Professional Documents
Culture Documents
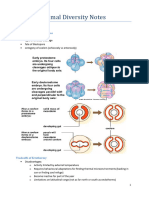
Deuterostomes: Anus Forms at or Near The Blastopore Radial and Indeterminate Cleavage Enterocoelous Coelomates
Uploaded by
Rj PanerioOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Deuterostomes: Anus Forms at or Near The Blastopore Radial and Indeterminate Cleavage Enterocoelous Coelomates
Uploaded by
Rj PanerioCopyright:
Available Formats
2/22/2011
Deuterostomes Echinodermata and Hemichordata
Anus forms at or near the blastopore Radial and indeterminate cleavage
Enterocoelous coelomates
Calcarea and Silicea ANCESTRAL PROTIST Eumetazoa Cnidaria
ZOO 3
Prof. Eleanor Aurellado
Common ancestor of all animals
Lophotrochozoa
Bilateria
Ecdysozoa
Deuterostomia
Echinodermata
Endoskeleton of
Water vascular system
Derived from the
calcareous ossicles often with spines
Pedicellariae pincers used for picking debris
coelom System of canals which open from the madreporite leading to tube feet or podia
Locomotion Feeding Respiration Sensing
2/22/2011
Pentaradial symmetry
Tube feet Adults show 5-part symmetry Larvae are bilateral
protrude through ambulacral grooves Ambulacral grooves can be open or closed
Fossil records also show bilateral ancestors
Development
Metamorphosis involves a reorganization into
Why five?
Evolution of endoskeleton may be responsible Skeleton is stronger if joints (weak points) are not
a radial juvenile.
Left/right becomes oral/aboral.
opposite each other
2/22/2011
Other characteristics
Decentralized nervous
Importance of echinoderms
Ornamental trade
system (nerve rings and radial nerves) No excretory or osmoregulatory system
Confined in marine habitats
Mutable connective
tissue
Capable of rapid reversible changes in stiffness
Ecological impacts
Hazardous
Acanthaster (crown-of-thorns starfish) feeding on coral
2/22/2011
Food
Habitat
Pearlfish living inside Bohadschia (sea cucumber)
Sea urchin roe or uni (Japanese sushi)
Clingfish living on arms of a feather star Sea cucumber (Chinese cuisine) Tripneustes
Echinoderm Classes
Class Crinoidea (feather stars and sea lilies)
2/22/2011
Form and function
Have feathery arms
Sea lilies
Have stalk for
with pinnules Ambulacral grooves ciliated and with tube feet Suspension feeders Both mouth and anus open on the upper surface
attachment to the bottom Dominated the Paleozoic fossil record Sessile lifestyle may explain why echinoderms became radially symmetrical
Feather stars
Modern sea lilies Has no stalk, found in coral reefs Can swim by undulating their arms
live in deep seas Some are known to creep along the ocean floor using their arms
Endoxocrinus
2/22/2011
Class Asteroidea (sea stars)
Form and function
Common on shores and coral reefs Arms broadly connected to central disk
Madreporite on aboral surface
Linckia laevigata
Protoreaster nodosus
Mouth on underside Open ambulacral grooves Podia with ampullae
Skin with gills called dermal branchiae With pedicellariae
2/22/2011
Feeding
Carnivorous Stomach everted
Regeneration
Can replace lost arms Can regenerate a new individual from an arm
through the mouth
Sea daisies
Formerly Class Concentricycloidea Discovered in 1986 from deep seas off New Water vascular system consists of a double
Zealand
ring of canals No arms
Xyloplax turnerae
2/22/2011
Class Ophiuroidea (brittlestars and basket stars)
Form and function
Arms distinctly marked
off from central disc Closed ambulacral grooves Podia for food gathering and w/o ampullae No anus and pedicellariae
Brittlestars or serpent stars
Madreporite on oral surface Bursae
Can cast off their arms (autotomy) Flexible unbranched arms used for
Respiration Reproduction
locomotion
2/22/2011
Basketstars
Sessile suspension feeders Branching arms
Class Echinoidea (sea urchins and sand dollars)
Form and function
Ossicles fused into a rigid test With spines and pedicellariae
Feeding
Herbivorous with long intestine Feeding apparatus called Aristotle's lantern
2/22/2011
Sea urchins
Pedicellariae sometimes with toxins Used to cover themselves with debris
Astropyga radiata Toxopneustes Tripneustes
Diadema setosum
Sand dollars
Flattened test with short spines Podia for food gathering and respiration
Class Holothuroidea (sea cucumbers)
which protrude through petaloids
10
2/22/2011
Form and function
Elongated body Reduced dermal ossicles
Madreporite internal Respiratory tree
Oral podia modified into
tentacles
Deposit feeders
Other sea cucumbers
Can eviscerate themselves in defense Cuvierian tubules Toxins Can regenerate
Synapta
Holothuria
11
You might also like
- Echinoderm CharacteristicsDocument19 pagesEchinoderm CharacteristicsjdriderNo ratings yet
- 7 - Echinoderms and HemichordataDocument51 pages7 - Echinoderms and HemichordataDwi HardiyantiNo ratings yet
- Group 6 - Boligao, Biano, Nere, OsmeñaDocument26 pagesGroup 6 - Boligao, Biano, Nere, OsmeñaJason Greyzon Boligao IndianaNo ratings yet
- Filum EchinodermataDocument15 pagesFilum EchinodermataForman SihombingNo ratings yet
- Kingdom AnimaliaDocument42 pagesKingdom AnimaliaGuffran septiahadiNo ratings yet
- Phylum Coenlenterata and Phylum CtenophoraDocument21 pagesPhylum Coenlenterata and Phylum CtenophoraYukimi SugitaNo ratings yet
- EchinodermsDocument31 pagesEchinodermsfkg unand 16100% (1)
- Sub-Phylum Cephalochordata (Lancelets) : ObjectivesDocument5 pagesSub-Phylum Cephalochordata (Lancelets) : ObjectivesMiftah RohmahNo ratings yet
- Flatworms Mollusks and AnnelidsDocument39 pagesFlatworms Mollusks and AnnelidsjdriderNo ratings yet
- Echinoderms LectureDocument6 pagesEchinoderms LectureMarjorie Rose TeodosioNo ratings yet
- (JR., Cleveland P Hickman, Larry S Roberts, Allan OrgDocument58 pages(JR., Cleveland P Hickman, Larry S Roberts, Allan Orgalem010No ratings yet
- The Phylum Echinodermata: A. AsteroideaDocument10 pagesThe Phylum Echinodermata: A. AsteroideaCindy RahmahNo ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University IslamabadDocument16 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University IslamabadAbdullah NagraNo ratings yet
- PHYLUMSDocument6 pagesPHYLUMSJanelle RedobladoNo ratings yet
- Z3 Echinodermatarev PDFDocument24 pagesZ3 Echinodermatarev PDFPat Peralta DaizNo ratings yet
- Bio 112Document3 pagesBio 112Ezekoko ChineseNo ratings yet
- Echinoderm at A StarfishDocument10 pagesEchinoderm at A StarfishBio SciencesNo ratings yet
- Practical Guide Invertebrates PDFDocument61 pagesPractical Guide Invertebrates PDFMOUSTAFA ALEMAMNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom (Phylum 1-7)Document4 pagesAnimal Kingdom (Phylum 1-7)AllenNo ratings yet
- Kingdom AnimaliaDocument4 pagesKingdom AnimaliamarkNo ratings yet
- Phylum Annelida (Segmented Worms) : College of Science Biological Sciences DepartmentDocument22 pagesPhylum Annelida (Segmented Worms) : College of Science Biological Sciences DepartmentPrateek JainNo ratings yet
- 2 Animal DiversityDocument27 pages2 Animal DiversityKochu NediyavilaNo ratings yet
- Notes in English of BiologyDocument3 pagesNotes in English of Biologylau fjNo ratings yet
- Invertebrate Gallery of Indian MuseumDocument58 pagesInvertebrate Gallery of Indian MuseumAkash NaskarNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 - MolluscaDocument18 pagesLab 4 - MolluscaArifameira KinantiNo ratings yet
- Reptilia-Characters & ClassificationDocument3 pagesReptilia-Characters & ClassificationAakash VNo ratings yet
- Chaetognaths Echinoderms and HemichordatesDocument54 pagesChaetognaths Echinoderms and HemichordatesKyrby CabalquintoNo ratings yet
- Animal Phyla Description ImageDocument4 pagesAnimal Phyla Description ImageJeff Raian BatongbakalNo ratings yet
- Echinodermata: Group MembersDocument7 pagesEchinodermata: Group MembersCamile Elaine Borromeo NocheNo ratings yet
- Practical 3Document2 pagesPractical 3Nick YuNo ratings yet
- Ctenophora Small BookDocument28 pagesCtenophora Small BookTaw GeimNo ratings yet
- Comparative Vertebrate AnatomyDocument9 pagesComparative Vertebrate AnatomyJayson Tafalla LopezNo ratings yet
- Class Anthozoa LectureDocument16 pagesClass Anthozoa LectureNora QuddsyNo ratings yet
- Phylum Echinodermata: Made Truly By: Samuel Enrique C. Patoc Sydrenz Anthony CaoDocument21 pagesPhylum Echinodermata: Made Truly By: Samuel Enrique C. Patoc Sydrenz Anthony CaoSamuel Enrique Cano PatocNo ratings yet
- Diversity in Living OrganismsDocument52 pagesDiversity in Living Organismsnonubansal18100% (2)
- PHYLUM CNIDARIA-Written ReportDocument6 pagesPHYLUM CNIDARIA-Written ReportTeacher MarianoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 06Document28 pagesLecture 06Wai Ateny WaiNo ratings yet
- CtenophoraDocument23 pagesCtenophoraAnonymous eOcg87KnNo ratings yet
- Echinodermata PDFDocument57 pagesEchinodermata PDFjerlimanmanalu100% (1)
- EchinodermsDocument7 pagesEchinodermsChristian Arm100% (1)
- Porifera: Sally P. Leys and Nathan FarrarDocument9 pagesPorifera: Sally P. Leys and Nathan FarrarFaradilla Aqidatul IzzahNo ratings yet
- Echinodermata PDFDocument65 pagesEchinodermata PDFandiriandikapNo ratings yet
- BZ Lab 5Document8 pagesBZ Lab 5Alexa Jean D. HonrejasNo ratings yet
- Phylum EchinodermataDocument88 pagesPhylum EchinodermataIkki PhoenixNo ratings yet
- Phylum PoriferaDocument5 pagesPhylum Poriferastudent10100No ratings yet
- Identification of Vertebrate Taxonomic CharacterDocument8 pagesIdentification of Vertebrate Taxonomic CharacterFitria RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Mollusc ADocument14 pagesMollusc ADhaffer Al-Mezhany100% (1)
- Echinoderm at ADocument9 pagesEchinoderm at ARiyah Zuhriyah TokappaNo ratings yet
- Animal Diversity II - Introduction (Protochordates) PDFDocument5 pagesAnimal Diversity II - Introduction (Protochordates) PDFinam ullahNo ratings yet
- Animals 2: Mollusc A, Ec Hi No Derma Ta, A Rthrop OdaDocument8 pagesAnimals 2: Mollusc A, Ec Hi No Derma Ta, A Rthrop OdaKaylaniNo ratings yet
- AnthozoaDocument21 pagesAnthozoaJagan JaganNo ratings yet
- Practical No 3 FYBSc.Document13 pagesPractical No 3 FYBSc.Vinod SNo ratings yet
- Activity Animal KingdomDocument8 pagesActivity Animal KingdomGerald Agacid BangeroNo ratings yet
- Animals - Adaptations Endoskeleton, Echinoderms, Invert Chordates, VertebratesDocument9 pagesAnimals - Adaptations Endoskeleton, Echinoderms, Invert Chordates, VertebratessmedificationNo ratings yet
- Hemichordates: Is Divided Into 3 PartsDocument8 pagesHemichordates: Is Divided Into 3 Partstaimoor shahzadNo ratings yet
- ChordataDocument41 pagesChordataHasna NanaNo ratings yet
- Echinodermata Notes - 2023Document2 pagesEchinodermata Notes - 2023BHEKUMUSA MASEKONo ratings yet
- 1 - 1 Abahan Kul PhylumDocument14 pages1 - 1 Abahan Kul PhylumMarda MarronNo ratings yet
- The Book of Frogs: A Life-Size Guide to Six Hundred Species from Around the WorldFrom EverandThe Book of Frogs: A Life-Size Guide to Six Hundred Species from Around the WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Fascinating Shells: An Introduction to 121 of the World’s Most Wonderful MollusksFrom EverandFascinating Shells: An Introduction to 121 of the World’s Most Wonderful MollusksNo ratings yet
- Gastropoda Pacifica, Christophe Avon 2016Document598 pagesGastropoda Pacifica, Christophe Avon 2016Christophe Avon100% (1)
- Chaetognaths Echinoderms and HemichordatesDocument54 pagesChaetognaths Echinoderms and HemichordatesKyrby CabalquintoNo ratings yet
- Phylum Echinodermata: Made Truly By: Samuel Enrique C. Patoc Sydrenz Anthony CaoDocument21 pagesPhylum Echinodermata: Made Truly By: Samuel Enrique C. Patoc Sydrenz Anthony CaoSamuel Enrique Cano PatocNo ratings yet
- Edited English - Long SizeDocument4 pagesEdited English - Long SizeLeur Ulanday RajebNo ratings yet
- Phylum PoriferaDocument18 pagesPhylum Poriferagonoles81No ratings yet
- Sea Star Prop.Document10 pagesSea Star Prop.Mia JaiNo ratings yet
- Sean Burke - Starfish Dissection QuestionsDocument3 pagesSean Burke - Starfish Dissection Questionsapi-386190429No ratings yet
- 2015 - Lowe - Deuterostome Context of Chordate OriginsDocument10 pages2015 - Lowe - Deuterostome Context of Chordate OriginsDredeltoNo ratings yet
- Hayward - More Lessons From A Starfish - Prefixial Flesh and Transspeciated SelvesDocument23 pagesHayward - More Lessons From A Starfish - Prefixial Flesh and Transspeciated SelvesOscar Armando Béjar GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom Echinodermata OnwarsDocument44 pagesAnimal Kingdom Echinodermata OnwarsKankana BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom BiologyDocument8 pagesAnimal Kingdom BiologyMary Ann SalvatierraNo ratings yet
- TESTING AND EVALUATION IN ELT Phase 2 FMDocument10 pagesTESTING AND EVALUATION IN ELT Phase 2 FMfabio montillaNo ratings yet
- Unit 8. InvertebratesDocument142 pagesUnit 8. InvertebratesPika PiNo ratings yet
- Starfish LanesDocument1 pageStarfish Lanesshabina921No ratings yet
- RemedisDocument28 pagesRemedisboraNo ratings yet
- Zoology Honours Second Semester 2020: Zoocor08: Larva of EchinodermsDocument2 pagesZoology Honours Second Semester 2020: Zoocor08: Larva of EchinodermsRidhi ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Palopolo Et Al 2021 ZoroDocument18 pagesPalopolo Et Al 2021 ZoroGeorge ThoreauNo ratings yet
- Sokoine University of Agriculture: ClassificationDocument75 pagesSokoine University of Agriculture: ClassificationToke SadockNo ratings yet
- (Biology and Ecology of Marine Life) David, Sheba Rani Nakka - Ramesh, Santhanam - Santhanam, Ramasamy - Biology and Ecology of Pharmaceutical Marine Life - echinoderms-CRC Press (20 PDFDocument435 pages(Biology and Ecology of Marine Life) David, Sheba Rani Nakka - Ramesh, Santhanam - Santhanam, Ramasamy - Biology and Ecology of Pharmaceutical Marine Life - echinoderms-CRC Press (20 PDFEmilio Lecaros Bustamante100% (1)
- 101 Writing Prompts For Fantasy - Laura GrantDocument90 pages101 Writing Prompts For Fantasy - Laura GrantGerman Enrique Martinez100% (1)
- Phylum EchinodermataDocument11 pagesPhylum Echinodermatakat_hildegardeNo ratings yet
- UNIT 7 Bahasa Inggris For TPL - 2022Document12 pagesUNIT 7 Bahasa Inggris For TPL - 2022kiki erryNo ratings yet
- Seychelles Wildlife Colouring BookDocument40 pagesSeychelles Wildlife Colouring Bookapi-348135772100% (1)
- Soal Us Bahasa Inggris SmaDocument7 pagesSoal Us Bahasa Inggris SmaDian OctavianiNo ratings yet
- BIO 111 - LECTURE - Phylum ECHINODERMATADocument116 pagesBIO 111 - LECTURE - Phylum ECHINODERMATAAnord EliasNo ratings yet
- Eton List Test - StarfishDocument3 pagesEton List Test - StarfishEunita KorankyeNo ratings yet
- 10 Things in Nature Related in MathematicsDocument2 pages10 Things in Nature Related in MathematicsKatrina Kye MaghanoyNo ratings yet
- BIO104 - Study Guide For Zoology Exam 2Document6 pagesBIO104 - Study Guide For Zoology Exam 2Róisín BlanksNo ratings yet
- Biology 101 Animals NotesDocument61 pagesBiology 101 Animals NotesAdam GlassnerNo ratings yet
- Tides DocumentDocument5 pagesTides DocumentOlivia JamesNo ratings yet