Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Semilla, Von Reo, Activity 2 & 3
Uploaded by
Von R SemillaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Semilla, Von Reo, Activity 2 & 3
Uploaded by
Von R SemillaCopyright:
Available Formats
VON REO SEMILLA 10/7/23
BSN2-B2 HES 032; MICROPARA
ACTIVITY 2
BACTERIAL CELL
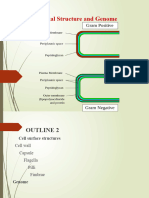
A. Structure external to the cell wall
1. Glycocalyx - An outward complex of polysaccharide on
the bacterial surface and other cells. It
helps the bacteria to attach to the surface
of solid objects or tissue.
2. Flagella - An exterior protein filament (flagellin) that
rotates and thus, causes bacteria to be
motile, exhibits motility for locomotion.
Also, important in survivability and
pathogenic ability of bacteria.
3. Fimbriae and Pili - Conjugation and attachment among most
gram-negative bacteria.
B. Cell Wall - Provide rigidity, shape, and protection.
C. Plasma (Cytoplasmic) Membrane - It encloses the cytoplasm, and has an
important role such as respiration,
photosynthesis, and the synthesis of lipids
and cell wall constituents. Also, it has a
selective permeability, meaning that they
allow only certain substances to pass
through them.
D. Structures internal to the cell wall
1. Nucleoid - Contains genetic material.
2. Cytoplasm - Embedded within the cytoplasm are
chromosomes, ribosomes, and other
cytoplasmic structures. Surrounded by a
cell wall, cell membrane, and sometimes a
capsule or slime layer.
3. Ribosomes - Play an important role in the synthesis of
proteins.
4. Inclusions
a. Metachromatic granules - Serve as the energy source or food reserve
b. Sulfur granules of the bacteria, and composed mainly of
c. Lipid inclusions polysaccharides, they lessen osmotic
d. Polysaccharide granules pressure.
5. Endospores - A small, dormant structure located inside
the bacterial cell. It aids in the survival of
bacterial against external conditions.
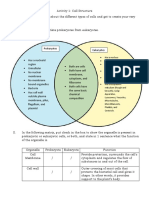
1. Differentiate the structure of prokaryotic from eukaryotic cells (tabular form).
Eukaryotic Cell Prokaryotic Cell
Most common Simplest form
Possess membrane bound structures and a Lack membrane bound structures
nucleus Lack true nucleus
Found in most living things
- Cytoplasmic Particles
- Nucleus - Glycocalyx (Slime layers and Capsules)
- Endoplasmic Reticulum - Pili (fimbriae)
- Ribosomes - Spores
- Golgi Complex - Plasmid
- Lysosomes - Ribosomes
- Peroxisomes
- Mitochondria
- Plastids
- Cytoskeleton
- Nuclear Membrane
2. Give the different arrangement of flagella and provide an example of each flagella
arrangement. (Illustrate each flagellar arrangement).
Flagella Type Description Example
Monotrichous Single flagella on one side Vibrio cholera
Lophotrichous Tuft of flagella on one end Pseudomonas Fluorescens
Amphitrichous Single or tuft on both ends Aqua spirillum Serpens
Peritrichous Flagella throughout the cells Salmonella typhi
ACTIVITY 3
STUDY GUIDE QUESTIONS:
1. Describe the effect of antibiotics that target cell wall to pleomorphic type of bacteria.
- Antibiotics function by preventing the production of peptidoglycan, a crucial element of
the bacterial cell wall. By weakening the cell wall and causing cell lysis, this finally causes
the bacterium to perish.
2. What is the distinguishing feature of spirochete?
- They have a long, thin, spiral or wavy cell bodies and endoflagella that live within the
periplasmic space.
3. How can you describe the arrangements of the following morphology types with a microscope?
a. Staphylococcus – grape like cluster
b. Streptococcus – chains
c. Streptobacillus – arranged in chains and loosely tangled clumps.
d. Coccobacillus – short rods-shaped or ovals.
e. Vibrio – single or strung together in s-shapes or spirals.
f. Treponema spp. – helically coiled, corkscrew-shaped cells
g. Borrelia spp. – helical, irregularly coiled motile
You might also like
- Nur - 100 Session 1 - SemillaDocument6 pagesNur - 100 Session 1 - SemillaVon R Semilla100% (2)
- STM 211 NoteDocument42 pagesSTM 211 NoteAkinpelu Joy100% (5)
- CytologyDocument20 pagesCytologykaziba stephen100% (1)
- Nur - 100 Session 2 - SemillaDocument6 pagesNur - 100 Session 2 - SemillaVon R Semilla100% (1)
- Palmer Nursing ReviewerDocument9 pagesPalmer Nursing ReviewerVon R Semilla100% (1)
- Biology - Study and Revision Guide - Andrew Davis and C. J. Clegg - Second Edition - Hodder 2017Document537 pagesBiology - Study and Revision Guide - Andrew Davis and C. J. Clegg - Second Edition - Hodder 2017ariel camposNo ratings yet
- Q1 General Biology Rev L2Document5 pagesQ1 General Biology Rev L2Dwen Kirby VillamorNo ratings yet
- Cell - The Unit of Life Mind MapDocument2 pagesCell - The Unit of Life Mind MapAshwath Kuttuva100% (1)
- Micro para 1Document4 pagesMicro para 1Reselle EspirituNo ratings yet
- NUDES Lab Activity 2Document5 pagesNUDES Lab Activity 2Ella RetizaNo ratings yet
- Cell The Unit of LifeDocument5 pagesCell The Unit of LifeRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure N Functions2Document5 pagesCell Structure N Functions2fariha khanNo ratings yet
- 8 Cell - The Unit of Life-NotesDocument6 pages8 Cell - The Unit of Life-NotesBhavanya RavichandrenNo ratings yet
- Microbio Lec 1 - Bacterial Morphology and Ultra StructureDocument8 pagesMicrobio Lec 1 - Bacterial Morphology and Ultra Structureapi-3743217100% (3)
- Chapter 3: Bacterial Morphology: Murein Sacculus. MucopeptideDocument3 pagesChapter 3: Bacterial Morphology: Murein Sacculus. MucopeptideNicole NipasNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Bacterial Structure - Overview & Glycocalyx 2020 PDFDocument31 pagesUnit 4 Bacterial Structure - Overview & Glycocalyx 2020 PDFhellokittyNo ratings yet
- Biology: Prokaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesBiology: Prokaryotic CellsVictoria IlaganNo ratings yet
- Act. 3 Cytology PeraltaDocument18 pagesAct. 3 Cytology PeraltaCogie PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Microbes & Health: An OverviewDocument13 pagesMicrobes & Health: An OverviewShairoz MevawallaNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument21 pagesCellsEXTRA ACCOUNTNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Taxonomy MuDocument86 pagesBacterial Taxonomy MuBiruck BirhanuNo ratings yet
- Scope of MicrobiologyDocument4 pagesScope of MicrobiologyFvckin NonsenseNo ratings yet
- Premidterms NotesDocument4 pagesPremidterms NotesRenee Andrei Concepcion MozarNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes: A Comparison of Cell Structure and FunctionDocument10 pagesProkaryotes vs Eukaryotes: A Comparison of Cell Structure and FunctionElla RelfNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument3 pagesEukaryotic Cell Structures and FunctionsPhantomNo ratings yet
- MICROBIOLOGYDocument5 pagesMICROBIOLOGYCia RraNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 2Document5 pagesLaboratory Activity 2Sabrina MascardoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument13 pagesChapter 3 Cell Structure and TaxonomyEarl Nikko ChingNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Cell Presentation2Document57 pagesBacterial Cell Presentation2rehanaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EukaryotesDocument2 pagesIntroduction To EukaryotesJero DaclanNo ratings yet
- Hillside School: Biology For Grade 12 Note 2 Topic: The Structure and Function of Bacterial CellDocument8 pagesHillside School: Biology For Grade 12 Note 2 Topic: The Structure and Function of Bacterial Celloli JrNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument50 pagesCell Structure and TaxonomyCarl Elexer Cuyugan AnoNo ratings yet
- NEET - Biology - Cell Structure and FunctionDocument38 pagesNEET - Biology - Cell Structure and Functionknlsinha67% (3)
- Bio Cells NotesDocument7 pagesBio Cells Notesnabita20211No ratings yet
- Bio 102 Lecture Note (Bacteria) - 3Document9 pagesBio 102 Lecture Note (Bacteria) - 3Yin KuzNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic CellDocument34 pagesProkaryotic CellRobelle Grace M. CulaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - The Cell - The Basic Unit of LifeDocument10 pagesLecture 2 - The Cell - The Basic Unit of LifeKaye EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cell and Prokaryotic CellDocument8 pagesCharacteristics of Eukaryotic Cell and Prokaryotic CellEnyell QtyNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 3: Structure of A Cell and MitosisDocument9 pagesActivity No. 3: Structure of A Cell and MitosisEricka GenoveNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory and StructureDocument2 pagesCell Theory and StructureManish KumarNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell: Cellular Structure and FunstionsDocument4 pagesEukaryotic Cell: Cellular Structure and FunstionsCiara PanenNo ratings yet
- Cell-The Unit of Life - Shobhit NirwanDocument23 pagesCell-The Unit of Life - Shobhit NirwanVraj M Barot57% (7)
- Cell The Unit of LifeDocument5 pagesCell The Unit of LifeeloelNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Bacterial Structure Prokaryotes Eukaryotes and ArchaebacteriaDocument9 pagesLesson 2 Bacterial Structure Prokaryotes Eukaryotes and ArchaebacteriaJoaqin CastroNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument6 pagesProkaryotes and EukaryotesC Bala DiwakeshNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument50 pagesCell Structure and Taxonomyporkypig100% (11)
- Microbial Diversity: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument6 pagesMicrobial Diversity: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsPonce Kristel Mae ONo ratings yet
- Central Mindanao University Department of Biology: "The CellDocument6 pagesCentral Mindanao University Department of Biology: "The CellNEIL MARTINEZNo ratings yet
- Morphology of BacteriaDocument44 pagesMorphology of BacteriaDr Harender SimarNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure ActivityDocument4 pagesCell Structure ActivitysharksiedNo ratings yet
- CELL Study MaterialDocument12 pagesCELL Study MaterialShyamasree SenguptaNo ratings yet
- CELL: It's A: CommunityDocument67 pagesCELL: It's A: Communitybae joohyunNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic CellsDocument28 pagesFunctional Anatomy of Prokaryotic CellsGabz GabbyNo ratings yet
- Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeDocument8 pagesCell: The Basic Unit of LifePradyun DSNo ratings yet
- Differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument4 pagesDifferences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellscarlNo ratings yet
- Bacterialmorphology 161031150548Document42 pagesBacterialmorphology 161031150548Namo namoNo ratings yet
- Cell TermsDocument3 pagesCell TermscheewyyyyNo ratings yet
- QMS MicrobiologyDocument21 pagesQMS MicrobiologyDr-Shubhaneel NeogiNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 The Cell 1Document6 pagesExercise 1 The Cell 1MJMadlangbayan100% (1)
- Lecture 3Document22 pagesLecture 3raja11160No ratings yet
- X Bio Masterkey Location & Function 23 - 24Document28 pagesX Bio Masterkey Location & Function 23 - 24chaitanya100% (3)
- Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic CellDocument49 pagesProkaryotic & Eukaryotic CellArthe RajarajanNo ratings yet
- StructureDocument15 pagesStructurefatimasanusimorikiNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Cytology and Physiology - BacteriologyDocument6 pagesBacterial Cytology and Physiology - BacteriologyMary Joy HersaliaNo ratings yet
- Nur - 100 Session 3 - SemillaDocument8 pagesNur - 100 Session 3 - SemillaVon R SemillaNo ratings yet
- Nur - 100 Session 3 - SemillaDocument8 pagesNur - 100 Session 3 - SemillaVon R SemillaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing (Nomral) : Psychiatric (Sigmund Freud) Nursing Concept Range Extends To The 18 MonthDocument6 pagesPediatric Nursing (Nomral) : Psychiatric (Sigmund Freud) Nursing Concept Range Extends To The 18 MonthVon R SemillaNo ratings yet
- Palmer Nursing ReviewerDocument9 pagesPalmer Nursing ReviewerVon R SemillaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing (Nomral) : Psychiatric (Sigmund Freud) Nursing Concept Range Extends To The 18 MonthDocument6 pagesPediatric Nursing (Nomral) : Psychiatric (Sigmund Freud) Nursing Concept Range Extends To The 18 MonthVon R SemillaNo ratings yet
- APPENDICITISDocument47 pagesAPPENDICITISVon R SemillaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Cardiology: Rebound HypertensionDocument8 pagesNursing Cardiology: Rebound HypertensionVon R SemillaNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 8Document15 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 8lavanya rajaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-Cytogenetics: An Introduction: GeneticsDocument26 pagesUnit 1-Cytogenetics: An Introduction: GeneticsKim Angelo del CastilloNo ratings yet
- Genbio1 Lesson4 Cell Surface ModificationsDocument19 pagesGenbio1 Lesson4 Cell Surface ModificationsWallace RamosNo ratings yet
- Medical Technology Assessment Program I: (Trans) : Bacterial Morphology and CytologyDocument3 pagesMedical Technology Assessment Program I: (Trans) : Bacterial Morphology and CytologyLaiza JanelleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AlgaeDocument45 pagesIntroduction To AlgaeAli AhmedNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Morphology: Lab Lesson 11Document8 pagesBacterial Morphology: Lab Lesson 11Not AvailableNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Morphology TypesDocument6 pagesBacterial Morphology TypesZainab MahmudNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Sample Test QuestionsDocument5 pagesMicrobiology Sample Test QuestionsMarife GuadalupeNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure (Compatibility Mode)Document40 pagesCell Structure (Compatibility Mode)Strive ShashaNo ratings yet
- Cilia and FlagellaDocument25 pagesCilia and FlagellaLia Savitri RomdaniNo ratings yet
- Microbiology AssignmentsDocument28 pagesMicrobiology AssignmentsDavid lufafaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MicrobiologyDocument5 pagesIntroduction To MicrobiologyChristina EscardaNo ratings yet
- Bacteria - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument31 pagesBacteria - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediavkg2140% (1)
- Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes Cell: Habtamu Biazin (BSC, MSC) Aau, CHS, Som Department of MipDocument83 pagesProkaryotes and Eukaryotes Cell: Habtamu Biazin (BSC, MSC) Aau, CHS, Som Department of MipQueng ElediaNo ratings yet
- CK-12 Biology Advanced Concepts Answer Key Chapter 3 Cell Biology (AdvancedDocument29 pagesCK-12 Biology Advanced Concepts Answer Key Chapter 3 Cell Biology (AdvancedMargie OpayNo ratings yet
- 7 Motility Determination by Hanging Drop TechniqueDocument5 pages7 Motility Determination by Hanging Drop TechniqueGaurav MudaduNo ratings yet
- Bact211 Lec Week 2 Taxonomy and ClassificationDocument6 pagesBact211 Lec Week 2 Taxonomy and ClassificationHana LunariaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Biosel Serial Endosymbiosis TheoryDocument4 pagesJurnal Biosel Serial Endosymbiosis TheoryHeny SinagaNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of Leishmania SPDocument3 pagesLife Cycle of Leishmania SPUttam Kr PatraNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document6 pagesQuiz 1jki idNo ratings yet
- Bacte Lec - Prelim ExamDocument84 pagesBacte Lec - Prelim ExamDanielle Anne LambanNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Structure and FunctionDocument45 pagesBacterial Structure and FunctionBROOKNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument53 pagesBacterial Anatomy & PhysiologylathaNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Structure and FunctionDocument36 pagesThe Cell: Structure and FunctionYla Mae Buo AcejoNo ratings yet
- AIIMS NEET Study Material Chapter on Biological ClassificationDocument6 pagesAIIMS NEET Study Material Chapter on Biological ClassificationJAYAGUHAN.V THAMBIRAJAHNo ratings yet
- Practical 18.5: Observing Single-Celled OrganismsDocument2 pagesPractical 18.5: Observing Single-Celled OrganismsMikeNo ratings yet
- LN Med Bact Final PDFDocument444 pagesLN Med Bact Final PDFPrince HimansuNo ratings yet
- Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology Volume 27 Issue 1 1980 (Doi 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1980.Tb04228.x) N. D. LEVINE J. O. CORLISS F. E. G. COX G. DEROUX J. GRAIN - A Newly Revised Classification oDocument22 pagesJournal of Eukaryotic Microbiology Volume 27 Issue 1 1980 (Doi 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1980.Tb04228.x) N. D. LEVINE J. O. CORLISS F. E. G. COX G. DEROUX J. GRAIN - A Newly Revised Classification oconniewlgNo ratings yet