Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biochemical Lab
Uploaded by
Eva DirrCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biochemical Lab
Uploaded by
Eva DirrCopyright:
Available Formats
Dirr 1
Eva Dirr
Kenya Goodson
ES 100
08 October 2020
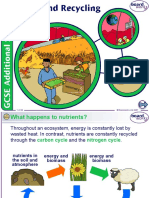
1. How does photosynthesis contribute to the carbon cycle?
Plants take in carbon dioxide from the atmosphere during photosynthesis
Use energy from the sun to combine the carbon dioxide and water to form
carbohydrates.
2. What is respiration?
Plants and animals release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere through the
process of respiration.
Respiration releases energy from carbohydrates, with carbon dioxide as a
waste product.
3. Why is deforestation a concern?
Plants store carbon as carbohydrates made from carbon dioxide from the
atmosphere.
Land plants take up about a quarter of all carbon dioxide that enters the
atmosphere.
If the forest are all getting cut down, there are less trees that take up the carbon
dioxide and therefore there is more pollution in the air.
4. What happens when carbon dioxide when it enters the ocean?
Most of the carbon entering the ocean ends up in the deep ocean
there it can be carried by currents for hundreds of years or be lost in sediments
5. What happens to the carbon cycle as a result of fossil fuel burning?
In fossil fuels, the carbon is stored in long-chain hydrocarbons
through combustion with oxygen in our cars or in factories, the carbon is
converted to CO2, which is released to the atmosphere.
In addition, a number of other byproductsare also produced through
inefficiencies in combustion like CO which are atmospheric pollutants.
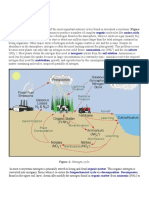
1. Why is nitrogen important for life?
Nitrogen is an element essential to life.
It is found in protein, DNA and RNA, and in chlorophyll molecules important
to photosynthesis.
Dirr 2
2. Why is fixation the important first step in the nitrogen cycle?
Fixation occurs when bacteria convert nitrogen gas into organic compounds that
living organisms can take up.
3. What is the difference between nitrification and denitrification?
Nitrification is a two-step process
o soil bacteria first convert ammonium ions into nitrite ions
o then convert nitrite ions into nitrate ions.
Denitrification occurs when soil bacteria convert nitrate ions into nitrogen gas.
4. What happens in ammonification?
Ammonification occurs when bacteria or fungi convert nitrogen gas or nitrogen
compounds into ammonium ions.
5. What happens sometimes when fertilizer is used for plants to grow?
Plants can absorb either nitrate ions or ammonium ions through their roots.
1. How does phosphorus enter the cycle through weathering?
Over time, rain and weathering cause rocks to release phosphate ionsand other
minerals.
This inorganic phosphate is then distributed in soils and water.
2. Why is phosphorus important for life?
Phosphorus is an essential nutrient for animals and plants.
It plays a critical role in cell development and is a key component
of molecules that store energy, such as ATP (adenosine
triphosphate), DNA and lipids (fats and oils).
Insufficient phosphorus in the soil can result in a decreased crop yield.
3. How do people contribute to the phosphorus cycle? Does it have positive or
negative impacts?
Humans fertilize fields and if they overfertilize it has a negative impact because
excess phosphate can be lost from the soil.
4. What happens when you have an excess of phosphorus in the water system?
When fields are overfertilised (through commercial fertilisers or manure), phosphate
not utilised by plants can be lost from the soil through leaching and water run-off.
Dirr 3
This phosphate ends up in waterways, lakes and estuaries. Excess phosphate causes
excessive growth of plants in waterways, lakes and estuaries leading
to eutrophication.
You might also like
- The 5 Nutrient Cycles - Science Book 3rd Grade | Children's Science Education booksFrom EverandThe 5 Nutrient Cycles - Science Book 3rd Grade | Children's Science Education booksNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical Cycles Webquest: Name Masilang, Philip Anthony L. Section ZGE 4301 - 2ADocument5 pagesBiogeochemical Cycles Webquest: Name Masilang, Philip Anthony L. Section ZGE 4301 - 2APHILIPANTHONY MASILANGNo ratings yet
- Biology Note On Nutrient Cycles & PopulationsDocument8 pagesBiology Note On Nutrient Cycles & PopulationsFritzNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical Cycles Webquest ActivityDocument5 pagesBiogeochemical Cycles Webquest Activitykate nicole labandriaNo ratings yet
- Change and Material Cycles: Prepared By: Arnold B. Fonollera, PHDDocument7 pagesChange and Material Cycles: Prepared By: Arnold B. Fonollera, PHDJoris YapNo ratings yet
- The EcosystemDocument9 pagesThe EcosystemLuz ManaloNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical Cycles - "Energy Flows and Matter Cycles" ANSWER KEYDocument2 pagesBiogeochemical Cycles - "Energy Flows and Matter Cycles" ANSWER KEYJay Astillo NicanorNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Environmental ScienceDocument18 pagesWeek 4 Environmental ScienceJosh AndradeNo ratings yet
- Biology Section 4Document4 pagesBiology Section 4BainsieNo ratings yet
- Biology Work 11Document7 pagesBiology Work 11charityadowimehNo ratings yet
- Waste Management-IDocument9 pagesWaste Management-ICricketer OPNo ratings yet
- Chem Form 4, Fertilisers and NitrogenDocument3 pagesChem Form 4, Fertilisers and NitrogenshshbshshsjsjNo ratings yet
- Additional Biogeochemical CycleDocument9 pagesAdditional Biogeochemical CycleYngrid Bless Z. CadenaNo ratings yet
- College of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesCollege of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesPatrick Philip BalletaNo ratings yet
- N CycleDocument2 pagesN CycleKhiro CapiliNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical Cycles (Nutrient CYCLES) - ContinuationDocument24 pagesBiogeochemical Cycles (Nutrient CYCLES) - ContinuationTimothy James M. MadridNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Affecting Wildflower DiversityDocument14 pagesAir Pollution Affecting Wildflower DiversityeverydaynabilNo ratings yet
- Biogeo Chemical CyclesDocument5 pagesBiogeo Chemical CyclesMalkish RajkumarNo ratings yet
- L-1 - Fate of Pollutants - Final (1) - 20Document21 pagesL-1 - Fate of Pollutants - Final (1) - 20Abdullah AkramNo ratings yet
- Decay and RecyclingDocument21 pagesDecay and RecyclingJeffrey PiggottNo ratings yet
- Water Cycle: Name Date PeriodDocument5 pagesWater Cycle: Name Date PeriodMrfatasianNo ratings yet
- Phosphorus CycleDocument5 pagesPhosphorus CycleBiencarlo PapinaNo ratings yet
- Cycles WorksheetDocument4 pagesCycles WorksheetRose Belle A. GarciaNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical Cycle by Poornima NadunDocument3 pagesBiogeochemical Cycle by Poornima NadunPoornima NadunNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Cycle NotesDocument2 pagesNitrogen Cycle NotesAjit PatelNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen 2Document23 pagesNitrogen 2Nebojša Filipović 3No ratings yet
- HW 5 - Stream ChemistryDocument3 pagesHW 5 - Stream ChemistryShapard CroftNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Inquiry Into Life 15th 12Document2 pagesStudy Guide Inquiry Into Life 15th 12Jose Douglas VelasquezNo ratings yet
- The Cycle of Nitrogen Sulphur & Carbon - Analysis by FahmidDocument5 pagesThe Cycle of Nitrogen Sulphur & Carbon - Analysis by FahmidFahmid Tousif KhanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6.1 PhotosynthesisDocument16 pagesLesson 6.1 PhotosynthesisrajzemjeoimojicaNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen and Carbon CycleDocument4 pagesNitrogen and Carbon CycleAnna Marie LaganzonNo ratings yet
- Iso 14000 & 18000Document11 pagesIso 14000 & 18000Suchiey Mei SaaNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Biogeochemical CyclesDocument8 pagesThe Importance of Biogeochemical CyclesTiktok FOOTBALLNo ratings yet
- 7-Discuss Briefly The Role of Microorganisms in Water Quality ?Document4 pages7-Discuss Briefly The Role of Microorganisms in Water Quality ?Salma AhmadNo ratings yet
- G-12 Biology, 2.1 Cycling Matter Through EcosystemsDocument6 pagesG-12 Biology, 2.1 Cycling Matter Through EcosystemsYohannes NigussieNo ratings yet
- SCI Mod 3Document7 pagesSCI Mod 3Maxine MedinaNo ratings yet
- Nutrient Cycles: Prof. Murray, Univ of Illinois at ChicagoDocument35 pagesNutrient Cycles: Prof. Murray, Univ of Illinois at Chicagomahesh nagarNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical CyclesDocument5 pagesBiogeochemical Cyclesjaimejeannepoot.martinezNo ratings yet
- Nutrient CyclingDocument24 pagesNutrient CyclingSofia Dicen100% (1)
- Lesson 4 Form 4 BiologyDocument3 pagesLesson 4 Form 4 BiologyTavonga ChinogureiNo ratings yet
- Nutrient cyclin-WPS OfficeDocument5 pagesNutrient cyclin-WPS OfficejoeNo ratings yet
- Nutrient CycleDocument5 pagesNutrient CycleKhadijah HabeebahNo ratings yet
- Homeword ESDocument4 pagesHomeword ESThuỳ DungNo ratings yet
- Chemistry and The AnthrosphereDocument22 pagesChemistry and The AnthrosphereMichelle Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical CyclesDocument7 pagesBiogeochemical CyclesAndrea LeopandoNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical CyclesDocument60 pagesBiogeochemical CyclesKyla BrillanteNo ratings yet
- University of Technology Faculty of Science and Sport: Module: Environmental Studies Lecture #3Document7 pagesUniversity of Technology Faculty of Science and Sport: Module: Environmental Studies Lecture #3Cördïî X CördïîNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Nitrogen Cycle: Proudly Present By, MD Adib Fikri Kavisya Logadharshini Suganeya AlkhalwarizmiDocument36 pagesCarbon and Nitrogen Cycle: Proudly Present By, MD Adib Fikri Kavisya Logadharshini Suganeya AlkhalwarizmiSuganeya UdiasoorianNo ratings yet
- Answers To Water, Carbon and Nitrogen Cycle Worksheet The Water CycleDocument2 pagesAnswers To Water, Carbon and Nitrogen Cycle Worksheet The Water CycleMrfatasianNo ratings yet
- Cyle of N, O and MineralDocument13 pagesCyle of N, O and MineralFikrah Hafiz SuniNo ratings yet
- Nasc Geed 20113Document2 pagesNasc Geed 20113NNHS- Jordan King CruzNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Cycle PDFDocument5 pagesNitrogen Cycle PDFJoshua Capa FrondaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.4. Water Cycle and Biogeochemical CyclesDocument3 pagesLesson 2.4. Water Cycle and Biogeochemical CyclesMitzlNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical Cycle - HandoutDocument6 pagesBiogeochemical Cycle - HandoutKrishnan Nicolai MiguelNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical Cycle - Phosphorus CycleDocument14 pagesBiogeochemical Cycle - Phosphorus CycleStevenzel Eala EstellaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Chemistry: Unit: 1Document13 pagesEnvironmental Chemistry: Unit: 1Premangshu GhoshalNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle Worksheet: NameDocument3 pagesCarbon Cycle Worksheet: NamePak RisNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Cycle W QuestionsDocument2 pagesNitrogen Cycle W QuestionsemmaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 Cpe 665 Air Pollution Individual Assignment: Prepared By: Aminatuzzaharah Binti Musa 2016250332 EH220 8FDocument6 pagesAssignment 3 Cpe 665 Air Pollution Individual Assignment: Prepared By: Aminatuzzaharah Binti Musa 2016250332 EH220 8FAminatuz ZaharahNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science Reviewer 1Document6 pagesEnvironmental Science Reviewer 1Jennylyn CariagaNo ratings yet
- NURS FPX 6410 Assessment 2 Executive Summary To AdministrationDocument7 pagesNURS FPX 6410 Assessment 2 Executive Summary To Administrationzadem5266No ratings yet
- Material Data Sheet Durapro Asa: DescriptionDocument1 pageMaterial Data Sheet Durapro Asa: DescriptionAlexandru NeacsuNo ratings yet
- Carac Biogas FlamelessDocument7 pagesCarac Biogas FlamelessTaine EstevesNo ratings yet
- CoC VampireCharacterPrimerPDFDocument5 pagesCoC VampireCharacterPrimerPDFDavid Alexander TomblinNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual For Microbiology Fundamentals A Clinical Approach 4Th Edition Susan Finazzo Full ChapterDocument51 pagesLaboratory Manual For Microbiology Fundamentals A Clinical Approach 4Th Edition Susan Finazzo Full Chapterlinda.ferguson121100% (7)
- Accessing The Healing Power of The Vagus NerveDocument9 pagesAccessing The Healing Power of The Vagus NerveShubham Doshi33% (3)
- Service ProgramDocument47 pagesService ProgramHuseyn aliyevNo ratings yet
- Aliyani Association Between Vitamin D Deficiency and Psoriasis A CasecontrolstudyDocument5 pagesAliyani Association Between Vitamin D Deficiency and Psoriasis A CasecontrolstudyAzmi FadhlihNo ratings yet
- CHEM 333: Lab Experiment 5: Introduction To Chromatography : Thin Layer and High Performance Liquid ChromatographyDocument5 pagesCHEM 333: Lab Experiment 5: Introduction To Chromatography : Thin Layer and High Performance Liquid ChromatographymanurihimalshaNo ratings yet
- 1501Document569 pages1501Ina Revenco33% (3)
- Compact Water Treatment 200 m3Document3 pagesCompact Water Treatment 200 m3civil eng915No ratings yet
- OFLOX-OZ TabletsDocument30 pagesOFLOX-OZ TabletsSilvio BarbosaNo ratings yet
- (Nikolaj Wolfson, Alexander Lerner, Leonid Roshal (B-Ok - CC)Document589 pages(Nikolaj Wolfson, Alexander Lerner, Leonid Roshal (B-Ok - CC)Andi sutandi100% (1)
- Physical, Biology and Chemical Environment: Its Effect On Ecology and Human HealthDocument24 pagesPhysical, Biology and Chemical Environment: Its Effect On Ecology and Human Health0395No ratings yet
- Awsum BrandingDocument18 pagesAwsum Brandingdharam123_904062105No ratings yet
- Soiltac Safety Data Sheet: Section 1 - IdentificationDocument9 pagesSoiltac Safety Data Sheet: Section 1 - IdentificationSameh AhmedNo ratings yet
- Glare CompositeDocument10 pagesGlare Compositewsjouri2510No ratings yet
- Professional DevelopmentDocument1 pageProfessional Developmentapi-488745276No ratings yet
- 3 D7 QC Physical and Chemical Tests Ok For EmailDocument17 pages3 D7 QC Physical and Chemical Tests Ok For EmailUbaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Paper 4 Nov 2000Document2 pagesPaper 4 Nov 2000MSHNo ratings yet
- IOC CoachingResearchStudiesList PDFDocument87 pagesIOC CoachingResearchStudiesList PDFJeane LucenaNo ratings yet
- Connection DesignDocument33 pagesConnection Designjesus curielNo ratings yet
- ES 92.05 D1 Fire ProofingDocument18 pagesES 92.05 D1 Fire ProofingKanjana LeardrakNo ratings yet
- 12 29 11editionDocument27 pages12 29 11editionSan Mateo Daily JournalNo ratings yet
- Alabama Religious Exemption AdvisoryDocument1 pageAlabama Religious Exemption AdvisoryABC 33/40No ratings yet
- Pengertian Recount Text Kls 9Document26 pagesPengertian Recount Text Kls 9MARINDRA RETNONo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Fitness Training PrinciplesDocument80 pagesChapter 10 Fitness Training Principlesapi-115744109No ratings yet
- Cockerspaniel Pra CarriersDocument28 pagesCockerspaniel Pra CarriersJo M. ChangNo ratings yet
- PT3 Practices EssayDocument61 pagesPT3 Practices EssayGolden Fingers100% (3)
- One Village One Product Movement in Laos: AbstractDocument5 pagesOne Village One Product Movement in Laos: Abstractoeleong19699685No ratings yet