Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CE EVALUATION EXAM No. 4 - MGT, Fluid Properties, Hydrostatic Force (Answer Key)
Uploaded by
Angelice Alliah De la CruzOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CE EVALUATION EXAM No. 4 - MGT, Fluid Properties, Hydrostatic Force (Answer Key)
Uploaded by
Angelice Alliah De la CruzCopyright:
Available Formats
EE No.
Republic of the Philippines
PROFESSIONAL REGULATION COMMISSION
Manila
BOARD OF CIVIL ENGINEERING
CIVIL ENGINEER Licensure Examination
Thursday, December 22, 2022 08:00 a.m. – 12:00 p.m.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
APPLIED MATH, SURVEYING, TRANSPORTATION & HIGHWAY ENG’G, CONST. MGT. SET A
HYDRAULICS AND PRINCIPLES OF GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING
INSTRUCTION: Select the correct answer for each of the following questions. Mark only one answer
for each item by shading the box corresponding to the letter of your choice on the answer sheet
provided. STRICTLY NO ERASURE ALLOWED. Use pencil no. 2 only.
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. Of all paths through the network, the critical path has the
A. maximum actual time C. maximum expected time
B. minimum actual time D. minimum expected time
2. Which of the following satisfy the requirements for estimating expected activity times in a
PERT network?
I. Makes use of three estimates
II. Puts the greatest weight on the most likely time estimate
III. Is motivated by the beta distribution
A. III only C. II only
B. I only D. All of the above
3. Which of the following is the calculation of the probability that the critical path will be
completed by the time T?
I. Assumes that the activity times are the statistically independent
II. Assumes that the total time of the critical path has approximately beta distribution
III. Requires knowledge of the standard deviation for all activities in the network
A. III only C. I only
B. II only D. All of the above
4. If you are preparing a report on PERT CPM network in a construction job, what time scheduling
should you consider in the preparation of the PERT CPM network diagram?
I. Pessimistic time
II. Optimistic time
III. Probable time
A. I only C. III only
B. II only D. All of the above
5. What height in meters of a column of special gage liquid having a specific gravity of 2.90
would exert the same pressure as a column of oil 6 m high having a specific gravity of 0.80?
A. 1.33 m C. 1.45 m
B. 1.66 m D. 1.93 m
6. An airplane flying at an altitude of 10 km dropped to a height of 6 km. What is the
corresponding change in pressure? Unit weight of air is 12 kN/m3.
A. 52 kPa C. 42 kPa
B. 45 kPa D. 48 kPa
7. A cubic meter of water is subjected to a pressure increase of 20 MPa. If the bulk modulus of
elasticity of the water is 2200 MPa, evaluate the change in volume in m3.
A. 0.01360 C. 0.01460
B. 0.01780 D. 0.00909
8. Given the unit weight of air to be constant at 12 N/m3, determine the approximate height of a
mountain, in meters, if a mercury barometer at its base reads 760 mm and at the same instant
another barometer at the top of the mountain reads 300 mm.
A. 5085 C. 5029
B. 5136 D. 5114
Aspire and Commit to Excellence!
CIVIL ENGINEER Licensure Examination Page 2
Thursday, December 22, 2022 - 08:00 a.m. – 12:00 p.m.
APPLIED MATH, SURVEYING, TRANSPORTATION & HIGHWAY ENG’G, CONST. MGT. EE No. 4
HYDRAULICS AND PRINCIPLES OF GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING
9. A monometer is attached to a conduit as shown.
Given: Specific gravity of liquid B = 13.6
h = 125 mm
d = 375 mm
Calculate the pressure at A.
A. 18.6 kPa C. 38.5 kPa
B. 29.5 kPa D. 45.1 kPa
10. The weight density of a mud is given by γ = 10 + 0.5h, where γ is in kN/m3 and h is in
meters. Determine the pressure, in kPa, at a depth of 5 m.
A. 56.25 kPa C. 62.50 kPa
B. 58.65 kPa D. 60.15 kPa
11. Glycerin having a volume of 0.452 m3 weighs 5,587 Newtons. What is the specific gravity of
glycerin?
A. 1.35 C. 1.26
B. 1.21 D. 1.08
12. A pressure gauge at elevation 6 m at the side of a tank containing liquid reads 90 kPa.
Another gauge at elevation 4 m reads 110 kPa. What is the density of the liquid?
A. none of the above C. 1,019.37 kg/cum.
B. 1,529.05 kg/cum D. 2,803.26 kg/cum
13. A pressure gauge at elevation 8 at the side of a tank containing a liquid reads 80 kPa.
Another gauge at elevation 3 reads 120 kPa. What is the specific gravity?
A. 1.63 C. 0.82
B. 1.26 D. 2.45
14. A pressure gage at elevation 6 m at the side of the tank with liquid reads 90 kPa. Another
gage at elevation 4 m reads 110 kPa. Compute the specific weight of the liquid.
A. 15.00 kN/m3 C. 22.50 kN/m3
B. 27.50 kN/m3 D. 10.00 kN/m3
15. Determine the absolute pressure at 250 cm below the free surface of oil (sg = 0.80) if the
atmospheric pressure is 101 kPa.
A. 136.25 kPa C. 125.42 kPa
B. 120.62 kPa D. 134.54 kPa
16. A barometer reads 760 mm Hg and a pressure gage attached to a tank of oil (sg = 0.80) reads
850 cm. What is the absolute pressure in the tank in kilogram per square centimeter?
A. 1.71 C. 2.54
B. 0.32 D. 3.21
17. A 12 mm thick steel pipe with inside diameter of 600 mm conveys water under a head of 350 m.
What is the tensile stress in the pipe wall in kN per meter?
A. 1030.05 C. 1247.65
B. 1102.58 D. 954.77
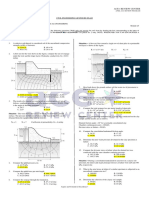
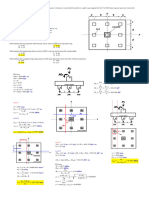
18. Determine the magnitude of the force on the inclined gate 1.5 m by 0.5 m as shown in Figure
001. The tank of water is completely closed and the pressure gage at the bottom of the tank
reads 90,000 N/m2. Use 9800 N/cum for water.
A. 44,600 N C. 38,802 N
B. 46,000 N D. 48,023 N
Aspire and Commit to Excellence!
CIVIL ENGINEER Licensure Examination Page 3
Thursday, December 22, 2022 - 08:00 a.m. – 12:00 p.m.
APPLIED MATH, SURVEYING, TRANSPORTATION & HIGHWAY ENG’G, CONST. MGT. EE No. 4
HYDRAULICS AND PRINCIPLES OF GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING
19. A rectangular gravity dam 4.2 m wide and 25 m high has 20.4 m deep of water at its upstream
side. What is the factor of safety against sliding? Assume µ = 0.6 and use unit weight of
concrete = 2310 kg/m3.
A. 0.6 C. 0.7
B. 0.8 D. 0.9
20. A rigid gate of a flood control structure in a river is 6 m wide by 4 m high and weighs 10
kN. With its longer edge horizontal, it is moved up and down with its short edges sliding in
vertical channel guides. Evaluate the force, in kN, needed to raise the gate when the surface
of the water is 2 m above its top edge. There is no water on the downstream side of the gate.
The coefficient of friction between the gate and the channel guides is 0.15. Neglect the
buoyant effect of the water on the gate and the weight of the cables connected to the gate.
A. 104 C. 151
B. 110 D. 92
21. The sector gate shown consists of a cylindrical surface, of which AB is
the trace. The length of the gate, perpendicular to the paper, is 10 m,
the radius R = 5 m, and the angle ϴ = 60º. Evaluate the total horizontal
force on the gate, in kN.
A. 1320 C. 1060
B. 1450 D. 920
Situation – Given the following data for a building to be constructed:
Nodes Activity Time (Weeks)
1-2 a Demolition and clearing 8
2-3 b Excavation 14
2-5 c Underground installations 6
3-4 d Foundation and columns 5
4-5 e Dummy 0
4-6 f Construction of second floor 6
4-7 g Roof framing and roofing 6
5-7 h Ground floor slab 4
5-8 i Mechanical and electrical services 12
6-7 j Construction of exterior walls 12
7-8 k Dummy 0
7-9 l Construction of interior partitions 10
8-9 m Mechanical and electrical fixtures 12
9-10 n Painting and finishing 8
22. Which of the following gives the critical path of the project?
A. a-c-i-m-n C. a-b-d-f-j-k-m-n
B. a-b-d-g-l-n D. a-b-d-g-k-m-n
23. Which of the following gives the duration of the project, in weeks?
A. 65 C. 63
B. 72 D. 59
24. Which of the following gives the earliest start of activity m in weeks?
A. 39 C. 45
B. 31 D. 57
Situation – The activities, duration, and cost under normal and accelerated conditions for a
network diagram is shown in the accompanying table.
Duration (Days) Cost (Pesos)
Activity Node
Normal Accelerated Normal Accelerated
A 0-1 5 3 1,000 1,600
B 0-2 5 4 3,000 4,000
D 0-3 3 2 12,000 15,000
C 1-2 7 5 3,000 3,500
E 2-3 4 3 1,000 1,500
F 3-4 5 3 1,000 1,800
25. Which of the following most nearly gives the cost of the project if it is to be accelerated
to its minimum duration?
A. Php 21,000 C. Php 24,100
B. Php 22,500 D. Php 23,400
Aspire and Commit to Excellence!
CIVIL ENGINEER Licensure Examination Page 4
Thursday, December 22, 2022 - 08:00 a.m. – 12:00 p.m.
APPLIED MATH, SURVEYING, TRANSPORTATION & HIGHWAY ENG’G, CONST. MGT. EE No. 4
HYDRAULICS AND PRINCIPLES OF GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING
26. For a total cost of Php 22,100, which of the following gives the number of days the job can
be accelerated for most economical result?
A. 17 days C. 18 days
B. 16 days D. 19 days
Situation – The activities, duration, and cost under normal and accelerated conditions for a
network diagram is shown in the accompanying table.
Normal Accelerated
Node Activity
Days Costs Days Costs
0-1 A Clearing and Grubbing 5 1,000 3 1,600
0-2 B Procurement of pipe/ other materials 5 3,000 4 4,000
1-2 C Roadway and drainage excavation 7 2,000 5 2,500
0-3 D Delivery of base course 3 12,000 2 12,000
2-3 E Excavate, lay pipe and backfill 4 1,000 3 1,500
3-4 F Spread and compact base course 5 2,000 3 2,800
27. Which of the following is the activity that is most cost efficient in converting to the
accelerated program?
A. Activity C C. Activity F
B. Activity A D. Activity E
28. If the maximum budget is Php 22,600.00, which of the following most nearly gives the
reduction in the number of days to complete the project?
A. 4 C. 7
B. 5 D. 6
29. If the project is to be accelerated by 4 days, which of the following most nearly gives the
minimum additional cost of the project?
A. Php 1,500 C. Php 900
B. Php 1,100 D. Php 1,300
Situation – The activities, duration, and cost under normal conditions for a network diagram is
shown in the accompanying table.
Normal
Node Activity
Days Costs
0-1 A Clearing and Grubbing 3 1,600
0-2 B Procurement of pipe/ other materials 4 4,000
1-2 C Roadway and drainage excavation 5 2,500
0-3 D Delivery of base course 2 12,000
2-3 E Excavate, lay pipe and backfill 3 1,500
3-4 F Spread and compact base course 3 2,800
30. Which of the following gives the critical path of the network?
A. B-C-E-F C. A-C-E-F
B. C-D-E-F D. B-E-F
31. Which of the following gives the duration of the project?
A. 15 C. 12
B. 14 D. 13
32. Which of the following gives the total cost of the project?
A. Php 24,400.00 C. Php 23,400.00
B. Php 22,400.00 D. Php 25,400.00
Situation – A rectangular gate 1.5 m wide and 3 m high is vertically submerged in water with its
top edge horizontal and 2 m below the water surface.
33. Evaluate the total force acting on one side of the gate, in kN.
A. 145.5 kN C. 154.5 kN
B. 165.5 kN D. 135.5 kN
34. Obtain the location of force from the center of gravity of the plate, in meters.
A. 0.214 m C. 0.251 m
B. 0.312 m D. 0.195 m
Aspire and Commit to Excellence!
CIVIL ENGINEER Licensure Examination Page 5
Thursday, December 22, 2022 - 08:00 a.m. – 12:00 p.m.
APPLIED MATH, SURVEYING, TRANSPORTATION & HIGHWAY ENG’G, CONST. MGT. EE No. 4
HYDRAULICS AND PRINCIPLES OF GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING
35. Obtain the location of force from the liquid surface, in meters.
A. 3.714 m C. 3.751 m
B. 3.812 m D. 3.695 m
Situation – At a certain elevation above sea level, a mercury barometer reads 700 mm.
36. What would be the corresponding reading of a water barometer, in mm?
A. 6700 C. 8240
B. 7650 D. 9520
37. Evaluate the atmospheric pressure, in kPa, at that level.
A. 87.6 C. 90.5
B. 88.8 D. 93.3
38. What is the approximate elevation above sea level, assuming normal atmospheric conditions?
Neglect vapor pressure. Air weighs 12 N/m3.
A. 6850 m C. 7840 m
B. 7780 m D. 8210 m
Situation – A square plate having one of its side equal to 3 m is immerse in a water surface in
a vertical position such that the two edges of the square would be horizontal in order that the
center of pressure shall be 8 cm from the center of gravity.
39. How far below the water surface should the upper plate be submerged?
A. 7.905 m C. 7.565 m
B. 6.925 m D. 7.875 m
40. What is the distance of the center of pressure from the water surface?
A. 9.445 m C. 8.445 m
B. 9.455 m D. 8.455 m
41. Determine the hydrostatic force acting on the plate at this position.
A. 793.39 kN C. 827.72 kN
B. 815.51 kN D. 842.24 kN
Situation – A triangular plate of height h = 1.2 m and base b = 2.0 m is submerged vertically in
water with its base at the liquid surface and parallel to it.
42. Evaluate the total force acting on one side of the plate, in kN.
A. 4.08 C. 4.32
B. 4.21 D. 4.71
43. Obtain the location of the force from the center of gravity of the plate.
A. 180 C. 200
B. 190 D. 210
44. Obtain the location of the force from the liquid surface.
A. 580 C. 600
B. 590 D. 610
Situation – A circular gate 1.5 m in diameter is inclined at an angle of 45º. Fresh water stands
on one side of the gate to a height of 10 m above the center of the gate.
45. Evaluate the total force on the gate.
A. 145.8 kN C. 173.4 kN
B. 206.2 kN D. 212.6 kN
46. Locate the point of action of the total force from the bottom on the plane of the gate.
A. 0.74 m C. 0.59 m
B. 0.26 m D. 1.12 m
47. If the gate is hinged at the top, evaluate the force normal to the gate at the bottom that
will require to open it in kN.
A. 106.2 kN C. 74.1 kN
B. 91.7 kN D. 87.8 kN
Aspire and Commit to Excellence!
CIVIL ENGINEER Licensure Examination Page 6
Thursday, December 22, 2022 - 08:00 a.m. – 12:00 p.m.
APPLIED MATH, SURVEYING, TRANSPORTATION & HIGHWAY ENG’G, CONST. MGT. EE No. 4
HYDRAULICS AND PRINCIPLES OF GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING
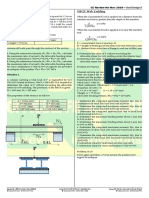
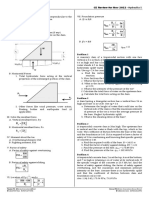
Situation – The section of a concrete gravity dam is shown below. The depth of water at the
upstream side is 6 m. Neglect hydrostatic uplift and use unit weight of concrete = 23.5 kN/m3.
Coefficient of friction between the base of the dam and the foundation is 0.6.
48. Which of the following is closest to the value of the factor of safety against sliding?
A. 2.54 C. 1.54
B. 1.75 D. 1.92
49. Which of the following is closest to the value of the factor of safety against overturning?
A. 2.4 C. 2.8
B. 3.9 D. 3.3
50. Which of the following is closest to the overturning moment acting against the dam in kN-m?
A. 353.16 C. 324.12
B. 285.63 D. 398.75
Aspire and Commit to Excellence!
You might also like
- Apr 2024 Preboard 1 HgeDocument3 pagesApr 2024 Preboard 1 HgeChrisjohn Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 2023 Nov Preboard 3 HgeDocument5 pages2023 Nov Preboard 3 HgeMarlou MabuteNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulics Civil Engineering - PRACTICE PROBLEMS - 2017 INSTRUCTION: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The FollowingDocument36 pagesFluid Mechanics & Hydraulics Civil Engineering - PRACTICE PROBLEMS - 2017 INSTRUCTION: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The FollowingFrancis Philippe CariñoNo ratings yet
- Refresher HYD Part2Document2 pagesRefresher HYD Part2Lionel LapuzNo ratings yet
- CE EVALUATION EXAM No. 5 - Buoyancy, Equilibrium, Fluid Flows (Answer Key)Document5 pagesCE EVALUATION EXAM No. 5 - Buoyancy, Equilibrium, Fluid Flows (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Problems: Properties of Fluids, Pressures & DamsDocument6 pagesIrrigation Problems: Properties of Fluids, Pressures & DamsJeiel ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Kippap-Handout-MSTE (05 Probability and Statistics)Document2 pagesKippap-Handout-MSTE (05 Probability and Statistics)NaniNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Engr. Jonathan C. BulagaoDocument5 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Engr. Jonathan C. BulagaoMichael James ll BanawisNo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2020 - Hydraulics - Set 13Document1 pageCE Board Nov 2020 - Hydraulics - Set 13Justine Ejay MoscosaNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Exam 2Document4 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Exam 2Jan Jan AnoNo ratings yet
- CE EVALUATION EXAM No. 6 - Channels, Weir, Hydrodynamics, Soil Prop (Answer Key)Document7 pagesCE EVALUATION EXAM No. 6 - Channels, Weir, Hydrodynamics, Soil Prop (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la Cruz100% (1)
- BESA Structural Design Preboard Solutions 19 Feb. 2022Document46 pagesBESA Structural Design Preboard Solutions 19 Feb. 2022Chaythina Corteza100% (1)
- Structural Engineering & ConstructionDocument13 pagesStructural Engineering & ConstructionREX AMPONGANNo ratings yet
- Nov23 Design 01 06 Nov. 2023Document19 pagesNov23 Design 01 06 Nov. 2023Jayson MariNo ratings yet
- PREBOARD EXAM 1 MATH, SURVEYING AND ECONOMICS REVIEWDocument6 pagesPREBOARD EXAM 1 MATH, SURVEYING AND ECONOMICS REVIEWWinter DeeneNo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2020 - RCD - Set 7 ColoredDocument1 pageCE Board Nov 2020 - RCD - Set 7 ColoredDale MalazzabNo ratings yet
- Agacita John PaulDocument10 pagesAgacita John PaulCarlo Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Activity 2Document2 pagesActivity 2Marben Leynes-Cereno Agustin-ViernesNo ratings yet
- Solutions For Quiz 7: Problem 1-3Document6 pagesSolutions For Quiz 7: Problem 1-3Von Andrei MedinaNo ratings yet
- Feu Hydraulics PreboardDocument2 pagesFeu Hydraulics PreboardEla Macabante100% (1)
- Final Preboard Exam - MSTE - SolutionDocument7 pagesFinal Preboard Exam - MSTE - SolutionKathryne BernardoNo ratings yet
- Structural Engg. Refresher (Sept. 22,2021)Document4 pagesStructural Engg. Refresher (Sept. 22,2021)ELMERNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Battery - 2Document4 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Battery - 2Aileen AntipoloNo ratings yet
- CE Module 25 - Soil Testing (Answer Key)Document3 pagesCE Module 25 - Soil Testing (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Review innovations mechanical engineering exam problemsDocument3 pagesReview innovations mechanical engineering exam problemsKian InductivoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics10 Neric10Document12 pagesHydraulics10 Neric10jrmmansayonNo ratings yet
- Slu Ce Structural June 2020 Problem SetDocument9 pagesSlu Ce Structural June 2020 Problem SetJonathan Basilio100% (1)
- Design Coaching 1 Practice Material and LectureDocument43 pagesDesign Coaching 1 Practice Material and LectureeklavurNo ratings yet
- Refresher Module 20 - (S6) - Basic-Structural-EngineeringDocument1 pageRefresher Module 20 - (S6) - Basic-Structural-EngineeringMadelyn Oronos100% (1)
- Hydraulics and Geotechnical Answer KeyDocument2 pagesHydraulics and Geotechnical Answer KeyAngelica RomeroNo ratings yet
- 1S1920 - SW - Fluid Mechanics: Name DateDocument12 pages1S1920 - SW - Fluid Mechanics: Name DateBosz' AceNo ratings yet
- Second Preboard Exam - MsteDocument8 pagesSecond Preboard Exam - MsteCzatrina QuintasNo ratings yet
- MidTerm HydraulicsDocument8 pagesMidTerm HydraulicsFernan FalogmeNo ratings yet
- Square FootingDocument9 pagesSquare FootingFrancis Ko Badongen-Cawi Tabaniag Jr.No ratings yet
- HGE#003-Hydraulics Engineering 3Document3 pagesHGE#003-Hydraulics Engineering 3Kim Ryan PomarNo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2021 - Geotechnical Engineering - Set 5Document2 pagesCE Board Nov 2021 - Geotechnical Engineering - Set 5Lemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- Steel Design 9 Nov 2020 PDFDocument1 pageSteel Design 9 Nov 2020 PDFJustine Ejay MoscosaNo ratings yet
- 2019 Hyd MayDocument13 pages2019 Hyd MayChantal Faye GacusanNo ratings yet
- Steel column design and analysis problemsDocument12 pagesSteel column design and analysis problemsDan Casurao100% (1)
- Refresher Module 16 (GH8) - Geotechnical Engineering and HydraulicsDocument1 pageRefresher Module 16 (GH8) - Geotechnical Engineering and HydraulicsMadelyn OronosNo ratings yet
- Geotech - Quiz 3 Sol. - 8 March 2022Document6 pagesGeotech - Quiz 3 Sol. - 8 March 2022Mayya BonaNo ratings yet
- CE Board Exam Review QuestionsDocument4 pagesCE Board Exam Review QuestionsMayya BonaNo ratings yet
- HF Using Manning Formula Sample Problems: Voice: Balase, Ann Maricar FDocument11 pagesHF Using Manning Formula Sample Problems: Voice: Balase, Ann Maricar FKyohai RinggoNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering and Hydraulics Final Coaching Nov 2018Document87 pagesGeotechnical Engineering and Hydraulics Final Coaching Nov 2018Jeremy Mark SorianoNo ratings yet
- Kippap Diagnostic Exam May 2022Document9 pagesKippap Diagnostic Exam May 2022Maryrose Aguirre SerranoNo ratings yet
- Pre-Board Hydraulics Geothecnical EngineeringDocument14 pagesPre-Board Hydraulics Geothecnical EngineeringPhreetzi ÜnseenNo ratings yet
- XVI To XVII PDFDocument28 pagesXVI To XVII PDFAmira Ramlee0% (1)
- Steel Design 8 Nov 2020Document1 pageSteel Design 8 Nov 2020Justine Ejay MoscosaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics review module on relative equilibrium of fluidsDocument1 pageHydraulics review module on relative equilibrium of fluidsYeddaMIlaganNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Set - ADocument4 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Set - AAnthony Jay Poraque0% (1)
- RC 3Document4 pagesRC 3Mayya BonaNo ratings yet
- Hge Mid PreboardDocument7 pagesHge Mid PreboardChrisneil Delosreyes0% (1)
- Hydraulics Plate 3 & 4asDocument3 pagesHydraulics Plate 3 & 4asNero James SiaNo ratings yet
- Preboard2 Psad Situation 2 Pile FootingDocument1 pagePreboard2 Psad Situation 2 Pile FootingAngelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Two Open TanksDocument10 pagesTwo Open TanksMaverick TimbolNo ratings yet
- CENG 197 Problem Set 2Document5 pagesCENG 197 Problem Set 2edmar limNo ratings yet
- Hyd 5Document1 pageHyd 5Franky MartinNo ratings yet
- ESAS ReviewerDocument316 pagesESAS ReviewerRoselyn Matienzo100% (2)
- Nov 2023 Preboard 2 Hge - DONEDocument6 pagesNov 2023 Preboard 2 Hge - DONEengr.jaysoncapadosamariNo ratings yet
- Local Media3983018567083363738Document6 pagesLocal Media3983018567083363738Venus Kate GevaNo ratings yet
- Custom Drink Rail DesignDocument1 pageCustom Drink Rail DesignAngelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- CE Module 21 - Fluid Flow in Pipes (Answer Key)Document7 pagesCE Module 21 - Fluid Flow in Pipes (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Preboard2 Psad Situation 2 Pile FootingDocument1 pagePreboard2 Psad Situation 2 Pile FootingAngelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- CE Module 20 - Relative Equilibrium (Principles)Document1 pageCE Module 20 - Relative Equilibrium (Principles)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- CE Module 22 - Open Channel and Weirs (Principle)Document3 pagesCE Module 22 - Open Channel and Weirs (Principle)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- CE Module 23 - Hydrodynamics and Water Hammer (Answer Key)Document3 pagesCE Module 23 - Hydrodynamics and Water Hammer (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la Cruz0% (1)
- CE EVALUATION EXAM No. 6 - Channels, Weir, Hydrodynamics, Soil Prop (Answer Key)Document7 pagesCE EVALUATION EXAM No. 6 - Channels, Weir, Hydrodynamics, Soil Prop (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la Cruz100% (1)
- CE Module 24 - Soil Properties (Answer Key)Document12 pagesCE Module 24 - Soil Properties (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- CE Module 9 - Physics (Principles)Document4 pagesCE Module 9 - Physics (Principles)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- CE Module 15 - Quantity Surveying (Answer Key)Document4 pagesCE Module 15 - Quantity Surveying (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la Cruz100% (1)
- MSTE Questions 2Document1 pageMSTE Questions 2Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- CE Module 14 - COSH (Principles)Document5 pagesCE Module 14 - COSH (Principles)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Legend of Symbols:: Detailed PlanDocument1 pageLegend of Symbols:: Detailed PlanAngelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- CE Module 24 - Soil Properties (Principle)Document8 pagesCE Module 24 - Soil Properties (Principle)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Classification and Pipe Schedules for Occupancy Light and Ordinary Hazard Sprinkler SystemsDocument24 pagesClassification and Pipe Schedules for Occupancy Light and Ordinary Hazard Sprinkler SystemsKhyle Laurenz DuroNo ratings yet
- NFPA 13 hydraulic calculation for ordinary hazard group 1Document2 pagesNFPA 13 hydraulic calculation for ordinary hazard group 1Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Preboard2 Psad Situation 2 Pile FootingDocument1 pagePreboard2 Psad Situation 2 Pile FootingAngelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Fire Flow Calculator Worksheet 2011Document7 pagesFire Flow Calculator Worksheet 2011walitedisonNo ratings yet
- Ecl Travellers Inn 4Document1 pageEcl Travellers Inn 4Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Design Calculation Sheet: 1-AbbreviationsDocument3 pagesDesign Calculation Sheet: 1-Abbreviationsmayukhguha1988No ratings yet
- Ecl Travellers Inn 3Document1 pageEcl Travellers Inn 3Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Legends & Symbols Electrical Panel DiagramDocument1 pageLegends & Symbols Electrical Panel DiagramAngelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Legend of Symbols:: Plumbing General NotesDocument1 pageLegend of Symbols:: Plumbing General NotesAngelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Beam DesignDocument2 pagesBeam DesignreynoldNo ratings yet
- Natural Law's Rise and FallDocument17 pagesNatural Law's Rise and FallNoel James100% (2)
- Activity Completion IN School-Based Seminar ON National Drug Education ProgramDocument12 pagesActivity Completion IN School-Based Seminar ON National Drug Education ProgramFATIMA APILADONo ratings yet
- Here The Whole Time ExcerptDocument18 pagesHere The Whole Time ExcerptI Read YA100% (1)
- Cases in OBLIGATIONS AND CONTRACTSDocument17 pagesCases in OBLIGATIONS AND CONTRACTSRommell Esteban ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Employment and Skill MismatchDocument20 pagesEmployment and Skill MismatchFarah LimNo ratings yet
- Study PlanDocument2 pagesStudy PlanAbu FatihNo ratings yet
- Motor Vehicles Act SummaryDocument111 pagesMotor Vehicles Act SummarySardaar Harpreet Singh HoraNo ratings yet
- Understand Quran 50 Percent Course Workbook Solution (UNDERSTAND AL-QUR'AAN ACADEMY)Document25 pagesUnderstand Quran 50 Percent Course Workbook Solution (UNDERSTAND AL-QUR'AAN ACADEMY)Al Huda75% (4)
- Cold WarDocument42 pagesCold WarTaiba HabibNo ratings yet
- Finals (3. LP) Termination and RepairDocument4 pagesFinals (3. LP) Termination and RepairAmelyn Goco MañosoNo ratings yet
- Neap and Seameo Batch 2 InfoDocument28 pagesNeap and Seameo Batch 2 InfoAPPLE GOLANGAYANNo ratings yet
- Gerunds and Infinitives 8897Document3 pagesGerunds and Infinitives 8897aura lucy estupiñan gutierrezNo ratings yet
- Activityideabank FinalDocument72 pagesActivityideabank FinalJoy Tu TranNo ratings yet
- 15-5240 enDocument14 pages15-5240 enRafa Lopez PuigdollersNo ratings yet
- STQ Issue 4 PDFDocument119 pagesSTQ Issue 4 PDFSiddhartha SinghNo ratings yet
- Amarok 2011Document79 pagesAmarok 2011NPNo ratings yet
- Impact of Product Rebranding On Organization ProfitabilityDocument63 pagesImpact of Product Rebranding On Organization ProfitabilityDaniel ObasiNo ratings yet
- Rdbms (Unit 2)Document9 pagesRdbms (Unit 2)hari karanNo ratings yet
- 01 - What Is The S3 ScannerDocument4 pages01 - What Is The S3 ScannerViet PhanNo ratings yet
- Procedures For Conducting Practical Tasks and Supervisor Instructions 0417Document5 pagesProcedures For Conducting Practical Tasks and Supervisor Instructions 0417Vignesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Storyboard: Video Script and Storyboard On Evaluating Functions LessonDocument2 pagesStoryboard: Video Script and Storyboard On Evaluating Functions LessonIvanhoe BalaroteNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Being A 21st Century LearnerDocument17 pagesTopic 1 Being A 21st Century LearnerNAZATUL EZETY BINTI AHMAD STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Les Colorants Textiles Et Methodes de TraitementDocument31 pagesLes Colorants Textiles Et Methodes de TraitementFATIMA ZAHRA KANOUN ALAOUINo ratings yet
- STOW - Vol. 3 - ScheduleDocument12 pagesSTOW - Vol. 3 - ScheduleDavid A. Malin Jr.100% (2)
- Beauty Paulor Management SystemDocument2 pagesBeauty Paulor Management SystemTheint Theint AungNo ratings yet
- Insurance Dispute Over Mortgaged PropertyDocument2 pagesInsurance Dispute Over Mortgaged PropertyBetson CajayonNo ratings yet
- Monetizing Judgments DatasheetDocument9 pagesMonetizing Judgments DatasheetJohnWilliams100% (4)
- NN47205-500 05.01 Config-SystemDocument328 pagesNN47205-500 05.01 Config-SystemMatias SalatinoNo ratings yet
- TOOLKIT For Case ManagementDocument313 pagesTOOLKIT For Case ManagementSaraNo ratings yet
- Bovee, Arens 150-170Document32 pagesBovee, Arens 150-170Mădălina-Cristiana PaţachiaNo ratings yet