Professional Documents
Culture Documents
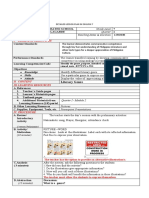
CONDITIONALS
CONDITIONALS
Uploaded by
alohaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CONDITIONALS
CONDITIONALS
Uploaded by
alohaCopyright:
Available Formats
CONDITIONALS describe the result of something that might happen (in the present or future) or might have happened
but didn’t (in the past).
There are four types of conditionals: zero conditional, first conditional, second conditional, and third conditional.
- Zero Conditional gives a fact, a rule, or a true situation. One thing follows the other. Zero conditionals follow this
structure:
If + subject + simple present verb tense … subject + simple present verb tense
Example:
subj
subj
ect
ect (It is always true, there can't be
If water reaches 100 degrees, it boils. a different result)
Simple present Simple present
tense tense
verb verb
subj subj
ect ect
If you combine carrots with cucumber, you create a heterogeneous mixture.
Simple present Simple present
tense tense
verb verb
- First conditional is used to talk about things which might happen in the future. It is possible and very likely that the
condition will be fulfilled. First conditionals follow this structure:
If + subject + simple present verb tense … subject + simple future verb tense
Example:
subj subj
ect ect
If I find her address, I will send her an invitation.
Simple present Simple future tense
tense verb (will + base form of the
verb verb)
subj subj
ect ect
If I have enough money, I will buy some new shoes.
Simple present Simple future tense
tense verb (will + base form of the
verb verb)
- Second conditional is used if the condition is possible but very unlikely to be fulfilled. Second conditionals follow this
structure:
If + subject + simple present verb tense … subject + would + base form verb
There are to application for the second conditional.
First, we can use it to talk about things in the future that are probably not going to be true. Maybe the speaker is
imagining some dream.
Example:
subj subj
ect ect
(The speaker probably
If I won the lottery, I would buy a big house. won't win the lottery)
Simple past tense (would + base form of
verb the verb)
subj subj
ect ect (She never studies, so
this won't happen)
If she studied, she would pass the exam.
Simple past tense (would + base
verb form of the verb)
Second, we can use it to talk about something in the present which is impossible, because it's not true.
Example:
subj
subj
ect
ect (I don't have his number
If I had his number, I would call him. now, so it's impossible for
me to call him)
Simple past tense (would + base
verb form of the
verb)
subj subj (The speaker
ect ect doesn’t have her
If I found her address, I would send her an invitation.
address now, so
it's impossible
Simple past tense (would + base for him/her to
verb form of the invite her)
verb)
- Third conditional talks about a past event. It's used to describe a situation that didn't happen, and to imagine the
result of this situation. Third conditionals follow this structure:
If + subject + past perfect tense verb… subject + would + have + past participle
Example:
subj subj
ect ect
If she had studied, she would have passed the exam
Past perfect tense would + have + past
(had + past participle
participle)
subj subj
ect ect
If she had gone to college, she would have become a teacher.
Past perfect tense would + have + past
(had + past participle
participle)
Note: the adverb “not” can be added on the if clause after “had” and on the second half of the conditional statement
after “would” to express negation. It can be shortened to the contractions “hadn’t” and “wouldn’t,” respectively.
subj subj
ect ect
If she had gone to bed earlier, she wouldn't have missed the flight.
Past perfect tense would + no t+ have
(had + past + past participle
participle)
subj subj
ect ect
If I hadn't eaten so much, I wouldn't have felt sick
Past perfect tense would + no t+ have
(had + not + past + past participle
participle)
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (347)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- DLP-COT Q1 Eng7 Module 3Document4 pagesDLP-COT Q1 Eng7 Module 3Kristell C. LagardeNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice For MLT GE Odd 2017Document41 pagesPassive Voice For MLT GE Odd 2017Fati Andari AlmahdiniNo ratings yet
- Correcting Sentence FragmentsDocument3 pagesCorrecting Sentence FragmentsbetelgueseNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in English 7: January, 24, 2020 EN7G-IV-b-4: Use of PrepositionsDocument2 pagesLesson Plan in English 7: January, 24, 2020 EN7G-IV-b-4: Use of PrepositionsKristell C. LagardeNo ratings yet
- German Reflexive Verbs and PrepositionsDocument3 pagesGerman Reflexive Verbs and Prepositions711debbie25% (4)
- DLP-COT Q1 Eng7 Module 1Document4 pagesDLP-COT Q1 Eng7 Module 1Kristell C. Lagarde100% (1)
- Lesson Korean NumbersDocument5 pagesLesson Korean NumbersLulu Afifah OctaviaNo ratings yet
- Tenses Made SimpleDocument10 pagesTenses Made SimpleAsad RazaNo ratings yet
- DLP-8-Q1mODULE-5-Remefe SolamilloDocument5 pagesDLP-8-Q1mODULE-5-Remefe SolamilloKristell C. Lagarde100% (1)
- 1st Summtive ExmDocument2 pages1st Summtive ExmKristell C. LagardeNo ratings yet
- DLP-COT Q1 Eng7 Module 2Document3 pagesDLP-COT Q1 Eng7 Module 2Kristell C. LagardeNo ratings yet
- 21stcenturylit S1 Q1 M1aDocument6 pages21stcenturylit S1 Q1 M1aKristell C. LagardeNo ratings yet
- Oralcomm S1 Q1 M5Document7 pagesOralcomm S1 Q1 M5Kristell C. LagardeNo ratings yet
- DLP Eng.-8-Q 1-M1-Lucille BarilloDocument9 pagesDLP Eng.-8-Q 1-M1-Lucille BarilloKristell C. LagardeNo ratings yet
- G9-Q1-Week2-Conditionals (Part 1)Document5 pagesG9-Q1-Week2-Conditionals (Part 1)Kristell C. LagardeNo ratings yet
- Title: School: Recipients: Program ContentDocument2 pagesTitle: School: Recipients: Program ContentKristell C. LagardeNo ratings yet
- Inset 2022Document19 pagesInset 2022Kristell C. LagardeNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment ReportDocument3 pagesAccomplishment ReportKristell C. LagardeNo ratings yet
- Principles and Methods OF Research: Kristell C. LagardeDocument18 pagesPrinciples and Methods OF Research: Kristell C. LagardeKristell C. LagardeNo ratings yet
- Be 2023Document1 pageBe 2023Kristell C. LagardeNo ratings yet
- Kristell C. Lagarde, LPT Maed-Elt: Synopsis/ SummaryDocument3 pagesKristell C. Lagarde, LPT Maed-Elt: Synopsis/ SummaryKristell C. LagardeNo ratings yet
- Tasks For The Entire ModuleDocument7 pagesTasks For The Entire ModuleKristell C. LagardeNo ratings yet
- English Grade X 1.1Document19 pagesEnglish Grade X 1.1Kristell C. LagardeNo ratings yet
- Proposal JsDocument1 pageProposal JsKristell C. LagardeNo ratings yet
- WHLP-JHS EnglishDocument14 pagesWHLP-JHS EnglishKristell C. LagardeNo ratings yet
- Weekly-Home-Learning-Plan 1.1Document20 pagesWeekly-Home-Learning-Plan 1.1Kristell C. LagardeNo ratings yet
- WHLP-JHS EnglishDocument14 pagesWHLP-JHS EnglishKristell C. LagardeNo ratings yet
- WHLP-SHS 21st CenturyDocument7 pagesWHLP-SHS 21st CenturyKristell C. Lagarde100% (4)
- Who or WhomDocument3 pagesWho or WhomAdi Koncara Part IINo ratings yet
- Rekap Tbi - 2 "STANNERS 2020": I'm Ready For The Next Stanners!Document10 pagesRekap Tbi - 2 "STANNERS 2020": I'm Ready For The Next Stanners!Fina Putri HastutiNo ratings yet
- 2e Starter Language Focus ReferenceDocument14 pages2e Starter Language Focus ReferenceCami AdornoNo ratings yet
- Kisi Kisi English 6Document1 pageKisi Kisi English 6servina 1402ASNo ratings yet
- Soal Bhs Inggris UtsDocument14 pagesSoal Bhs Inggris UtsRati AfdalianiNo ratings yet
- Suffixes Added To Base Words Change The Meaning and Part of Speech of The Base WordDocument1 pageSuffixes Added To Base Words Change The Meaning and Part of Speech of The Base Wordapi-235473756No ratings yet
- Verb To Be PresentDocument1 pageVerb To Be PresentElia MuñozNo ratings yet
- Classwork # 2 Second Term Panama University Code 5642Document9 pagesClasswork # 2 Second Term Panama University Code 5642Tashany HumphreyNo ratings yet
- Amusing StoriesDocument12 pagesAmusing StoriesAulia Andikarani WaskitoNo ratings yet
- .Portions For Common Assessment, Term 2 2022 - 2023 (Grade 5)Document3 pages.Portions For Common Assessment, Term 2 2022 - 2023 (Grade 5)geethabanoth80No ratings yet
- Past Perfect - Past SimpleDocument5 pagesPast Perfect - Past SimpleOoll LlooNo ratings yet
- m2 WordformationDocument21 pagesm2 Wordformationairies92100% (2)
- Learning Languages: Let's Talk AboutDocument2 pagesLearning Languages: Let's Talk AboutPutriRahimaSariNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH PAGE - Future Conditionals PDFDocument5 pagesENGLISH PAGE - Future Conditionals PDFВыда ГафитасNo ratings yet
- Adjectives To Nouns: General VocabularyDocument4 pagesAdjectives To Nouns: General VocabularyZoe78No ratings yet
- TSPH 1Document5 pagesTSPH 1aeadNo ratings yet
- Engish Homework Part 4Document16 pagesEngish Homework Part 4Putri Aisyah UtamiNo ratings yet
- Niveles de Examen ResumenDocument14 pagesNiveles de Examen ResumenMili LopezNo ratings yet
- Audric Kls. 8Document27 pagesAudric Kls. 8Daffa SyauqiaqillaNo ratings yet
- Grammar Notes For Lesson 11: 1. Formulations With The Te-FormDocument19 pagesGrammar Notes For Lesson 11: 1. Formulations With The Te-FormSofía YamanakaNo ratings yet
- Negative PrefixesDocument4 pagesNegative PrefixesNU MaseNo ratings yet
- Grapheme Phoneme Correspondence in RP English With KeyDocument2 pagesGrapheme Phoneme Correspondence in RP English With KeyJoaquin Toro MaturanaNo ratings yet
- Free Vs Bound Morphemes - NormaCuevasDocument1 pageFree Vs Bound Morphemes - NormaCuevasnormacuevasqNo ratings yet
- First Conditional Practice 3rd Secondary SchoolDocument1 pageFirst Conditional Practice 3rd Secondary SchoolEnglish straight to the point straight to the pointNo ratings yet
- FINAL REVIEW Unit 7, 8, 9Document16 pagesFINAL REVIEW Unit 7, 8, 9kaiser phanNo ratings yet