Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CE Module 2 - Trigonometry (Principles)
CE Module 2 - Trigonometry (Principles)
Uploaded by
Angelice Alliah De la CruzCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CE Module 2 - Trigonometry (Principles)
CE Module 2 - Trigonometry (Principles)
Uploaded by
Angelice Alliah De la CruzCopyright:
Available Formats
ACE+ REVIEW CENTER
APRIL 2023 REVIEW PROGRAM
CIVIL ENGINEERING LICENSURE EXAM
APPLIED MATH, SURVEYING, TRANSPORTATION & HIGHWAY ENG’G, CONST. MGT.
Tuesday, November 29, 2022 Module 02
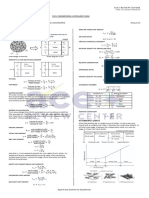
FUNCTIONS OF A RIGHT TRIANGLE
opposite side a adjacent side b
sin θ = = cot θ = =
hypotenuse c opposite side a
adjacent side b hypotenuse c
cos θ = = sec θ = =
hypotenuse c adjacent side b
𝜃 tan θ =
opposite side
=
a
csc θ =
hypotenuse
=
c
adjacent side b opposite side a
PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM
In any right triangle, the square of the longest side (hypotenuse) equals the sum of the squares of the other
two sides.
c2 = a2 + b2
BASIC IDENTITIES
sin θ cos θ 1 1
tan θ = cot θ = sec θ = csc θ =
cos θ sin θ cos θ sin θ
PYTHAGOREAN RELATIONS
sin2 θ + cos2 θ = 1 tan2 θ + 1 = sec2 θ 1 + cot2 θ = csc2 θ
OBLIQUE TRIANGLES
An oblique triangle is any triangle that is not a right triangle. It could be an acute triangle (all three
angles of the triangle are less than right angles) or it could be an obtuse triangle (one of the three angles is
greater than a right angle).
SINE LAW
In any triangle, the ratio of any one side to the sine of its opposite angle is constant. (This constant ratio
is the diameter of the circle circumscribing the triangle.)
a b c
= =
sin A sin B sin C
COSINE LAW
In any triangle, the square of any one side equals the sum of the squares of the other two sides, diminished by
twice their product to the cosine of its included angle.
a2 = b2 + c2 – 2bc cos A
b2 = a2 + c2 – 2ac cos B
c2 = a2 + b2 – 2ab cos C
ANGLE
An acute angle is an angle < 90º
A right angle is an angle = 90º
An obtuse angle is an angle > 90º
A straight angle is an angle = 180º
A reflex angle is an angle > 180º
Complementary angles are angles whose sum is 90º
Supplementary angles are angles whose sum is 180º
Explementary angles are angles whose sum is 360º
UNITS OF ANGLE
90º = π/2 radians = 100 grads = 1600 mils
1 radian is the angle subtended by an arc of a circle whose length is one radius.
AREA OF TRIANGLE
Given base and altitude, Area = ½ bh
Given two sides and included angle, Area = ½ ab sin θ
Given three sides (Hero’s Formula), Area = √s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)
Where, s = (a + b + c)/2
a2 sin B sin C
Given three angles, Area =
2 sin A
Aspire and Commit to Excellence!
ACE+ REVIEW CENTER
APRIL 2023 REVIEW PROGRAM
MEDIAN OF A TRIANGLE
The median of a triangle is the line drawn from one vertex to the midpoint of its opposite side. The medians of
a triangle intersect at a common point called centroid of the triangle.
4ma2 = 2b2 + 2c2 – a2
4mb2 = 2a2 + 2c2 – b2
4mc2 = 2a2 + 2b2 – c2
ALTITUDES OF A TRIANGLE
The altitude of a triangle is the line drawn from one vertex perpendicular to its opposite side. The altitudes
of a triangle intersect at a point called the orthocenter of the triangle.
ANGLE BISECTOR OF A TRIANGLE
The angle bisector of a triangle is the line drawn from one vertex to the opposite side bisecting the angle
included between the other two sides. The angle bisectors of a triangle intersect at a point called the incenter
of the triangle.
2
ba = √bcs(s − a)
b+c
2 a+b+c
bb = √acs(s − b) s=
a+c 2
2
bc = √abs(s − c)
a+b
SPHERICAL TRIANGLE
A spherical triangle is the triangle enclosed by arcs of great circles of a sphere.
The sum of the interior angles of a spherical triangle is greater than 180º and less than 540º.
AREA OF SPHERICAL TRIANGLE
πR2 E
A=
180°
Spherical Excess, E = A + B + C - 180º
For an arc of a great circle of the earth, the distance equivalent to 1 minute (0º1’) of the arc is one (1)
nautical mile (6080 ft).
RIGHT SPHERICAL TRIANGLE
The Napier’s circle indicates the sides and angle of the triangle in consecutive order, not including the right
angle.
̅ = 90 − A
A ̅ = 90 − B
B c̅ = 90 − c
Napier’s Rule:
1. The sine of any middle part is equal to product of the cosines of its opposite parts. SIN-COOP
2. The sine of any middle part is equal to the product of the tangents of its adjacent parts. SIN-TAAD
Aspire and Commit to Excellence!
ACE+ REVIEW CENTER
APRIL 2023 REVIEW PROGRAM
OBLIQUE SPHERICAL TRIANGLE
Law of Sines:
sin a sin b sin c
= =
sin A sin B sin C
Law of Cosines for Sides:
cos a = cos b cos c + sin b sin c cos A cos b = cos a cos c + sin a sin c cos B cos c = cos a cos b + sin a sin b cos C
Law of Cosines for Angles:
cos A = − cos B cos C + sin B sin C cos a cos B = − cos A cos C + sin A sin C cos b cos C = − cos A cos B + sin A sin B cos c
THE TERRESTRIAL SPHERE
Meridian – is a great circle passing through the North and South Poles
Equator – is a great circle perpendicular to the meridians
Parallels or Latitudes – are small circles parallel to the equator. Its measure is from 0º to 90º.
Prime Meridian – is the meridian passing through Greenwich England
GMT – Greenwich Mean Time
The earth rotates 360º in 24 hours or 15º every hour. Therefore, every 15º interval of longitude has a time
difference of one hour.
The mean radius of the earth is 6373 km (3959 miles), usually take as 6400 km (40000 miles).
One nautical mile = 6080 ft. This is the length of arc on the surface of the earth subtended by one (1) minute
of an arc of the great circle.
Aspire and Commit to Excellence!
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- CE Module 21 - Fluid Flow in Pipes (Answer Key)Document7 pagesCE Module 21 - Fluid Flow in Pipes (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- CE Module 22 - Open Channel and Weirs (Principle)Document3 pagesCE Module 22 - Open Channel and Weirs (Principle)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Preboard2 Psad Situation 2 Pile FootingDocument1 pagePreboard2 Psad Situation 2 Pile FootingAngelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Preboard2 Psad Situation 2 Pile FootingDocument1 pagePreboard2 Psad Situation 2 Pile FootingAngelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- CE Module 20 - Relative Equilibrium (Principles)Document1 pageCE Module 20 - Relative Equilibrium (Principles)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Custom Drink Rail DesignDocument1 pageCustom Drink Rail DesignAngelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- CE EVALUATION EXAM No. 4 - MGT, Fluid Properties, Hydrostatic Force (Answer Key)Document6 pagesCE EVALUATION EXAM No. 4 - MGT, Fluid Properties, Hydrostatic Force (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- CE Module 23 - Hydrodynamics and Water Hammer (Answer Key)Document3 pagesCE Module 23 - Hydrodynamics and Water Hammer (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la Cruz0% (1)
- CE Module 15 - Quantity Surveying (Answer Key)Document4 pagesCE Module 15 - Quantity Surveying (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la Cruz100% (1)
- CE Module 24 - Soil Properties (Principle)Document8 pagesCE Module 24 - Soil Properties (Principle)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- CE EVALUATION EXAM No. 6 - Channels, Weir, Hydrodynamics, Soil Prop (Answer Key)Document7 pagesCE EVALUATION EXAM No. 6 - Channels, Weir, Hydrodynamics, Soil Prop (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la Cruz100% (1)
- CE Module 24 - Soil Properties (Answer Key)Document12 pagesCE Module 24 - Soil Properties (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la Cruz100% (1)
- CE Module 4 - Analytic Geometry (Principles)Document4 pagesCE Module 4 - Analytic Geometry (Principles)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- CE Module 8 - Statistics and Probability (Principles)Document3 pagesCE Module 8 - Statistics and Probability (Principles)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- CE Module 11 - Surveying (Answer Key)Document6 pagesCE Module 11 - Surveying (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Legend of Symbols:: Detailed PlanDocument1 pageLegend of Symbols:: Detailed PlanAngelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- CE Module 14 - COSH (Principles)Document5 pagesCE Module 14 - COSH (Principles)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- CE Module 9 - Physics (Principles)Document4 pagesCE Module 9 - Physics (Principles)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Preboard2 Psad Situation 7 Interaction DiagramDocument1 pagePreboard2 Psad Situation 7 Interaction DiagramAngelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- MSTE Questions 2Document1 pageMSTE Questions 2Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- CE Module 4 - Analytic Geometry (Answer Key)Document4 pagesCE Module 4 - Analytic Geometry (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Preboard2 Psad Situation 3 Pile FootingDocument1 pagePreboard2 Psad Situation 3 Pile FootingAngelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- CE Module 19 - Buoyancy (Answer Key)Document4 pagesCE Module 19 - Buoyancy (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Legend of Symbols:: Plumbing General NotesDocument1 pageLegend of Symbols:: Plumbing General NotesAngelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Ecl Travellers Inn 3Document1 pageEcl Travellers Inn 3Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Schedule of Loads: Notes and SpecificationsDocument1 pageSchedule of Loads: Notes and SpecificationsAngelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Ecl Travellers Inn 4Document1 pageEcl Travellers Inn 4Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet