha0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views29 pages1) The document discusses three common skin conditions - acne, scabies, and eczema.
2) For acne, it describes classifications, causes, and treatment options including topical and oral medications to induce clearance and maintain remission.
3) For scabies, it provides details on diagnosis, treating all contacts, removing all contaminated items, applying medication thoroughly, and using prescription creams or lindane.
4) For eczema, it lists different types and emphasizes moisturizing, preventing dryness, avoiding irritants, using steroids as needed, and managing itch to help control flares.
Original Description:
Original Title
T6 ACNE, SCABIES, ECZEMA.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) The document discusses three common skin conditions - acne, scabies, and eczema.
2) For acne, it describes classifications, causes, and treatment options including topical and oral medications to induce clearance and maintain remission.
3) For scabies, it provides details on diagnosis, treating all contacts, removing all contaminated items, applying medication thoroughly, and using prescription creams or lindane.
4) For eczema, it lists different types and emphasizes moisturizing, preventing dryness, avoiding irritants, using steroids as needed, and managing itch to help control flares.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views29 pagesT6 Acne, Scabies, Eczema
Uploaded by
tarsha1) The document discusses three common skin conditions - acne, scabies, and eczema.
2) For acne, it describes classifications, causes, and treatment options including topical and oral medications to induce clearance and maintain remission.
3) For scabies, it provides details on diagnosis, treating all contacts, removing all contaminated items, applying medication thoroughly, and using prescription creams or lindane.
4) For eczema, it lists different types and emphasizes moisturizing, preventing dryness, avoiding irritants, using steroids as needed, and managing itch to help control flares.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 29
Acne, Scabies and Eczema
Dr Han Yung Wen
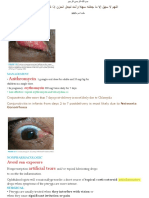
• A 22-year-old woman presents with the following facial lesions for the
past 2 weeks.
• What are your differential diagnosis?
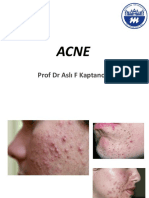
Acne
• Acne is a disease of pilosebaceous units in the skin.
• Colonization of Propionibacterium acnes
• Classification: mild, moderate and severe
• Classified by type of lesion—comedonal, papulopustular, and
nodulocystic. Pustules and cysts are considered inflammatory acne.
• Different classification system – follow CPG Malaysia 2012
Aims of management
• To induce clearance
• To maintain remission and prevent relapse
• To prevent physical and psychological complications
Induce clearance
• Topical agents • Systemic agents
• Topical benzoyl peroxide (BPO) • Oral antibiotics
• Topical retinoids • Tetracycline
• Topical tretinoin • Doxycycline
• Topical adapalene • Erythromycin
• Topical isoretinoin • Clindamycin
• Topical tazarotene • Minocycline
• Topical antibiotics - erythromycin • Co-trimoxazole/ trimethoprim alone
• Topical Azelaic acid • Oral hormonal treatment
• COCs
• Topical salicylate acid
• Spironolactone
• Topical sulphur and its combination • Other antiadrogenic agents - flutamide
• Topical Dapsone • Isoretinoin
• Topical Fixed combination
Maintainence
• Cleaniness
• Topical agents
• Comedone extraction – not widely recommended
• Others - Chemical peel, phototherapy, photodynamic therapy
• Don’t forget psychological well-being
References
• Pochi PE, Shalita AR, Strauss JS, Webster SB, Cunliffe WJ, Katz HI, et al.
Report of the Consensus Conference on Acne Classification.
Washington, D.C., March 24 and 25, 1990. J Am Acad Dermatol.
1991;24:495–500.
• Management of Acne, Clinical Practice Guidelines, Malaysia 2012
• A 10-year-old boy was brought to you by his parents because of the
itchy rashes over his hands for the past 2 weeks.
Burrows
Management
• Diagnosis under microscope – fix with oil
• Education – explain to patient about scabies
• Treat all close contacts
• If the medication is wipe off e.g. during hand washing, make sure
reapply
• Need to get rid of all scabies hiding areas – all clothings, bed linens
etc either boil (>50ᴼC), or keep in plastic bag >72 hours (scabies can’t
live separated from human host for >72 hours
• Apply the medication neck down (except babies), including all skin
folds
• Choice of meds: Permethrin 5%; Benzyl benzoate 10-25%; Precipitate
sulphur 6-10%; crotamiton 10%; Lindane 1%; Ivemectin (oral)
References
• Guideline for management of scabies in adult and children, Clinical
Practice Guidelines Malaysia 2015
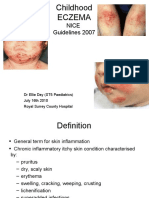
• A 70-year-old man presents with persistent itchiness over both his
legs for the past 6 months. He has seen various GPs and
dermatologists, given topical medication, resolved temporarily but
recur. He is keen to know his condition.
• What are your differential diagnosis?
Types of eczema
• Endogenous • Exogenous
• Atopic or IgE • Allergic
• Seborrheic • Toxic irritant contact
• Discoid or nummular • Photosensitive
• Pompholyx
• Venous
• Asteatotic
• Juvenile plantar
• Erythroderma
Management
• MOISTURISE, MOISTURISE, MOISTURISE
• Prevent further dryness – avoid hot shower, avoid strong soap,
use mild soap or soap substitute
• Apply moisturiser after shower on soften keratin layer
• Use liberally, apply as often as needed
• May use with steroids cream
• Avoid the itch-scratch-itch-scratch cycle
• May need to add antihistamine
• Wet wrap
• Use cotton undergarments, avoid synthetic materials
• Avoid perfumes/ cosmetics especially if it worsens the eczema
References
• Guidelines for the care of the management of atopic dermatitis,
American Academy of Dermatology 2014
Thank you
You might also like
- Holistic Microneedling: The Manual of Natural Skin Needing and Derma Roller UseFrom EverandHolistic Microneedling: The Manual of Natural Skin Needing and Derma Roller UseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- DR Meera Kuppusamy MBBS (IMU), MRCP (UK), Adv Derm Masters (UKM) Consultant Dermatologist Columbia Asia KlangDocument86 pagesDR Meera Kuppusamy MBBS (IMU), MRCP (UK), Adv Derm Masters (UKM) Consultant Dermatologist Columbia Asia KlangdnaielNo ratings yet
- Caninedemodicosis SheilaTorres 211127 143246Document64 pagesCaninedemodicosis SheilaTorres 211127 143246Ahmed eisaNo ratings yet
- Skin Diseases: Acne Vulgaris Allergic DermatitisDocument32 pagesSkin Diseases: Acne Vulgaris Allergic DermatitisJuma SammyNo ratings yet
- AcneDocument41 pagesAcneBLennTambling100% (1)
- Treatment Options For Lichenoid DiseaseDocument8 pagesTreatment Options For Lichenoid DiseasedrbhaveshpNo ratings yet
- Sunil S. Dhawan, MD, FACP: Prevalence of Acne Among Adolescents and Young AdultsDocument15 pagesSunil S. Dhawan, MD, FACP: Prevalence of Acne Among Adolescents and Young AdultsSalmaaAlsNo ratings yet
- Derma ADDocument49 pagesDerma ADFatima Marwa Teo MaghinayNo ratings yet
- Emergency Care For MO - General Approach To Poison ManagementDocument40 pagesEmergency Care For MO - General Approach To Poison Managementanupam mishraNo ratings yet
- Nurse Emma King - Paediatric Skin Conditions and Their TreatmentDocument33 pagesNurse Emma King - Paediatric Skin Conditions and Their Treatmentgaspe1999No ratings yet
- Can Atopic Dermatitis Be Prevented?Document60 pagesCan Atopic Dermatitis Be Prevented?IkshavakuNo ratings yet
- Drug Used in Skin and Mucus MembraneDocument35 pagesDrug Used in Skin and Mucus MembraneMamta Yadav100% (1)
- The Principles of Dermatologic and Local TreatmentDocument24 pagesThe Principles of Dermatologic and Local TreatmentMojeeb Rahman AhadiNo ratings yet
- Acne VulgarisDocument67 pagesAcne VulgarisSloOw JamZzNo ratings yet
- Dermatitis 1-2023Document20 pagesDermatitis 1-2023Maryam ElammaryNo ratings yet
- Acne Vulgaris-1Document7 pagesAcne Vulgaris-1amanabduwahabNo ratings yet
- Elderly Skin CareDocument46 pagesElderly Skin CareRobbyNo ratings yet
- K27. Dermatologic PharmacologyDocument41 pagesK27. Dermatologic PharmacologyFajar Cristianta GintingNo ratings yet
- 8 Chemotherapy PPDocument67 pages8 Chemotherapy PPjericho dinglasanNo ratings yet
- Fungal Infectious TherapyDocument43 pagesFungal Infectious TherapyNoor AliNo ratings yet
- ملف الصور الاهم - - -Document100 pagesملف الصور الاهم - - -mohamedeen hamzaNo ratings yet
- ws08 Elderly Skin CareDocument46 pagesws08 Elderly Skin CareRobbyNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading Guidelines of Care For Management of Acne VulgarisDocument18 pagesJournal Reading Guidelines of Care For Management of Acne VulgarisRidho Mochine FisciensaNo ratings yet
- Derma RXDocument46 pagesDerma RXBayisa GirmaNo ratings yet
- Acne Slide Demomu 2019Document48 pagesAcne Slide Demomu 2019Ali ÇevikNo ratings yet
- AcneDocument11 pagesAcneDfree FerdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Sahida Skin InfctionssDocument65 pagesSahida Skin InfctionssSHANo ratings yet
- Atopic Eczema 2Document27 pagesAtopic Eczema 2Pierre-Charles WoodNo ratings yet
- Atopic SeminarDocument34 pagesAtopic SeminarJeeban Jyoti MishraNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Sweat and Sebaceous GlandsDocument43 pagesDisorders of Sweat and Sebaceous GlandsSantosh ThapaNo ratings yet
- Group 1 SpottingDocument167 pagesGroup 1 SpottingKritick BhandariNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapeutic and ImmunosupressiveDocument43 pagesChemotherapeutic and Immunosupressivearmanuel1390antNo ratings yet
- Acne Vulgaris DiscussionDocument46 pagesAcne Vulgaris Discussiondrsaleemraza2004No ratings yet
- Atopic Eczema SlidesDocument15 pagesAtopic Eczema SlidesShivangi LodhaNo ratings yet
- Leilani O. Estacio, Man RN: Chemotherapeutic Agents, Antibiotics, Immunosuppressive DrugsDocument42 pagesLeilani O. Estacio, Man RN: Chemotherapeutic Agents, Antibiotics, Immunosuppressive DrugsHERLIN HOBAYANNo ratings yet
- Acne Vulgaris: Basic Dermatology CurriculumDocument58 pagesAcne Vulgaris: Basic Dermatology CurriculumJhoel Jhonatan Torres MuñozNo ratings yet
- The Decision To Go Systemic: Vivian Shi, MDDocument21 pagesThe Decision To Go Systemic: Vivian Shi, MDSebastian GrosuNo ratings yet
- Keloids: A Review: Journal ReadingDocument22 pagesKeloids: A Review: Journal ReadingYunita SalakaNo ratings yet
- Acne Vulgaris: Cynthia Salinas, M.D. PGY-3 Patient Conference February 2, 2005Document29 pagesAcne Vulgaris: Cynthia Salinas, M.D. PGY-3 Patient Conference February 2, 2005Agnes NesiaNo ratings yet
- Care of The Child With An Integumentary Disorder: Nursing 346Document15 pagesCare of The Child With An Integumentary Disorder: Nursing 346Glory MimiNo ratings yet
- Topic 14 - Dermatologic AgentsDocument4 pagesTopic 14 - Dermatologic AgentsReanne Mae AbreraNo ratings yet
- 11 DermatitisDocument39 pages11 DermatitisLQYNo ratings yet
- Acne Vulgaris DiscussionDocument46 pagesAcne Vulgaris DiscussionDwi ErmawatiNo ratings yet
- PP Nurse AdviceDocument25 pagesPP Nurse AdviceAnonymous BrasMuKxUONo ratings yet
- Common Bacterial and Viral Infection Key Answer FinalDocument10 pagesCommon Bacterial and Viral Infection Key Answer FinalAnu KrupaNo ratings yet
- VPHM55 Lesson 16 and 17Document94 pagesVPHM55 Lesson 16 and 17Camille Faith MaglaquiNo ratings yet
- Eczematous Disorders CFM REPORT 2Document32 pagesEczematous Disorders CFM REPORT 2Arianne CortezNo ratings yet
- Acne-Skin Disease Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument28 pagesAcne-Skin Disease Diagnosis and Treatmentkamardin zakuaniNo ratings yet
- Handouts - OncologyDocument7 pagesHandouts - OncologylibalibzyrelleNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy Handbook 9th Edition 2015-BAB KULITDocument19 pagesPharmacotherapy Handbook 9th Edition 2015-BAB KULITCrista Resti StarillaNo ratings yet
- Adebola Ogunbiyi, FMCP, FWACP, FRCP, FNAMED UCH, IbadanDocument63 pagesAdebola Ogunbiyi, FMCP, FWACP, FRCP, FNAMED UCH, Ibadanadamu mohammadNo ratings yet
- Cellular Regulation Student VersionDocument15 pagesCellular Regulation Student VersionCruz YrNo ratings yet
- Activity 10 CPP LabDocument8 pagesActivity 10 CPP Labmohammad abdusalimNo ratings yet
- Efloresensi Polimorfik Dan Kelainan Pigmentasi: Dr. Dr. Linda J Wijayadi SP - KK FINSDVDocument50 pagesEfloresensi Polimorfik Dan Kelainan Pigmentasi: Dr. Dr. Linda J Wijayadi SP - KK FINSDVFarahditya PutriNo ratings yet
- Bathing Guide en WebDocument20 pagesBathing Guide en WebkupitiroNo ratings yet
- PsoriasisDocument21 pagesPsoriasisRamalakshmi LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Gabungan Materi FarmakoterapiDocument235 pagesGabungan Materi FarmakoterapiIndah PrayestiNo ratings yet
- Dermatology in 2hrsDocument222 pagesDermatology in 2hrslarisaP100% (4)
- Hyper-Pigmentation Of The Skin A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment, And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHyper-Pigmentation Of The Skin A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment, And Related ConditionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Radiant Beauty: Nurturing Your Skin with Nature's ElixirsFrom EverandRadiant Beauty: Nurturing Your Skin with Nature's ElixirsNo ratings yet
- 301 Stainless SteelDocument1 page301 Stainless SteelDanielNo ratings yet
- Section 2: Structure and Written ExpressionDocument6 pagesSection 2: Structure and Written ExpressionMalik RidwanNo ratings yet
- USP-NF Alginic AcidDocument2 pagesUSP-NF Alginic AcidK.m. Ehsan Morshed RanaNo ratings yet
- Generation of Electrical Energy Using Hybrid Energy of PV Solar Cell, Wind Turbine, Rain Water and Perpetual MotionDocument10 pagesGeneration of Electrical Energy Using Hybrid Energy of PV Solar Cell, Wind Turbine, Rain Water and Perpetual MotionGhafar HassanNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 107 Report 1Document16 pagesAssignment - 107 Report 1Warla Rahman Maha 2131503630No ratings yet
- Coloration TechnologyDocument17 pagesColoration Technologyfathi mustafaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Exemplar Dry RunDocument5 pagesLesson Exemplar Dry Runcristito inovalNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Cbse Project: Preparation of InkDocument16 pagesClass 12 Cbse Project: Preparation of InkAdarsh GopakumarNo ratings yet
- PharmaceuticalsDocument23 pagesPharmaceuticalsISHITA NAGPALNo ratings yet
- P Block Elements (Group 15, 16, 17 & 18) - JEE Main 2024 January Question Bank - MathonGoDocument6 pagesP Block Elements (Group 15, 16, 17 & 18) - JEE Main 2024 January Question Bank - MathonGorohansardar0102No ratings yet
- Cocoa Butter Alternative FatsDocument20 pagesCocoa Butter Alternative FatsMarco HernandezNo ratings yet
- 5-Peptides and Proteins Medicine 2010-2011Document6 pages5-Peptides and Proteins Medicine 2010-2011Mohammed SallamNo ratings yet
- Benson-Taylor Taribo IT ReportDocument48 pagesBenson-Taylor Taribo IT ReportTaribo Benson-TaylorNo ratings yet
- IX - InTSO - Worksheet - 1 (Atoms & Molecules)Document3 pagesIX - InTSO - Worksheet - 1 (Atoms & Molecules)arush0156No ratings yet
- 657f2fc1ba44990018f402f1 ## Practice Test-04 Question PaperDocument18 pages657f2fc1ba44990018f402f1 ## Practice Test-04 Question PaperSiya JaniNo ratings yet
- Urine Strips Brochure - 2Document2 pagesUrine Strips Brochure - 2Trần Thanh ViệnNo ratings yet
- Empirical and Molecular FormulaeDocument5 pagesEmpirical and Molecular FormulaeMohd Jamalil Azam MustafaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Combined Science 0653/33Document24 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Combined Science 0653/33Dimitrios KoulianosNo ratings yet
- SD FINE Price List 22-23Document161 pagesSD FINE Price List 22-23bhartipkoliNo ratings yet
- MN4213 enDocument8 pagesMN4213 enArif ZakuanNo ratings yet
- Avista PDS Vitec 7000 LDocument1 pageAvista PDS Vitec 7000 LCommercial HWTNo ratings yet
- ASCE-PartB - P4Document10 pagesASCE-PartB - P4Singh RichaNo ratings yet
- Cell DisruptionDocument62 pagesCell DisruptionSreejesh P C100% (2)
- OxoneDocument2 pagesOxoneSha Hriyar HNo ratings yet
- Ample IST: PpendixDocument58 pagesAmple IST: PpendixRegina EfraimNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Recovery of Metals From SlagsDocument17 pagesAn Overview of Recovery of Metals From SlagsPauloValdiviesoNo ratings yet
- GB Twin Shafts Paddle MixerDocument2 pagesGB Twin Shafts Paddle MixerBanzragch JamsranNo ratings yet
- SGE Analytical Science Product Data and Part Numbers 1 1Document258 pagesSGE Analytical Science Product Data and Part Numbers 1 1Sofhy SofhyNo ratings yet
- A Brief Review On Micromachining of MaterialsDocument6 pagesA Brief Review On Micromachining of Materialsprasanth kNo ratings yet
- Patricles and Solutions WorkbookDocument45 pagesPatricles and Solutions WorkbookCool ManNo ratings yet