Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Circles English
Uploaded by
Satya Prakash ChaudharyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Circles English
Uploaded by
Satya Prakash ChaudharyCopyright:
Available Formats
Join Our Classroom Program Now
In this article, we will discuss the Circles and various theorem related to it. The circle
is the most important topic of Geometry. In this article, I have covers tangents,
chords and some important short trick also.
Important Geometry Notes on Circle
1. A circle is a set of point or locus of a point which are at a fixed distance from a
point called as a centre.
2. The distance of any point on the circumference of the circle from the centre of the
circle is equal.
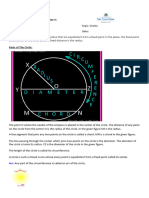
Diameter:
Diameter is double of the radius .i.e. D=2R.
Diameter is the chord which passes through the centre of the circle.
Tangent: A line which touch the circle at only one point at its circumference.
Secant: A line which touch the circle at two distinct points.
Chord: A line Segment which lie inside the circle and its end points are always lie on
the circle.
Join Our Classroom Program Now
Important theorem and results of the circle:
(1) Of the two chords of the circles, the one which is greater is nearer to the centre.
(2) The perpendicular from the centre of the circle bisect the chord i.e. radius always
bisect the chord if perpendicular
(3) Any line segment joining the centre of the circle and the mid point of the chord
is perpendicular to the chord.
If AM=MB then OM is perpendicular to the AB.(reference to above fogure)
(4)Equal chord of the circle always subtends the equal angles at the centre of the
circle.
i.e. if AB=CD then ∠1=∠2
(5) If angle subtended by the two chord at the centre are equal then the chords are
always equal.
(3) Equal chords of the circle are at equal distance from the centre.
(6) Chords which are at equidistant from the centre of the circle are always equal.
Join Our Classroom Program Now
(7) Angle subtended by any arc at the centre of the circle is double the angle
subtended by it at any point on the remaining part of the circle.
∠x=2∠y
(8) Angle subtended by an arc in the same segment of the circle are equal.
∠ACB=∠ADB
(9) Angle in a semi circle is a right angle. i.e the angle subtended by the diameter
is always right angle.
(10) The circle drawn with hypotenuse of a right angle triangle as diameter, passes
through its opposite vertex.
(11) The sum of the opposite angle of a cyclic quadrilateral is always 180°.
Cyclic quadrilateral is that quadrilateral whose all point lie on the circumference of
the circle.
Join Our Classroom Program Now
∠A+∠C=∠B+∠D
(12) If a side of a cyclic quadrilateral is produced then the exterior angle is equal to
the interior opposite angle.
∠1=∠2
Some important points of tangents
(1)Tangent and radius always make the angle of 90 at the point of meeting of
tangent with the circle.
If AB is a tangent at P, then OP is perpendicular to AB.
(2) The length of the two tangent drawn from the same external point to a circle is
always equal.
AP=AQ
Join Our Classroom Program Now
(3) If two chords AB and CD intersect internally or externally at point P then.
PA*PB=PC*PD
(4) If PAB is a secant which intersects the circle at A and B and PT be a tangent at
T, then
Join Our Classroom Program Now
PT2=PA*PB
(5) If from the point of contact of tangent with circle, a chord is drawn ,then the
angles which the chord makes with the tangent line are equal respectively to the
angles formed in the corresponding alternate segment.
∠BAT=∠BCA=∠1
∠BAP=∠BDA=∠2
(6) If two circles touch each other internally or externally the point of contacts lies
on the line joining their centres.
Join Our Classroom Program Now
Distance between the cntres
When touch internally, distance=AP-BP
When touch externally, distance =AP+BP
Some Important Results:
(1)If two tangent PA and PB are drawn from the external point P, then
∠1=∠2 and ∠3=∠4
OP is perpendicular to AB and AC=BC
(2) r1 and r2 are the radius of two circles and d is the distance between the centres
of the circle then the length of the common tangent of two circles is given by
Join Our Classroom Program Now
(3) If r1 and r2 are the two radius of the circle and "d" is the distance between
them then the length of the transverse common tangent is given by
(4) If a circle touches all the four sides of a quadrilateral then the sum of opposite
pair of sides are equal.
i.e. AB+CD=AD+BC
(5) If two chords AB and AC of a circle are equal then the bisector of ∠BAC passes
through the centre O of the cirlcle.
(6) The equilateral formed by the angle bisector of a cyclic quadrilateral is also
cyclic.
(7) If a cyclic trapezium is isosceles then its diagonals are equal
Join Our Classroom Program Now
i.e if AB parallel DC and AD=BC then AC=BD
(8) Angle in the major segment of a circle is acute and angle in minor segment is
obtuse.
(9) If two circles of same radius r are such that the centre of one lies on the
circumference of the other then the length of the common chord is given by l=√3*r
(10) If 2a and 2b are length of two chords which intersects at right angle and if the
distance between the centre of the circle and intersecting point of the chords is C
then the radius of circle is given by]
(11) If three circles of radius r are bound by a rubber band then the length of rubber
band is given by
6r+2πr
Join Our Classroom Program Now
All the Best
DREAM, STRIVE & SUCCEED With US!
Check OUT
SSC 2023 उद्दे श्य Batch : Comprehensive course for SSC CGL & CHSL (Hindi Batch)
3 Crore+ Registered Aspirants | 2.5 Crore Downloads | 50,000+ Selections
So why wait? Update your app right away!
Join Our Classroom Program Now
Join Our Classroom Program Now
You might also like
- Important Theorems of Geometry by Abhishek Jain Very Important For All SSC ExamsDocument22 pagesImportant Theorems of Geometry by Abhishek Jain Very Important For All SSC ExamsStudy IQ92% (38)
- Circles RevisionDocument31 pagesCircles RevisionTuition MastersNo ratings yet
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CirclesDocument11 pagesCirclesSumit KumarNo ratings yet
- Circle Geometry Test ReviewDocument0 pagesCircle Geometry Test ReviewUpasna KhastgirNo ratings yet
- Geometry and Locus (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandGeometry and Locus (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Ch-10 Maths NotesDocument7 pagesCh-10 Maths NotesJsjn NNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document10 pagesChapter 10Jitesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Geometry Capsule For SSC Railway Exams Watermark - PDF 70Document13 pagesGeometry Capsule For SSC Railway Exams Watermark - PDF 70Tapas SwainNo ratings yet
- 07 GemoetryDocument11 pages07 GemoetryKomanduri Murali SrinivasNo ratings yet
- In Euclidean GeometryDocument32 pagesIn Euclidean GeometryGilar JatisundaNo ratings yet
- Circles Chapter QuestionsDocument40 pagesCircles Chapter Questionstest testNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Class 9 Math Chapter 10 CirclesDocument48 pagesNcert Solutions Class 9 Math Chapter 10 CirclesShubham VishwakaramaNo ratings yet
- Segments of A CircleDocument25 pagesSegments of A CircleJoyce Estrevencion100% (1)
- Circles and Its Related Terms ExplainedDocument20 pagesCircles and Its Related Terms Explainedtaha maroofNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - CirclesDocument27 pagesModule 1 - CirclesHenry Languisan50% (2)
- 12th Standard Maths Chapter CircleDocument16 pages12th Standard Maths Chapter CircleTabassum BakarNo ratings yet
- CirclesDocument24 pagesCirclesVicky SinghNo ratings yet
- Circle Ps01Document4 pagesCircle Ps01Future Politics of INDIANo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Circles 10Document4 pagesMicrosoft Word - Circles 10jitender8No ratings yet
- Important Questions on Circles from Class IX Mathematics Assignments (Term 2Document25 pagesImportant Questions on Circles from Class IX Mathematics Assignments (Term 2sshoeburrahman100% (1)
- Maths Project on CirclesDocument18 pagesMaths Project on CirclesJohn Nguyen57% (42)
- What Is The Pythagorean TheoremDocument6 pagesWhat Is The Pythagorean Theoremapi-126876773No ratings yet
- 6.1 Circle and Related Segments and AnglesDocument42 pages6.1 Circle and Related Segments and AnglesJV GamoNo ratings yet
- Class IX Chapter 10Document12 pagesClass IX Chapter 10Keshav AarjuNo ratings yet
- Geometry ProblemsDocument54 pagesGeometry Problemshvphatak80% (5)
- Circles Tangents and Intersecting ChordsDocument3 pagesCircles Tangents and Intersecting ChordsBinu Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Geometry 1st ChapterDocument20 pagesGeometry 1st ChaptersanthoshNo ratings yet
- Circles 131126094958 Phpapp01Document25 pagesCircles 131126094958 Phpapp01Jamjam CopasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 CirclesDocument9 pagesChapter 10 CirclesrachelbuchananNo ratings yet
- Precalc Solid Geometry 2020-2021Document19 pagesPrecalc Solid Geometry 2020-2021Noel S. De Juan Jr.No ratings yet
- NCERT Grade 09 Mathematics CirclesDocument22 pagesNCERT Grade 09 Mathematics CirclesSheikhFaysalNo ratings yet
- Circles, Tangent-Chord Theorem, Intersecting Chord Theorem and Tangent-Secant TheoremDocument11 pagesCircles, Tangent-Chord Theorem, Intersecting Chord Theorem and Tangent-Secant TheoremStefanie BargoNo ratings yet
- List-4 Dest 09052019Document5 pagesList-4 Dest 09052019SANJEEV KUMARNo ratings yet
- Circles GD 9 Ws Shiv NaDocument4 pagesCircles GD 9 Ws Shiv Naabeer.bhatia1506No ratings yet
- Circle - 1Document5 pagesCircle - 1parthdbz2005No ratings yet
- Kamal Roop Class Ix - CDocument15 pagesKamal Roop Class Ix - CPuneet SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Ircle: Mathematics - Shishir Kant SinghDocument8 pagesIrcle: Mathematics - Shishir Kant SinghShishir Kant SinghNo ratings yet
- Snap It With SCMHRD: Formulae For Quantitative and Data Interpretation Sections AlgebraDocument20 pagesSnap It With SCMHRD: Formulae For Quantitative and Data Interpretation Sections AlgebraAditya SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Plane Geometry 1Document9 pagesPlane Geometry 1Rehman AhabathNo ratings yet
- Circle and TangentsDocument8 pagesCircle and Tangentssiddhartha khatuaNo ratings yet
- Circle, Geometrical Constructions Statistics & ProbabilityDocument127 pagesCircle, Geometrical Constructions Statistics & ProbabilitythinkiitNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya NepanagarDocument37 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya NepanagarSunny KhanNo ratings yet
- Maths Class 9 Notes For CirclesDocument3 pagesMaths Class 9 Notes For CirclesAdnan BashirNo ratings yet
- Angles Properties in CirclesDocument13 pagesAngles Properties in Circlesjavaria227204No ratings yet
- CirclesDocument26 pagesCirclesNeha ThakurNo ratings yet
- SDMDocument9 pagesSDMSoumya PattnaikNo ratings yet
- Exercise 16.1 Page No: 16.5: RD Sharma Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 16 CirclesDocument36 pagesExercise 16.1 Page No: 16.5: RD Sharma Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 16 CircleskeerthuhariNo ratings yet
- Circle theorems and propertiesDocument71 pagesCircle theorems and propertiesTanya JainNo ratings yet
- Angles Made by A Transverse Line:: Congruent and Similar TriangleDocument9 pagesAngles Made by A Transverse Line:: Congruent and Similar TriangleRitsikaGurramNo ratings yet
- Center, Then They Are CongruentDocument9 pagesCenter, Then They Are CongruentAnwie ChuaNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 10-Circles: Exercise: 10.1 (Page No: 171)Document28 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 10-Circles: Exercise: 10.1 (Page No: 171)Tushar BhattNo ratings yet
- Geometry Dba Study Guide 07.07Document3 pagesGeometry Dba Study Guide 07.07Tyler CosgroveNo ratings yet
- CirclesDocument60 pagesCirclesbhaskar51178No ratings yet
- CircleDocument8 pagesCircleShirjak ThokarNo ratings yet
- 16.co Ordinate GeometryDocument8 pages16.co Ordinate GeometrykeerthanasubramaniNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Maths Circles Module 3Document9 pagesClass 9 Maths Circles Module 3Manju prasadNo ratings yet
- Geometry Basics VOCABULARY LISTDocument39 pagesGeometry Basics VOCABULARY LISTIsrael Jimenez FelixNo ratings yet
- MCQ in Plane Trigonometry Part 3 ECE Board Exam PDFDocument8 pagesMCQ in Plane Trigonometry Part 3 ECE Board Exam PDFJed LavuNo ratings yet
- Advance Math PDFDocument2 pagesAdvance Math PDFhallelNo ratings yet
- MLL Study Materials Maths Basic Class X 2019 20Document71 pagesMLL Study Materials Maths Basic Class X 2019 20cvsingh007No ratings yet
- Maths Test Paper-CBSE Grade 10Document91 pagesMaths Test Paper-CBSE Grade 10selva.uae8207No ratings yet
- Properties of Circle (Notes)Document28 pagesProperties of Circle (Notes)Sachi AlamNo ratings yet
- Olympian Minimal ToolkitDocument40 pagesOlympian Minimal ToolkitgabNo ratings yet
- Geometry Problem Set SolutionsDocument13 pagesGeometry Problem Set SolutionssayemNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument1 pageConcept Mapapi-434839539No ratings yet
- SSC 31 NoRestrictionDocument15 pagesSSC 31 NoRestrictionBhawna SinghNo ratings yet
- Aryabhatta: The Mathematics GeniusDocument67 pagesAryabhatta: The Mathematics Geniusrajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Formulae of Mathematics PDFDocument301 pagesFormulae of Mathematics PDFRahul SoodNo ratings yet
- Straight LinesDocument6 pagesStraight LinesSarangNo ratings yet
- Of The Just Shaping of Letters - Durer, AlbrechtDocument52 pagesOf The Just Shaping of Letters - Durer, AlbrechtCarlos AguilarNo ratings yet
- For A Good Start & Practice In: Prepared by T. Ibrahim KhalilDocument42 pagesFor A Good Start & Practice In: Prepared by T. Ibrahim KhalilKhoderMais100% (1)
- Glencoe Mathematics Grade 7 - Glencoe - Mcgraw-HillDocument88 pagesGlencoe Mathematics Grade 7 - Glencoe - Mcgraw-HillJulius Cagampang100% (1)
- UTME Math Syllabus BreakdownDocument7 pagesUTME Math Syllabus BreakdownAdeola MojeedNo ratings yet
- Assignment Class 9 CH 6,7Document2 pagesAssignment Class 9 CH 6,7Balbir KaurNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Problem Solving - An Evolving Research and Practice DomainDocument14 pagesMathematical Problem Solving - An Evolving Research and Practice DomainIsaid ReyesNo ratings yet
- Imo 2010 Official SolutionsDocument15 pagesImo 2010 Official Solutionsrysanal100% (1)
- Study Circles for IIT JEEDocument20 pagesStudy Circles for IIT JEEShweta SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document18 pagesChapter 12tirumalaNo ratings yet
- Geometry StandardsDocument19 pagesGeometry Standardsapi-487859818No ratings yet
- 2002 GeomDocument8 pages2002 Geombiswajit karNo ratings yet
- 3D Geometry EssentialsDocument61 pages3D Geometry Essentialssihg Jaiswal100% (1)
- Udaan Class XI Maths Part 1Document168 pagesUdaan Class XI Maths Part 1Tejas PagareNo ratings yet
- The Olympiad Corner: No. 307 Nicolae StrungaruDocument6 pagesThe Olympiad Corner: No. 307 Nicolae StrungaruFustei BogdanNo ratings yet
- Bridge The Gap: A Project Based Instruction Unit Grade 10 - Geometry By: Jamie Burrows and Shala NailDocument29 pagesBridge The Gap: A Project Based Instruction Unit Grade 10 - Geometry By: Jamie Burrows and Shala Nailapi-357163625No ratings yet
- Steiner Lehmus TheoremDocument3 pagesSteiner Lehmus Theoremmathitis20084477No ratings yet
- 2019 WTS 12 Euclidean GeometryDocument105 pages2019 WTS 12 Euclidean GeometryMaria-Regina UkatuNo ratings yet