Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acetazolamide
Uploaded by
Ankit Ruhil0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views4 pagesAcetazolamide
Original Title
acetazolamide
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAcetazolamide
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views4 pagesAcetazolamide
Uploaded by
Ankit RuhilAcetazolamide
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
acetazolamide
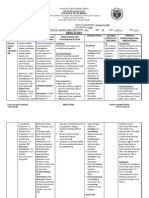
CIMS Class : ( Diuretics ) , ( Anticonvulsants ) , ( Antiglaucoma Preparations )
acetazolamide
P - Contraindicated in pregnancy
L - Contraindicated in lactation
Lab ¤ - Lab interference
related acetazolamide information
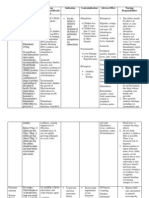
Indication & Oral
Dosage Diuresis
Adult: 250-375 mg once daily or on alternate days.
Intermittent treatment is needed for continued efficacy.
Oral
Preoperative management of angle-closure glaucoma
Adult: 250-1000 mg daily in divided doses.
Child: 1 mth-12 yr: 10-20 mg/kg daily. Max: 750 mg daily, in
2-4 divided doses.
Oral
Adjunct in open-angle glaucoma
Adult: 250-1000 mg daily in divided doses.
Child: 1 mth-12 yr: 10-20 mg/kg daily. Max: 750 mg daily, in
2-4 divided doses.
Oral
Epilepsy
Adult: Either alone or with other antiepileptics: 250-1000 mg
daily in divided doses.
Child: Neonates and up to 12 yr: Initially, 2.5 mg/kg bid-tid;
maintenance: 5-7 mg/kg bid-tid. Max: 750 mg daily.
Oral
Prophylaxis of high-altitude disorders
Adult: 500-1000 mg daily in divided doses. Prompt descent
is still advised if severe symptoms such as cerebral
or pulmonary oedema occur.
Intravenous
Chronic open-angle glaucoma
Adult: As an adjunct, 0.25-1 g every 24 hr, usually in divided
doses. Adjust dose according to symptomatology and
or pulmonary oedema occur.
Intravenous
Chronic open-angle glaucoma
Adult: As an adjunct, 0.25-1 g every 24 hr, usually in divided
doses. Adjust dose according to symptomatology and
ocular tension.
Intravenous
Acute closed angle glaucoma
Adult: 250-500 mg. may repeat 2-4 hr later if needed. Max: 1
g daily.
Intravenous
Epilepsy
Adult: 8-30 mg/kg daily in divided doses. Optimum dose:
375-1000 mg daily. When used with other anticonvulsants,
initiate at 250 mg once daily in addition to existing
medications and adjust accordingly.
Reconstitution: Reconstitute with at least 5 ml of sterile
water for inj to produce a solution containing = 100 mg/ml.
Further dilute with 5% dextrose solution or normal saline for
IV infusion.
Incompatibility: Admixture incompatibility: Multivitamins.
Administration Should be taken with food.
Overdosage Symptoms may include electrolyte imbalance, acidotic state
and central nervous effects. Monitor serum electrolyte levels
(particularly potassium) and blood pH levels. Supportive
measures are required to restore electrolyte and pH balance.
Acidotic state can usually be corrected by the admin of
bicarbonate.
Contraindications Hypersensitivity to sulphonamides; sodium or potassium
depletion, hepatic insufficiency; hepatic cirrhosis;
hyperchloraemic acidosis; severe renal impairment; severe
pulmonary obstruction; chronic noncongestive angle-closure
glaucoma; adrenocortical insufficiency. Pregnancy, lactation.
Special Potassium supplements may be required. Impaired hepatic
Precautions or renal function; diabetes. Monitor plasma electrolytes and
blood count regularly. IM route is not recommended. Caution
when driving or operating machinery. Elderly.
Adverse Drug Drowsiness, paraesthesia, ataxia, dizziness, thirst, anorexia,
Reactions headache; confusion, malaise, depression; GI distress,
metabolic acidosis, polyuria, hyperuricaemia, renal calculi,
nephrotoxicity, hepatic dysfunction.
Potentially Fatal: Rarely, skin reactions or blood dyscrasias.
Drug Interactions Aids penetration of weakly acidic substances like
sulphonamides across blood and CSF barrier. May inhibit
renal excretion of basic drugs (e.g. quinidine, ephedrine,
amphetamines) and promotes excretion of acidic drugs. May
increase salicylate toxicity (acidosis). Hypokalaemia with
corticosteroids and potassium-wasting diuretics. May
sulphonamides across blood and CSF barrier. May inhibit
renal excretion of basic drugs (e.g. quinidine, ephedrine,
amphetamines) and promotes excretion of acidic drugs. May
increase salicylate toxicity (acidosis). Hypokalaemia with
corticosteroids and potassium-wasting diuretics. May
increase excretion of lithium and primidone. May cause
osteomalacia with anticonvulsants.
Potentially Fatal: May potentiate effect of folic acid
antagonists, oral hypoglycaemic agents, oral anticoagulants
and severe reactions to sulphonamides.
Lab Interference May cause false positive results for urinary protein. Interferes
with HPLC theophylline assay and serum uric acid levels.
Pregnancy
Category (US
FDA) Category C: Either studies in animals have revealed
adverse effects on the foetus (teratogenic or embryocidal or
other) and there are no controlled studies in women or
studies in women and animals are not available. Drugs
should be given only if the potential benefit justifies the
potential risk to the foetus.
Storage Intravenous: Store between 15-30°C (59-86°F).
Reconstituted solution may be stored at for 3 days at 2-8°C
(36-46°C) or 12 hr at 15-30°C (59-86°F). Oral: Store at
15-30°C.
Mechanism of Acetazolamide specifically inhibits the enzyme carbonic
Action anhydrase which catalyses the reversible reaction involving
the hydration of CO2 and dehydration of carbonic acid. It
increases the excretion of HCO3 ions and as well as Na and
K leading to alkaline diuresis. Carbonic anhydrase is also
inhibited in the CNS to retard abnormal and excessive
discharge from neurons.
Onset: 60-90 minutes (oral); 2 minutes (IV).
Duration: 8-12 hr (oral); 4-5 hr (IV).
Absorption: Moderately rapid absorption from the GI tract;
peak plasma concentrations after 2 hr (oral).
Distribution: Concentrates in the red blood cells and renal
cortex; enters the breast milk. Protein-binding: High.
Excretion: Urine (as unchanged drug); 3-6 hr (elimination
half-life).
CIMS Class Diuretics / Anticonvulsants / Antiglaucoma Preparations
ATC S01EC01 - acetazolamide; Belongs to the class of carbonic
Classification anhydrase inhibitors used in the treatment of glaucoma and
miosis.
*acetazolamide information:
Note that there are some more drugs interacting with acetazolamide
acetazolamide
acetazolamide brands available in India
Always prescribe with Generic Name : acetazolamide, formulation, and dose
Always prescribe with Generic Name : acetazolamide, formulation, and dose
(along with brand name if required)
CIMS eBook Home
Index of all generic drugs
CIMS Abbreviation Index
MIMS Abbreviation Index
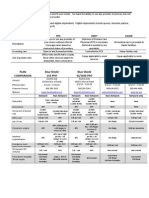
Brands : ACETAMIDE tab ACETAMIN tab , ACETARIV tab , AVVA SR-cap ,
AVVA tab , DIAMOX tab , IOPAR-SR cap , SYNOMAX tab , ZOLAMIDE
tab
Copyright © 2008 MIMS & © 2010 Dr John ( http://medical.fundazone.com )
#A B C D E F G H I J K L M
N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
( [all drugs])
You might also like
- Drug Study FinalDocument11 pagesDrug Study FinalKadymars JaboneroNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument5 pagesAcetazolamideIanDiel ParagosoNo ratings yet
- Acetazolamide/diamoxDocument3 pagesAcetazolamide/diamoxjedisay1100% (1)
- Cardiovascular Agent Central-Acting, Antihypertensive Autonomic Nervous System Agent Alpha-Adrenergic Agonist (Sympathomimetic)Document13 pagesCardiovascular Agent Central-Acting, Antihypertensive Autonomic Nervous System Agent Alpha-Adrenergic Agonist (Sympathomimetic)Maica EspañolaNo ratings yet
- Co-Amoxiclav: Adult & Childn 12 Yr Mild To Moderate Infections 375 MG 8 Hrly or 625 MG 12 Hrly. DentalDocument1 pageCo-Amoxiclav: Adult & Childn 12 Yr Mild To Moderate Infections 375 MG 8 Hrly or 625 MG 12 Hrly. DentalEricsonMitraNo ratings yet
- PLASIL antiemetics classificationDocument5 pagesPLASIL antiemetics classificationAbby MontealegreNo ratings yet
- Keto LogDocument7 pagesKeto LogKim Justin InfantadoNo ratings yet
- AzithromycinDocument4 pagesAzithromycinBrittany ClontzNo ratings yet
- 33-36 Medications PDFDocument15 pages33-36 Medications PDFJeraldine GumpalNo ratings yet
- General: Genetic Implications: Pronunciation: Maz Trade Name(s)Document7 pagesGeneral: Genetic Implications: Pronunciation: Maz Trade Name(s)jenm1228No ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument3 pagesAcetazolamidejeihanalkhairNo ratings yet
- Metoclopramide uses and dosageDocument9 pagesMetoclopramide uses and dosageDominique RamosNo ratings yet
- Metoclopramide: GIT Regulators, Antiflatulents & Anti-Inflammatories Antiemetics See Available Brands of MetoclopramideDocument9 pagesMetoclopramide: GIT Regulators, Antiflatulents & Anti-Inflammatories Antiemetics See Available Brands of MetoclopramideDominique RamosNo ratings yet
- Complete Albendazole Information From DrugsDocument4 pagesComplete Albendazole Information From DrugselephantynoseNo ratings yet
- w15 - Drug StudyDocument4 pagesw15 - Drug StudyGeneva LatorreNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: VORICONAZOLE Brand Name: Vfend Classification: Azole Antifungal Dosage/frequency and RouteDocument26 pagesGeneric Name: VORICONAZOLE Brand Name: Vfend Classification: Azole Antifungal Dosage/frequency and Routeanne marieNo ratings yet
- Pedia Drug StudyDocument11 pagesPedia Drug StudyPeetah PanNo ratings yet
- C - VVV VV VVVV VVV - VVV VV - VVVV VV VVDocument3 pagesC - VVV VV VVVV VVV - VVV VV - VVVV VV VVBea Angela Bithao AnonoyNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Generic Name: FUROSEMIDEDocument12 pagesDiuretics: Generic Name: FUROSEMIDEJR BetonioNo ratings yet
- Formulations of Representative Drugs From Antibiotics, Antipyretics, Steroids, Injectables and VitaminsDocument4 pagesFormulations of Representative Drugs From Antibiotics, Antipyretics, Steroids, Injectables and VitaminsChandraprakash JangidNo ratings yet
- Valproic AcidDocument4 pagesValproic Acidapi-3797941100% (2)
- PP ObatDocument7 pagesPP ObatSaifan AbdurrohmanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For ITPDocument25 pagesDrug Study For ITPMary Ann QuinonesNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate Drug Classification, Dosage and Side EffectsDocument4 pagesCalcium Gluconate Drug Classification, Dosage and Side EffectsStacy MC PelitoNo ratings yet
- Albuterol sulfate for asthma reliefDocument19 pagesAlbuterol sulfate for asthma reliefCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Acetazolamide For Injection, USPDocument5 pagesAcetazolamide For Injection, USPbishoy.youssef.cpiNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid Indication, Dosage, Side Effect, Precaution MIMS MalaysiaDocument1 pageMefenamic Acid Indication, Dosage, Side Effect, Precaution MIMS MalaysianuruladyanisaifuzzamanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Case PresentationDocument5 pagesDrug Study Case PresentationRobert MedinaNo ratings yet
- Acarbose: Drug Information: Brand Names: USDocument9 pagesAcarbose: Drug Information: Brand Names: USAnonymous wmF9p2ejNo ratings yet
- DrugDocument13 pagesDrugkhesler BacallaNo ratings yet
- Antipyretics: Instiaty Tropical Infection Module 2017-2018 Dept of Pharmacology and Therapeutics FkuiDocument22 pagesAntipyretics: Instiaty Tropical Infection Module 2017-2018 Dept of Pharmacology and Therapeutics Fkuisalsa2506No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyFranco ObedozaNo ratings yet
- Drugs of MineDocument16 pagesDrugs of MineJoan GungobNo ratings yet
- Availability: Verapamil HydrochlorideDocument21 pagesAvailability: Verapamil Hydrochloridesteffy sojanNo ratings yet
- Nrn101 and Nrn102 Drug Card: 500mg BID 10-16yrs 850mg QD 2000mg Max 2550mg Max Daily DoseDocument1 pageNrn101 and Nrn102 Drug Card: 500mg BID 10-16yrs 850mg QD 2000mg Max 2550mg Max Daily DoseJanet SheldonNo ratings yet
- Assignment: ON AntilipidemicsDocument15 pagesAssignment: ON AntilipidemicsMansi DabolaNo ratings yet
- Magnesium SulfateDocument2 pagesMagnesium SulfateKarla Karina Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Valproic AcidDocument4 pagesValproic AcidAndrea Huecas TriaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) : Drug Information: Pharmacologic Category Dosing: AdultDocument6 pagesVitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) : Drug Information: Pharmacologic Category Dosing: AdultVictoria Eliza InguilloNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug Studymaryhiromi10No ratings yet
- Loop Diuretic LasixDocument4 pagesLoop Diuretic LasixSabita PaudelNo ratings yet
- Lisinopril PDFDocument3 pagesLisinopril PDFHannaNo ratings yet
- Dipyrone (Metamizole) : Pronunciation Brand Names: InternationalDocument9 pagesDipyrone (Metamizole) : Pronunciation Brand Names: InternationalRismaya AminiNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol IV administration side effects nursing considerationsDocument7 pagesParacetamol IV administration side effects nursing considerationsCharm LorenzoNo ratings yet
- Cephalexin: Adjust-A-Dose (For All Indications)Document3 pagesCephalexin: Adjust-A-Dose (For All Indications)HannaNo ratings yet
- Folic Acid Benefits, Uses, InteractionsDocument15 pagesFolic Acid Benefits, Uses, InteractionsLene Derlene Gerona100% (2)
- Buffered Aspirin ProductsDocument7 pagesBuffered Aspirin ProductsKimsha ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- DRUG SODIUM VALPROATE (Depakote, Epilim, Episenta)Document5 pagesDRUG SODIUM VALPROATE (Depakote, Epilim, Episenta)Pearl Princess Guerrero100% (2)
- Olanzapine C Loza Pine, Drug StudyDocument7 pagesOlanzapine C Loza Pine, Drug StudyAubrey MacNo ratings yet
- Myrin P ForteDocument3 pagesMyrin P ForteJohn Zedric Villanueva ArciagaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyJoan RabeNo ratings yet
- TB medications overviewDocument7 pagesTB medications overviewANNIE SHINE MAGSACAYNo ratings yet
- AllopurinolDocument48 pagesAllopurinolFarha Elein KukihiNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument8 pagesDrugsShizuka Marycris AmaneNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol and Levofloxacin Drug StudyDocument9 pagesParacetamol and Levofloxacin Drug StudyKevin Sam AguirreNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs: (A Drug Study)Document13 pagesEmergency Drugs: (A Drug Study)Marichu BajadoNo ratings yet
- Adult: PO HTN Initial: 12.5 Mg/day, May Increase To 25-50 MG Once Daily, Either Alone or WDocument3 pagesAdult: PO HTN Initial: 12.5 Mg/day, May Increase To 25-50 MG Once Daily, Either Alone or WrLythaaaNo ratings yet
- Pritor PlusDocument4 pagesPritor Plusianecunar100% (2)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- A Proposed Project of Zinbinger Officinale (Ginger) As An Ointment/Vapor Rub For Headache and Nasal CongestionDocument2 pagesA Proposed Project of Zinbinger Officinale (Ginger) As An Ointment/Vapor Rub For Headache and Nasal CongestionKaren PadillaNo ratings yet
- Distal Biceps Tendon InjuriesDocument9 pagesDistal Biceps Tendon InjuriesEllan Giulianno FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Intensive Care Unit Admissions After Adolescent Suicide Attempts During The PandemicDocument26 pagesPediatric Intensive Care Unit Admissions After Adolescent Suicide Attempts During The PandemicCordula GoergenNo ratings yet
- Oxford Case Histories in General Surgery (gnv64) PDFDocument514 pagesOxford Case Histories in General Surgery (gnv64) PDFTelugukurraaadu100% (3)
- Sensus Jamal Terbaru (Fix)Document38 pagesSensus Jamal Terbaru (Fix)chrisvivani ruatakureiNo ratings yet
- Interaksi Obat AntiaritmiaDocument24 pagesInteraksi Obat AntiaritmiaDian Ulfa Rianda96No ratings yet
- Cervical SpondylosisDocument9 pagesCervical SpondylosisNurHidayah Borhanudin100% (1)
- Book IV Medicine (De Medicina)Document8 pagesBook IV Medicine (De Medicina)Marcus Annaeus LucanusNo ratings yet
- Mania: Caring For A Person ExperiencingDocument6 pagesMania: Caring For A Person ExperiencingGutsy JewelNo ratings yet
- Kimone Wright - Registered Nurse ResumeDocument2 pagesKimone Wright - Registered Nurse Resumeapi-365123958No ratings yet
- Application of Rapid Prototyping in Maxillofacial Surgery: 2. Implementation of The ProjectDocument6 pagesApplication of Rapid Prototyping in Maxillofacial Surgery: 2. Implementation of The ProjectManoj AlvandarNo ratings yet
- Understanding Respiratory FailureDocument34 pagesUnderstanding Respiratory FailureFariz Auliadi KhalilNo ratings yet
- 162 Dham 8 1999Document6 pages162 Dham 8 1999Nur Sidiq Agung SNo ratings yet
- A Current Review of Cytochrome P450 Interactions of Psychotropic DrugsDocument19 pagesA Current Review of Cytochrome P450 Interactions of Psychotropic Drugsdrguillermomedina100% (1)
- Medical RealDocument1 pageMedical Realapi-252555369No ratings yet
- Environmental Law ProjectDocument19 pagesEnvironmental Law ProjectShailesh KumarNo ratings yet
- CH 3-5 MRI Contrast Spatial LocalizationDocument109 pagesCH 3-5 MRI Contrast Spatial LocalizationYuda FhunkshyangNo ratings yet
- Urine Screening of Metabolic DisordersDocument24 pagesUrine Screening of Metabolic DisordersMark Arlo Hernandez SegundoNo ratings yet
- MAPEH 10 TOS 1st GradingDocument4 pagesMAPEH 10 TOS 1st Gradingelyn75% (4)
- Superstitious BeliefsDocument16 pagesSuperstitious BeliefsLyca EugenioNo ratings yet
- Burpee Challenge: Build Anaerobic Capacity in MinutesDocument12 pagesBurpee Challenge: Build Anaerobic Capacity in MinutesninoNo ratings yet
- Topnotch ECG Interpretation For MoonlightersDocument25 pagesTopnotch ECG Interpretation For Moonlightersmefav7778520100% (1)
- 210-241 UrinaryDocument34 pages210-241 UrinaryYaj Cruzada100% (1)
- FC Orth (SA) Intermediate Past Papers - 2012 Sept 28-3-2015Document2 pagesFC Orth (SA) Intermediate Past Papers - 2012 Sept 28-3-2015Uhuebor DavidNo ratings yet
- KDM - Sid's Record Sheets v1.5Document14 pagesKDM - Sid's Record Sheets v1.5Blackops559No ratings yet
- HospDocument414 pagesHospjnaguNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Trauma Assessment GuideDocument135 pagesAbdominal Trauma Assessment GuidewidyastutiNo ratings yet
- Innovative-Strategies-for-Teaching-in-the-Plant-Sciences (1) - 1 PDFDocument319 pagesInnovative-Strategies-for-Teaching-in-the-Plant-Sciences (1) - 1 PDFanon_50332441050% (2)
- 1 SM PDFDocument4 pages1 SM PDFUtibe Tibz IkpembeNo ratings yet
- Affidavit Form Medical Clinic Fire SafetyDocument2 pagesAffidavit Form Medical Clinic Fire SafetysrinivasuNo ratings yet