Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Term 1 GR 10 - Mock
Uploaded by
KirtikaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Term 1 GR 10 - Mock
Uploaded by
KirtikaCopyright:
Available Formats
Date : Term 1-Mock Duration: 3 hrs.
Subject : Science Grade : 10
Name : Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions:
i. This question paper consists of 39 questions in 5 sections.
ii. All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions. A student is
expected to attempt only one of these questions.
iii. Section A consists of 20 objective type questions carrying 1 mark each.
iv. Section B consists of 6 Very Short questions carrying 02 marks each. Answers to these questions
should in the range of 30 to 50 words.
v. Section C consists of 7 Short Answer type questions carrying 03 marks each. Answers to these
questions should in the range of 50 to 80 words
vi. Section D consists of 3 Long Answer type questions carrying 05 marks each. Answer to these
questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
vii. Section E consists of 3 source-based/case-based units of assessment of 04 marks each with sub-parts.
SECTION-A
Select and write one most appropriate option out of the four options given for each of the questions 1 -
20
Q. Questions Marks
No.
1. What happens when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to iron fillings? pick the correct 1
answer.
(a) Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced.
(b) Chlorine gas and iron hydroxide are produced.
(c) No reaction takes place.
(d) Iron salt and water are produced.
2. Give the ratio in which hydrogen and oxygen are present in water by volume 1
(a) 1:2
(b) 1:1
(c) 2:1
(d) 1:8
3. Na2CO3.10H2O is known as- 1
(a) Baking Soda
(b) Baking Powder
(c) Washing Soda
(d) Bleaching Powder
4. CuSO4.5H2O In this Compound the water molecule is called – 1
(a) Pure Water
Grade10/ Subject: Science 1
(b) Water of Crystallization
(c) Soda Water
(d) None of these
5. Source of tartaric acid is 1
(a) Ant sting
(b) Vinegar
(c) Tamarind
(d) Milk
6. The pH of three solutions A, B and C are 4, 9 and 6 respectively. Arrange them in 1
increasing order of acidic strength.
(a)A<C<B
(b)B<C<A
(c)C<A<B
(d)B<A<C
7. The pH of a solution is 7. How can you increase its pH? 1
(a) By adding a small amount of acid
(b) By adding a small amount of base.
(c) By adding a small amount of salt.
(d) By passing carbon dioxide gas through it.
8. Arteries and veins are connected by a network of extremely narrow tubes called: 1
a. Sieve tubes b. Capillaries c. Vena cava d. Valves
9. Which of the following are digestive enzymes contained in the pancreatic juice? 1
i. Lipase ii. Hydrochloric acid iii. Mucus iv. Trypsin
(a) (i) and (ii) ( b)(i) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii) (d) (i) and (iii)
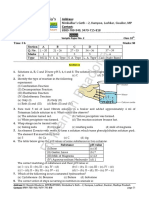
10. Observe the figure given below and identify the correct type of tropism. 1
(a)Both root and stem are positively phototrophic.
(b)Both root and stem are negatively phototrophic.
(c)Root is positive and shoot is negatively phototrophic.
(d)Shoot is positive and root is negatively phototrophic.
Grade10/ Subject: Science 2
11. Observe the experimental set-up and analyze the conclusion: 1
(a)Solution (a) turns milky white in less time.
(b)Solution (b) turns milky white in less time.
(c)No change in test tube (a)
(d)None of the above.
12. The blood vessel which carries deoxygenated blood from the heart is: 1
(a)Pulmonary artery
(b)Pulmonary vein
(c)Vena cava
(d)aorta
13. When the object is placed between f and 2f of a convex lens, the image formed is 1
(a) at f
(b) at 2f
(c) beyond 2f
(d) between O and f
14. A full length image of a distant tall building can definitely be seen by using 1
(a) a concave mirror
(b) a convex mirror
(c) a plane mirror
(d) both concave as well as plane mirror
15. Ability of the eye lens to adjust its focal length is called 1
(a). Accommodation
(b). Adjustment
(c). Power
(d). None of the above
16. The change in the direction of a wave passing from one medium to another is termed as __. 1
(a)Interference
(b)Mirage
Grade10/ Subject: Science 3
(c)Diffraction
(d)Refraction
Question no 17-20 are assertion reasoning questions. 1
These consists of two statements- Assertion(A) and Reason(R). Answer these questions
selecting the appropriate option given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
(e) Both A and R are false.
17. (A) Blue colour of copper sulphate solution fades when an iron nail is dipped. 1
(R) Copper displaces iron from the reaction.
18. (A) The purpose of making urine is to filter out undigested food. 1
(R) Kidneys filter the waste and produce urine.
19. (A) Aerobic animals are not truly aerobic. 1
(R) They produce lactic acid anaerobically.
20. Assertion(A): Hypermetropia is the defect of the eye in which only farther objects are seen. 1
Reason (R) : Hypermetropia is corrected by using converging lens.
SECTION-B
Q. no-21-26 are very short answer questions.
21. i) Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions 2
(a)Aluminium + Copper chloride → Aluminium chloride + Copper
(bBarium chloride + Potassium sulphate → Barium sulphate + Potassium chloride
OR
ii) a) Identify the compound X on the basis of the reactions given below. Also, write the
name and chemical formulae of A, B and C.
22. 2
(a) Why does milkman add a very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk.
(b) What does baking powder contain?
Grade10/ Subject: Science 4
23. 2
(a)Identify any two parts labelled in the above figure.
(b)Name the blood vessel which carries oxygenated blood to the lungs? Which chamber
receives it?
24. Secretions of growth hormone must be specific in the human body? Justify the statement 2
with examples.
25. A student has difficulty in reading the blackboard while sitting in the last row. What could 2
be the defect the child is suffering from? How could it be corrected?
OR
State two factors which determine lateral displacement of a ray of light passing through a
rectangular glass slab.
26. 2
a. Name the hormone secreted by “a”
b. Name the mineral required for the production of hormone secreted by “b’ gland.
c. Identify the gland from the figure given above that produces the emergency hormone.
Why is it called so?
SECTION-C
Q. no 27-33 are short answer questions with 3 marks each.
27. 1 g of copper powder was taken in a China dish and heated. 3
(a)What change takes place on heating? Give the chemical equations of reactions, the name
and the colour of the products formed.
(b)Write chemical equation for the reaction of the formed product with water.
28. (a)What happens when nitric acid is added to an eggshell? Explain with equation. 3
(a)Plaster of Paris should be stored in moisture proof container. Explain why?
Grade10/ Subject: Science 5
29. Give reasons for the following: 3
(a) Ventricles have thicker walls than arteries.
(b) The volume of glomerular filtrate produced is 18L but the volume of urine excreted is
just 2 L.
(c) Rate of breathing in aquatic organisms are faster than in terrestrial organisms.
Or
(a)Aves and mammals have 4 chambered heart whereas fishes have 2 chambered heart.
(b)Sphincter muscles are present in human digestive system.
(c) Athletes have muscular cramps.
30. A concave lens has a focal length of 10 cm. An object 2.5 cm high is placed 30 cm from the 3
lens. Determine the position and size of the image.
31. What is ‘dispersion of white light’? State its cause. Draw a ray diagram to show the 3
dispersion of white light by a glass prism
32. Explain with the help of diagram why the sun is visible to us two minutes before the actual 3
sun-rise and two minutes after the sunset.
OR
A narrow PQ of white light is passing through a glass prism ABC as shown in the diagram.
(i) Trace it on your answer sheet and show the path of the emergent beam as observed on
the screen DE.
(ii) Write the name and cause of the phenomenon observed.
(iii) Where else in nature is this phenomenon observed?
33. a). List the sequence of events that occur when a plant is exposed to unidirectional light, 3
leading to bending of a growing shoot. Also name the hormone and the type of movement.
b). How is the timing and amount of hormone secreted by a gland regulated?
Explain with an example.
SECTION-D
Q. no 34 to 36 are long answer questions with 5 marks each
34. To the three solutions listed below, a few drops of phenolphthalein and red litmus were 5
added separately. Specify the colour change in each case,
Name of the solution With phenolphthalein With red litmus
Na2CO3 (A) (B)
HCl Colourless (C)
Grade10/ Subject: Science 6
NaCl (D) (E)
(F) Turns Pink No Change
i) Find ‘A,B,C,D,E and F’ ?
ii) Draw a labelled diagram to show the preparation of hydrogen gas in laboratory.
35. (a)Draw a schematic representation of transport and exchange of oxygen and carbon 5
dioxide during transportation of blood in human beings and label on it:
Lung capillaries, Pulmonary artery to lungs, Aorta to body, Pulmonary veins from lungs.
(b) What is the advantage of separate channels in mammals and birds for oxygenated and
deoxygenated blood?
(c)When we breathe out why does the air passage not collapse?
OR
(a)Draw the L.S of leaf and label 4 important parts.
(b) How is the opening and closing of stomata done in leaves? Explain.
(c) Write the chemical equation of photosynthesis.
36. (a) Define the following terms in the context of spherical mirrors: 5
(i) Pole
(ii) Centre of curvature
(iii) Principal axis
(iv) Principal focus
(b) Draw ray diagrams to show the principal focus of a
(i) Concave mirror and (ii) Convex mirror
SECTION E
Q no 37 to 39 are case based/data based questions with short sub –parts. Internal
choice is provided in one of the sub-parts.
37. During a chemical reaction, the substances that react are known as reactants whereas the 4
substances that are formed during a chemical reaction are known as products. A chemical
reaction is typically followed by physical signs that are readily detected, such as heat and
light emission, precipitate formation, gas evolution, or a change of appearance. Chemical
reactions are of many types, decomposition reaction combination reaction, combustion
reaction neutralization reaction, single displacement reaction, double displacement reaction,
precipitation etc
i) Calcium oxide reacts vigorously with water to produce slaked lime.
CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq)
This reaction can be classified as
(A) Combination reaction
(B) Exothermic reaction
(C) Endothermic reaction
Grade10/ Subject: Science 7
(D) Oxidation reaction
Which of the following is a correct option?
(a) (A) and (C)
(b) (C) and (D)
(c) (A), (C) and (D)
(d) (A) and (B )
ii) When hydrogen sulphide gas is passed through a blue solution of copper sulphate, a
black precipitate of copper sulphide is obtained and the sulphuric acid so formed
remains in the solution. The reaction is an example of a
(a) combination reaction
(b) displacement reaction
(c) decomposition reaction
(d) double displacement reaction.
iii) In which of the following, the identity of initial substance remains unchanged?
(a) Curdling of milk
(b) Formation of crystals by process of crystallization
(c) Fermentation of grapes
(d) Digestion of food
iv) X + Y SO4 → X SO4 + Y
Y + X SO4 → No reaction
Of the two elements X and Y which is more reactive?
(a) X (b) Y (c) Both are of same reactivity
38. Read the following and answer questions from (i) to (iv). 4
Heterotrophic nutrition is a mode of nutrition in which organisms obtain readymade
organic food from outside sources. The organisms that depend upon outside sources
for obtaining organic nutrients are called heterotrophs.
Heterotrophic nutrition is of three types: saprophytic, parasitic and holozoic
nutrition
i. In which of the following groups of organisms food material is broken outside the
body and absorbed?
(a)Mushroom,green plants, Amoeba
(b) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould
Grade10/ Subject: Science 8
(c) Paramecium, Amoeba, Cuscuta
(d) Cuscuta, lice, tapeworm
ii. Which of the following is a parasite?
(a) Yeast
(b) Tape worm
(c) Amoeba
(d) Earthworm
iii. Which of the following is an example of saprotroph?
(a) Grass
(b) Mushroom
(c) Amoeba
(d) Paramecium
iv. Heterotrophic nutrition involves
(a) production of simple sugar from inorganic compounds
(b) utilisation of chemical energy to prepare food
(c) utilisation of energy obtained by plants
(d) all of these.
OR
v. The mode of nutrition found in fungi is:
(a) Parasitic nutrition
(b) Holozoic nutrition
(c) Autotrophic nutrition
(d) Saprotrophic nutrition
39. Read the following and answer the questions 4
The spherical mirror forms different types of images when the object is placed at different
locations. When the image is formed on screen, the image is real and when the image does
not form on screen, the image is virtual. When the two reflected rays meet actually, the
image is real and when they appear to meet, the image is virtual.
A concave mirror always forms a real and inverted image for different positions of the
object. But if the object is placed between the focus and pole. the image formed is virtual
and erect.
A convex mirror always forms a virtual, erect and diminished image. A concave mirror is
used as doctor’s head mirror to focus light on body parts like eyes, ears, nose etc., to be
examined because it can form erect and magnified image of the object. The convex mirror
is used as a rear view mirrors in automobiles because it can form a small and erect image of
an object.
Grade10/ Subject: Science 9
(i) When an object is placed at the center of curvature of a concave mirror, the image
formed is
(a) larger than the object (b) smaller than the object
(c) same size as that of the object (d) highly enlarged.
(ii) No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror is
likely to be
(a) plane (b) concave
(c) convex (d) either plane or convex.
(iii) A child is standing in front of a magic mirror. She finds the image of her head bigger,
the middle portion of her body of the same size and that of the legs smaller. The following
is the order of combinations for the magic mirror from the top.
(a) Plane, convex and concave (b) Convex, concave and plane
(c) Concave, plane and convex (d) Convex, plane and concave
(iv) To get an image larger than the object, one can use
(a) convex mirror but not a concave mirror
(b) a concave mirror but not a convex mirror
(c) either a convex mirror or a concave mirror
(d) a plane mirror.
OR
(iv) When an object is placed at 2F in front of concave mirror the image will be formed at
(a) infinity
(b) principal focus
(c) 2F
(d) all of the above
Grade10/ Subject: Science 10
You might also like
- Mock Examination Half Yearly 23Document10 pagesMock Examination Half Yearly 23shouryaxd3639No ratings yet
- PB Class X Science 2023-24Document9 pagesPB Class X Science 2023-24smarty boysNo ratings yet
- CBSE Science Paper 1 (QP)Document8 pagesCBSE Science Paper 1 (QP)Acharya Dronacharya Foundation CenterNo ratings yet
- JSC Science SQP-4 2023-24Document5 pagesJSC Science SQP-4 2023-24Jayant ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Science X QP Set CDocument7 pagesScience X QP Set CYogesh KhannaNo ratings yet
- Science Exam Questions Cover Key ConceptsDocument8 pagesScience Exam Questions Cover Key ConceptsGurukul PatnaNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan Chennai Region Sample Question Paper (Term-I) 2021-22 Class X (SCIENCE 086) Time: 90 Minutes General InstructionsDocument21 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan Chennai Region Sample Question Paper (Term-I) 2021-22 Class X (SCIENCE 086) Time: 90 Minutes General InstructionsVVS. G.S1074100% (1)
- X Science QP Set-1 PB-2Document10 pagesX Science QP Set-1 PB-2akhileshjnv6393No ratings yet
- 10 Science Term1 Sp07Document17 pages10 Science Term1 Sp07Vivek KumarNo ratings yet
- 01 Subjective Test-02 X Science 25122022 QPDocument6 pages01 Subjective Test-02 X Science 25122022 QPViswa DharshanNo ratings yet
- Set 2 - Class-10 PB - QP - Science - 2022-23Document12 pagesSet 2 - Class-10 PB - QP - Science - 2022-23hetansh2404No ratings yet
- 7679 Ques Sheet 2981GRADE 10 SCIENCE QP SET A PREBOARD 1 TERM 1 1Document16 pages7679 Ques Sheet 2981GRADE 10 SCIENCE QP SET A PREBOARD 1 TERM 1 1jatintheboyNo ratings yet
- 10th science paper half yearly ( Ch 1,2,3,5,6,9,10)Document4 pages10th science paper half yearly ( Ch 1,2,3,5,6,9,10)Vidyesh KrishnanNo ratings yet
- CBSE 10th Pre Board Exam Model Question Paper 9 - ScienceDocument11 pagesCBSE 10th Pre Board Exam Model Question Paper 9 - Sciencermgokul78No ratings yet
- PB X Science QP Nov 2022Document8 pagesPB X Science QP Nov 2022Chilakamarthy srinivasaprasadNo ratings yet
- 10th Science Practice TestDocument13 pages10th Science Practice Testavinash960No ratings yet
- 10 Science Eng PP 2023 24 2Document8 pages10 Science Eng PP 2023 24 2aniketyadav122311No ratings yet
- Class X Science Question PaperDocument24 pagesClass X Science Question PaperKalpna RaniNo ratings yet
- CSSC - Qp-Science-10-Cssc-Set 1Document8 pagesCSSC - Qp-Science-10-Cssc-Set 1Mathan100% (1)
- JSC Science SQP-3 2023-24Document5 pagesJSC Science SQP-3 2023-24Jayant ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Ta'Sees X Science - Pre Board Question Paper - FinalDocument10 pagesTa'Sees X Science - Pre Board Question Paper - Finalzqmqgr9mj5No ratings yet
- Chennai Sahodaya Science Set 1 QP 2022-23 - FOR PRACTICE ONLYDocument7 pagesChennai Sahodaya Science Set 1 QP 2022-23 - FOR PRACTICE ONLYvro hamza100% (14)
- General InstructionsDocument4 pagesGeneral InstructionsRichi SahooNo ratings yet
- KVS Class X Science Half Yearly Exam QuestionsDocument8 pagesKVS Class X Science Half Yearly Exam QuestionsVarsha.V.NairNo ratings yet
- Class-10 - Science - Practice - 2022-23 - 1Document8 pagesClass-10 - Science - Practice - 2022-23 - 1Tanish MehtaNo ratings yet
- X ScienceDocument5 pagesX ScienceMickey xzNo ratings yet
- Class10 ScienceDocument7 pagesClass10 SciencePragadeeshwaran PragadeeshwaranNo ratings yet
- Science Preboard PaperDocument8 pagesScience Preboard Paperamogh biyalNo ratings yet
- CBSC Periodic AssessmentDocument4 pagesCBSC Periodic Assessmentsreelal cgNo ratings yet
- PB II Class X Sci QP Jan 2023Document9 pagesPB II Class X Sci QP Jan 2023Mickey xz0% (1)
- S 2023 31-4-1 PDFDocument11 pagesS 2023 31-4-1 PDFSrikanth JammulaNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Sci Set 1Document15 pagesClass 10 Sci Set 1Aditya VenkatNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper (Science)Document7 pagesSample Paper (Science)sedsoupNo ratings yet
- DAV - Preboard - 12 - 12 - 2022 - 23 - 1Document10 pagesDAV - Preboard - 12 - 12 - 2022 - 23 - 1karmohit285No ratings yet
- Section A: Sample/Pre-Board Paper 2 Class X Term 1 Exam Nov - Dec 2021 ScienceDocument6 pagesSection A: Sample/Pre-Board Paper 2 Class X Term 1 Exam Nov - Dec 2021 ScienceCharushree ChundawatNo ratings yet
- Sahodaya 23-24 Copy of Science Set 2Document12 pagesSahodaya 23-24 Copy of Science Set 2Aparajita Bose100% (1)
- Sample Question Paper (TERM - I) 2021-22: Class X ScienceDocument24 pagesSample Question Paper (TERM - I) 2021-22: Class X ScienceSiddhant SinghNo ratings yet
- X SciencepracticepaperDocument7 pagesX Sciencepracticepaper6A 29 Ruchit AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Section A: Sample/Pre-Board Paper 8 Class X Term 1 Exam Nov - Dec 2021 ScienceDocument14 pagesSection A: Sample/Pre-Board Paper 8 Class X Term 1 Exam Nov - Dec 2021 ScienceDrive With RahulNo ratings yet
- Science Board Exam 2023 Class 10th Sample Paper Address and ContactDocument6 pagesScience Board Exam 2023 Class 10th Sample Paper Address and ContactMonika JasujaNo ratings yet
- Science Sample QP - 1Document16 pagesScience Sample QP - 1Aswathi KrishnanNo ratings yet
- CBSE Science Class 10 Sample Paper 4Document11 pagesCBSE Science Class 10 Sample Paper 4manojboa100% (1)
- JSC Science SQP-1 2023-24Document6 pagesJSC Science SQP-1 2023-24Jayant ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Class 10 ScienceDocument5 pagesClass 10 ScienceDivyanshNo ratings yet
- Science X QP Set BDocument7 pagesScience X QP Set BYogesh KhannaNo ratings yet
- Code No. 86 Pre-Board Examination-2 (January - 2020) : General Instructions: (I) (Ii) (Iii) (Iv) (V) (Vi) (Vii)Document6 pagesCode No. 86 Pre-Board Examination-2 (January - 2020) : General Instructions: (I) (Ii) (Iii) (Iv) (V) (Vi) (Vii)Sara 15No ratings yet
- Science X QP PB 2022-23 1-ADocument10 pagesScience X QP PB 2022-23 1-ADrone Max0% (1)
- Science Class X Sample Paper Test 06 Term IDocument12 pagesScience Class X Sample Paper Test 06 Term IMayankNo ratings yet
- Jescspsu 28Document7 pagesJescspsu 28Santha KumarNo ratings yet
- Section A: The Oxford SchoolDocument8 pagesSection A: The Oxford Schoolfathima MiranNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper Pre Board X Science 2023-24Document10 pagesPractice Paper Pre Board X Science 2023-24Manish MishraNo ratings yet
- 2023 SCIENCE All Region Question PapersDocument106 pages2023 SCIENCE All Region Question Papersnakshu.prasannaNo ratings yet
- Science SQP-01 2024Document13 pagesScience SQP-01 2024badasserytechNo ratings yet
- 7920science Sample Paper 2 Class 10thDocument6 pages7920science Sample Paper 2 Class 10throseanneblossom.kimNo ratings yet
- Class X Science Practice Test Ak 2022-23Document15 pagesClass X Science Practice Test Ak 2022-23Tanish MehtaNo ratings yet
- Section - A: General InstructionsDocument8 pagesSection - A: General InstructionsTricX AKR YTNo ratings yet
- JSC Science SQP-2 2023-24Document6 pagesJSC Science SQP-2 2023-24Jayant ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Class X Science Set 2Document10 pagesClass X Science Set 2vro hamzaNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper X Science PT 2 Cumulative 2023-24-1Document11 pagesPractice Paper X Science PT 2 Cumulative 2023-24-1saumya judeNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 6th Social Science History Chapter 2 On The Trial of The Earliest PeopleDocument19 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 6th Social Science History Chapter 2 On The Trial of The Earliest Peopledhwanil shahNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Passive Fun Activities Games - 138412Document9 pagesPresent Simple Passive Fun Activities Games - 138412ANA BARBARA VALLE ECHEVARRIANo ratings yet
- Acquaculture 11 Q1 W5-6 M4 LDS Aquaculture-Facilities2 ALG RTPDocument9 pagesAcquaculture 11 Q1 W5-6 M4 LDS Aquaculture-Facilities2 ALG RTPHelen SabuquelNo ratings yet
- Avatar: The Age of YimiDocument11 pagesAvatar: The Age of Yimidyap000No ratings yet
- Crossword Worksheet2Document2 pagesCrossword Worksheet2Rock StarNo ratings yet
- Best Culinary College in India - Culinary Arts Courses - SymbiosisDocument4 pagesBest Culinary College in India - Culinary Arts Courses - Symbiosissscapune1No ratings yet
- Tree of Life Center US: Slow Oxidizer ProfileDocument2 pagesTree of Life Center US: Slow Oxidizer ProfileAnne Marie GordonNo ratings yet
- Michelle ObamaDocument2 pagesMichelle Obamamariana mNo ratings yet
- דף עבודה באנגלית 2Document1 pageדף עבודה באנגלית 2Freddy Perez GasparNo ratings yet
- Biscuit Cracker and Cookie Recipes For TDocument200 pagesBiscuit Cracker and Cookie Recipes For TNever step back SClub100% (1)
- Adjectives B2 LevelDocument10 pagesAdjectives B2 LevelВалентинаNo ratings yet
- Nothing To Lose by Fei Tian Ye Xiang (MTL)Document507 pagesNothing To Lose by Fei Tian Ye Xiang (MTL)Thea ClonesNo ratings yet
- Comparatives & SuperlativesDocument5 pagesComparatives & SuperlativesMaria Eugenia Gomez GabrielliNo ratings yet
- NALETSANADocument1,020 pagesNALETSANAkhubonethembelihle343No ratings yet
- PHM 508 (Integrated Pest Management) - 2Document25 pagesPHM 508 (Integrated Pest Management) - 2Karl DiomoNo ratings yet
- Mcdelivery Menu 971Document1 pageMcdelivery Menu 971Shehariyar KNo ratings yet
- Exploring Bangkok and Thailand's Best SitesDocument9 pagesExploring Bangkok and Thailand's Best SitesAngelys CuellarNo ratings yet
- Thesis StrawberryDocument6 pagesThesis Strawberryafiboeolrhismk100% (2)
- Weeknights CookbookDocument11 pagesWeeknights CookbookNj ZaNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Potato ProductionDocument4 pagesLiterature Review On Potato Productionc5rh6ras100% (1)
- Dish Washer ManuelDocument32 pagesDish Washer ManuelretishambatNo ratings yet
- Practical HACCP BookDocument127 pagesPractical HACCP Bookanil rautNo ratings yet
- Taal Menu VEG & Non-veg Buffet OptionsDocument6 pagesTaal Menu VEG & Non-veg Buffet OptionsQwertyNo ratings yet
- Proscovia Nayiruba Nanny CVDocument1 pageProscovia Nayiruba Nanny CVZac PhotographyNo ratings yet
- Learning Modules - Cookery 9Document81 pagesLearning Modules - Cookery 9Glee LeeNo ratings yet
- The Adopted SonDocument7 pagesThe Adopted SonNaishika VadakattuNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Manual 13th EditionDocument127 pagesDokumen - Tips - Manual 13th EditionAbdur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Vegan Meatball One-Pot Pasta Recipe - BBC FoodDocument3 pagesVegan Meatball One-Pot Pasta Recipe - BBC FoodkkNo ratings yet
- 99 Surprising Foods Which Have Gluten EbookDocument3 pages99 Surprising Foods Which Have Gluten EbookShivshankar IyerNo ratings yet
- SPELLING BEE - Banco de Palabras 2021Document9 pagesSPELLING BEE - Banco de Palabras 2021JORGE ALEJANDRO REYES HERNANDEZNo ratings yet