Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Terishna - MICR215 SI Worksheet 7 - 3oct
Uploaded by
Nondumiso MavundlaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Terishna - MICR215 SI Worksheet 7 - 3oct
Uploaded by
Nondumiso MavundlaCopyright:
Available Formats
Terishna Mahabally
220013329@stu.ukzn.ac.za
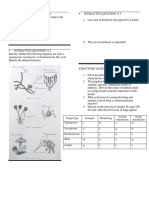
MICR215 SI worksheet 7.
Fungal nutrition and reproduction.
1. Fungi are chlorophyll deficient cannot synthesis their own food. Discuss How fungi
secure food.
-Fungi secrete enzyme into the surface which they are growing .The enzymes digest
the food, which then is absorbed directly through the hyphal walls. Food must be in
a solution in order to enter the hyphae and the entire mycelial surface of a fungus is
capable of absorbing materials dissolve in water.
2. Define the following:
i. Saprophytes : getting their nourishment from dead organic matter
ii. Symbiote : mutually beneficial with another organism, often a plant.
iii. Parasitic : causing serious damage to their host.
iv. Heterotrophs : they obtain their nutrients by absorbing simple, soluble nutrients.
3. Describe how parasitism occurs in humans. Provide an example.
Parasitic fungi most commonly enter the body through a wound in the epidermis.
Example of a fungus that causes disease in humans is Claviceps purpurea, the cause
of ergotism. Ergot, contains a number of poisonous organic compounds called
alkaloids.
4. Explain the symbiotic relationship between mycorrhiza and plants.
Mycorrhiza where large number of fungi infect the roots of the plants. The fungus
invade the roots to absorb nutrients.Mycorrhiza fungi establish a mild form of
parasitism that is mutualistic.
5. Name and explain the Two main types of mycorrhiza.
Ectomycorrhizae: are fungi that are only externally associated with the plant root.
Endomycorrhizae: form their associations within the cells of the host.
6. List 4 different ways fungi nutrients can be assimilated through.
passive diffusion, facilitated diffusion, diffusion channels,active transport.
7. Differentiate between asexual and sexual reproduction.
Asexual occurs via Budding /Fusion and an Asexual spore is produced. Sexual
occurs by Fusion or union of gametes via meiosis to produced sexual spores.
Terishna Mahabally
220013329@stu.ukzn.ac.za
8. Match column A with column B.
Column A Column B Answers
i. Sporangiophore A. Multiple/single spore C
are produced at the
end of aerial hyphae
ii. Conidiophore B. Candida Albicans A
iii. Basidiophore C. Sporangium incase D
this spores at the end
of aerial hyphae
iv. Blastopores D. Sexual spore B
v. Chlamydospores E. Cell swells up & E
develops thick
resistant wall
9. Provide the names of the male and female sex organs for fungi.
Male sex organ – Antheridium. Female sex organ – Oogonium
10. Differentiate between monoecious and dioecious.
Monoecious- Male & female sex organ in same thallus. Dioecious- Male & female
sex organ in separate thallus
11. Name the 3 stages that occurs under meiosis
Stage I – Plasmogamy .Stage II – Karyogamy .Stage III – Spore formation.
12. Which class does mushroom belong to and describe its spore arrangement.
Basidiomycota. Spores are present in 4 in numbers in one basidium.
1. What is a zygospore?
fusion of 2 gametes.
13. Name two species that form ascospores.
Aspergillus Sp. Penicillium Sp
14. Define budding.
cells buds off to form parent cell.
You might also like
- Nervous System NotesDocument25 pagesNervous System NotesRhey BascosNo ratings yet
- Genetics and Heredity Exam ReviewDocument9 pagesGenetics and Heredity Exam ReviewHendrix Antonni AmanteNo ratings yet
- CHNOPS Monster - Protein SynthesisDocument8 pagesCHNOPS Monster - Protein SynthesisDaniel De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology: Male Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesAnatomy & Physiology: Male Reproductive Systemkristel ludangcoNo ratings yet
- Myco NotesDocument36 pagesMyco NotesJoan ClaveNo ratings yet
- Fungi QuestionsDocument2 pagesFungi QuestionsAnanda Mutiara AlhakimahNo ratings yet
- 2021-2022 Final Exam General Biology 2Document6 pages2021-2022 Final Exam General Biology 2Mark De VeraNo ratings yet
- Mycology 1Document123 pagesMycology 1lyka deguzman100% (2)
- Earth and Life Science Quarter 2 Module 4 FinalDocument14 pagesEarth and Life Science Quarter 2 Module 4 FinalNaima Kahlen100% (1)
- Notes FungiDocument4 pagesNotes FungiRandy NaraineNo ratings yet
- Chapter 30 FungiDocument5 pagesChapter 30 FungiNadeem IqbalNo ratings yet
- 2nd Periodical Exam in Science 7Document5 pages2nd Periodical Exam in Science 7KeannoNo ratings yet
- KirbyAnne Plessala fungi worksheetDocument3 pagesKirbyAnne Plessala fungi worksheetJashayla GillespieNo ratings yet
- CBSE NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 02: Back of Chapter QuestionsDocument7 pagesCBSE NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 02: Back of Chapter QuestionsTarandeep PawarNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Biology NCERT Textbook Chapter 2 Biological ClassificationDocument5 pagesClass 11 Biology NCERT Textbook Chapter 2 Biological ClassificationTitan 2000No ratings yet
- Biological ClassificationDocument4 pagesBiological ClassificationssNo ratings yet
- 1 BiodiversityDocument15 pages1 BiodiversityAra KarimNo ratings yet
- Ncert Feb2021 Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 2Document4 pagesNcert Feb2021 Solutions For Class 11 Biology Chapter 2Gufran AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7EDocument9 pagesChapter 7EChandan KumarNo ratings yet
- G 12 FungiDocument11 pagesG 12 Fungibenyamsolomon444No ratings yet
- PLANT KINGDOM CHAPTERDocument6 pagesPLANT KINGDOM CHAPTERMonica BaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27 Protists I. Evolution of EukaryotesDocument7 pagesChapter 27 Protists I. Evolution of EukaryotesNadeem IqbalNo ratings yet
- Protists and Fungi Review: Key Terms and ConceptsDocument8 pagesProtists and Fungi Review: Key Terms and ConceptsChris MackNo ratings yet
- Classification of OrganismsDocument35 pagesClassification of OrganismsABEL JEDIDIAHNo ratings yet
- Guess Paper of Botany (11) As Per CBSE Pattern: SECTION-A (Long Answer Type) Marks 5Document65 pagesGuess Paper of Botany (11) As Per CBSE Pattern: SECTION-A (Long Answer Type) Marks 5Yasir SaleemNo ratings yet
- Short Question and Answers: The Kingdom FungiDocument9 pagesShort Question and Answers: The Kingdom FungiNadeem ArainNo ratings yet
- Soil ScienceDocument4 pagesSoil ScienceBheeyahh Marie AvilaNo ratings yet
- 1 ESO BilingualDocument4 pages1 ESO Bilingualamartind11No ratings yet
- Notes For FungiDocument10 pagesNotes For FungiФMuhammdф Atif .No ratings yet
- Classification of PlantsDocument10 pagesClassification of PlantsKARTHIK UNo ratings yet
- Answer To Question #1Document18 pagesAnswer To Question #1JAp BlancoNo ratings yet
- Answer To Question #1Document18 pagesAnswer To Question #1JAp BlancoNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Name - Guided Reading Chapter 31Document6 pagesAP Biology Name - Guided Reading Chapter 31Jackie Gillis67% (3)
- Xi - Biology - Work Sheet - Competency Based QNSDocument9 pagesXi - Biology - Work Sheet - Competency Based QNSSudhansu SahooNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 7 Fungi PDF FreeDocument4 pagesLesson Plan 7 Fungi PDF FreeMariel BuesingNo ratings yet
- Bio Classification NotesDocument8 pagesBio Classification NotesJames MundakayamNo ratings yet
- Biological ClassificationDocument15 pagesBiological Classificationanita meena94138gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Xi Botany em MLM-1Document48 pagesXi Botany em MLM-1prabhu100% (1)
- Fungi: Diversity of Fungi Reproduction & Classification Ecological Roles and DiseaseDocument46 pagesFungi: Diversity of Fungi Reproduction & Classification Ecological Roles and DiseaseehshonorsbioNo ratings yet
- CH 12 Instructor GuideDocument11 pagesCH 12 Instructor GuideVee Nara0% (1)
- Full Test of Neet 2024Document24 pagesFull Test of Neet 2024bhavyakhandelwal2302No ratings yet
- Grade 11 Chapter 2 Biological ClassificationDocument4 pagesGrade 11 Chapter 2 Biological ClassificationsanaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 BiologyDocument22 pagesLesson 6 Biologylilithescuela14No ratings yet
- Science ReviewDocument5 pagesScience ReviewBeatbot GamerNo ratings yet
- Fungi: Great Resources!Document5 pagesFungi: Great Resources!GUIDO ERNESTO VILLOTA CALVACHINo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument15 pagesLab ReportValentinoDullSatinNo ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom-Important QuestionsDocument3 pagesPlant Kingdom-Important QuestionsAnirudh KhannaNo ratings yet
- Quiz #2Document25 pagesQuiz #2Beverly Anne GaranNo ratings yet
- Five Kingdom ClassificationDocument6 pagesFive Kingdom ClassificationRonnith NandyNo ratings yet
- Fungigigigi 2Document2 pagesFungigigigi 2BridiniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9-FungiDocument14 pagesChapter 9-FungiAurora IslamNo ratings yet
- Bio CH-2 AnsDocument6 pagesBio CH-2 AnsSimran Kaur100% (1)
- Class 11 Biology Botany em Revised Edition-2020 English Medium Book Back Answers C.kishore KumarDocument51 pagesClass 11 Biology Botany em Revised Edition-2020 English Medium Book Back Answers C.kishore KumarRagaviNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Science 4th Quarter: B. Canis Familiaris C. Chanos ChanosDocument2 pagesGrade 8 Science 4th Quarter: B. Canis Familiaris C. Chanos ChanosZephieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Biology Class 11Document7 pagesChapter 2 Biology Class 11vaibhav ChandraNo ratings yet
- Examen Tipo TestDocument2 pagesExamen Tipo TestMarta CalleNo ratings yet
- LIVING WORLDDocument51 pagesLIVING WORLDPrasanth PrasanthNo ratings yet
- Biology Grade 12 Unit One (Microbiology)Document12 pagesBiology Grade 12 Unit One (Microbiology)Feven AsefaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For G7 Biology2Document4 pagesReviewer For G7 Biology2Jeal Amyrrh CaratiquitNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document8 pagesLesson 2Kezia Shayen RagualNo ratings yet
- FUNGIDocument10 pagesFUNGIAnonymous pICw4fQNo ratings yet
- Fungi Reproduction ExplainedDocument11 pagesFungi Reproduction ExplainedEesha NoorNo ratings yet
- Fungi Review Key SummaryDocument3 pagesFungi Review Key SummaryquimicosorioNo ratings yet
- CLASS 11 Biological Classification Part 2 Kingdom Fungi To Lichens.Document11 pagesCLASS 11 Biological Classification Part 2 Kingdom Fungi To Lichens.Rozita PraveenNo ratings yet
- Flashcards - 2f Respiration - Edexcel Biology IGCSEDocument17 pagesFlashcards - 2f Respiration - Edexcel Biology IGCSEsohaila ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Timer CAR-T ASHG2021 Abstract OdP1419Document2 pagesTimer CAR-T ASHG2021 Abstract OdP1419Shamsudheen MarakkarNo ratings yet
- Animal PhysiologyDocument12 pagesAnimal PhysiologyIsabel Grace GatpatanNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka - 2Document4 pagesDaftar Pustaka - 2akun pwmidNo ratings yet
- Lecture Title: Gross Human Structural BiologyDocument2 pagesLecture Title: Gross Human Structural BiologyLaish Christle CapiendoNo ratings yet
- Mosquitoes' attraction to human sweat mechanismDocument3 pagesMosquitoes' attraction to human sweat mechanismiftitah salsabilaNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi 12th Bio-Botany Unit VI Surya Biology Guide em PDFDocument39 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Bio-Botany Unit VI Surya Biology Guide em PDFEswara perumalNo ratings yet
- Week 5 G7Document3 pagesWeek 5 G7Mary Grace del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Worksheet For Feb 5 - ANSWERS PDFDocument4 pagesWorksheet For Feb 5 - ANSWERS PDFMary TaklaNo ratings yet
- FGIKReplication Student HandoutDocument16 pagesFGIKReplication Student Handoutnj saim100% (1)
- Biodesulfurizare 1Document30 pagesBiodesulfurizare 1Stan Dragos-MihaiNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Virus Lytic CycleDocument5 pagesStudent Exploration: Virus Lytic CycleBryce Mattox100% (1)
- Chapter 2 - Cell: The Unit of Life Exercise Ex. 1: Solution 1Document8 pagesChapter 2 - Cell: The Unit of Life Exercise Ex. 1: Solution 1Arpan KaurNo ratings yet
- Benign Epithelial Tumors of Oral CavityDocument84 pagesBenign Epithelial Tumors of Oral CavityMadhura ShekatkarNo ratings yet
- 7 Study or Research ProposalDocument3 pages7 Study or Research ProposalMir Sajjad HüSsàïñNo ratings yet
- Vet Obst Lecture 1 Pregnancy in Domestic AnimalsDocument53 pagesVet Obst Lecture 1 Pregnancy in Domestic AnimalsgnpobsNo ratings yet
- Penyuluhan Penyakit Genetika Serta Cara Pencegahannya Di Kelurahan Duri Kepa Jakarta BaratDocument6 pagesPenyuluhan Penyakit Genetika Serta Cara Pencegahannya Di Kelurahan Duri Kepa Jakarta BaratHesty RosaryNo ratings yet
- Dr. B. VictorDocument29 pagesDr. B. VictorBnr GoudNo ratings yet
- Internal and External Structure of ChickensDocument7 pagesInternal and External Structure of ChickensBerry PrinNo ratings yet
- Human Biological DiversityDocument5 pagesHuman Biological DiversityJoyce Sarmiento100% (1)
- Ritcha Saxena, MD Forensic PathologyDocument2 pagesRitcha Saxena, MD Forensic PathologyDr. Ritcha SaxenaNo ratings yet
- The Parts of The Cell and Their FunctionsDocument2 pagesThe Parts of The Cell and Their Functionsraphael100% (1)
- Essay On Long-Term PotentiationDocument8 pagesEssay On Long-Term PotentiationJayNo ratings yet
- Third Assignment (Forensic)Document2 pagesThird Assignment (Forensic)Dean Mark AnacioNo ratings yet
- NIMBBDocument35 pagesNIMBBjaacostajr1No ratings yet