Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eukaryotic Cell: Cellular Structure and Funstions
Uploaded by
Ciara PanenOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Eukaryotic Cell: Cellular Structure and Funstions
Uploaded by
Ciara PanenCopyright:
Available Formats
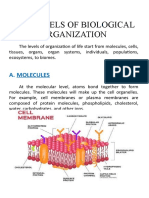
CELLULAR STRUCTURE AND FUNSTIONS
THREE DIFFERENT ELEMENTS in the body
Cells
Intercellular Substances
Body Fluids
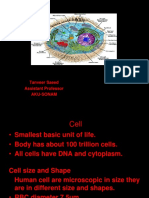
CELL
- Smallest functional and structural units of the body
- Basic unit of life.
TWO BASIC CELL TYPES
Eukaryotic Cell
- Cell which has true nucleus and surrounded by a nucleus and surrounded by a nuclear membrane
or nuclear envelope.
Prokaryotic Cell
- Cell which has no presence of nucleus.
- Lacking of nuclear envelope.
- Nuclear substance is mixed or in direct contact with the rest of the cytoplasm.
PHYSIOLOGIC PROPERTIES OF PROTOPLASM
Irritability Eu karyote - nucleus
Contractility True
Conductivity
Absorption and Secretion Pro karyote - nucleus
Excretion False
Respirations
Growth and Reproduction
PRINCIPAL PARTS OF THE CELL
Cell Membrane
- Trilaminar layer.
- Can only see in plants.
- Membrane lipids, mostly Phospholipids have a Hydrophilic Phosphate which is polar in nature and a
Hydrophobic which is a non-polar end.
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
FUNCTION OF THE CELL MEMBRANE
Gives shape to the cell
Delimits or separate the cell from the environment
Regulates the passage of materials in and out of the call
Serves as the recognition site acting as antigenic determinants
Serves as the selective barriers providing for the selection of what enters and leaves the cell
Selective permeability
MODIFICATION OF SPECIALIZATION OF THE CELL MEMBRANE
1. Junctional Complex - (Taytay Junction )
- Structures that provide for cell attachments.
- One area to another.
TYPES OF JUNCTIONAL COMPLEXES
a. Desmosomes – other term “Macula Adherens”
- Points of firm intercellular adhesions.
- Abundant in Stratified Epithelia of the Mouth, Esophagus, Skin and Vagina.
b. Intermediate Junctions – other terms “Zonula Adherens / Fascia Adherens”
- The intercellular space if filled with electron dense amorphous materials.
- It is quite extensive in the intercalated discs of cardiac muscle.
c. Nexus / Gap Junction
- Concerned with cell to cell communication.
- Usually seen in Epithelial, Muscular and Nervous Tissue.
d. Tight Junction – other term “Zonula Occludens”
- Important in the formation of a barrier prevents the free passage of the substances across
the epithelium.
- Commonly found in the Git and Inter-Endothelial contacts of brain tissue as well as capillary.
2. Invaginations
a. Vesicular pits – occur as phagocytic and pinocytic vesicles.
b. Infoldings – greatly increase of the cell surface because of their inward projections.
3. Microvilli
- Non-motile cellular extensions which serves to increase the absorptive surface of cells.
- Fascilitate movements and passage of the substances in between other cells and interstitial
components.
FORMS OF MICROVILLI
a. Striated Borders – D. in the absorptive cells of the Intestinal Epithelium.
b. Brush Borders – FD. In the cells of the Proximal Convoluted Tubules of the KIDNEY.
c. Stereocilia – FD. In the cells of some testicular ducts as in the ductus epididymis and ductus
deferens.
4. Cilia
- Motile projections and characterized by a rapid forward stroke and slow backward stroke.
- Found in the cells lining the upper respiratory tract.
II. CYTOPLASM
Protoplasm outside the nucleus which contains organelles and inclusions.
Contains the biochemical components of the cytoplasm.
Contains Chons, Lipids and CHO
1. Organelles – living substances performing definite or specific functions.
2. Inclusions – inert or non-living substances that do not perform definite function.
EX. Vacuoles, Crystals, Droplets, Lipids, Glycogen, Secretory Granules
TYPES OF ORGANELLES
1. Membrane Bound Organelles – Mitochondria, ER, Golgi complex, Lysosomes and Microbodies.
2. Non-Membrane Bound Organelles – Ribosomes, Centrioles, Microtubules and Microfilaments.
Mitochondria – powerhouse of the cell
- Concerned primarily with the production of energy and are abundant with high metabolic rates.
- Synthesize ATP – energy source of the cell.
ADDITIONAL FUNCTIONS OF MITOCHONDRIA
1. Accumulations of calcium
2. Synthesis of nucleic acids and chons
3. Oxidation of fatty acids
Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Chon synthesis
- Complex network of paired membranes, saccules, vacuoles and tubules with flattened cisternae.
Types of ER
1. Rough ER – granular ER because it contains attached ribosomes and concerned with chon
synthesis.
2. Smooth ER – non-granular ER and does not contain ribosomes.
Several Functions of SMOOTH ER
1. In striated muscles, it is concerned with the release and recapture of calcium ions during
contraction and relaxation of muscles.
2. Synthesis of steroid hormones in some endocrine glds.
3. Detoxification of toxic substances especially in the liver.
4. Lipid and cholesterol metabolism in the liver
5. Formation of HCL in the parietal
Golgi complex
- Golgi bodies
- Golgi apparatus other term
- Dictyosomes
- Packaging area of the cell
- Accumulate and concentrate the secretory products of the cell
- Site of sulfation
Consists of Golgi apparatus
a. Saccules
b. Vesicles
c. Vacuoles
Lysosomes – suicide bag of the cell.
- Contain hydrolytic enzymes called as acid hydrolases which is responsible for the intracellular
digestion.
Enzymes – chemical reaction
- Speeds off hydro late enzyme
-
TYPES OF LYSOSOMES
1. Primary Lysosomes – not engaged in enzymatic activities
2. Secondary Lysosomes – involved in enzymatic activities
FUNCTION OF LYSOSOMES
1. Defense Mechanism – being the site of destruction of foreign bodies. EX. Transplant
2. Participate in the normal replacement of cell components and organelles
3. Its deficiency can cause metachromatic leukodystrophy.
Centrioles
- Center of activities associated with cell division
- Self-duplicating organelles and are prominent in mitotic cell division.
FUNCTIONS OF CENTRIOLES
Serves as basal bodies and sites of epithelial cilia
Determine the polarity of the cells
Peroxisomes
- Micro bodies
- Producing hydrogen peroxide
- Abundant in the liver, kidneys, bronchioles and odonthoblast
Filaments
1. Microfilaments – contractile filaments
- Actin and Myosin
2. Intermediate Filaments – cytoskeleton in epithelial tissue
- Known as tonofilaments
- in nervous tissue –
3. Neurofilaments and are seen in axons and dendrites.
Microtubules
Functions:
1. Functional elements of the spindle apparatus in diving cells
2. Form the mitotic spindles along which the chromosomes move
3. Play an important rolein maintaining different cell shape
You might also like
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- General Biology 1Document12 pagesGeneral Biology 1Samariah Nicole AbajeroNo ratings yet
- g11 Els OrganellesDocument3 pagesg11 Els OrganellesJarod PeñaflorNo ratings yet
- MIC 311 Lecture NoteDocument107 pagesMIC 311 Lecture NotesiwetwakuNo ratings yet
- m2 DraftDocument4 pagesm2 DraftMae lea AndoloyNo ratings yet
- GenBio Notes Lesson 1 and 2Document7 pagesGenBio Notes Lesson 1 and 2The GreatNo ratings yet
- Cell StructuresDocument81 pagesCell Structuresnurshuhada zainuddinNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Worksheet 2Document5 pagesLaboratory Worksheet 2Johanna AlexaNo ratings yet
- The Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument10 pagesThe Cell Structure and TaxonomyKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- MODULE 2.2 Cellular Level of OrganizationDocument11 pagesMODULE 2.2 Cellular Level of OrganizationKate Andrea PanizalesNo ratings yet
- Plant CellDocument17 pagesPlant Cellrjjain07No ratings yet
- A. Parts of The Cell 1. Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane)Document3 pagesA. Parts of The Cell 1. Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane)akosidanielaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure Function and PropertiesDocument10 pagesCell Structure Function and PropertiesWanda JohnNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument2 pagesCell OrganellesSurminie Muksin100% (1)
- Worksheet: Name: - Class: - DateDocument7 pagesWorksheet: Name: - Class: - DateKaung Myat SanNo ratings yet
- Biology Handouts: I.Cell and Cellular ProcessesDocument37 pagesBiology Handouts: I.Cell and Cellular ProcessesIanDiel ParagosoNo ratings yet
- Earth and ScieDocument3 pagesEarth and SciesideyysNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Chapter-Ii Introduction To The Detailed Structure of The BodyDocument31 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Chapter-Ii Introduction To The Detailed Structure of The BodyAzher MahmoodNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2.3 Basic Cell TypesDocument6 pagesLESSON 2.3 Basic Cell TypessandraNo ratings yet
- 3 CellsDocument6 pages3 CellsEly FructuosoNo ratings yet
- Act 1. Physiology Lab. Group 5Document21 pagesAct 1. Physiology Lab. Group 5YEO, REGGIE ALBERT A.No ratings yet
- General Biology ReviewerDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerBaby AleiraNo ratings yet
- Ch. 3 Cell ReviewDocument5 pagesCh. 3 Cell ReviewDivine GelasiusNo ratings yet
- Cellular Organization Part2Document4 pagesCellular Organization Part2Vince CedricNo ratings yet
- Cell and Cell OrganellesDocument36 pagesCell and Cell OrganellesHeartleene BagainNo ratings yet
- Sec 3Document28 pagesSec 3Jana Moataz Mohamed G02No ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument6 pagesCell OrganellesMark Kenneth CastilloNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Review Notes: MembraneDocument18 pagesBiochemistry Review Notes: MembraneRanielle Samson100% (1)
- Cellular Structure and Function Lectrue 4Document24 pagesCellular Structure and Function Lectrue 4madhav biyaniNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4: Chapter 2: Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument4 pagesBiology Form 4: Chapter 2: Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationSera ChanNo ratings yet
- 2 Animal CellDocument5 pages2 Animal CellDaxx Kenu TanNo ratings yet
- WEEK 3 Cell Structures and PhysiologyDocument9 pagesWEEK 3 Cell Structures and PhysiologyMarjorie Lyka LingatNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes-Part-2Document8 pagesBio Notes-Part-2kreigblitz9801No ratings yet
- Cell Te Unit of Life Revision NotesDocument8 pagesCell Te Unit of Life Revision NotesHarismita AlagurajNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of Life: Q 1 .State Cell Theory - Who Proposed It?Document10 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of Life: Q 1 .State Cell Theory - Who Proposed It?Justin RajanNo ratings yet
- Module For Anaphy CellDocument11 pagesModule For Anaphy CellBJ Bernardo IlNo ratings yet
- Levels of Biological OrganizationsDocument23 pagesLevels of Biological OrganizationsYuu KieNo ratings yet
- Cell ConstituentsDocument39 pagesCell ConstituentsMilky YadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Compartmentation: Cells and Tissues: Functional Compartments of The BodyDocument10 pagesChapter 3: Compartmentation: Cells and Tissues: Functional Compartments of The BodyShivani RailowalNo ratings yet
- Ch2. Notes - CellsDocument7 pagesCh2. Notes - Cellsmelodyau.seNo ratings yet
- Cell Classix Session3 Made by Purnima Sharma 1Document7 pagesCell Classix Session3 Made by Purnima Sharma 1jeetjyoti787No ratings yet
- Gen Bio - First GradingDocument5 pagesGen Bio - First GradingCasey PedrayaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures 2: Hamilton High School Biology Chapter 3Document27 pagesCell Structures 2: Hamilton High School Biology Chapter 3PiereNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure FunctionDocument43 pagesCell Structure Functioneishawajid75No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Cell OrganellesDocument3 pagesLesson 2 - Cell OrganellesAly FayeNo ratings yet
- HDTD-B-4 - Cell OrganellesDocument43 pagesHDTD-B-4 - Cell OrganellesMariam Qais100% (1)
- Cytoplasm 2.: Cell OrganellesDocument6 pagesCytoplasm 2.: Cell OrganellesSai Deekshita VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Genbio I ReviewerDocument12 pagesGenbio I Reviewerjustanony92No ratings yet
- PLB Plant Biology: Introduction To CellDocument9 pagesPLB Plant Biology: Introduction To CellElle AdetounNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of CellDocument11 pagesStructure and Function of CellWoobin RealNo ratings yet
- Cell 3Document25 pagesCell 3Rashul ChutaniNo ratings yet
- Life Science I. Introduction To Life ScienceDocument4 pagesLife Science I. Introduction To Life ScienceJohn LeviNo ratings yet
- CellDocument7 pagesCellnik29569No ratings yet
- Cells OrganellesDocument3 pagesCells OrganellesLaya ShrbagiNo ratings yet
- Cells OrganellesDocument3 pagesCells OrganellesLaya ShrbagiNo ratings yet
- General Biology ReviewerDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerJm Gutierrez50% (6)
- Cell and TissuesDocument18 pagesCell and Tissuesalvin jr ayugatNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Structures and Function of The CellDocument65 pagesWeek 1 Structures and Function of The CellPortia EgkenNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument6 pagesCell Biologyakash kumarNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iii: Chapter-8: Cell The Unit of Life: Cbse + 1 Botany CDF MaterialDocument8 pagesUnit-Iii: Chapter-8: Cell The Unit of Life: Cbse + 1 Botany CDF Materialsimhaenator7109No ratings yet
- Microbiology Chapter 1 2Document69 pagesMicrobiology Chapter 1 2joshNo ratings yet
- Cell AssignmentDocument3 pagesCell AssignmentDreamy AspirationsNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Biology HandoutDocument18 pagesModule 1 Biology Handouthappiebunnie71% (7)
- Science7 Q2 M3 V4no Key AnswerDocument26 pagesScience7 Q2 M3 V4no Key AnswerCastolo Bayucot JvjcNo ratings yet
- 1 Cell: The Unit of Life: SolutionsDocument16 pages1 Cell: The Unit of Life: SolutionsBarnavo DasNo ratings yet
- SOW GCE A Level - Biology - Grade10GenDocument48 pagesSOW GCE A Level - Biology - Grade10Gennugroho sumantoNo ratings yet
- Color Atlas Histology Gartner PDFDocument454 pagesColor Atlas Histology Gartner PDFrafaelalmadapicardiNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument7 pagesAnimal CellLezircYojDapmalNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of Life - Cell PDFDocument12 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of Life - Cell PDFDhiman DeyNo ratings yet
- Endomembrane SystemDocument56 pagesEndomembrane SystemSteven Joshua DrizNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document4 pagesChapter 2Natalie AspinallNo ratings yet
- BIO 315. NotesDocument42 pagesBIO 315. NotesKevin KipropNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules and Cells NotesDocument81 pagesBiomolecules and Cells NotesLily RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Cell and Cytology Resonance PDFDocument79 pagesCell and Cytology Resonance PDFEkta Manglani100% (1)
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument33 pagesCell Structure and FunctionNaveelaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 - Edible Cell ActivityDocument9 pagesScience 9 - Edible Cell ActivitySheena Mar dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 120 MinutesDocument12 pages120 MinutesSooraj Matter LabNo ratings yet
- The Physics of CancerDocument183 pagesThe Physics of CancerClaudio PerezNo ratings yet
- GR 10 Biology - Tissues Organs and System of Living ThingDocument28 pagesGR 10 Biology - Tissues Organs and System of Living Thingapi-301141568No ratings yet
- Ap BiologyDocument11 pagesAp BiologyChandra NekkantiNo ratings yet
- Cell The Unit of Life DPP 05of Lecture 08 Yakeen NEET 2024Document4 pagesCell The Unit of Life DPP 05of Lecture 08 Yakeen NEET 2024SubhrantNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Lysosome-Related Organelle BiogenesisDocument34 pagesDisorders of Lysosome-Related Organelle BiogenesisMaria AnggieNo ratings yet
- CH - 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Text Book ExercisesDocument6 pagesCH - 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Text Book ExercisesUnkown HumanNo ratings yet
- Zoology (Book)Document26 pagesZoology (Book)sme olaplNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On CellsDocument6 pagesWorksheet On CellshatchdogNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio - TGDocument85 pagesGen Bio - TGTintin AfableNo ratings yet
- IX Class NotesDocument60 pagesIX Class NotesNitin ThakurNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure SEDocument7 pagesCell Structure SENithya Majeti100% (1)
- An#Animal#Cell: Let's#Build: Anchor#ChartDocument18 pagesAn#Animal#Cell: Let's#Build: Anchor#Chartapi-289179102No ratings yet
- Cells The Building Blocks of Life - Learning MaterialDocument12 pagesCells The Building Blocks of Life - Learning MaterialRaven BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)From EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (378)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperFrom EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (516)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouFrom EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (62)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueFrom EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Inside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowFrom EverandInside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (390)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemFrom EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (115)
- The Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightFrom EverandThe Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (215)
- The Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineFrom EverandThe Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)