Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH 1
Uploaded by
Muqadas NazOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CH 1
Uploaded by
Muqadas NazCopyright:
Available Formats
Ch#1 : INTRODUCTION TO CHEMISTRY
DEFINITION
Chemistry is the branch of natural science which deals with the study of composition of matter
and properties of matter. It also deals with the laws and principles governing these changes.
BRANCHES OF CHEMISTRY
Due to wide range of study of matter, chemistry has been divided into various branches. The
main branches of chemistry are:
1. Physical chemistry
2. Organic Chemistry
3. Inorganic Chemistry
4. Analytical Chemistry
5. Bio Chemistry
6. Industrial/Applied Chemistry
7. Nuclear Chemistry
8. Environmental Chemistry
9. Polymer Chemistry
1. Physical Chemistry:
It is the branch of chemistry which deals with the physical properties of substances and their
dependence on chemical bonding. It also explains the laws and principles governing the
combination of atoms and molecules in chemical reaction.
2. Inorganic Chemistry:
It is the branch of chemistry which deals with the study of elements and their compounds
generally obtained from non-living organisms i-e from minerals.
3. Organic Chemistry:
It is the branch of chemistry which deals with the study of carbon containing compounds with
the exceptions of carbonates (CO3-2), bicarbonates (HCO3-1), cyanides (CN-1), cyanates (CNO-1),
thiocyanate (CN5), carbides (C-4) and oxides of carbons (CO and CO2). Actually it is the study of
hydrocarbons and their derivatives.
4. Analytical Chemistry:
It is the branch of chemistry that deals with the study of methods and techniques involved to
determine the kinds, quantity and quality of various compounds in a given substance.
5. Bio Chemistry:
It is the branch of chemistry which deals with the study of compounds and their reaction
(metabolism) occurring in the bodies of living organisms i-e plants and animals.
6. Industrial Chemistry:
It is the branch of chemistry which deals with the study of different chemical processes involved
in the chemical industries for the manufacture of synthetic products like glass, cement, paper,
soda ash, fertilizers, medicines etc.
7. Nuclear Chemistry:
It is branch of chemistry which deals with the study of changes occurring in the nuclei of atoms,
accompanied by the emission of invisible radiations.
8. Environmental Chemistry:
It is the branch of chemistry that deals with the study of the interaction of chemical materials and
their effects on the environment of plants and animals. Personal hygiene, pollution and health
hazards are important areas of environmental chemistry.
Prepared By: Miss ShijrahEllahiShaikh Page 1
Ch#1 : INTRODUCTION TO CHEMISTRY
9.Polymer Chemistry:
It is the branch of chemistry that deals with the study of process of polymerization and products
obtained through the process of polymerization such as plastics, synthetic fibers etc.
IMPORTANCE OF CHEMISTRY
Chemistry plays an important role in the society as it is the study of materials and substances and
we are surrounded by them.
Chemistry has helped us in improving the quality of life and is very important to us. Fertilizers,
medicines, plastics, clothing polymers, cement, glass, detergents, paints and thousands of various
chemicals all add to the comfort of society and improve our way of living.
ROLE OF CHEMISTRY IN SOCIETY
Chemistry plays an important role in our daily life. It has not only changed the standard of living
but also has improved our health conditions. There are many lifesaving drugs.
There are many chemicals which have become essential ingredient of our lives. For
instance Chlorine has become an important chemical substance. Nowadays thousands of useful
chemical substances are made from chlorine which has great importance in chemical industry
like Poly Vinyl Chloride (PVC) which is a plastic and is used in making pipes.
Chemistry plays an important role for the modern world e.g. food synthetic fibers, plastic,
medicines, soaps, explosives all are gifts of chemistry.
LANDMARKS IN THE STUDY OF CHEMISTRY
Chemistry is as old as human civilization. Over the centuries chemistry has under gone
remarkable progress. The development of chemistry can be divided into following periods.
a) The Greek Period
b) The Muslims or Al- Chemical Period
c) The Modern Period
THE GREEK PERIOD
I) The Greek philosophers Plato, Aristotle and Democritus and few others took part in the
early development of chemistry.
II) They presented the concept of elements, atoms and chemical reactions.
III) They believe that the universe was made of four elements i-e air, water, earth and fire and
that one material could be converted into another.
IV) The Greeks were the first to use the word atom.
V) Unfortunately, the Greeks presented sciences as a theory subject. They were not serious
about the experiments and chemistry is basically a practical (experimental) science.
Therefore chemistry could not make great progress during this period.
THE MUSLIM PERIOD / Al- CHEMICAL PERIOD
I) During the Muslim period (600-1600) foundation of modern science took place. The
Muslim scientist made rich contribution to various branches of science.
II) They made use of scientific methods and treated chemistry as an experimental science.
III) Muslim scientists developed laboratory equipment such as funnels, beakers, balances,
weighing scales, crucibles (for melting metals) etc.
IV) They discovered fundamental methods of chemistry like filtration, distillation,
sublimation, crystallization and fermentations.
THE MODERN PERIOD
Modern chemistry began in the 17th and 18th century as a result of experimentation, free
discussion and communication of work of chemists through out the world.
Prepared By: Miss ShijrahEllahiShaikh Page 2
Ch#1 : INTRODUCTION TO CHEMISTRY
CONTRIBUTION OF MUSLIM CHEMISTS
JABIR BIN HAYYAN (721- 803 A.D)
He is known as the father of chemistry. He built first chemical
laboratory. He developed various chemical methods such as
filtration, distillation, sublimation and crystallization. He
discovered the methods for the extraction of metals from their ores.
He was familiar with the making of steel and dyeing of clothes. He
invented experimental methods for the preparation of mineral acids
like nitric acids and hydrochloric acid. He also discovered the
method for the preparation of white lead.
Al- RAZI (862-930 A.D)
Al- Razi was a physician, chemist and philosopher. He was an
expert surgeon. He was the first who used opium as an anesthesia.
He divided the substances on the basis of living and nonliving
organisms. He prepared sulphuric acid. He prepared alcohol by the
fermentation process.
ABU REHAN Al- BERUNI (973-1048 A.D.)
He contributed in chemistry, physics, geography, history and
mathematics. He measured the circumference of the earth. He
determined the densities of various.
IBN-E-SINA (980-1037)
Ibn-e-Sina was an expert physician. He described the composition
and function of more than 760 medicines. He was probably the 1st
scientist who rejected the idea that a base metal can be converted
into gold. He wrote more than 100 books on different subjects
related to science.
Prepared By: Miss ShijrahEllahiShaikh Page 3
Ch#1 : INTRODUCTION TO CHEMISTRY
THE MODERN PERIOD
Following are the contribution of modern scientists to the field of chemistry.
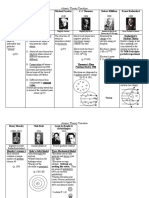
1. ROBERT BOYLE (1627-1691)
He is considered as the Father of Modern Chemistry. He studies the behavior of gases.
2. JOSEPH BLACK (1728-1799)
He described the study of CO2 gas.
3. SCHEELE (1742-17868)
He Discovered Chlorine Gas.
4. LAVOISER (1743-1794)
He discovered that oxygen gas constitutes about one fifth of the air. He invented the
physical balances.
5. JOHN DALTON (1786-1844)
He proposed the famous atomic theory.
6. CAVENDISH (1731-1810)
He discovered and explained the properties of Hydrogen Gas.
7. GAY LUSSAC (1778-1850)
He studied the diffusion of gases. He also proposed a law which is called as law of
combining volumes.
8. AVOGADRO (1776-1856)
He studied the relative atomic masses of different substances
9. BERZELLIUS (1779-1848)
He introduces the idea of symbols and chemical formulae of different substances.
10. MENDELEEV (1824-1907)
Dimitri Mendeleev published the periodic table of elements.
11. ARRHENIUS (1859-1927)
He explained the behavior of electrolyte. He gave the concept of acids and bases.
12. MICHAEL FARADAY (1791-1867)
He put forwarded law of electrolysis.
13. J.J THOMPSON (1856-1940)
He studied the properties of cathode rays and discovered electrons.
14. HENRY BECQUEREL (1852-1908)
He studied the properties of radioactive substances.
15. MADAM CURIE (1867-1934)
She discovered the nature and properties of radioactive substances.
16. RUTHERFORD ( 1891-1937)
He discovered nucleus and proposed a model of atom.
17. NEIL BOHR (1885-1962)
He put forwarded a model of atom by improving the Rutherford’s model.
18. JOSEPH PRIESTLY (1733-1804)
He discovered Oxygen gas, sulphur dioxide gas, and hydrogen chloride gas.
Prepared By: Miss ShijrahEllahiShaikh Page 4
Ch#1 : INTRODUCTION TO CHEMISTRY
SCIENTIFIC METHOD
It is a systematic manner in which scientists’ works or their methods of inquiry which
involves resolving the scientific problems are called scientific method.
STEPS OF SCIENTIFIC METHODS
OBESERVATION
Scientists make observations when they note and record facts about natural phenomenon.
HYPOTHESIS
It is an “Intelligent Guess” which explains “how” or “why” something happens. Then
experiments are made.
THEORY
If the hypothesis held true under any circumstances, with only very few exceptions then it
is called a theory. If a hypothesis does not hold true, it is either modified or finally
rejected.
SCIENTIFIC LAW
A scientific law is a concise statement that summarizes the results of wide variety of
observations and experiments.
DIFFERENTIATES
HYPOTHESIS THEORY
A hypothesis is simply a guess or an A theory is thoroughly tested
intelligent guess. hypothesis.
A hypothesis follows repeated A theory also follows further
experiments. experiments.
A hypothesis can become a theory or be A theory can become a scientific law or
modified or even discarded. be discarded.
THEORY SCIENTIFIC LAW
A theory is a thoroughly tested model A scientific law is different form of
that explains why experiments give theory in that it only describes a natural
certain results phenomenon
A theory can never be proved. A scientific law can often be expressed
or proved by simple mathematical
relationships.
A theory follows a hypothesis A scientific law follows a theory
FILL IN THE BLANKS
1. The early Greeks believe that everything in the universe was made up of four elements
earth, air, fire, and water.
2. Al- Razi chemical substances on the basis of their origin.
3. Organic chemistry is the branch of chemistry which deals with the carbon compounds.
4. Biochemistry is the backbone of medical sciences.
5. PVC which is a plastic is the short name of Polyvinyl chloride.
6. Oxygen was discovered by Priestley.
7. The best disinfectant is chlorine.
8. The periodic arrangement was the result of Mendeleev work.
Prepared By: Miss ShijrahEllahiShaikh Page 5
You might also like
- Atomic Structure ExamDocument6 pagesAtomic Structure Examapi-292403332No ratings yet
- Unit I: Introduction To Chemistry: LEARNING OUTCOMES: After Successful Completion of This Unit, You Should Be Able ToDocument23 pagesUnit I: Introduction To Chemistry: LEARNING OUTCOMES: After Successful Completion of This Unit, You Should Be Able ToMabale, Joyce Danielle H.No ratings yet
- Class IX Chemistry Chapter 01Document6 pagesClass IX Chemistry Chapter 01Sam Fisher100% (2)
- Chemistry Notes For Students SECONDARY SDocument70 pagesChemistry Notes For Students SECONDARY Skcgno72No ratings yet
- Class Ix Chemisty NotesDocument70 pagesClass Ix Chemisty NotesBasim blouchNo ratings yet
- 9th Class-Chapter-1-Chemistry Notes-Sindh Board PDFDocument14 pages9th Class-Chapter-1-Chemistry Notes-Sindh Board PDFMohsin AliNo ratings yet
- Chemisty Notes Class 9 IxDocument70 pagesChemisty Notes Class 9 IxMuhammad Iqbal72% (43)
- Chemistry Chapter1 FinalDocument18 pagesChemistry Chapter1 FinalNaveed Ur Rehman LuckyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter1 FinalDocument18 pagesChemistry Chapter1 FinalHassanNo ratings yet
- Humana Science NiDocument62 pagesHumana Science NiRascel SumalinogNo ratings yet
- A Guide For ChemistsDocument188 pagesA Guide For Chemistsneculaitarabuta100% (2)
- Introduction to ChemistryDocument5 pagesIntroduction to ChemistryHina RabbaniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Introduction To ChemistryDocument5 pagesLesson 1 Introduction To ChemistryEnrico Sapitula Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document5 pagesChapter 1Mark Euan B. DolosoNo ratings yet
- History: Chemistry Is TheDocument4 pagesHistory: Chemistry Is TheKim Caitlin Carbolico ClasieteNo ratings yet
- Yeah! Science Qwikipedia ChemistryDocument22 pagesYeah! Science Qwikipedia ChemistryAmy Cecilia LeighNo ratings yet
- The Scope and Disciplines of ChemistryDocument60 pagesThe Scope and Disciplines of ChemistryDeane Marc TorioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 General View of Chemistry and MatterDocument17 pagesChapter 1 General View of Chemistry and MatterJoshua Kulot100% (1)
- Introduction To Chemistry Detailed For Class IXDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Chemistry Detailed For Class IXShazil HameedNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: ScienceDocument11 pagesChemistry: ScienceChe MatNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document16 pagesModule 1Joan Dadivas AmancioNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument16 pagesDocumentHersheykris PimentelNo ratings yet
- 0 Introduction v2 ADDITUM 23-24Document3 pages0 Introduction v2 ADDITUM 23-24susimposterNo ratings yet
- ModernchemistryDocument7 pagesModernchemistryprinceuduma2021No ratings yet
- Module 1 - The Nature of ChemistryDocument12 pagesModule 1 - The Nature of ChemistryElhamae Sindatoc100% (1)
- The Study of Matter and Its CompositionDocument9 pagesThe Study of Matter and Its CompositionEller-jed M. MendozaNo ratings yet
- General and Inorganic ChemistryhandoutDocument25 pagesGeneral and Inorganic ChemistryhandoutleapapayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Chemistry Sindhi Text BoardDocument4 pagesChapter 1 Chemistry Sindhi Text BoardMansoorAliNo ratings yet
- The Scope of ChemistryDocument5 pagesThe Scope of ChemistryBishnu GhoshNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts Class XiDocument44 pagesBasic Concepts Class Xipreeti.2405No ratings yet
- CH 1Document28 pagesCH 1Umme Abdullah100% (1)
- Module 1 Lesson 1Document3 pagesModule 1 Lesson 1Nataniel DoctoleroNo ratings yet
- Objective Mathematics by R D SharmaDocument16 pagesObjective Mathematics by R D SharmaRohanNo ratings yet
- Main Branches of ChemistryDocument7 pagesMain Branches of ChemistryImmortal DynastyNo ratings yet
- Chem 500 General ChemistryDocument6 pagesChem 500 General ChemistrySheila Marie AmigoNo ratings yet
- Adge CompiledDocument18 pagesAdge CompiledNovelyn LumboyNo ratings yet
- From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument27 pagesFrom Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaJhunelynNo ratings yet
- History of Organic ChemistryDocument16 pagesHistory of Organic ChemistrypugandjNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry PDFDocument62 pagesGeneral Chemistry PDFRolando Jerome MagoNo ratings yet
- Inorganic ChemistryDocument2 pagesInorganic ChemistryNicole LaquilacNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ChemistryDocument33 pagesIntroduction To ChemistryJeNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry q1Document57 pagesGeneral Chemistry q1Dianna Rose QuintoNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry PDFDocument11 pagesOrganic Chemistry PDFAli AyanNo ratings yet
- OXYGEN AND HYDROGEN EXPERIMENTDocument16 pagesOXYGEN AND HYDROGEN EXPERIMENTRos Vincent AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Is A Branch Of: (Hide)Document8 pagesChemistry Is A Branch Of: (Hide)TaniaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Before Modern HistoryDocument26 pagesChemistry Before Modern Historypepito protacioNo ratings yet
- How Has The Evolution of Chemical Engineering Affected The World of ScienceDocument3 pagesHow Has The Evolution of Chemical Engineering Affected The World of ScienceSahana Ram PrasadNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument84 pagesChemistryMaria Regina SantosNo ratings yet
- Chem 1 Lecture NotesDocument87 pagesChem 1 Lecture NotesGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- The Scope of ChemistryDocument6 pagesThe Scope of ChemistryOsa EmmauelNo ratings yet
- General ChemistryDocument12 pagesGeneral ChemistryAlmira MejoradaNo ratings yet
- 1. Alchemy2. Alchemy 3. Jabir Ibn-Hayyan4. Jabir Ibn-Hayyan5. Chinese6. Mesopotamians7. Aristotle 8. Plato9. Anaxagoras10. AtomismDocument9 pages1. Alchemy2. Alchemy 3. Jabir Ibn-Hayyan4. Jabir Ibn-Hayyan5. Chinese6. Mesopotamians7. Aristotle 8. Plato9. Anaxagoras10. AtomismRommel DesuyoNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry - WikipediaDocument14 pagesBiochemistry - WikipediaAchilles ManthosNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 2 Development of Organic Chemistry As A StudyDocument4 pagesLesson 1 2 Development of Organic Chemistry As A Studyyuan sanchezNo ratings yet
- Organic and Inorganic Chemistry: Presented By: Memoona Memon AND Fazila KanwalDocument19 pagesOrganic and Inorganic Chemistry: Presented By: Memoona Memon AND Fazila KanwalMehak KhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ChemistryDocument17 pagesIntroduction To ChemistryLeovihilda BalalangNo ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument206 pagesPhysical SciencecasimiroaltheaeuniceNo ratings yet
- Organic: Chemistry Is The Scientific Discipline Involved With Compounds ComposedDocument2 pagesOrganic: Chemistry Is The Scientific Discipline Involved With Compounds ComposedNawanshika MendisNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Advanced ChemistryDocument25 pagesModule 1 Advanced Chemistryaljurbrix suano100% (1)
- 9th Class SyllabusDocument2 pages9th Class SyllabusMuqadas NazNo ratings yet
- Final Model Paper Physics SSC-I RevisedDocument7 pagesFinal Model Paper Physics SSC-I RevisedWaheedkhanNo ratings yet
- AnswerKey Chapter5Document3 pagesAnswerKey Chapter5Muqadas NazNo ratings yet
- Final SSC-I Biology Model PaperDocument10 pagesFinal SSC-I Biology Model PaperMuqadas NazNo ratings yet
- Physics 10th Class SHM and WavesDocument21 pagesPhysics 10th Class SHM and WavesHaroon Khan0% (1)
- PrintappjobsDocument2 pagesPrintappjobsMuqadas NazNo ratings yet
- MycvprintDocument1 pageMycvprintMuqadas NazNo ratings yet
- Transcript 21683Document8 pagesTranscript 21683Muqadas NazNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDocument4 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelLaleen AkhunzadaNo ratings yet
- Past Paper 9th Class Federal Board Chemistry English Medium Objective 2020Document1 pagePast Paper 9th Class Federal Board Chemistry English Medium Objective 2020Muqadas NazNo ratings yet
- Grade Thresholds - June 2022: Cambridge O Level Second Language Urdu (3248)Document1 pageGrade Thresholds - June 2022: Cambridge O Level Second Language Urdu (3248)Muqadas NazNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Second Language Urdu 3248/01 May/June 2021Document11 pagesCambridge O Level: Second Language Urdu 3248/01 May/June 2021DescaroNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Second Language Urdu 3248/02 October/November 2020Document5 pagesCambridge O Level: Second Language Urdu 3248/02 October/November 2020Humna AsifNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Second Language Urdu 3248/01Document8 pagesCambridge O Level: Second Language Urdu 3248/01Muqadas NazNo ratings yet
- Next Step Slide PresentationDocument14 pagesNext Step Slide PresentationMuqadas NazNo ratings yet
- Trip To Shugraan: Here Are Some Pics of My Shugraan Tour: 1Document5 pagesTrip To Shugraan: Here Are Some Pics of My Shugraan Tour: 1Muqadas NazNo ratings yet
- Nexus BizzDocument5 pagesNexus BizzMuqadas NazNo ratings yet
- Atomic Models ExplainedDocument85 pagesAtomic Models ExplainedFranciscoTestaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Module 2 2Document7 pagesPhysical Science Module 2 2Khrisha TindoyNo ratings yet
- CH (13) NucleiDocument24 pagesCH (13) Nucleikhurafati.amratanshNo ratings yet
- Russell, Bertrand - ABC of Atoms (Dutton, 1923) PDFDocument171 pagesRussell, Bertrand - ABC of Atoms (Dutton, 1923) PDFGerardo HerculesNo ratings yet
- History of RadioactivityDocument2 pagesHistory of RadioactivityAndre SumampouwNo ratings yet
- History and Models of The Atom: Click On MeDocument26 pagesHistory and Models of The Atom: Click On MeeriksonmurilloNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Models Through HistoryDocument7 pagesAtomic Structure Models Through HistoryAdrian SwiftNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 1 NotesDocument47 pagesGen Chem 1 NotesMilescent Rose Juguilon PadillaNo ratings yet
- Greatest PhysicistsDocument2 pagesGreatest PhysicistsekantotNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar - Science - Class 9 PDFDocument173 pagesNCERT Exemplar - Science - Class 9 PDFsiddharthNo ratings yet
- Why Is Ernest Rutherford A Good Person For A Whanau House To Be Named After?Document3 pagesWhy Is Ernest Rutherford A Good Person For A Whanau House To Be Named After?SmilesNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory Timeline: Democritus John Dalton Michael Faraday J. J. Thomson Robert Millikan Ernest RutherfordDocument2 pagesAtomic Theory Timeline: Democritus John Dalton Michael Faraday J. J. Thomson Robert Millikan Ernest RutherfordRicky Jay PadasasNo ratings yet
- Rutherford Scattering-Cross-SectionsDocument12 pagesRutherford Scattering-Cross-Sectionsapi-26870484No ratings yet
- Yee, Ryan Glenn B. Bsee Iii-8 ES 19 Assignment #2Document3 pagesYee, Ryan Glenn B. Bsee Iii-8 ES 19 Assignment #2Cinderella WhiteNo ratings yet
- Science8 Q3 Module3 Week6 ActivitySheetsDocument5 pagesScience8 Q3 Module3 Week6 ActivitySheetsJohn Reymart NateNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Knowledge Organiser - Foundation and HigherDocument2 pagesAtomic Structure Knowledge Organiser - Foundation and HigheranqelineeNo ratings yet
- BrainPOP Notes Atomic ModelDocument2 pagesBrainPOP Notes Atomic ModeljeffsorceNo ratings yet
- Determining Avogadro's Number Using Molecular DimensionsDocument9 pagesDetermining Avogadro's Number Using Molecular DimensionsKashif HussainNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Timeline of Atomic Models July 202020 1Document33 pagesPhysical Science Timeline of Atomic Models July 202020 1Policarpio R Princess LynNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter DLP 18 MODULE 2Document4 pages3rd Quarter DLP 18 MODULE 2Jim Alesther LapinaNo ratings yet
- Name of All Scientists and Their Inventions - Google SearchDocument3 pagesName of All Scientists and Their Inventions - Google SearchunerbesNo ratings yet
- The New PhysicsDocument156 pagesThe New PhysicsSaim KingNo ratings yet
- The Historical Development of Atom2Document1 pageThe Historical Development of Atom2Nor anisa BaguindaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Atomic Structure Theory Examples ExercisesDocument49 pagesChemistry Atomic Structure Theory Examples ExercisesMohit Yadav100% (1)
- Chapter 4 - Atomic StructureDocument30 pagesChapter 4 - Atomic StructureAmrit NumanNo ratings yet
- Physical-Science-Module 4 The Development of The Atomic StructureDocument23 pagesPhysical-Science-Module 4 The Development of The Atomic StructureJoana CastilloNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nuclear Physics Book SummarizedDocument480 pagesFundamentals of Nuclear Physics Book SummarizedNikhil Manjrekar100% (1)
- Chemistry S4 SB PDFDocument480 pagesChemistry S4 SB PDFRoykin Mugisha82% (11)
- On Nuclear EnergyDocument10 pagesOn Nuclear EnergyRemus BabeuNo ratings yet