Professional Documents
Culture Documents
M2 - L3. DNA - The Genetic Materia
Uploaded by
Princess Paula ArguidasOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
M2 - L3. DNA - The Genetic Materia
Uploaded by
Princess Paula ArguidasCopyright:
Available Formats
8/26/23, 8:55 AM M2 - L3. DNA: The Genetic Material: General Zoology-IRROMERO 8/26/23, 8:55 AM M2 - L3.
gy-IRROMERO 8/26/23, 8:55 AM M2 - L3. DNA: The Genetic Material: General Zoology-IRROMERO
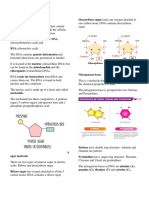
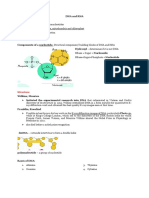
guanine of the purine group, and the
M2 - L3. DNA: The Genetic Material cytosine and thymine of the pyrimidine
group.
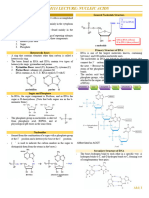
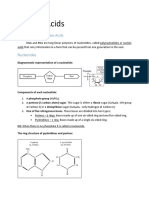
The sequence of the nitrogenous bases on one
strand of a DNA molecule is matched in a
particular way with the sequence on the other
strand. This pairing is due to the different
chemical structures of the bases. The cytosine
and thymine which are the pyrimidines, have
one ring, and the adenine and guanine which are the purines, have two rings. The
pyrimidines are paired with the purines, so that cytosine is paired with guanine, and
adenine with thymine.
WHILE-TASK
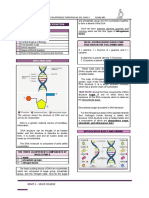
Humans and almost all organisms are composed of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
which is a molecule that contains the genetic code of organisms, and thus considered
as the genetic material . . . So, What is DNA? . . . What is this Genetic Material? .
. . What does this Genetic Material made of? . . . Why is DNA called Genetic
Material?
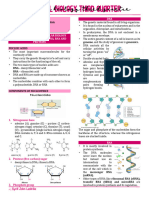
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a biological macromolecule with structural unit, the
nucleotide that is composed of sugar molecule, phosphate group, and nitrogenous
base.
The two strands of the double helix are antiparallel, which means that they run in
The DNA has two twisted strands, called double helix, and described like a twisted opposite direction, wherein the 5’ end of one strand matches with the 3’ end of the
ladder. The sides of the ladder is made up of alternating molecules of phosphate and other. This orientation of the DNA strands permits base pairing by providing
sugar (deoxyribose) in which covalent bonds join the sugar of one nucleotide to the complementarity between the two bases, which is important for DNA replication.
phosphate group of the next nucleotide, forming the sugar-phosphate backbone.
Whereas, the rungs are composed of the nitrogenous bases, the adenine and
https://ceu.instructure.com/courses/30921/pages/m2-l3-dna-the-genetic-material?module_item_id=2332788 1/5 https://ceu.instructure.com/courses/30921/pages/m2-l3-dna-the-genetic-material?module_item_id=2332788 2/5
8/26/23, 8:55 AM M2 - L3. DNA: The Genetic Material: General Zoology-IRROMERO 8/26/23, 8:55 AM M2 - L3. DNA: The Genetic Material: General Zoology-IRROMERO
Fork formation is the split of the two(2) strands of DNA, in which each of the single
strands becomes the template of the new strand of a complementary DNA. This is
the pairing of the bases in the template strand, the adenine paired with thymine,
and guanine with cytosine.
Primer Binding is the binding of primers to DNA template by complementary base
pairing to start the replication. A primer refers to the nucleotides of DNA, with 18 to
24 base pairs in length.
Elongation is the lengthening of the DNA by the addition of nucleotides to the 3’
end of the newly synthesized strand. The DNA nucleotides added are specified by
the template strand, as to whether A, T, C, or G.
The Termination Phase is the end of DNA synthesis. This happens when the two
replication forks meet, DNA is unwound, and gaps are filled.
DNA is considered as the genetic material for it is important in the coding of protein
and genetic information guide for life and its processes. It stores, copies and
transmits genetic information for the development and reproduction of organisms.
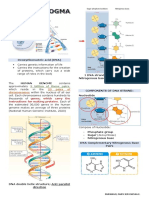
The “Central Dogma” refers to the processes involved on how the genetic
information of the DNA is converted into gene products, RNAs and proteins. These
processes are:
2. Transcription, when DNA makes new RNA. In this process, DNA segment is
copied into RNA molecules, the messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA leaves the
nucleus and goes out to the cytoplasm to direct protein synthesis. This time, thymine is
replaced by uracil.
1. DNA Replication, by which DNA makes new DNA. This is a biological process in 3. Translation, in which proteins are made from RNA. This is a process when mRNA
which DNA makes a copy of itself. It has four(4) steps, these are fork formation, primer acts as a template in the synthesis of protein.
binding, elongation and termination.
https://ceu.instructure.com/courses/30921/pages/m2-l3-dna-the-genetic-material?module_item_id=2332788 3/5 https://ceu.instructure.com/courses/30921/pages/m2-l3-dna-the-genetic-material?module_item_id=2332788 4/5
8/26/23, 8:55 AM M2 - L3. DNA: The Genetic Material: General Zoology-IRROMERO
To be more familiar with the DNA as the Genetic Material, watch this VIDEOS:
"Evidence that DNA is Genetic Material 1 and
2" https://www.khanacademy.org/test-prep/mcat/biomolecules/chromosomal-
inheritance/v/evidence-that-dna-is-genetic-material-1
(https://www.khanacademy.org/test-prep/mcat/biomolecules/chromosomal-
inheritance/v/evidence-that-dna-is-genetic-material-1)
(https://www.khanacademy.org/test-prep/mcat/biomolecules/chromosomal-
inheritance/v/evidence-that-dna-is-genetic-material-1) "Central Dogma of Molecular
Biology" https://www.khanacademy.org/science/in-in-class-12-biology-
india/xc09ed98f7a9e671b:in-in-the-molecular-basis-of-
inheritance/xc09ed98f7a9e671b:in-in-transcription-and-rna-
processing/v/central-dogma-of-molecular-biology-2
(https://www.khanacademy.org/science/in-in-class-12-biology-
india/xc09ed98f7a9e671b:in-in-the-molecular-basis-of-
inheritance/xc09ed98f7a9e671b:in-in-transcription-and-rna-processing/v/central-
dogma-of-molecular-biology-2)
and browse this POWERPOINT provided, DNAGeneticMaterial.pdf
(https://ceu.instructure.com/courses/30921/files/10345432?wrap=1)
(https://ceu.instructure.com/courses/30921/files/10345432/download?download_frd=1)
ILazoR
https://ceu.instructure.com/courses/30921/pages/m2-l3-dna-the-genetic-material?module_item_id=2332788 5/5
You might also like
- Chapter 22 GuideDocument7 pagesChapter 22 GuideEmily Lehman0% (1)
- (Download) (Epub) Morpho: Simplified Forms: Anatomy For Artists BY: Michel LauricellaDocument12 pages(Download) (Epub) Morpho: Simplified Forms: Anatomy For Artists BY: Michel LauricellaMbank Knabm0% (7)
- DNA Structure and ReplicationDocument12 pagesDNA Structure and ReplicationJhune Dominique GalangNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionDocument8 pagesLesson 2 Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionGreatel Elijah TorregosaNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics - Lesson 2 - Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionDocument8 pagesCytogenetics - Lesson 2 - Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionAli TaguibaoNo ratings yet
- The Dna: Learning Objectives (L.O.)Document13 pagesThe Dna: Learning Objectives (L.O.)masa bedaNo ratings yet
- Central DogmaDocument4 pagesCentral DogmaalxndrasenalesNo ratings yet
- Genstics Reading Comprehension TextDocument5 pagesGenstics Reading Comprehension TextOliwka INo ratings yet
- Watson-Crick Model: Purine: It Is A Double-Ringed Structure With Nitrogen at Positions at 1,3,7 and 9 PositionsDocument3 pagesWatson-Crick Model: Purine: It Is A Double-Ringed Structure With Nitrogen at Positions at 1,3,7 and 9 PositionsSeekerNo ratings yet
- Molecular BiologyDocument2 pagesMolecular BiologyJaymark HisonaNo ratings yet
- Dna ANDYDocument12 pagesDna ANDYAndy Morales100% (1)
- Cell CycleDocument23 pagesCell Cyclefrank menshaNo ratings yet
- CYTOGENDocument7 pagesCYTOGENRio CamoniasNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Introduction To Genetics PDFDocument19 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To Genetics PDFAsh MiNo ratings yet
- Self Assessment Answers 6 Asal Biology CBDocument2 pagesSelf Assessment Answers 6 Asal Biology CBsaeed.khedrizaNo ratings yet
- GenBIO REVIEWERDocument39 pagesGenBIO REVIEWERblismae genotivaNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules AQA AS Biology 5Document1 pageBiological Molecules AQA AS Biology 5RanaNo ratings yet
- Genetics Midterm Exam ReviewerDocument4 pagesGenetics Midterm Exam ReviewerChristianAvelinoNo ratings yet
- CYTOGENDocument8 pagesCYTOGENRio CamoniasNo ratings yet
- 3 Billion of These PairsDocument10 pages3 Billion of These PairsYlooner Quits100% (1)
- DNA NotesDocument12 pagesDNA NotesSeekerNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids SummaryDocument4 pagesNucleic Acids SummaryIvan MiglioriniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.2 MB DNA StruDocument62 pagesChapter 3.2 MB DNA StruMustee TeferaNo ratings yet
- AS - DNA ReplicationDocument2 pagesAS - DNA ReplicationAraijan AbaiNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument37 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritancechristopher lopezNo ratings yet
- 6 Nucleic AcidsDocument3 pages6 Nucleic AcidsTala AlkhawajaNo ratings yet
- Notes Chap 06Document21 pagesNotes Chap 06umamahfarooq75No ratings yet
- Gen Bio 3rd QuarterDocument6 pagesGen Bio 3rd QuarterzafmustaphaNo ratings yet
- Force Motion and EnergyDocument6 pagesForce Motion and EnergyJennyNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNADocument3 pagesDNA and RNAHans PNo ratings yet
- ReplicationDocument16 pagesReplicationRakshit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids BrochureDocument2 pagesNucleic Acids BrochureCring-cring NavarroNo ratings yet
- X-Sheet 1 The Nucleus and DNA: Life Sciences X-SheetsDocument5 pagesX-Sheet 1 The Nucleus and DNA: Life Sciences X-SheetsYadhirNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics - Lesson 3 - Dna Replication - Transcription - TranslationDocument14 pagesCytogenetics - Lesson 3 - Dna Replication - Transcription - TranslationAli TaguibaoNo ratings yet
- Jeeheheb GRRDocument22 pagesJeeheheb GRRahhhyiNo ratings yet
- L1+2 - Nucleic Acids and Structure StudentDocument29 pagesL1+2 - Nucleic Acids and Structure StudentHaris KhokharNo ratings yet
- DNA Synthesis and SequenceDocument6 pagesDNA Synthesis and SequenceInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- WK8-9 - Nucleic Acids 1 - 2Document7 pagesWK8-9 - Nucleic Acids 1 - 2opingaangelamae.opingaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry BrochureDocument2 pagesBiochemistry BrochureCaryl Alvarado SilangNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance: WWW - Ncert.onlineDocument31 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance: WWW - Ncert.onlineMamataMaharanaNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument10 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of InheritanceSneha HipparkarNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance - Short Notes - Lakshya NEET 2025Document3 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance - Short Notes - Lakshya NEET 2025anantpounikar02No ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance - Short NotesDocument3 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance - Short Notesp11925885No ratings yet
- BioA4 27. Basic GeneticsDocument5 pagesBioA4 27. Basic Geneticsthanks btNo ratings yet
- Lebo106 PDFDocument31 pagesLebo106 PDFakhil_reddy7352No ratings yet
- Molecular Genetics of Bacteria - The Bacterial Chromosome (1) (1) - 1-6 - CompressedDocument6 pagesMolecular Genetics of Bacteria - The Bacterial Chromosome (1) (1) - 1-6 - CompressedAlonso MejíaNo ratings yet
- Molecular GeneticsDocument15 pagesMolecular GeneticsBiruk SamuelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DNA Fingerprinting (Definition, Importance of DNA Fingerprinting in Forensic Science)Document20 pagesIntroduction To DNA Fingerprinting (Definition, Importance of DNA Fingerprinting in Forensic Science)DeMetrius Sam DanielNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument15 pagesDNA ReplicationAví Síngh KhökhárNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication PDFDocument7 pagesDNA Replication PDFPiyush ChandraNo ratings yet
- Biochem Reviewer FinalsDocument18 pagesBiochem Reviewer Finalscha cuteNo ratings yet
- What You'll Learn: You Will Distinguish Among Different Types of MutationsDocument35 pagesWhat You'll Learn: You Will Distinguish Among Different Types of MutationsSeemaNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3.3 Heredity NotesdocxDocument2 pagesLESSON 3.3 Heredity NotesdocxJedy IvoryNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Biochem For NucleotidesDocument3 pagesReviewer Biochem For NucleotidesNino D. AtilanoNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNADocument3 pagesDNA and RNANakajima AtsushiNo ratings yet
- DNA Sequence Recognition by Proteins: GlossaryDocument5 pagesDNA Sequence Recognition by Proteins: GlossaryCindy GarciaNo ratings yet
- 1 Nucleic AcidsDocument11 pages1 Nucleic AcidsSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Revision Notes Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument10 pagesCBSE Class 12 Biology Revision Notes Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of InheritancesahanaNo ratings yet
- Biology Nucleic A-Level OCR NotesDocument11 pagesBiology Nucleic A-Level OCR Notestbrook2017No ratings yet
- Flashcards For Neet Biology 12 Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument17 pagesFlashcards For Neet Biology 12 Molecular Basis of InheritanceJazz KulshresthaNo ratings yet
- (5L18) NG Chi Inn Camille - 5.3 Classification of BiodiversityDocument5 pages(5L18) NG Chi Inn Camille - 5.3 Classification of BiodiversityCamille Ng Chi InnNo ratings yet
- Ensayo Sobre Madres TrabajadorasDocument5 pagesEnsayo Sobre Madres Trabajadorasafmohycix100% (1)
- TOS 2nd Quarter ExamDocument3 pagesTOS 2nd Quarter Examxandra joy abadezaNo ratings yet
- Conservation Assessment of The Critically Endangered Burmese Star Tortoise in Chatthin Wildlife Sanctuary, Myanmar (20 July 2018)Document42 pagesConservation Assessment of The Critically Endangered Burmese Star Tortoise in Chatthin Wildlife Sanctuary, Myanmar (20 July 2018)AyeChan AungNo ratings yet
- Utkalendu Resume-Data ScienceDocument2 pagesUtkalendu Resume-Data Sciencejames neeshamNo ratings yet
- An Experimental Investigation On The Performance of Bacterial ConcreteDocument7 pagesAn Experimental Investigation On The Performance of Bacterial ConcreteMD MostofaNo ratings yet
- Medusas en MexicoDocument12 pagesMedusas en MexicoSiervoupNo ratings yet
- Introductory Guide Cell Culture Basics Cls An 724Document11 pagesIntroductory Guide Cell Culture Basics Cls An 724francisco calderon estrellaNo ratings yet
- Strategies in Answering Reading Comprehension: Vocabulary Questions. The First Type Asks You To Answer QuestionsDocument9 pagesStrategies in Answering Reading Comprehension: Vocabulary Questions. The First Type Asks You To Answer QuestionsDuvi Ahmad Duvi DekanNo ratings yet
- Advantage of Ecological System TheoryDocument2 pagesAdvantage of Ecological System TheoryRonnie Serrano Pueda100% (2)
- PDF Mitosis and Meiosis Lecture Presentations by Cindy Malone California Stat DLDocument26 pagesPDF Mitosis and Meiosis Lecture Presentations by Cindy Malone California Stat DLMajdi AkNo ratings yet
- Answer The Following:: Central Bicol State University of AgricultureDocument1 pageAnswer The Following:: Central Bicol State University of Agriculturechloe annNo ratings yet
- Midterm Mathayom 3Document8 pagesMidterm Mathayom 3AbdullohNo ratings yet
- SR Eng 2021 Int p2 Adobe Scan Jul 14, 2023Document6 pagesSR Eng 2021 Int p2 Adobe Scan Jul 14, 2023Misheck D BandaNo ratings yet
- Cyto 2Document80 pagesCyto 2newusernvNo ratings yet
- Atlantic Forest Terrestrial Molluscs of The Taquara Municipal Nature Park, State of Rio de Janeiro, BrazilDocument55 pagesAtlantic Forest Terrestrial Molluscs of The Taquara Municipal Nature Park, State of Rio de Janeiro, BrazilpigzxcNo ratings yet
- Impact of Seawater and Canopy Cover On The Phyllosphere Bacterial Community of Rhizophora Mucronata LeavesDocument12 pagesImpact of Seawater and Canopy Cover On The Phyllosphere Bacterial Community of Rhizophora Mucronata LeavesIJAERS JOURNALNo ratings yet
- ABS ALL NEW Presentation PDFDocument48 pagesABS ALL NEW Presentation PDFVivek MishraNo ratings yet
- Aseptic Technique Biotech Protocol 2017Document3 pagesAseptic Technique Biotech Protocol 2017babobusikNo ratings yet
- Pemetaan Zonasi Daerah Rawan Kebakaran Hutan Dan Lahan Di Kabupaten GowaDocument9 pagesPemetaan Zonasi Daerah Rawan Kebakaran Hutan Dan Lahan Di Kabupaten GowaRifki BocahNo ratings yet
- First Contact - Billy MeierDocument221 pagesFirst Contact - Billy Meiertdelgros100% (2)
- Introduction of AnatomyDocument18 pagesIntroduction of Anatomyjames nginyangiNo ratings yet
- Chytridiomycota: Zoosporic FungiDocument37 pagesChytridiomycota: Zoosporic FungiAINAYA HANIFA NUR AISYANo ratings yet
- BiotDocument13 pagesBiotJOSCEL SYJONGTIANNo ratings yet
- W9-SIO1003 Practical 4-QuestionsDocument6 pagesW9-SIO1003 Practical 4-Questions23005852No ratings yet
- Human Blood DNA Isolation: Lab Report 4Document5 pagesHuman Blood DNA Isolation: Lab Report 4Omar Mohsen SarhanNo ratings yet
- Molecular Plant Taxonomy. Methods in Molecular Biology (2021)Document407 pagesMolecular Plant Taxonomy. Methods in Molecular Biology (2021)Giovanni Celso Paton MamaniNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition 1 QPDocument4 pagesPlant Nutrition 1 QPMenaga IlangkovanNo ratings yet