Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SP22 DE Midterm Part 1
Uploaded by
Minhong KimOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SP22 DE Midterm Part 1
Uploaded by
Minhong KimCopyright:
Available Formats
Di↵erential Equations (MTH20101,2)
Spring 2022 Midterm Exam ( Part I )
Please write down the following honor pledge and sign it. “I affirm that I will not give or receive
any unauthorized help on this exam, and that all work will be my own. Sign: ”
or “òî ¡X‡ ≥≥Xå ‹ÿ– Q` ÉD ⌧}i»‰.” ⌧Ö: ”
1. (8 points) Solve the initial value problem, and determine the interval on which the solution is
defined.
dy 1
t + (t + 2)y = e t cos t; y(⇡) = 0
dt t
2. Consider an initial value problem
x
y0 = ; y(0) = 1.
x2 +y
(a) (2 points) Show that the equation is not exact.
(b) (10 points) Find the solution to the initial value problem.
(Hint: Try to use an integration factor µ(y).)
dy
3. (a) (7 points) Find a general solution of dx
= y 3 , if it exists. If not, verify your answer.
dy
(b) (3 points) Find the explicit solution to the initial value problem dx
= y3; y(0) = 1,
and determine the domain of the solution.
4. Consider the di↵erential equation
y0 = y3 3y.
(a) (4 points) Sketch the phase line for the equation; Mark on it all critical points; Label each
critical point as asymptotically stable, unstable, or neither.
(b) (6 points) Sketch solutions for the equation with initial conditions y(0) = 2, y(0) = 32 , and
y(0) = 12 in the ty-plane considering the concavity of solutions.
5. Consider the di↵erential equation
y 00 + by 0 + 16y = 0.
(a) (6 points) Find the value(s) of b for which the solution
(i) decays exponentially to 0 as t ! 1.
(ii) oscillates with constant amplitude.
(iii) is a growing oscillation.
(b) (4 points) For b = 10, find the solution to the initial value problem satisfying y(0) =
0, y 0 (0) = 6.
( page 1 of 1)
You might also like
- Exam 1 - Math 212Document1 pageExam 1 - Math 212Taleb AbboudNo ratings yet
- 121 0Document4 pages121 0Taesoo LeeNo ratings yet
- MATH 2260 (Ordinary Differential Equations I) - Fall 2014 Midterm Exam #1Document2 pagesMATH 2260 (Ordinary Differential Equations I) - Fall 2014 Midterm Exam #1Zhichao WangNo ratings yet
- ME 201/MTH 281/ME 400/CHE 400 Assignment #1 2009: Lecture Schedule and ReadingDocument2 pagesME 201/MTH 281/ME 400/CHE 400 Assignment #1 2009: Lecture Schedule and Readingsoccerrocker808No ratings yet
- MAST20030: Di Fferential Equations: Second Semester, 2016 School of Mathematics and StatisticsDocument3 pagesMAST20030: Di Fferential Equations: Second Semester, 2016 School of Mathematics and StatisticsAnohhNo ratings yet
- Exam 3Document1 pageExam 3sgNo ratings yet
- AU17 de MidtermDocument2 pagesAU17 de Midterm김재윤No ratings yet
- Mathematical Methods (Math 562) Fall '09 Mid TermDocument2 pagesMathematical Methods (Math 562) Fall '09 Mid Termabdul haseebNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 Spring 2011Document8 pagesQuiz 2 Spring 2011Jean Paul AzziNo ratings yet
- Exercises of Chapter 3Document2 pagesExercises of Chapter 3Anh Tuấn PhanNo ratings yet
- Math217 Midterm1 PracticeDocument2 pagesMath217 Midterm1 Practiceozcan8479No ratings yet
- SP18 de Fianl Exam PractiveDocument2 pagesSP18 de Fianl Exam Practive김재윤No ratings yet
- Sin 3x 6Document2 pagesSin 3x 6Дмитрий АртюхNo ratings yet
- Math24-1 LQ2 2014-2015 4QDocument1 pageMath24-1 LQ2 2014-2015 4QDilip ThummarNo ratings yet
- XCGFFKHGFDocument2 pagesXCGFFKHGFUrielNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology Mandi, H. P. India Engineering Mathematics - IC 110 Tutorial-8 Odd Semester (2019-20)Document1 pageIndian Institute of Technology Mandi, H. P. India Engineering Mathematics - IC 110 Tutorial-8 Odd Semester (2019-20)Amit ProNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Tripos Part IA: Complete Answers Are Preferred To FragmentsDocument9 pagesMathematical Tripos Part IA: Complete Answers Are Preferred To FragmentsKrishna OochitNo ratings yet
- Week0 SolnDocument6 pagesWeek0 SolnpattunnarajamphdNo ratings yet
- SMA 2232 Exam July 2020-1 PRINTDocument3 pagesSMA 2232 Exam July 2020-1 PRINTIsaac OgolaNo ratings yet
- Homework 5 Problem 1Document4 pagesHomework 5 Problem 1沈智恩No ratings yet
- Ass 6 2020Document2 pagesAss 6 2020Sketchily SebenteNo ratings yet
- MZB127 Practice TestDocument9 pagesMZB127 Practice TestZayd RayNo ratings yet
- 1 ExDocument7 pages1 Exvennela sainathNo ratings yet
- Sample Exam.: Math 251H First Midterm ExamDocument8 pagesSample Exam.: Math 251H First Midterm ExamRAJESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Quiz 4: NameDocument3 pagesQuiz 4: NameEphrathahNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Methods - Assignment 3: Deadline - 5th DecemberDocument2 pagesMathematical Methods - Assignment 3: Deadline - 5th DecemberJAGANNATH RANANo ratings yet
- P4 Differential Equations QPDocument2 pagesP4 Differential Equations QPAFRAH ANEESNo ratings yet
- Ordinary Differential Equations 17Document3 pagesOrdinary Differential Equations 17rapsjadeNo ratings yet
- Mock Exam MM201Document4 pagesMock Exam MM201Wonji Park100% (1)
- Marist Avenue, General Santos City: Notre Dame of Dadiangas UniversityDocument2 pagesMarist Avenue, General Santos City: Notre Dame of Dadiangas UniversityJosh T CONLUNo ratings yet
- Dy DX D y DX D y DX y D y DX Dy DX D Q DT R DQ DT Q C EsinwtDocument2 pagesDy DX D y DX D y DX y D y DX Dy DX D Q DT R DQ DT Q C Esinwtdaniel ayobamiNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - Iii Tutorial-7Document1 pageMathematics - Iii Tutorial-7Aditya JabadeNo ratings yet
- Instructor: Dr. J. C. Kalita and Dr. Shubhamay SahaDocument3 pagesInstructor: Dr. J. C. Kalita and Dr. Shubhamay SahaMichael CorleoneNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6Document2 pagesTutorial 6zassinvisoofficialNo ratings yet
- EngineeringDocument4 pagesEngineeringAbdul MunamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 First Order ODE (Part II)Document23 pagesChapter 1 First Order ODE (Part II)qurratulainnn19No ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet Two-2 092724Document3 pagesTutorial Sheet Two-2 092724iddi5504No ratings yet
- MATH 250 Midterm Exam I February 24, 2005 Name: Student Number: Instructor: SectionDocument10 pagesMATH 250 Midterm Exam I February 24, 2005 Name: Student Number: Instructor: SectionRAJESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- BSEH Practice Paper (March 2024) : Marking SchemeDocument24 pagesBSEH Practice Paper (March 2024) : Marking Schemehimeshrao263No ratings yet
- Delft University of Technology Faculty of Elec. Eng, Mathematics and Comp. SCDocument2 pagesDelft University of Technology Faculty of Elec. Eng, Mathematics and Comp. SCPythonraptorNo ratings yet
- Unit III (O.D.E.)Document15 pagesUnit III (O.D.E.)tfantuNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 SolutionsDocument7 pagesAssignment 2 SolutionshussainNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 SolutionsDocument7 pagesAssignment 2 SolutionsShafry YusufNo ratings yet
- ECON 3551 - Homework Assignment 3Document2 pagesECON 3551 - Homework Assignment 3Ammar JaweedNo ratings yet
- Linear Second Order Ode: Differential EquationsDocument36 pagesLinear Second Order Ode: Differential EquationsThurkhesan MuruganNo ratings yet
- UBC Math 255 Practice Midterm 1Document4 pagesUBC Math 255 Practice Midterm 1Keith RussellNo ratings yet
- MH1811 Final Exam 16-17 Sem 1Document12 pagesMH1811 Final Exam 16-17 Sem 1Mia SohNo ratings yet
- Final Examination Differential EquationDocument2 pagesFinal Examination Differential EquationKirk Daniel ObregonNo ratings yet
- 1 Guia 111026 CDocument5 pages1 Guia 111026 CAlexandra ZeaNo ratings yet
- MATH 202-Final-Summer17Document12 pagesMATH 202-Final-Summer17Diana BeirutiNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological University: InstructionsJainish JariwalaNo ratings yet
- Test1 FR KEYDocument11 pagesTest1 FR KEYUnitedSlayerNo ratings yet
- Test 2018 1Document1 pageTest 2018 1semihkilic1997No ratings yet
- Exercises From Differential EquationsDocument3 pagesExercises From Differential Equationsm3hediiNo ratings yet
- M 2 PaperDocument6 pagesM 2 PapermeteoricvincentNo ratings yet
- Final Examination Contents - BTB10403Document11 pagesFinal Examination Contents - BTB10403Muhd AfiqNo ratings yet
- This Set of Exercises Is Provided For Practice Only, and Do Not Count Toward The Final MarkDocument1 pageThis Set of Exercises Is Provided For Practice Only, and Do Not Count Toward The Final MarkWéi Guāng BìNo ratings yet
- Examination For Mathematics (45 Min.)Document6 pagesExamination For Mathematics (45 Min.)Mohamed EL QarouaouiNo ratings yet
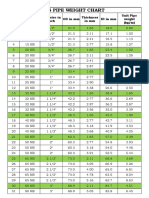
- Ms Pipe Weight Chart: Sl. No. Odinmm Idinmm Pipe Size in NB Pipe Size in Inch Thickness in MM Unit Pipe Weight (KG/M)Document32 pagesMs Pipe Weight Chart: Sl. No. Odinmm Idinmm Pipe Size in NB Pipe Size in Inch Thickness in MM Unit Pipe Weight (KG/M)Prashant33% (3)
- Marcet Boiler CharacteristicsDocument12 pagesMarcet Boiler CharacteristicsJuniorNo ratings yet
- Order of Magnitude AnalysisDocument15 pagesOrder of Magnitude AnalysisPramodVermaNo ratings yet
- MONORAIL and AMS Product Catalogue ENDocument211 pagesMONORAIL and AMS Product Catalogue ENCicero MelloNo ratings yet
- Bioengineering Analysis of Orthodontic Mechanics PDFDocument491 pagesBioengineering Analysis of Orthodontic Mechanics PDFdaniela2201100% (1)
- Molecular Vibrations of Crystal of Poly (Vinylidene: Fluoride)Document14 pagesMolecular Vibrations of Crystal of Poly (Vinylidene: Fluoride)Rana Sabouni TabariNo ratings yet
- CMS-application FormDocument6 pagesCMS-application FormHarsh BhimaniNo ratings yet
- Data Hujan Kota MeureuduDocument33 pagesData Hujan Kota MeureuduFerry FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- 39 Schelling Understanding German Idealism 1Document135 pages39 Schelling Understanding German Idealism 1Matteo de DonatoNo ratings yet
- Epfl Th3214 App ADocument47 pagesEpfl Th3214 App Avlad lupasteanuNo ratings yet
- Design Procedure For Statically Loaded BoltDocument14 pagesDesign Procedure For Statically Loaded BoltAnonymous DJrec2100% (1)
- Computed Tomography Principles, Design, Artifacts, and Recent AdvancesDocument562 pagesComputed Tomography Principles, Design, Artifacts, and Recent AdvancesLaura Ospina100% (2)
- Poweroil To 1020 60 SNX: SR No Characteristics Unit Test Method Guaranteed Data Min MaxDocument1 pagePoweroil To 1020 60 SNX: SR No Characteristics Unit Test Method Guaranteed Data Min MaxWellington SilvaNo ratings yet
- SKF3013 Physical Chemistry I: Prof. Dr. Ramli Ibrahim Dr. Norlaili Abu BakarDocument24 pagesSKF3013 Physical Chemistry I: Prof. Dr. Ramli Ibrahim Dr. Norlaili Abu BakarAisha NajihaNo ratings yet
- Exp 2 Performance of A Steam Plant PDFDocument8 pagesExp 2 Performance of A Steam Plant PDFfaris_hamir33% (3)
- Marvin Reaction PaperDocument15 pagesMarvin Reaction PaperMarvin SurioNo ratings yet
- UIMO OPP Class 02Document45 pagesUIMO OPP Class 02yedidi67% (3)
- Physics ResearchDocument2 pagesPhysics ResearchKrystel IsidroNo ratings yet
- Iii Liiil: Mathematics Module 2 (Algebra and Calculus) Question-Answer BookDocument24 pagesIii Liiil: Mathematics Module 2 (Algebra and Calculus) Question-Answer BookbyobbyobNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Induction MachinesDocument70 pagesAnalysis of Induction MachinesKyambi MutiaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2589234722001324 Main - 3Document77 pages1 s2.0 S2589234722001324 Main - 3mohammadNo ratings yet
- Motion and Time Class 7, 2022Document61 pagesMotion and Time Class 7, 2022Theia JacobNo ratings yet
- Phys471Course Chap 0Document8 pagesPhys471Course Chap 0eniNo ratings yet
- Awards and Honours 2024Document8 pagesAwards and Honours 2024iamahmed2212No ratings yet
- NATO STO CPoW 2021Document71 pagesNATO STO CPoW 2021iagaruNo ratings yet
- Placement Brochure: Indian Institute of Technology, IndoreDocument24 pagesPlacement Brochure: Indian Institute of Technology, IndoreKang ChulNo ratings yet
- 5 TidesDocument5 pages5 TidesJonas CabacunganNo ratings yet
- Vol. 43 No. 2, January 2021Document40 pagesVol. 43 No. 2, January 2021alialjobouri2006No ratings yet
- On P-Groups of Maximal Class: August 2019Document9 pagesOn P-Groups of Maximal Class: August 2019JodeNo ratings yet
- Fluid-Dynamic LiftDocument507 pagesFluid-Dynamic LiftMike Corvin100% (1)