Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Isi Zulu
Uploaded by
Sesiyabonga NgubaneOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Isi Zulu
Uploaded by
Sesiyabonga NgubaneCopyright:
Available Formats
QUESTION 1
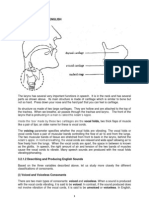
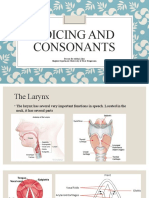
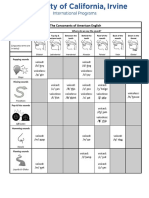
1.1. The difference between voiced and voiceless consonants is in the presence or absence of vocal cord
vibration during the articulation of the sound.
- Voiced consonants: These are produced with vocal cord vibration. Examples include /b/ as in
“bed” and /z/ as in “zip”.
- Voiceless consonants: These are produced without vocal cord vibration. Examples include /p/ as
in “pat” and /s/ as in “sit”.
1.2. The initial sounds in the following words:
a. Chin: [tʃ] – voiceless palatal affricate. It is produced by placing the tip of the tongue against the
hard palate and releasing a burst of air while the vocal cords remain inactive.
b. Physical: [f] – voiceless labiodental fricative. It is produced by placing the lower lip against the
upper teeth and letting air escape through the narrow gap in between, without vocal cord
vibration.
c. Psychology: [s] – voiceless alveolar fricative. It is produced by placing the tip of the tongue
against the alveolar ridge and forcing air through the narrow gap, without vocal cord vibration.
d. Knee: [n] – voiced alveolar nasal. It is produced by placing the tip of the tongue against the
alveolar ridge and allowing the air to flow through the nose, while the vocal cords vibrate.
e. Jean: [dʒ] – voiced palatal affricate. It is produced by placing the tip of the tongue against the
hard palate and releasing a burst of air while the vocal cords vibrate.
1.3 The allophones of the phoneme /t/ in the following words/environments are:
a. Tool: [t]
b. Stool: [t̪]
c. Responsibility: [ɾ]
d. Eighth: [t]
e. Part: [t]
1.4 The differentiation between a closed and an open syllable is as follows:
- Closed syllable: A closed syllable is a syllable that ends with a consonant sound. The vowel in a
closed syllable is typically short. Examples include “cat” and “stop”. In “cat”, the closed syllable
is /kæt/ with the final /t/ creating a closed syllable.
- Open syllable: An open syllable is a syllable that ends with a vowel sound. The vowel in an open
syllable is typically long. Examples include “me” and “go”. In “me”, the open syllable is /mi/ with
the final /i/ creating an open syllable.
1.5 The phonetic transcriptions for the following words are:
a. Book: /bʊk/
b. Me: /mi/
REFERENCES:
Krashen, S.D. (1983). The Natural Approach: Language Acquisition in the Classroom. Hemisphere
Publishing Corporation.
Skinner, B.F. (1958). Teaching Machines. Science, 128(3330), 969-977
Wikipedia; 2023; ‘English FAL Pdf’, retrieved online: www.wikipedia.com; (accessed on 10 September
2023)
You might also like
- النظام الصوتي المرحلة الاولى الملف الكاملDocument48 pagesالنظام الصوتي المرحلة الاولى الملف الكاملjyx9sbghgvNo ratings yet
- Speech and Theater ExamDocument22 pagesSpeech and Theater ExamCres Jules ArdoNo ratings yet
- Linguistics - Unit 3Document5 pagesLinguistics - Unit 3Appas SahaNo ratings yet
- Consonant SoundsDocument8 pagesConsonant SoundsKhairul Nizam HamzahNo ratings yet
- Uas Alrino Ode MasimuDocument10 pagesUas Alrino Ode MasimuArif FlouncxNo ratings yet
- What aspects of language are studied in articulatory, acoustic and auditory phoneticsDocument8 pagesWhat aspects of language are studied in articulatory, acoustic and auditory phoneticsesha khanNo ratings yet
- Unit-IV: Phonetics 4.1 IPA SymbolsDocument27 pagesUnit-IV: Phonetics 4.1 IPA SymbolsAngel Mae RamosNo ratings yet
- PHONETICS AND PHONOLOGY: SPEECH ORGANS AND SOUND CLASSIFICATIONDocument134 pagesPHONETICS AND PHONOLOGY: SPEECH ORGANS AND SOUND CLASSIFICATIONKim Khánh LêNo ratings yet
- Speech Organs Produce The Many Sounds Needed For LanguageDocument7 pagesSpeech Organs Produce The Many Sounds Needed For LanguageSherwin Ryan AvilaNo ratings yet
- Phonetic and PhonologyDocument8 pagesPhonetic and PhonologyIzha AshariNo ratings yet
- Organs of SpeechDocument5 pagesOrgans of Speechlittle large2100% (1)
- Organ of Speech Airstream Mechanism (Kel 1)Document7 pagesOrgan of Speech Airstream Mechanism (Kel 1)Vera AsifaNo ratings yet
- Organs of SpeechDocument3 pagesOrgans of SpeechSujatha MenonNo ratings yet
- Speech MechanismDocument3 pagesSpeech Mechanismহুমায়রা জাহানNo ratings yet
- Ngân Hàng Câu Hỏi Môn Phonetics And Phonology (Khóa Nna-2019) A- Lý Thuyết 1. On the diagram provided, give the names for the articulatorsDocument20 pagesNgân Hàng Câu Hỏi Môn Phonetics And Phonology (Khóa Nna-2019) A- Lý Thuyết 1. On the diagram provided, give the names for the articulatorsTạ Hoàng AnhNo ratings yet
- English Lab NotesDocument40 pagesEnglish Lab Noteskgiridharreddy2022No ratings yet
- Articulators/ Speech Organs: 1. The Larynx & The Vocal FoldsDocument6 pagesArticulators/ Speech Organs: 1. The Larynx & The Vocal FoldsGulfam RiazNo ratings yet
- Speech OrgansDocument5 pagesSpeech OrgansprivateceeNo ratings yet
- Principles of E Phonetics and PhonologyDocument74 pagesPrinciples of E Phonetics and PhonologyDuy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- الثاني صوتDocument13 pagesالثاني صوتg7j85hvb52No ratings yet
- Phonetics: The Study of Speech SoundsDocument10 pagesPhonetics: The Study of Speech SoundsSindy Blandon RiosNo ratings yet
- PhoneticsDocument4 pagesPhoneticsnhutduynguyen31No ratings yet
- English ConsonantsDocument28 pagesEnglish ConsonantsIzzati AzmanNo ratings yet
- Phonetics-The Basics: Chapter 4: The Sounds of Language (Document18 pagesPhonetics-The Basics: Chapter 4: The Sounds of Language (AlbaNo ratings yet
- DescriptiveDocument75 pagesDescriptiveAmani SalmanNo ratings yet
- Organ of SpeechDocument10 pagesOrgan of SpeechWinda Rizki Listia DamanikNo ratings yet
- Articulatory Phonetics: 1) VoiceDocument3 pagesArticulatory Phonetics: 1) VoiceDorepeNo ratings yet
- 2 Seminar TypologyDocument32 pages2 Seminar TypologytoshkulovagulasalNo ratings yet
- SPEECH ORGAN INTRODUCTIONDocument9 pagesSPEECH ORGAN INTRODUCTIONEka MelyanaNo ratings yet
- Articulatory PhoneticsDocument3 pagesArticulatory PhoneticszelindaaNo ratings yet
- Intro Ling Unit 3Document14 pagesIntro Ling Unit 3Zain ChNo ratings yet
- 2 PhonologyDocument10 pages2 PhonologyNaoufal FouadNo ratings yet
- Handout Chapter 2 Phonetics Spring Semester 2023Document11 pagesHandout Chapter 2 Phonetics Spring Semester 2023mhmddhwyb8No ratings yet
- Manner of Articulation DefinitionDocument9 pagesManner of Articulation DefinitionAdmin LinguizNo ratings yet
- Organs of SpeechDocument5 pagesOrgans of SpeechMohd Shahrin BasniNo ratings yet
- NAAVDocument20 pagesNAAVd.duongnguyen1901No ratings yet
- Practicas Discursivas de La Comunicación Oral 1Document6 pagesPracticas Discursivas de La Comunicación Oral 1Brenda GutierrezNo ratings yet
- English Phonetics Lesson 3Document14 pagesEnglish Phonetics Lesson 3Doaa Fat-hyNo ratings yet
- Phonetics: Speech Sounds ExplainedDocument22 pagesPhonetics: Speech Sounds ExplainedYulia DeaNo ratings yet
- Phonetics & Spoken EnglishDocument12 pagesPhonetics & Spoken EnglishCharanjit SinghNo ratings yet
- English Phonology GuideDocument22 pagesEnglish Phonology Guidesari wulandaryNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and Phonology 2021Document21 pagesPhonetics and Phonology 2021Anaíde dos Santos RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Lesson3 English Consonants Description PDFDocument5 pagesLesson3 English Consonants Description PDFsami karemNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and Phonology GuideDocument62 pagesPhonetics and Phonology GuideCarlos Rojas CamachoNo ratings yet
- Phonetics: The Study of Speech SoundsDocument18 pagesPhonetics: The Study of Speech SoundsAneu DamayantiNo ratings yet
- Day 2Document39 pagesDay 2KuIl PhạmNo ratings yet
- Ibn Tofail University LevelDocument23 pagesIbn Tofail University LevelImad Es SaouabiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 & 5 - Special TopicsDocument15 pagesChapter 4 & 5 - Special TopicsBearish PaleroNo ratings yet
- Speech Sounds Segmentation GuideDocument7 pagesSpeech Sounds Segmentation GuideNhân ĐặngNo ratings yet
- Bài giảng Ngữ âm lý thuyết EHOU Bài 1Document6 pagesBài giảng Ngữ âm lý thuyết EHOU Bài 1tranthanhtambrNo ratings yet
- English Phonetics and Phonology: Chapter 1 - 11Document48 pagesEnglish Phonetics and Phonology: Chapter 1 - 11Trung HậuNo ratings yet
- Voice and Accent Training ModuleDocument12 pagesVoice and Accent Training ModuleAditi GhaiNo ratings yet
- The Representation of Speech SoundsDocument4 pagesThe Representation of Speech SoundsJuwita AnggreliaNo ratings yet
- Institute of New Khmer: Subject: Applied Linguistics Teach By: Lecturer Prepared By: Group 6 Student NameDocument27 pagesInstitute of New Khmer: Subject: Applied Linguistics Teach By: Lecturer Prepared By: Group 6 Student NameHafiz ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Types of Phonemes Definitions PDFDocument3 pagesTypes of Phonemes Definitions PDFLovely FinuliarNo ratings yet
- Phonetic and Phonology": Miranti Widyasari Tatebale 17091102047Document12 pagesPhonetic and Phonology": Miranti Widyasari Tatebale 17091102047MIRANTI WIDYASARI TATEBALENo ratings yet
- Topic 8: Phonological System of The English Language Ii: Consonants. Phonetic SymbolsDocument8 pagesTopic 8: Phonological System of The English Language Ii: Consonants. Phonetic SymbolsLaura Irina Lara SánchezNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and Phonology: A Study of English Speech SoundsDocument10 pagesPhonetics and Phonology: A Study of English Speech SoundsRoxana Aguirre100% (1)
- Voicing and Consonants: Present by Afdhol Zikri English Department University of Pasir PengaraianDocument14 pagesVoicing and Consonants: Present by Afdhol Zikri English Department University of Pasir PengaraianlucianoNo ratings yet
- 6 Suprasegmental Phonology Pp186 238Document27 pages6 Suprasegmental Phonology Pp186 238Bee BrightNo ratings yet
- Marck Antony No Me AmesDocument14 pagesMarck Antony No Me AmesKeivys Bracho BNo ratings yet
- Speech MechanismDocument2 pagesSpeech MechanismangelicaNo ratings yet
- English PronunciationDocument16 pagesEnglish PronunciationSacha ClaesNo ratings yet
- Lich Su Phat Trien Tieng AnhDocument60 pagesLich Su Phat Trien Tieng AnhUyen Pham100% (1)
- Representation of IPA With ASCIIDocument38 pagesRepresentation of IPA With ASCIIKarelBRGNo ratings yet
- Verb Conjugation Exercises - LösungenDocument37 pagesVerb Conjugation Exercises - LösungenAdlyn NatashaNo ratings yet
- The Consonants of American English: A Visual GuideDocument2 pagesThe Consonants of American English: A Visual GuideHien TaNo ratings yet
- Linguistics Review - CDEDocument55 pagesLinguistics Review - CDEClau DuarteNo ratings yet
- Help:Pronunciation Respelling Key: Information PageDocument1 pageHelp:Pronunciation Respelling Key: Information PageKarthi KeyanNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Mandarin Textbook IDocument207 pagesComprehensive Mandarin Textbook IVierka Donicova83% (6)
- Final Paper ProjectDocument28 pagesFinal Paper Projectapi-361147266No ratings yet
- Project ARTT Lessons Timeline Using E-ApplicationDocument11 pagesProject ARTT Lessons Timeline Using E-ApplicationEugeniaBabe Cocamas Amora KinakinNo ratings yet
- IPA VowelsDocument45 pagesIPA VowelsWinefredo Quiapo PaghubasanNo ratings yet
- 3partofpoem PDFDocument1 page3partofpoem PDFNarvy R. SorianoNo ratings yet
- Phonological AwarenessDocument14 pagesPhonological AwarenessCarson Yeap100% (1)
- ENG503 Mids SolvedDocument19 pagesENG503 Mids Solvedhania noorNo ratings yet
- Hualde - A Lexical Phonology of Basque PDFDocument323 pagesHualde - A Lexical Phonology of Basque PDFGiada GrandiniNo ratings yet
- Enga LanguageDocument3 pagesEnga LanguageowenpatiliuNo ratings yet
- Consonant ClusterDocument1 pageConsonant Clusterdesys_4No ratings yet
- Murekatete Brigitte General LiguisticDocument2 pagesMurekatete Brigitte General LiguisticJabiro emmanuelNo ratings yet
- 100 Most MispronouncedDocument2 pages100 Most Mispronouncedkch369No ratings yet
- Pronunciation Bank: Activities: Unit 1Document1 pagePronunciation Bank: Activities: Unit 1Maria Da Conceição MoraisNo ratings yet
- 1890 Strong Greek Dictionary PDFDocument77 pages1890 Strong Greek Dictionary PDFYemir MendezNo ratings yet
- Automatic Grapheme - To - Phoneme Conversion of Arabic TextDocument8 pagesAutomatic Grapheme - To - Phoneme Conversion of Arabic TextAbbas YerimaNo ratings yet
- Phonology III Resumen LUCIA JUAN PROFE FALCONIDocument17 pagesPhonology III Resumen LUCIA JUAN PROFE FALCONIRegina ErcoleNo ratings yet
- CLC 100 Introduction To The Study of Language-1Document2 pagesCLC 100 Introduction To The Study of Language-1erickkinyanjui88No ratings yet
- IPA Chart 1Document2 pagesIPA Chart 1Song Ji Hyo100% (1)
- Reading Intervention Plan Sabang National High SchoolDocument4 pagesReading Intervention Plan Sabang National High SchoolMikaela RoblesNo ratings yet
- The Mitten Phonological AwarenessDocument55 pagesThe Mitten Phonological AwarenesssmillsNo ratings yet